Did you know that the patella, commonly known as the kneecap, is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body? Sesamoid bones are small bones embedded within muscles or tendons near joint surfaces, and the patella is a prime example of this unique bone type.
Sesamoid bones are found throughout the body, but the patella holds special significance due to its crucial role in the biomechanics of the knee joint. Connected to the muscles via tendons, sesamoid bones act as pulleys, alleviating stress on the muscles and tendons and enhancing joint leverage.
In this article, we will explore the anatomy and functions of the patella, its role in the knee joint, and the rehabilitation strategies for sesamoid bone injuries, shedding light on the importance of this small but mighty bone. So, let’s dive in and unravel the mysteries of the remarkable patella!
Structure and Function of the Patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is an essential bone located within the patellar tendon, connecting the quadriceps muscles to the tibia. It plays a crucial role in the biomechanics of the knee joint and the extensor mechanism, enabling the extension of the knee.
Functionally, the patella acts as an attachment point for the quadriceps tendon and the patellar ligament, enhancing the extension capacity of the quadriceps and providing mechanical advantage to the thigh muscles. During activities such as walking and running, the patella guides the knee into a flexed position, ensuring smooth and efficient movement.
Proper patellar alignment is critical for optimal knee function. Disruption in the patellar tracking can lead to conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome, characterized by anterior knee pain. To address these issues, closed-chain eccentric exercises are often recommended. These exercises involve eccentric muscle contractions during knee extension, helping to strengthen the quadriceps muscles and improve muscle-tendon coordination without placing excessive force on the patella and the knee joint.
Understanding the structure and function of the patella is vital in diagnosing and treating various knee conditions. By optimizing patellar alignment and implementing appropriate rehabilitation strategies, we can enhance knee joint biomechanics and minimize the risk of patellofemoral pain and other related problems.
Knee Extension: The Role of the Patella
Knee extension is a fundamental movement facilitated by the patella. During knee extension, the quadriceps muscles contract, pulling on the patellar tendon and extending the knee. The patella acts as a fulcrum, increasing the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps and allowing for more efficient force transmission.
![]()
To ensure proper knee extension, the patella must track smoothly within the patellar groove of the femur. Patellar tracking refers to the alignment and movement of the patella during knee motion. Deviations in patellar tracking can cause patellar malalignment and lead to knee issues, such as patellofemoral pain syndrome.
By strengthening the quadriceps and improving patellar tracking through targeted exercises, such as closed-chain eccentric exercises, we can promote optimal knee extension and reduce the risk of patellofemoral pain. Implementing a comprehensive rehabilitation program that addresses muscle imbalances, improves patellar alignment, and enhances biomechanics is crucial for successful treatment.
| Benefits of Closed-Chain Eccentric Exercise for Patellofemoral Pain: | Guidelines for Performing Closed-Chain Eccentric Exercise: |
|---|---|
| 1. Strengthening quadriceps muscles 2. Improving muscle-tendon coordination 3. Alleviating knee pain and discomfort 4. Enhancing knee joint stability | 1. Start with low resistance 2. Gradually increase resistance as tolerated 3. Perform exercises under the guidance of a healthcare professional 4. Maintain proper form and technique |
The Role of Sesamoid Bones in the Hand and Foot
Sesamoid bones are not only found in the knee but also in the hand and foot. In the hand, most people have five sesamoid bones, with two located at the base of the thumb. These hand sesamoid bones play a crucial role in providing stability and enabling fine motor movements of the thumb. However, injuries to these hand sesamoids can be challenging to diagnose due to their small size and complex anatomy.
When hand sesamoid injuries occur, they should not be overlooked as they can cause significant pain and lead to decreased hand function. Treatment for hand sesamoid injuries will vary depending on the severity of the injury, but it may involve surgical intervention, immobilization with braces or splints, and rehabilitation exercises to restore normal movement and strength.
In the foot, the tibial and fibular sesamoids are located within the big toe. These foot sesamoids play a critical role in weight-bearing and force transfer during activities such as walking and running. However, injuries to these sesamoids, commonly known as turf toe, can cause short- and long-term discomfort and affect the overall functionality of the foot.
Rehabilitation for foot sesamoid injuries typically involves a comprehensive approach. Pain management techniques, such as icing and anti-inflammatory medication, may be used initially to alleviate discomfort. Additionally, taping and bracing can help provide support and stabilize the sesamoids while they heal. Calf stretching exercises are often recommended to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle imbalances.
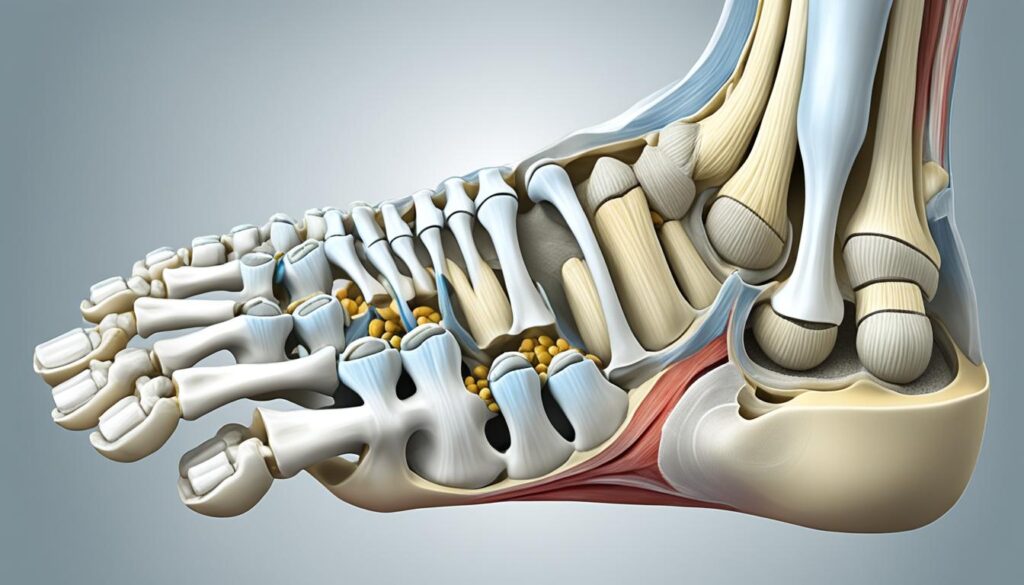
Furthermore, recommending orthotic shoes with firm soles can help redistribute weight throughout the foot, reducing unnecessary pressure on the sesamoids. Strengthening the structures surrounding the foot sesamoids, such as the calf muscles and intrinsic foot muscles, through specific exercises is vital for successful rehabilitation. Isolated movements that target these muscles, combined with functional exercises that simulate walking or running, can help restore balance and overall foot function.
Overall, the role of sesamoid bones in the hand and foot cannot be understated. Injuries to these sesamoids can significantly impact daily activities and require specialized rehabilitation to restore normal function. By understanding the unique anatomy and function of hand and foot sesamoid bones, healthcare professionals can develop effective treatment plans that address the specific needs of each patient.
Sesamoid Bones in the Hand and Foot
| Location | Number |
|---|---|
| Hand | 5 (2 at the base of the thumb) |
| Foot | Tibial and fibular sesamoids in the big toe |
Treatment and Rehabilitation Strategies for Sesamoid Injuries
Treating sesamoid injuries requires a tailored approach based on the specific location and severity of the injury. Whether it’s patellar tendonitis, hand sesamoid injuries, or foot sesamoid injuries, a combination of treatment modalities and rehabilitation strategies can help alleviate pain and restore function.
Treating Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis, a common sesamoid-related condition, can be effectively managed by addressing biomechanical factors that contribute to inflammation and pain. One widely recommended approach is closed-chain eccentric exercise, focusing on the quadriceps muscles and patellar ligament. This type of exercise strengthens the muscles and tendons without placing excessive force on the knee joint, promoting healing and reducing symptoms.
Hand Sesamoid Rehab Techniques
Rehabilitation strategies for hand sesamoid injuries typically involve a combination of isolated movements and functional exercises. Isolated movements target the hand and wrist, such as grip and pinch exercises, to improve strength and mobility. These exercises are followed by functional exercises that simulate real-life movements, helping restore normal use and function of the hand.
Foot Sesamoid Rehab Techniques
Rehabilitation for foot sesamoid injuries often involves a comprehensive approach to pain management and functional recovery. Techniques such as taping, bracing, and calf stretching can help alleviate pain and promote healing. Additionally, recommending orthotic shoes with firm soles provides support and reduces stress on the foot sesamoids. Strengthening the structures surrounding the injury and addressing any deficits within the kinetic chain are crucial for full rehabilitation.
Prehab Sessions and Pain Management
Prehabilitation sessions, which involve strengthening and training the muscles before surgery, can significantly improve post-surgery recovery outcomes. These sessions help optimize muscle function and enhance the body’s ability to recover from surgery or injury. Pain management strategies, tailored to the specific injury and individual, play a vital role in the rehabilitation process. Effective pain management techniques can include physical therapy, medications, and alternative therapies.
Overall, a comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation plan for sesamoid injuries may include a combination of isolated movements, functional exercises, pain management strategies, bracing, and the use of orthotic shoes. Working with a healthcare professional who specializes in musculoskeletal injuries can help ensure the most effective and personalized approach to recovery.
| Treatment and Rehabilitation Strategies for Sesamoid Injuries | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Closed-chain eccentric exercise | – Strengthen muscles and tendons without excessive force on the knee joint – Promote healing of patellar tendonitis |
| Hand sesamoid rehab techniques | – Improve hand and wrist strength and mobility – Restore normal use and function |
| Foot sesamoid rehab techniques | – Alleviate foot sesamoid pain – Promote healing and functional recovery |
| Prehab sessions and pain management | – Optimize post-surgery recovery outcomes – Minimize pain during the rehabilitation process |
Conclusion
Sesamoid bones, such as the patella, play essential roles in the biomechanics and range of motion of the human body. They function as leverage points, reducing friction, and dispersing forces within muscles and tendons, safeguarding them from strain and injury. Understanding the structure and function of sesamoid bones, including their significance in specific joints like the knee, hand, and foot, is crucial for effective treatment and rehabilitation of sesamoid bone injuries.
Rehabilitation strategies for sesamoid injuries typically involve a comprehensive approach. This includes managing pain, implementing targeted strengthening exercises, performing functional movements, and addressing biomechanical factors that contribute to the injury. By recognizing the importance of sesamoid bones in everyday movement and prioritizing proper care and rehabilitation, individuals can maintain mobility and overall musculoskeletal health.
From the patella’s role in the knee joint to the sesamoid bones found in the hand and foot, these small yet significant skeletal structures deserve attention and care. Whether it be through pain management, exercise, or preventive measures, promoting the health and functionality of sesamoid bones is vital. By understanding their functions and implementing appropriate rehabilitation strategies, individuals can improve recovery outcomes and continue to lead active and pain-free lives.
FAQ
Why is the patella called a sesamoid bone?
The patella is called a sesamoid bone because it is a small bone embedded within the tendon of a muscle near a joint surface, resembling a sesame seed. It is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
What is the function of the patella?
The patella plays a critical role in the biomechanics of the knee joint. It enhances joint leverage, contributes to the knee’s extensor properties, and guides the knee into a flexed position, ensuring smooth movement during activities like walking and running.
How is the patella structured?
The patella is formed through endochondral ossification during fetal development. It continues to grow and ossify throughout childhood and adolescence. It has a rich blood supply and extensive innervation, ensuring its nourishment and sensory function.
What are sesamoid bones in the body?
Sesamoid bones are small bones commonly found embedded within muscles or tendons near joint surfaces. Besides the patella, sesamoid bones are also found in the hand and foot. They play a crucial role in weight-bearing, force transfer, and joint stability.
How do sesamoid bone injuries in the hand and foot occur?
Injuries to sesamoid bones in the hand and foot can occur due to trauma, overuse, or repetitive stress. They can cause pain, decreased function, and instability in these areas.
What are some rehabilitation strategies for sesamoid injuries?
Rehabilitation for sesamoid injuries includes pain management, exercise, taping, bracing, and orthotic shoes. Techniques such as closed-chain eccentric exercise, isolated movements, and functional exercises are often recommended for effective rehabilitation.
Why is the proper alignment of the patella important?
Proper patellar alignment is essential for the normal functioning of the knee joint. It ensures optimal movement, stability, and weight-bearing capacity during activities. Disruption of patellar alignment can lead to conditions like patellofemoral pain syndrome.
How can closed-chain eccentric exercise help with patellofemoral pain?
Closed-chain eccentric exercise is often recommended for the treatment of patellofemoral pain. It helps strengthen the quadriceps muscles and improve muscle-tendon coordination without placing excessive force on the patella and the knee joint.
What is the role of the patella as a sesamoid bone?
The patella, as a sesamoid bone, plays a crucial role in the knee joint’s biomechanics and range of motion. It provides leverage, decreases friction, and distributes forces throughout the muscles and tendons, protecting them from strain and injury.
Why should the care and rehabilitation of sesamoid injuries be prioritized?
Proper care and rehabilitation of sesamoid injuries are crucial for maintaining mobility and overall musculoskeletal health. Sesamoid bones, such as the patella, are important for everyday movement, and addressing these injuries can prevent long-term discomfort and functional limitations.
Leave a Reply