Are you experiencing pain and swelling around your knee and wondering what could be the cause? Knee bursitis is a common condition that affects many individuals, particularly athletes and those with certain occupations.
Inflammation of the bursae around the knee joint can lead to this condition, which manifests in different forms, including anserine and prepatellar bursitis. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
The impact of knee bursitis on the knee joint can be significant, affecting mobility and causing discomfort. By exploring the distinct characteristics of anserine and prepatellar bursitis, individuals can better understand their condition and seek appropriate medical care.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the differences between anserine and prepatellar bursitis is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Knee bursitis is a common condition affecting athletes and individuals with certain occupations.
- Inflammation of the bursae around the knee joint leads to knee bursitis.
- Anserine and prepatellar bursitis have distinct characteristics.
- Proper diagnosis is essential for appropriate medical care.
Definition of Knee Bursitis
Understanding knee bursitis requires a look into the inflammation of bursae, the fluid-filled sacs that cushion joints. Knee bursitis is a condition that affects these sacs, leading to pain and discomfort in the knee area.
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis refers to the inflammation of a bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between bones, tendons, and ligaments. When a bursa becomes inflamed, it can cause significant pain and limit the mobility of the affected joint.
Types of Knee Bursitis
There are several types of knee bursitis, each affecting different bursae around the knee. The most common types include:
- Prepatellar Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa in front of the kneecap.
- Anserine Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa on the lower inner aspect of the knee.
- Other less common types that may affect different bursae around the knee.
Understanding the specific type of knee bursitis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment.
Importance of Understanding Knee Bursitis
Recognizing the causes, symptoms of knee bursitis, and the process for knee bursitis diagnosis is vital for effective management. Knee bursitis can result from knee bursitis causes such as overuse, direct trauma, or conditions like arthritis. Proper understanding helps in seeking the right medical attention and treatment, thereby reducing the risk of complications.

By comprehending the nature of knee bursitis, individuals can take proactive steps towards prevention and treatment, ultimately improving their quality of life.
Overview of Anserine Bursitis
The anserine bursa, located on the inner aspect of the knee, can become inflamed, leading to a condition known as anserine bursitis. This condition is characterized by pain and swelling in the lower inner part of the knee.
Anserine bursitis is common among athletes, particularly runners, and individuals with knee osteoarthritis. Activities that involve repetitive knee movements or direct pressure on the knee can exacerbate the condition.

Causes of Anserine Bursitis
The primary cause of anserine bursitis is the inflammation of the anserine bursa due to friction or direct trauma. Repetitive stress from activities such as running or cycling can irritate the bursa, leading to inflammation.
- Overuse or repetitive stress on the knee
- Direct trauma to the knee
- Knee osteoarthritis
- Poor training habits or improper footwear
Symptoms to Look For
Individuals with anserine bursitis often experience pain on the lower inner aspect of the knee, which can be accompanied by swelling and tenderness. The pain can be particularly noticeable when climbing stairs, standing up from a seated position, or during activities that involve knee flexion.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness on the inner knee
- Swelling or redness in the affected area
- Warmth or tenderness to the touch
Treatment Options for Anserine Bursitis
Treatment for anserine bursitis typically involves a combination of conservative measures aimed at reducing inflammation and alleviating pain. Initial steps may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to help reduce swelling.
Additional treatments may involve:
- Physical therapy to improve knee mobility and strength
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling
- Corticosteroid injections to decrease inflammation
Overview of Prepatellar Bursitis
The prepatellar bursa, located at the front of the kneecap, is susceptible to inflammation, leading to prepatellar bursitis. This condition is often associated with individuals who frequently kneel, hence the common name “housemaid’s knee.”
Prepatellar bursitis is characterized by swelling and tenderness at the front of the knee. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management.
Causes of Prepatellar Bursitis
Prepatellar bursitis is primarily caused by repetitive kneeling, which leads to friction and irritation of the prepatellar bursa. Other causes include:
- Direct blow to the knee
- Infection
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
Occupations or activities that involve frequent kneeling, such as plumbing, gardening, or carpet laying, increase the risk of developing prepatellar bursitis.
Symptoms of Prepatellar Bursitis
The symptoms of prepatellar bursitis include:
- Swelling in front of the kneecap
- Pain or tenderness when kneeling or pressing on the knee
- Redness and warmth around the affected area
- Limited range of motion due to swelling
In cases where the bursitis is caused by infection, additional symptoms such as fever and increased redness may be present.
Treatment Options for Prepatellar Bursitis
Treatment for prepatellar bursitis focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving symptoms, and preventing recurrence. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Ice: Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition and applying ice to reduce swelling.
- Compression and Elevation: Using compression bandages and elevating the knee to reduce swelling.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Aspiration and Injection: In some cases, draining the bursa or injecting corticosteroids may be necessary.
In recurrent or severe cases, surgical removal of the bursa may be considered.
Comparing Symptoms: Anserine vs Prepatellar
The symptoms of anserine and prepatellar bursitis can be similar, yet distinct differences exist. Both conditions involve inflammation of the bursae around the knee, leading to pain and discomfort. However, the location and nature of the pain can vary significantly between the two conditions.
Similar Symptoms
Both anserine and prepatellar bursitis present with knee pain, swelling, and limited mobility. The pain can be exacerbated by movement and relieved by rest. In some cases, the affected area may be warm to the touch and tender. These similarities can make diagnosis challenging without a thorough examination.
Distinguishing Factors
The primary distinguishing factor between anserine and prepatellar bursitis lies in the location of the pain. Anserine bursitis typically affects the lower inner aspect of the knee, about 2-3 inches below the joint line, causing pain when climbing stairs or getting up from a seated position. On the other hand, prepatellar bursitis affects the front of the kneecap, leading to swelling and pain directly over the kneecap, often associated with kneeling.
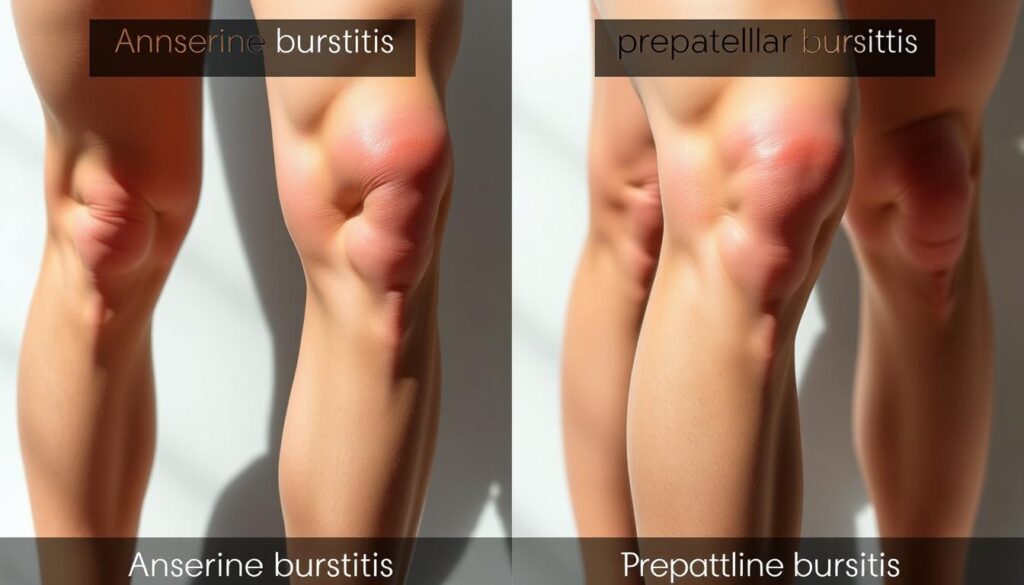
Understanding these differences is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. While both conditions may benefit from rest, ice, and anti-inflammatory medications, the specific location and nature of the pain can dictate additional treatments, such as physical therapy for anserine bursitis or aspiration of the bursa for prepatellar bursitis.
Diagnosis of Knee Bursitis
Knee bursitis diagnosis involves a comprehensive medical evaluation. This process is crucial for determining the presence and type of bursitis, which in turn guides the treatment plan.
Medical Evaluation Process
The medical evaluation for knee bursitis begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. During the history taking, the healthcare provider will ask questions about the onset of symptoms, the nature of the pain, and any activities that may have contributed to the condition. The physical examination involves assessing the knee for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
A healthcare professional may perform specific tests to differentiate between types of knee bursitis, such as anserine and prepatellar bursitis. For instance, tenderness in the lower inner aspect of the knee may indicate anserine bursitis, while swelling at the front of the knee could suggest prepatellar bursitis. More information on the diagnosis and treatment can be found on Mayo Clinic.
Imaging Techniques Used
In some cases, imaging studies are necessary to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other conditions. Common imaging techniques used include:
- X-rays: To rule out bone-related issues such as fractures.
- Ultrasound: Useful for visualizing soft tissue and detecting fluid accumulation in the bursa.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including bursae, tendons, and ligaments.
For a detailed understanding of how these imaging techniques aid in diagnosis, consider visiting KneeHurt.com for additional insights.
| Imaging Technique | Use in Knee Bursitis Diagnosis |
|---|---|
| X-ray | Rules out bone-related issues |
| Ultrasound | Detects fluid accumulation in the bursa |
| MRI | Provides detailed images of soft tissues |
Risk Factors for Bursitis
Understanding the risk factors associated with knee bursitis is crucial for prevention and effective management. Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing this condition, and being aware of these can help in taking preventive measures.
Common Risk Factors for Anserine Bursitis
Anserine bursitis is often associated with specific risk factors, including obesity and knee arthritis. These conditions can put additional stress on the knee, increasing the risk of bursitis. Activities that involve repetitive knee movements, such as cycling or running, can also contribute to the development of anserine bursitis.
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact on Anserine Bursitis |
|---|---|---|
| Obesity | Increased weight puts additional stress on the knee. | Higher risk due to increased pressure. |
| Knee Arthritis | Inflammation and degeneration of the knee joint. | Increased risk due to joint instability. |
| Repetitive Knee Movements | Activities like cycling or running. | Increased friction and irritation. |
Common Risk Factors for Prepatellar Bursitis
Prepatellar bursitis is commonly associated with activities that involve frequent kneeling, such as carpet laying or gardening. This condition is also known as “housemaid’s knee.” Other risk factors include direct blows to the knee and infections.
- Frequent kneeling
- Direct blows to the knee
- Infections
Lifestyle Considerations
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of knee bursitis. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk, as can avoiding activities that put repetitive stress on the knee. Proper knee protection during sports and activities can also help prevent bursitis.
By understanding these risk factors and making appropriate lifestyle adjustments, individuals can reduce their likelihood of developing knee bursitis. Prevention strategies, including proper knee care and protection, are essential for maintaining knee health.
Prevention Strategies
Effective prevention of knee bursitis requires a combination of maintaining a healthy weight, minimizing repetitive knee stress, and employing proper activity techniques. By adopting these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing both anserine and prepatellar bursitis.
Preventing Anserine Bursitis
Anserine bursitis is often associated with activities that involve repetitive knee flexion and stress on the medial (inner) aspect of the knee. To prevent this condition, it’s essential to strengthen the muscles around the knee, particularly the hamstring muscles, through targeted exercises. Additionally, proper training techniques during sports or activities that involve running, cycling, or repetitive knee movements can help mitigate the risk.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also crucial, as excess weight can put additional stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of developing anserine bursitis. For more information on managing knee pain, visit Understanding and Managing Knee Pain When.
Preventing Prepatellar Bursitis
Prepatellar bursitis, commonly known as “housemaid’s knee,” is often caused by repetitive pressure or friction on the front of the knee. Prevention strategies include avoiding prolonged kneeling or using knee pads to cushion the knee during activities that require kneeling. It’s also beneficial to take regular breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around, reducing prolonged pressure on the knee.
Furthermore, strengthening the quadriceps muscles through exercises like squats and lunges can help stabilize the knee and reduce the risk of prepatellar bursitis. Ensuring proper technique during activities and avoiding direct blows to the knee can also contribute to prevention.
By understanding and implementing these prevention strategies, individuals can effectively manage and reduce their risk of knee bursitis, maintaining healthier knees and overall mobility.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery from knee bursitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes rest, rehabilitation, and specific exercises. This multifaceted strategy is crucial for healing, strengthening the knee, and preventing future occurrences.
Importance of Rest
Giving your knee adequate rest is the first step towards recovery. This means avoiding activities that aggravate the condition, such as repetitive kneeling or direct pressure on the knee. Rest allows the inflamed bursa to heal, reducing pain and swelling.
During the initial rest period, it’s also beneficial to apply ice to the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain. This should be done for 15-20 minutes, several times a day. Elevating the knee above the level of the heart can also help reduce swelling.
Rehabilitation Strategies
Once the initial pain and inflammation have subsided, rehabilitation exercises can begin. These exercises are designed to improve knee mobility, strengthen the surrounding muscles, and enhance overall knee function.
A physical therapist can tailor a rehabilitation program to the individual’s needs, which may include:
- Range of motion exercises to improve flexibility
- Strengthening exercises for the quadriceps and hamstring muscles
- Functional training to improve knee function during daily activities
Sample Rehabilitation Exercises
| Exercise | Description | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|
| Straight Leg Raise | Lift your leg straight out in front of you, keeping it straight, then lower it back down. | 3 sets of 10 |
| Quad Sets | Tighten your quadriceps muscles by straightening your knee, hold for 5 seconds. | 3 sets of 10 |
| Hamstring Curls | Bend your knee, bringing your heel towards your buttocks, then straighten your knee. | 3 sets of 10 |
It’s essential to progress through these exercises gradually, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, to avoid re-injury. Consistency and patience are key to a successful rehabilitation program.
By understanding the importance of rest and rehabilitation, and by incorporating specific exercises into your recovery plan, you can effectively manage knee bursitis and work towards a full recovery.
When to Seek Medical Help
Understanding when to seek medical attention is crucial for effective treatment for knee bursitis. If left untreated, bursitis can lead to chronic pain and potentially serious complications.
Recognizing the Signs
It’s essential to be aware of the signs that indicate a need for professional care. Persistent pain, swelling, or redness around the knee are indicators that medical evaluation is necessary. Additionally, if the knee is warm to the touch or if there’s a significant decrease in mobility, seeking medical help is advisable.
Potential Complications
Untreated bursitis can result in infection or chronic inflammation, significantly impacting quality of life. Prompt medical attention can help prevent these complications and improve outcomes. Knee bursitis prevention strategies, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding repetitive knee motions, can also play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing bursitis.
By being proactive about knee health and seeking timely medical intervention, individuals can effectively manage knee bursitis and prevent long-term damage.

Leave a Reply