Have you ever wondered why your knees hurt after sitting in a cross-legged position, a common posture in meditation and yoga practices?
This discomfort can be a significant issue for those who regularly adopt this position, affecting their ability to fully engage in their preferred activities. Understanding the reasons behind this discomfort is crucial for finding relief and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The connection between sitting cross-legged and knee pain is complex, involving factors such as posture, anatomy, and potentially underlying health conditions. This article aims to explore these factors and provide guidance on alleviating the discomfort associated with this common sitting position.
Key Takeaways
- Common causes of knee pain after sitting cross-legged
- The role of posture and anatomy in knee discomfort
- Potential underlying health conditions contributing to pain
- Strategies for alleviating knee pain
- Tips for maintaining healthy knees while practicing yoga or meditation
Understanding Knee Pain and Its Causes
Understanding the causes of knee pain is crucial for effective management and relief. Knee pain is a widespread issue that affects individuals of all ages and activity levels, impacting their quality of life.
What Is Knee Pain?
Knee pain refers to any discomfort or pain in or around the knee joint. It can result from various factors, including injuries, health conditions, and repetitive strain. The knee joint, being one of the body’s major weight-bearing joints, is susceptible to pain and injury.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
The causes of knee pain are diverse and can include:
- Injuries such as sprains, strains, and fractures
- Medical conditions like arthritis, tendinitis, and bursitis
- Overuse or repetitive strain on the knee joint
Understanding these causes is essential for determining the appropriate knee pain relief measures.
| Cause | Description | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Injuries | Sprains, strains, fractures | Pain, swelling, bruising |
| Arthritis | Inflammation of the joint | Pain, stiffness, limited mobility |
| Overuse | Repetitive strain | Pain, swelling, fatigue |
How Sitting Cross-Legged Affects Your Knees
Sitting cross-legged can exacerbate knee pain due to the pressure it puts on the knee joint. This posture can lead to strain on the ligaments and tendons surrounding the knee, potentially causing or worsening pain.
By understanding how different factors, including sitting postures, contribute to knee pain, individuals can take steps towards knee pain relief and prevention.
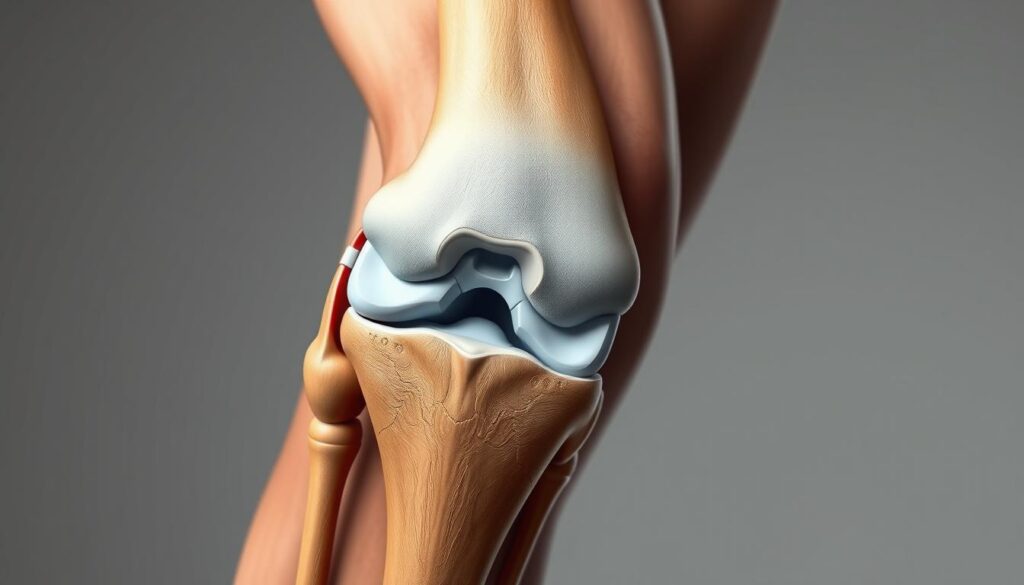
The Anatomy of the Knee Joint
Understanding the knee joint’s anatomy is crucial for addressing knee pain issues. The knee joint is a complex structure that facilitates a wide range of movements, making it one of the most critical components of our musculoskeletal system.
Key Components of the Knee Joint
The knee joint is primarily composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. The bones involved are the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). Articular cartilage covers the ends of these bones, reducing friction during movement. Ligaments connect bones to each other, providing stability, while tendons connect muscles to bones, enabling movement.
How Movement Impacts Knee Health
Movement and posture significantly impact knee health. Activities or positions that put unusual stress on the knee joint can lead to pain and injury. For example, sitting cross-legged can sometimes contribute to knee pain due to the unnatural positioning of the knee. It’s essential to understand how different movements affect knee health to manage and prevent knee pain effectively.
Effective knee pain management involves understanding the causes of knee pain and adopting appropriate knee pain treatment strategies. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in gentle exercises, and avoiding activities that exacerbate the condition.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint
- Engaging in gentle exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee
- Avoiding activities that exacerbate knee pain
Nerve and Muscle Involvement
Understanding how muscles and nerves interact is key to managing knee pain effectively. The knee joint is supported by a complex system of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to provide stability and facilitate movement.
Role of Muscles in Supporting the Knee
Muscles play a crucial role in supporting the knee joint. The quadriceps and hamstring muscles, for example, work together to straighten and bend the knee. Strong and balanced muscles are essential for knee health, as they help absorb shock, stabilize the joint, and facilitate smooth movement.
When the muscles around the knee are weak or imbalanced, it can lead to poor knee alignment and increased stress on the joint, potentially resulting in pain. Therefore, strengthening exercises are often recommended as part of a knee pain management plan.
Nerves and Sensations of Pain
Nerves are responsible for transmitting signals, including pain, from the knee to the brain. The sensation of pain can be influenced by various factors, including inflammation, injury, or compression of nerves. Nerve compression or irritation can cause sharp, shooting pains or numbness in the knee and surrounding areas.
“Pain is a complex phenomenon that involves not just the nerves but also how the brain interprets signals.”
Understanding the role of nerves in knee pain is crucial for effective management. This includes being aware of conditions that may affect nerve health, such as neuropathy, and taking steps to prevent nerve compression or damage.
By addressing both muscle and nerve health, individuals can take a comprehensive approach to knee pain relief and knee pain prevention. This may involve a combination of strengthening exercises, improving posture, and managing conditions that could impact nerve health.
Risk Factors for Knee Pain
The risk of knee pain is influenced by several key factors. Understanding these can help in both prevention and management.
Age and Degeneration
As people age, the wear and tear on their joints increase, making older adults more susceptible to knee pain. Degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis are common among the elderly, where the cartilage that cushions the joints deteriorates over time.
“Age is a significant risk factor for knee pain, primarily due to the degenerative changes that occur in the joint over time,” says a leading orthopedic specialist.
Previous Injuries and Conditions
Individuals with a history of knee injuries, such as ligament sprains or meniscal tears, are at a higher risk of developing chronic knee pain. Previous conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can also contribute to ongoing knee issues.
- Previous ligament or meniscal injuries
- History of surgeries on the knee
- Chronic conditions such as arthritis
Impact of Obesity on Knee Health
Obesity is another significant risk factor for knee pain. Excess weight puts additional strain on the knee joint, accelerating wear and tear. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing the risk of knee pain and managing existing pain.

By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing knee pain or managing its impact.
Symptoms Associated with Knee Pain
Identifying the symptoms associated with knee pain is the first step towards relief. Knee pain can manifest differently in various individuals, making it crucial to understand the range of possible symptoms.
Location of Pain: Where Does It Hurt?
The location of knee pain can provide significant clues about its cause. Pain can be felt in different areas around the knee, including the front, sides, or back. For instance, pain at the front of the knee might be associated with patellofemoral pain syndrome, often seen in runners or cyclists. On the other hand, pain on the sides or back of the knee could indicate issues such as ligament sprains or meniscal tears.
Other Signs to Look Out For
Apart from pain, there are other signs that may indicate knee problems. These include:
- Swelling or redness around the knee
- Stiffness, particularly after periods of rest
- Instability or a feeling that the knee is going to give way
- Clicking or grinding sensations when moving the knee
- Weakness in the leg
These symptoms can vary in severity and impact daily activities to different extents. Recognizing these signs early on can help in seeking appropriate knee pain relief measures.
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
|---|---|
| Pain at the front of the knee | Patellofemoral pain syndrome |
| Pain on the sides or back of the knee | Ligament sprains or meniscal tears |
| Swelling or redness | Inflammation or infection |
| Stiffness | Osteoarthritis or tendonitis |
Understanding these knee pain symptoms is crucial for determining the appropriate course of action. Whether it’s modifying activities, seeking medical attention, or exploring knee pain relief options, being informed is key to managing knee pain effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Knee Pain
It’s essential to recognize the signs that indicate the need for medical evaluation for knee pain. Knee pain can range from mild to severe and may be acute or chronic. Understanding when to seek medical attention for knee pain is crucial for effective treatment and preventing further injury.
Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Certain symptoms indicate the need for immediate medical evaluation. These include:
- Sudden severe pain
- Significant swelling
- Instability or buckling of the knee
- Inability to bear weight
- Signs of infection (redness, warmth, fever)
These signs suggest that the knee pain may be related to a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
Recommended Medical Professionals to Consult
For knee pain, it’s advisable to consult healthcare professionals who specialize in musculoskeletal issues. These may include:
- Orthopedic specialists
- Rheumatologists
- Physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) doctors

| Medical Professional | Specialty |
|---|---|
| Orthopedic Specialist | Surgical and non-surgical treatment of musculoskeletal disorders |
| Rheumatologist | Diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases |
| PM&R Doctor | Helping patients with chronic pain or musculoskeletal injuries through non-surgical means |
Consulting the right medical professional can significantly impact the effectiveness of the knee pain treatment plan.
Home Remedies for Alleviating Pain
Alleviating knee pain doesn’t always require medical intervention; several home remedies can be effective. These remedies focus on reducing discomfort and improving knee function through simple, non-invasive techniques.
Applying Ice or Heat
One of the most common home remedies for knee pain involves applying ice or heat to the affected area. Ice helps reduce inflammation, which can be particularly beneficial after an injury or during flare-ups. On the other hand, heat therapy relaxes the muscles and increases blood flow, aiding in the healing process. It’s recommended to use ice for acute injuries and heat for chronic pain.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief Options
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relief medications are another effective home remedy for knee pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation. It’s essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any underlying conditions or concerns.
Stretching and Gentle Exercises
Gentle exercises and stretching can also alleviate knee pain by improving flexibility and strengthening the muscles around the knee. Low-impact activities such as cycling, swimming, or yoga can be beneficial. It’s crucial to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity to avoid exacerbating the condition.
Incorporating these home remedies into your daily routine can significantly reduce knee pain and improve overall knee health. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or exercise regimen.
Preventive Measures for Future Pain
Preventing knee pain involves a combination of proper ergonomics, sitting posture, and strengthening exercises. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of knee pain associated with sitting cross-legged.
Ergonomics and Sitting Posture Tips
Maintaining good ergonomics and sitting posture is crucial for preventing knee pain. This includes ensuring that your workspace is set up to promote good posture, such as keeping your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest, keeping your knees at or below hip level, and avoiding crossing your legs for extended periods.
Tips for Good Sitting Posture:
- Keep your back straight and supported.
- Avoid sitting for long periods without taking a break.
- Use a chair with proper lumbar support.
Importance of Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings, can help support the knee joint and reduce the risk of pain. Strengthening exercises can be done through various activities such as squats, lunges, and leg press exercises.
“Exercise is a celebration of what your body can do, not a punishment for what you ate.” – Unknown
It’s essential to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity of these exercises to avoid putting excessive strain on the knee.
The Role of Physical Therapy
The role of physical therapy in alleviating knee pain is multifaceted, involving tailored exercises and manual therapies. Physical therapy is recognized as a cornerstone in the management of knee pain, offering a non-invasive approach to improving knee function and reducing pain.
What to Expect in Physical Therapy
When undergoing physical therapy for knee pain, patients can expect a comprehensive evaluation of their condition. This includes an assessment of their medical history, current symptoms, and physical capabilities. Based on this evaluation, a personalized treatment plan is developed, which may include:
- Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee
- Manual therapy techniques to improve joint mobility
- Modalities such as heat or cold therapy to reduce pain and inflammation
- Education on proper movement techniques to avoid exacerbating the condition
Physical therapists work closely with patients to ensure that the treatment plan is both effective and tailored to their specific needs. The goal is not only to alleviate current pain but also to prevent future episodes by enhancing knee strength and flexibility.
Benefits of Working with a Physical Therapist
Working with a physical therapist offers several benefits for individuals suffering from knee pain. These benefits include:
- Personalized care: Treatment plans are customized to address the individual’s specific condition and needs.
- Improved function: Physical therapy can help restore normal knee function, enabling individuals to perform daily activities with greater ease.
- Pain reduction: Through a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and other modalities, physical therapy can significantly reduce knee pain.
- Prevention: By strengthening the knee and improving mobility, physical therapy can help prevent future knee problems.
By addressing the root causes of knee pain and implementing a comprehensive treatment plan, physical therapy plays a vital role in helping individuals regain knee health and improve their quality of life.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Knee Pain
Simple adjustments to daily habits can make a substantial difference in reducing knee pain. By focusing on a few key areas, individuals can alleviate discomfort and improve their overall knee health.
Weight Management Tips
Managing weight is crucial for reducing knee pain, as excess weight puts additional strain on the knee joint. Aiming for a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly alleviate pressure on the knees.
A combination of cardiovascular exercises, such as swimming or cycling, and strength training can help achieve and maintain weight loss. It’s also beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional or a nutritionist to develop a personalized weight management plan.
| Weight Management Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Balanced Diet | Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins | Supports overall health and weight loss |
| Regular Exercise | Engaging in physical activities like walking, cycling, or swimming | Burns calories and strengthens muscles around the knee |
| Hydration | Drinking plenty of water throughout the day | Aids in digestion and overall bodily functions |
Safe Alternatives to Sitting Cross-Legged
For those who are accustomed to sitting cross-legged, finding alternative sitting positions is essential to reduce knee strain. Using ergonomic furniture or adjusting sitting postures can help.
Some safe alternatives include sitting on a chair with proper back support or using a meditation bench. It’s also helpful to take regular breaks to stand and stretch, reducing prolonged pressure on the knees.
Conclusion: Managing Knee Pain Beyond Sitting
Effective knee pain management involves a multi-faceted approach that includes consistent relief strategies and a commitment to staying active. Understanding the causes of knee pain is crucial for implementing preventive measures that reduce discomfort and improve overall knee health.
Relief Strategies
Knee pain relief can be achieved through a combination of home remedies and professional interventions. Gentle exercises, such as those taught in physical therapy sessions, can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing support and stability. Using ice or heat therapy and over-the-counter pain relief options can also alleviate symptoms.
Active Knee Care
Engaging in low-impact activities like cycling or swimming can help maintain healthy knees while staying active. Practicing good ergonomics when sitting and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce strain on the knees. By adopting these strategies, individuals can enjoy improved knee health and reduced pain, enabling them to stay active and mobile.

Leave a Reply