
Knee Post-Traumatic Arthritis
Knee post-traumatic arthritis is a condition that can develop after an injury to the knee. It is a type of osteoarthritis that occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. This condition can be debilitating and significantly impact a person’s quality of life.


Understanding knee post-traumatic arthritis is essential for those who have experienced a knee injury or are at risk of developing this condition. Causes and risk factors can include previous knee injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, as well as age and obesity. Early diagnosis and progression monitoring are crucial for effective treatment and management of knee post-traumatic arthritis.
Post-traumatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that occurs after an injury to a joint. When the knee joint is injured, it can lead to inflammation and damage to the articular cartilage, which is the smooth surface that covers the ends of the bones in the joint. If the cartilage is damaged, it can lead to chronic joint pain and inflammation, which can eventually lead to osteoarthritis.
Knee post-traumatic arthritis is a common condition that can affect people of all ages. It is most often caused by a joint injury, such as a fracture, dislocation, or ligament tear. The severity of the injury can determine the risk of developing post-traumatic arthritis.
The symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis can include joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. In some cases, the joint may feel unstable or give way. Over time, the joint may become more damaged, leading to cartilage loss and bone spurs.
Treatment for knee post-traumatic arthritis depends on the severity of the condition. In some cases, conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and medication may be enough to manage symptoms. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the damaged joint.
In conclusion, knee post-traumatic arthritis is a chronic condition that can lead to joint pain and inflammation. If you have experienced a knee injury, it is important to seek medical attention to prevent or manage post-traumatic arthritis.
Post-traumatic arthritis (PTA) of the knee is a type of arthritis that occurs after a severe injury or trauma to the knee joint. In this section, we will explore the causes and risk factors associated with PTA of the knee.
Injury and trauma to the knee joint are the most common causes of PTA. This includes acute injuries such as bone fractures, dislocations, meniscus injuries, and ACL ruptures. Internal bleeding and joint instability can also contribute to the development of PTA.
PTA can also develop as a result of chronic wear and tear on the knee joint. This is more common in older individuals and those who engage in activities that put a lot of stress on the knee joint, such as athletes.
Other risk factors for PTA include aging, a history of joint injuries or surgeries, and certain medical conditions that affect the immune system. Women are also more likely to develop PTA than men.
In summary, PTA of the knee is typically caused by injury or trauma to the knee joint, but can also develop as a result of chronic wear and tear or underlying medical conditions. Understanding the risk factors associated with PTA can help individuals take steps to prevent its development and seek appropriate treatment if necessary.
When a patient presents with symptoms of knee pain, stiffness, and swelling, we consider the possibility of knee post-traumatic arthritis (PTA) as a potential diagnosis. To confirm the diagnosis, we typically perform a physical examination and imaging techniques.
During the physical exam, we assess the patient’s knee for signs of synovial effusion, which is a buildup of fluid in the joint. We also evaluate the patient’s range of motion, looking for any limitations or stiffness. Additionally, we may ask the patient about their medical history and any previous knee injuries.
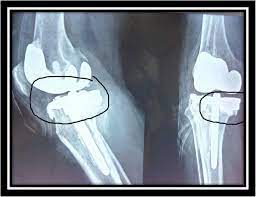
Imaging techniques, such as x-rays, are also used to diagnose knee PTA. X-rays can show changes in the joint space, bone spurs, and other signs of osteoarthritis. MRI scans may also be used to evaluate the soft tissues of the knee.
Once knee PTA has been diagnosed, we monitor the progression of the disease. The progression of knee PTA varies from patient to patient, but it generally worsens over time. Patients may experience increasing pain, stiffness, and limitations in mobility.
In some cases, knee PTA can lead to knee osteoarthritis, which is a chronic condition that may require ongoing treatment. It is important to diagnose and manage knee PTA early to prevent further damage to the joint.
When it comes to treating knee post-traumatic arthritis, there are several options available to improve quality of life, function, and mobility. In this section, we will discuss the different treatments and management strategies available for this condition.
Medications and injections can help manage pain and inflammation associated with knee post-traumatic arthritis. Analgesics, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can be taken orally to help manage pain. Intra-articular injections, such as corticosteroids and hyaluronic acid, can also be administered to reduce inflammation and improve joint lubrication.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat knee post-traumatic arthritis. Joint replacement (arthroplasty) is a common surgical procedure that involves replacing the damaged joint with a prosthetic one. This can help improve mobility and reduce pain associated with the condition.
Exercise and physical therapy can help improve knee function and mobility in patients with knee post-traumatic arthritis. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming and cycling, can help improve joint flexibility and strength. Physical therapy can also help patients learn exercises to improve range of motion and reduce pain.
Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and avoiding high-impact activities, can also help manage knee post-traumatic arthritis. This can reduce stress on the knee joint and improve overall joint health.
In conclusion, there are several treatment and management options available for knee post-traumatic arthritis. Medications and injections can help manage pain and inflammation, while surgery and physical therapy can improve knee function and mobility. Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding high-impact activities, can also help manage the condition.
Symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis in the knee include pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. The pain may be worse with activity and may improve with rest. Some people may also experience a grinding or clicking sensation in the knee joint.
Treatment options for post-traumatic arthritis in the knee may include non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and injections. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joint tissues.
While it may not be possible to completely prevent post-traumatic arthritis in the knee, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. These include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the knee joint, and wearing protective gear when participating in sports or other high-impact activities.
Post-traumatic arthritis can develop at any time after a knee injury, but it may take several years for symptoms to appear. The risk of developing post-traumatic arthritis increases with the severity of the initial injury.
Post-traumatic arthritis in the knee is a chronic condition that can be managed with appropriate treatment, but it is generally not curable. However, with proper care, many people with post-traumatic arthritis in the knee are able to maintain an active lifestyle.
While post-traumatic arthritis in the knee may not improve on its own, many people are able to find relief from their symptoms with appropriate treatment. With physical therapy, medications, and other interventions, it may be possible to improve joint function and reduce pain and stiffness.
Introduction If you're an athlete or someone who leads an active lifestyle, you've likely heard…
Key Takeaways Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for knee health Proper…
Ever finished a run and felt your knee throbbing? You're not alone. Many athletes face…
https://youtu.be/YRrppL1WuCw Introduction As a weight lifter, you're no stranger to pushing your body to its…
Ever wondered why some hikers seem to move easily on tough trails while others find…
Are you an active person dealing with knee pain that stops you from doing what…