
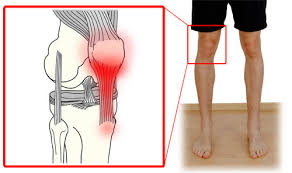
Patellar Tendonitis
Did you know that patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, affects millions of people worldwide and is a common cause of knee pain and injury?
Patellar tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation and pain in the front of the knee, specifically in the patellar tendon. It’s often caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as jumping or running on hard surfaces.
If you are suffering from knee pain and suspect patellar tendonitis, it’s crucial to take the right steps to overcome this condition and achieve lasting relief. In this article, we will provide you with valuable insights, diagnosis methods, treatment options, self-care measures, and prevention strategies to help you manage and recover from patellar tendonitis effectively.
Diagnosing patellar tendonitis is a critical first step in managing this condition. A thorough knee exam conducted by a doctor is usually the initial diagnostic method. During the exam, the doctor will carefully apply pressure to different parts of the knee to determine the exact source of pain. In the case of patellar tendonitis, patients typically experience pain on the front part of the knee, just below the kneecap.
In order to obtain a more detailed assessment of the patellar tendon and rule out other potential causes of knee pain, imaging tests are often recommended. These tests help identify any tears or abnormalities in the tendon and provide crucial information for creating an effective treatment plan.
There are several imaging tests that may be used:
With the information gathered from the knee exam and imaging tests, healthcare professionals can make an accurate patellar tendonitis diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment strategies.
The treatment of patellar tendonitis begins with conservative options to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Depending on the severity of the condition, various treatment strategies may be employed:
It’s important to note that the specific treatment plan for patellar tendonitis will vary depending on individual circumstances. A healthcare professional will assess the severity of the condition and tailor a treatment approach that best meets the patient’s needs.
In addition to medical treatment, self-care measures can greatly assist in the management of patellar tendonitis. It is important to take proactive steps to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Here are some self-care strategies:
To manage the pain associated with patellar tendonitis, over-the-counter pain relievers can be helpful. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium, can provide temporary relief. However, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional if the pain persists or worsens.
Modifying activities that exacerbate the pain is crucial for recovery. Avoiding high-impact sports or activities that put excessive strain on the knee can prevent further damage and allow the tendon to heal. Consider low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, to maintain fitness while reducing the stress on the affected area.
Applying ice to the affected area after activity can help reduce inflammation and swelling. Cold therapy can be effective in managing pain and promoting healing. Use an ice pack or wrap ice in a cloth and apply it to the knee for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
Resting the knee and allowing it time to heal is crucial for recovery. Avoid activities that aggravate the pain and give your body the opportunity to repair the damaged tendon. Consider incorporating periods of rest into your daily routine and gradually reintroduce activities as the pain subsides.
“Self-care measures, such as pain management techniques and activity modification, play a vital role in the management of patellar tendonitis. By taking proactive steps to alleviate symptoms and promote healing, individuals can achieve lasting relief and support the recovery process.”
By implementing these self-care measures, individuals can play an active role in managing patellar tendonitis and supporting the healing process. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Effective management of patellar tendonitis involves several key strategies that focus on reducing pain, promoting strength, and improving overall knee health. By incorporating the following techniques into your routine, you can enhance your ability to manage this condition and prevent further aggravation of the tendon.
Isometric exercises, which involve static muscle contractions without joint movement, can be beneficial in reducing pain and strengthening the affected patellar tendon. These exercises help to improve stability and promote healing. Incorporate exercises such as quadriceps sets, where you tighten the front thigh muscle and hold for a few seconds, into your daily routine.
When managing patellar tendonitis, it is crucial to prioritize pain management. This can be achieved through the use of over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium, as recommended by your doctor. It’s essential to strike a balance between managing pain and listening to your body’s limits to avoid exacerbating the condition.
Engaging in tissue work techniques, such as deep tissue massage or foam rolling, can help reduce tension and compressive forces on the knee. Focusing on the quadriceps muscles can provide targeted relief and support proper alignment of the patellar tendon. Incorporate these techniques into your routine to enhance tissue flexibility and promote healing.
Eccentric strengthening exercises involve controlled, slow lowering movements, which help to stimulate the healing process and improve the capacity of the patellar tendon to handle daily load. Include exercises such as eccentric squats and heel drops in your exercise routine to promote strength and stability in the knee joint.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively manage patellar tendonitis and reduce discomfort while promoting healing. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise or treatment plan to ensure it is appropriate for your individual needs.
Jumper’s knee, also known as patellar tendonitis, is a common condition that involves inflammation of the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the shin bone. It is often caused by overuse and repetitive stress on the knee joint, particularly in activities that require jumping or running. This can lead to microtears and degeneration of the tendon, resulting in pain and discomfort.
People with jumper’s knee may experience symptoms such as pain and tenderness around the patellar tendon, swelling, and pain with movement. The pain is usually localized to the front of the knee, just below the kneecap. The intensity of the pain may vary, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain that limits daily activities.
Diagnosing jumper’s knee involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. The doctor will evaluate the symptoms, assess the location and severity of the pain, and may order X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans to rule out other possible causes of knee pain and to assess the condition of the patellar tendon.
The treatment of jumper’s knee focuses on reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and promoting healing of the patellar tendon. Initially, conservative measures such as rest, ice, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process, which may include stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, and modalities such as ultrasound therapy or electrical stimulation.
In more severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, additional interventions such as corticosteroid injections or extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) may be considered. In rare cases, surgical options like arthroscopic surgery or patellar tendon debridement may be necessary to repair or remove damaged tissue.
Table:
| Causes of Jumper’s Knee | Symptoms of Jumper’s Knee | Diagnosis of Jumper’s Knee | Treatment of Jumper’s Knee |
|---|---|---|---|
| – Overuse and repetitive stress on the knee joint. | – Pain and tenderness around the patellar tendon. | – Medical history and physical exam. | – Rest and activity modification. |
| – Sports activities involving jumping or running. | – Swelling and pain with movement. | – Imaging tests (X-rays, ultrasound, MRI). | – Medications for pain and inflammation. |
| – Physical therapy (exercises, modalities). | |||
| – Injections (corticosteroids, ESWT). | |||
| – Surgical options (arthroscopy, debridement). |
It is important to seek early intervention for jumper’s knee to prevent further damage and facilitate a faster recovery. Following a comprehensive treatment plan, including rest, appropriate exercises, and self-care measures, can help alleviate symptoms, improve function, and prevent recurrence of the condition.
In order to prevent patellar tendonitis, it is crucial to take certain precautions to protect the health of your knees. By incorporating warm-up exercises, using proper technique, gradually progressing in training, and cross-training, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Before engaging in any physical activity, it is essential to warm up and stretch the muscles around your knees. This helps prepare your body for exercise and reduces the risk of injury. Incorporate dynamic movements such as leg swings, knee circles, and lunges into your warm-up routine to increase blood flow and flexibility.
Using proper technique and form during activities can play a significant role in preventing patellar tendonitis. Make sure to maintain good posture, engage your core muscles, and avoid excessive stress on the patellar tendon. If you are unsure about the correct technique, consult with a qualified trainer or coach who can guide you in performing exercises and movements correctly.
Avoiding sudden increases in intensity, duration, and frequency of training is crucial for preventing overuse injuries like patellar tendonitis. Instead, gradually progress in your training by increasing one element at a time, such as distance, load, or speed. This allows your body to adapt and strengthen over time, reducing the strain on your knees.
Engaging in cross-training activities, such as swimming, cycling, or yoga, can be beneficial in preventing patellar tendonitis. By incorporating different types of exercises into your fitness routine, you can distribute the load across different muscle groups and reduce the likelihood of developing overuse injuries. Cross-training also helps improve overall strength, flexibility, and endurance, contributing to better knee health.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing patellar tendonitis and maintain the health and functionality of your knees.
| Prevention Strategies | |
|---|---|
| 1 | Warm-up exercises |
| 2 | Proper technique |
| 3 | Gradual progression |
| 4 | Cross-training |
Overcoming patellar tendonitis and finding lasting relief from knee pain is possible with the right approach to treatment and preventive measures. Diagnosing patellar tendonitis involves a thorough physical examination and may require imaging tests to accurately assess the condition. Treatment options for patellar tendonitis range from conservative measures, such as medication and physical therapy, to more invasive procedures like injections or surgery.
Additionally, self-care measures play a crucial role in the recovery process. Implementing pain management techniques and modifying activities to avoid further strain on the knee can contribute to the healing process. By incorporating warm-up exercises, using proper technique, and gradually progressing training, individuals can reduce the risk of developing patellar tendonitis and maintain overall knee health.
Remember, overcoming patellar tendonitis requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both treatment and prevention. With dedication and perseverance, individuals can overcome this condition and achieve lasting relief from knee pain.
Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is a condition characterized by inflammation and pain in the front of the knee, specifically in the patellar tendon.
Patellar tendonitis is often caused by overuse or repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as jumping or running on hard surfaces.
The symptoms of patellar tendonitis may include pain and tenderness around the patellar tendon, swelling, pain with movement, and tenderness behind the lower part of the kneecap.
The diagnosis of patellar tendonitis begins with a thorough knee exam conducted by a doctor. Imaging tests, such as X-rays, ultrasound, and MRI, may be recommended to provide a more detailed assessment of the patellar tendon.
Treatment options for patellar tendonitis typically include conservative measures such as medication, physical therapy, stretching exercises, and the use of a patellar tendon strap. In some cases, therapies such as iontophoresis, corticosteroid injection, platelet-rich plasma injection, or an oscillating needle procedure may be recommended. Surgery is considered rare and only used if other treatments have failed.
Self-care measures for patellar tendonitis include over-the-counter pain relievers, activity modification, applying ice to the affected area, and resting the knee.
Effective management of patellar tendonitis involves isometric exercises, pain management techniques, tissue work, and eccentric strengthening exercises.
Jumper’s knee, also known as patellar tendonitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap to the shin bone.
Preventing patellar tendonitis can be achieved by warming up and stretching before physical activity, using proper technique, gradually progressing in training, and incorporating different types of exercises into a fitness routine.
Overcoming patellar tendonitis and achieving lasting knee pain relief involves following the appropriate treatment approach, taking preventive measures, and maintaining overall knee health.
As a physical therapist with over 30 years of experience, I've helped countless patients identify…
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that follows a progressive course, typically worsening…
Discover how to alleviate Knee pain when vacuuming on carpet with our expert tips and…
Discover the best foam padding for carpet knee pain. We review top products to help…
We're analyzing Carpet vs. hard floor knee pressure to help you decide which flooring is…
Discover how Knee bursitis and carpet surfaces are connected in our Ultimate Guide. Learn the…