Osteoarthritis knee pain can be debilitating and impact everyday life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management options is crucial for individuals dealing with this condition. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of managing osteoarthritis knee pain and provide valuable insights for those seeking relief.
Key Takeaways
- Regular exercise can help reduce knee pain and improve mobility.
- Medication, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can provide relief from knee pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy can strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility, reducing pain and enhancing function.
- Maintaining a healthy weight can alleviate pressure on the knees and reduce the risk of further damage from osteoarthritis.
- Lifestyle changes, including proper footwear and supportive devices, can ease knee pain and improve overall quality of life.
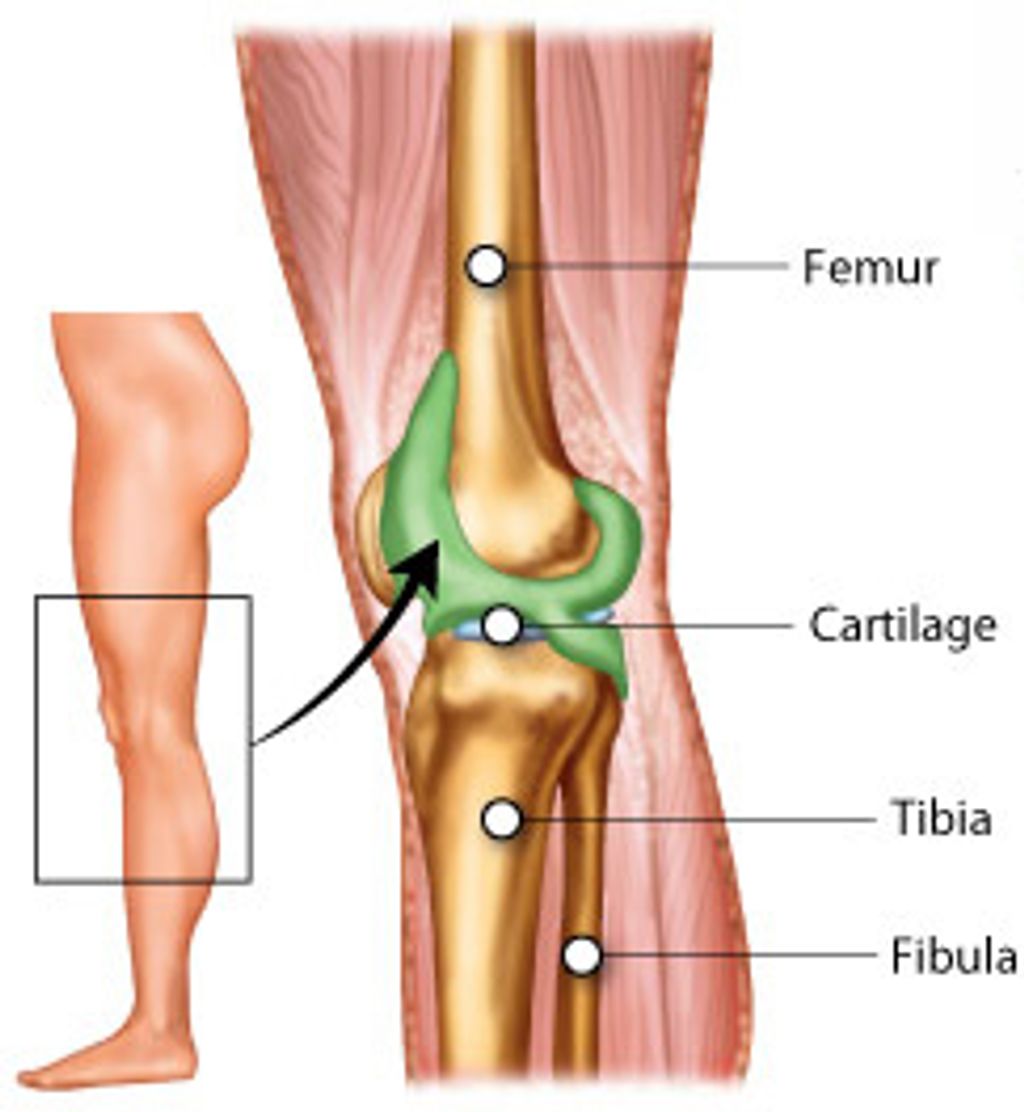
Understanding Osteoarthritis Knee Pain
Causes of Osteoarthritis Knee Pain
We often see osteoarthritis as a natural part of the aging process, but it’s more complex than simply getting older. The causes of osteoarthritis knee pain are multifaceted, involving a combination of factors. Genetics play a significant role, as do lifestyle choices and past injuries.
Weight is a critical factor; the more we weigh, the more stress we put on our joints, particularly the knees. Occupations that demand repetitive stress on the joints can also contribute to the development of osteoarthritis. Here’s a quick look at some common contributing factors:
- Age: The risk increases as we age.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis after menopause.
- Joint injuries: Past injuries can lead to osteoarthritis later in life.
- Bone deformities: Congenital or developmental conditions may predispose individuals to osteoarthritis.
Tip: Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding joint overuse can help manage the risk of developing osteoarthritis knee pain.
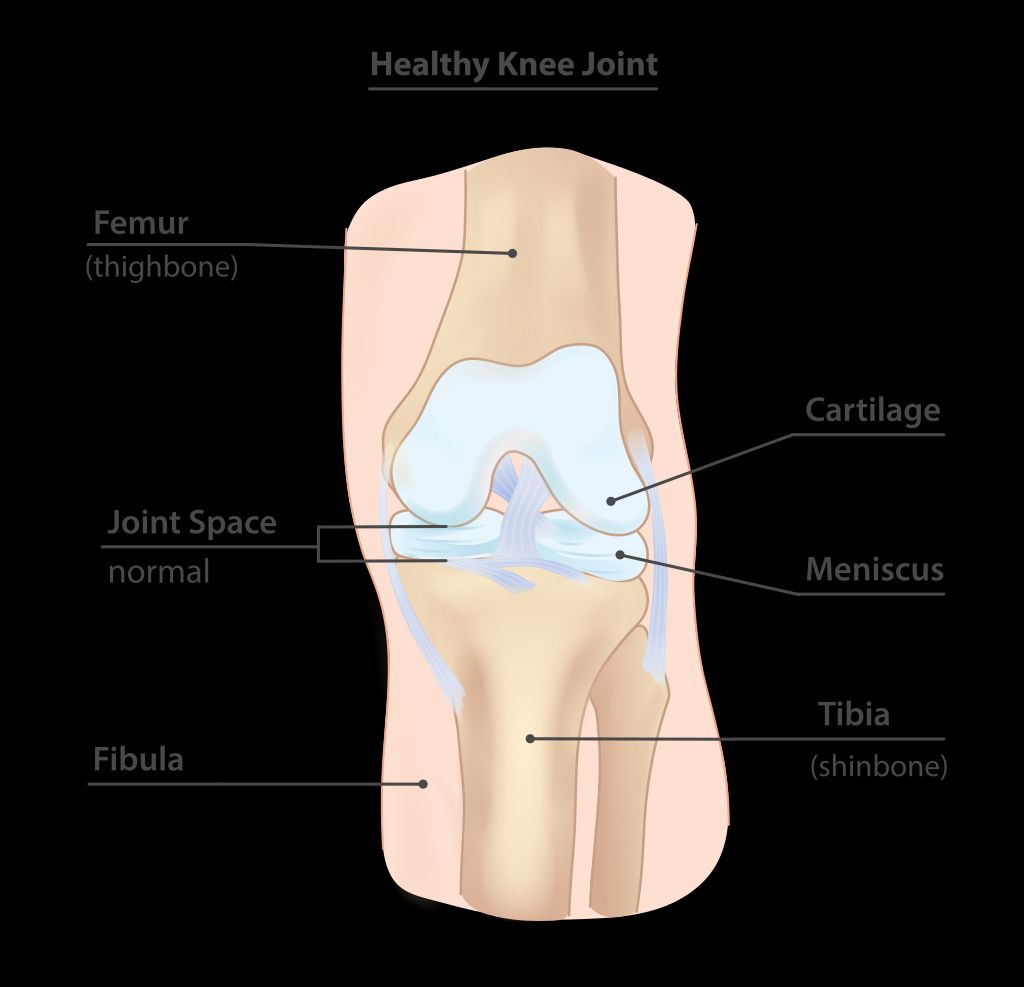
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis Knee Pain
We often observe that individuals with osteoarthritis knee pain experience a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity. The most common symptom is a persistent pain in the knee, which may worsen with activity and improve with rest. Stiffness, particularly in the morning or after sitting for long periods, is also frequently reported.
Another notable symptom is a decreased range of motion in the knee joint, which can make it difficult to perform everyday activities such as walking or climbing stairs. Some may hear or feel a grating sensation when moving the knee. Swelling can occur, especially after extended activity.
Tip: Gentle stretching and warming up before activities can help reduce stiffness and improve joint mobility.
Here is a list of common symptoms associated with osteoarthritis knee pain:
- Persistent knee pain
- Stiffness in the knee
- Decreased range of motion
- Grating sensation
- Swelling after activity
It’s important to recognize these symptoms early and consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis Knee Pain
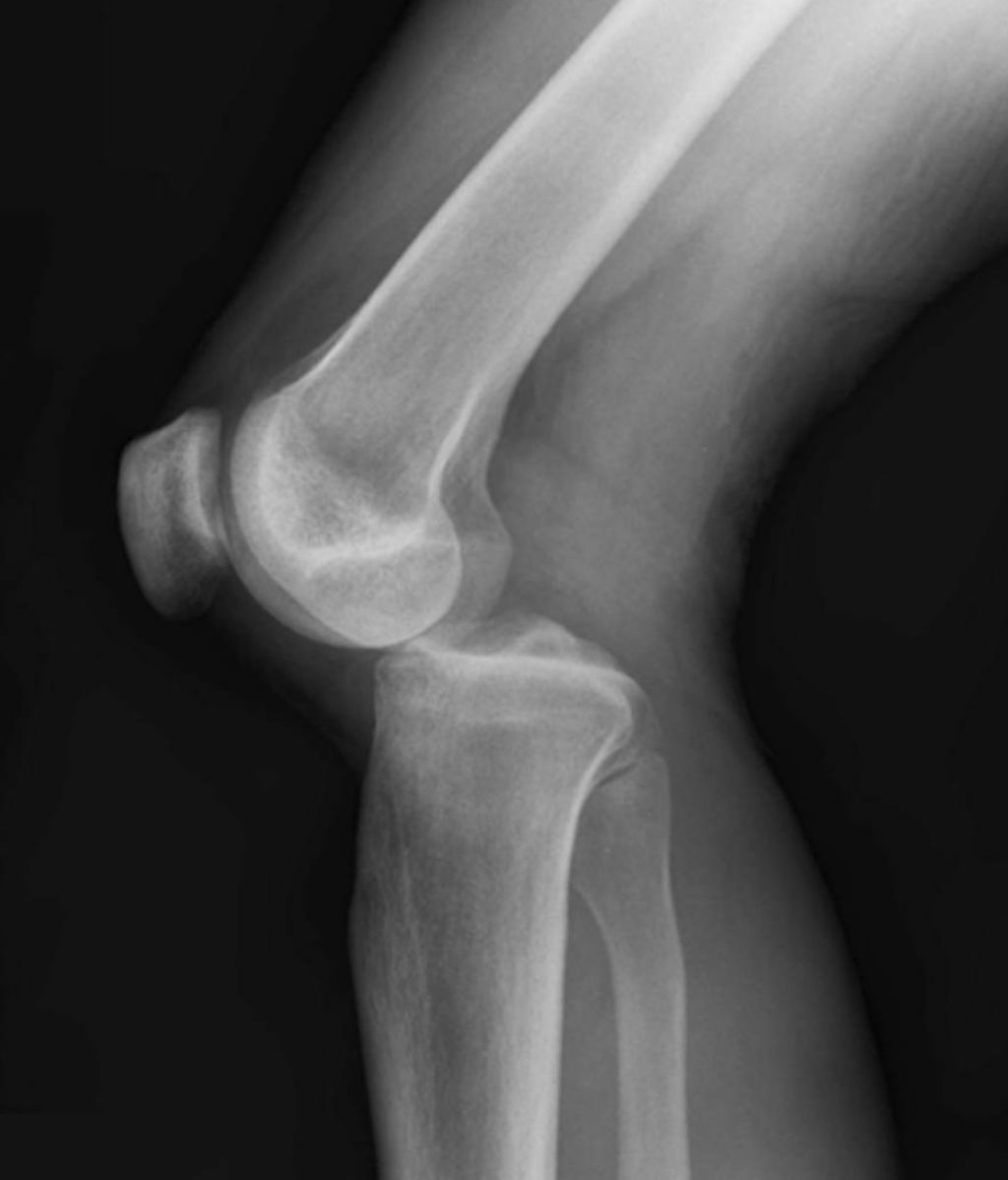
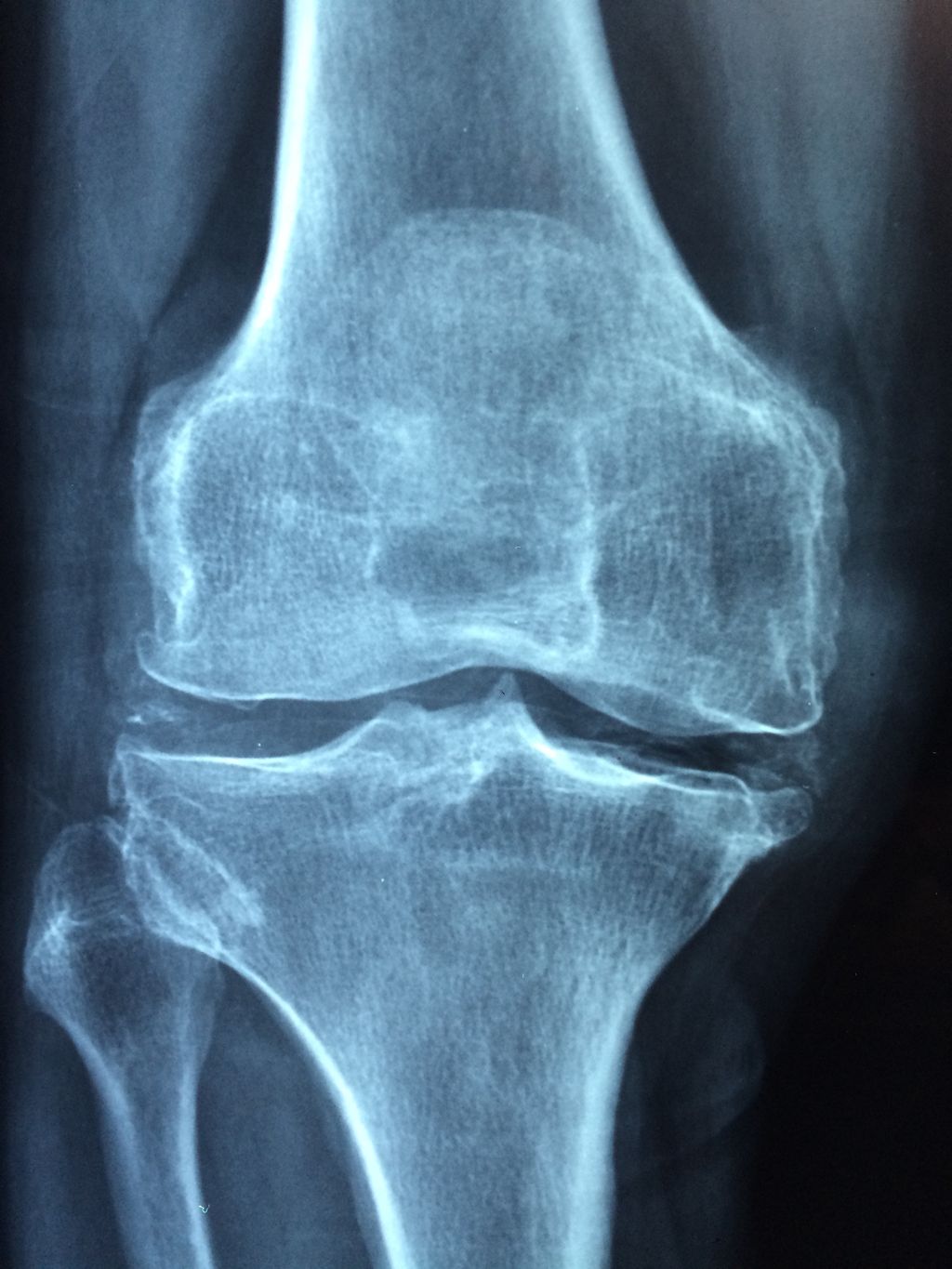
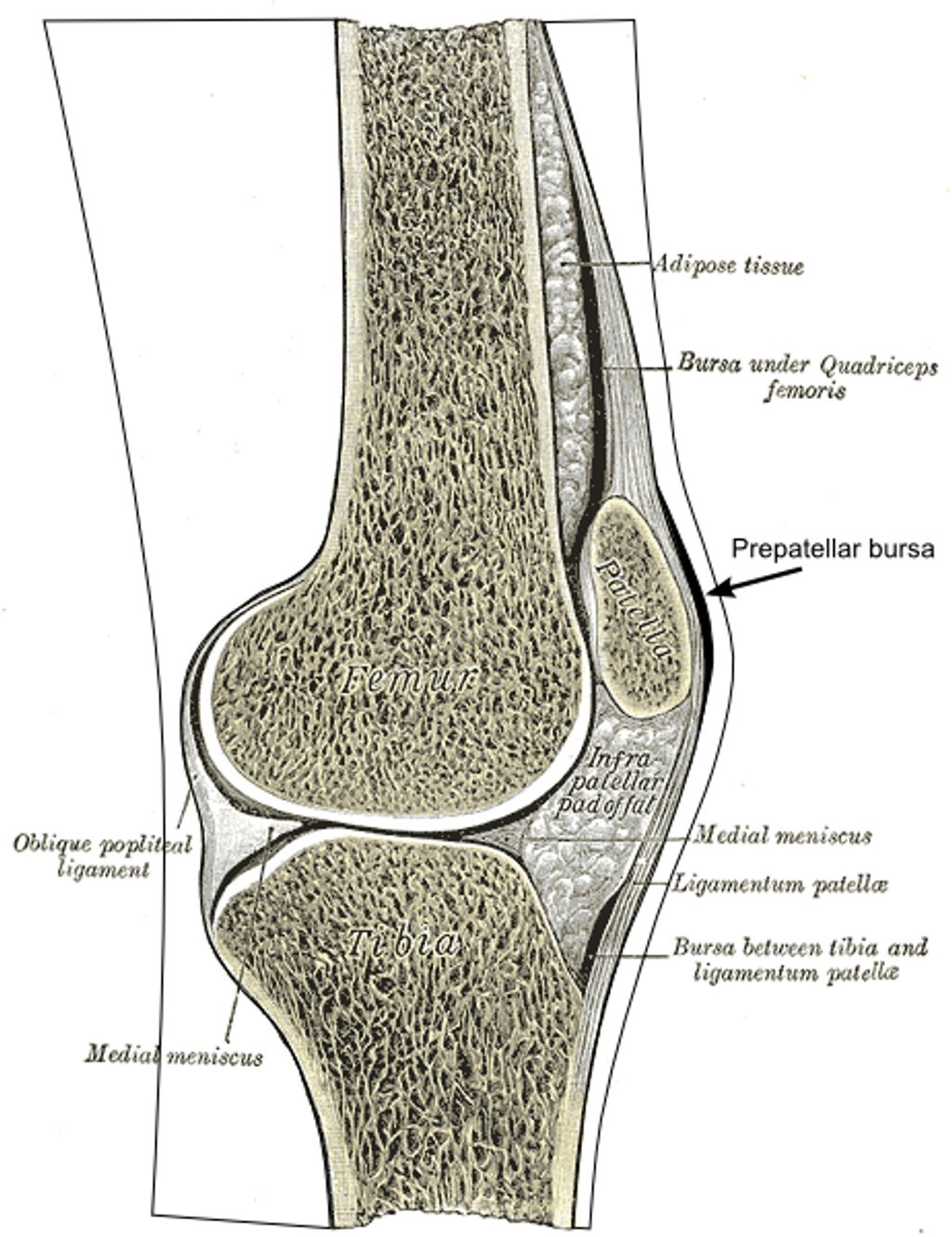
After recognizing the symptoms of osteoarthritis knee pain, we proceed to its diagnosis, which is crucial for tailoring the most effective management strategies. We begin with a thorough medical history and a physical examination. The presence of joint stiffness, swelling, and pain during movement can be indicative of osteoarthritis. To confirm the diagnosis, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans are often employed. These tests reveal the extent of joint damage, including loss of cartilage and changes in bone structure.
Imaging Tests for Osteoarthritis Knee Pain:
- X-rays: Show bone spurs and cartilage loss
- MRI: Provides detailed images of soft tissues
Tip: Early diagnosis can lead to better management of knee pain and potentially slow the progression of osteoarthritis.
It’s also important to rule out other conditions that can mimic osteoarthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Blood tests and joint fluid analysis may be conducted to differentiate these conditions. Once osteoarthritis is confirmed, we can explore various treatment options to manage knee pain effectively.
Managing Osteoarthritis Knee Pain
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Knee Pain
After making the necessary lifestyle changes to manage knee pain, it is important to monitor the progress and make adjustments as needed. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for managing osteoarthritis knee pain. It is also beneficial to incorporate low-impact activities such as swimming or cycling into our routine. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can help reduce inflammation and support overall joint health.
When considering medication options, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan. This may include the use of over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications to alleviate discomfort and manage inflammation. Physical therapy is another valuable resource for managing knee pain, providing tailored exercises and techniques to improve strength, flexibility, and mobility. Together, these approaches form a comprehensive strategy for effectively managing osteoarthritis knee pain.
Medication Options for Knee Pain
When considering medication options for knee pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication. Additionally, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects, such as gastrointestinal irritation and increased risk of cardiovascular events. Monitoring for these side effects and discussing any concerns with a healthcare provider is essential for safe and effective management of knee pain. We emphasize the importance of informed decision-making and regular communication with healthcare professionals to ensure personalized and optimal treatment.
Physical Therapy for Knee Pain
After discussing the benefits of physical therapy for knee pain, lifestyle changes and medication options should also be considered. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific condition. In some cases, a combination of these approaches may be recommended to effectively manage osteoarthritis knee pain. It’s crucial to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen and maintain open communication with your healthcare provider to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments. Additionally, engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help improve joint flexibility and reduce discomfort. It’s essential to prioritize self-care and adopt a proactive approach to managing osteoarthritis knee pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of osteoarthritis knee pain is a complex and multifaceted endeavor that requires a comprehensive approach. By understanding the underlying mechanisms of the condition, implementing evidence-based interventions, and promoting patient education and self-management, healthcare professionals can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from osteoarthritis. It is imperative to emphasize the importance of early intervention and the adoption of a holistic treatment plan that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition. Through ongoing research and advancements in medical technology, the future holds promise for more effective and personalized strategies in the management of osteoarthritis knee pain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risk factors for developing osteoarthritis knee pain?
Risk factors for developing osteoarthritis knee pain include age, obesity, previous knee injury, genetics, and overuse of the knee joint.
Is exercise beneficial for managing osteoarthritis knee pain?
Yes, regular exercise can help improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase mobility for individuals with osteoarthritis knee pain. It is important to engage in low-impact exercises and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized exercise recommendations.
What are the common medications used to manage osteoarthritis knee pain?
Common medications used to manage osteoarthritis knee pain include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, corticosteroid injections, and hyaluronic acid injections.
Can dietary changes help in managing osteoarthritis knee pain?
Yes, certain dietary changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, consuming anti-inflammatory foods, and incorporating joint-friendly nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to managing osteoarthritis knee pain.
How effective is physical therapy in managing osteoarthritis knee pain?
Physical therapy is highly effective in managing osteoarthritis knee pain as it focuses on strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility, and providing personalized exercises to enhance joint function and reduce pain.
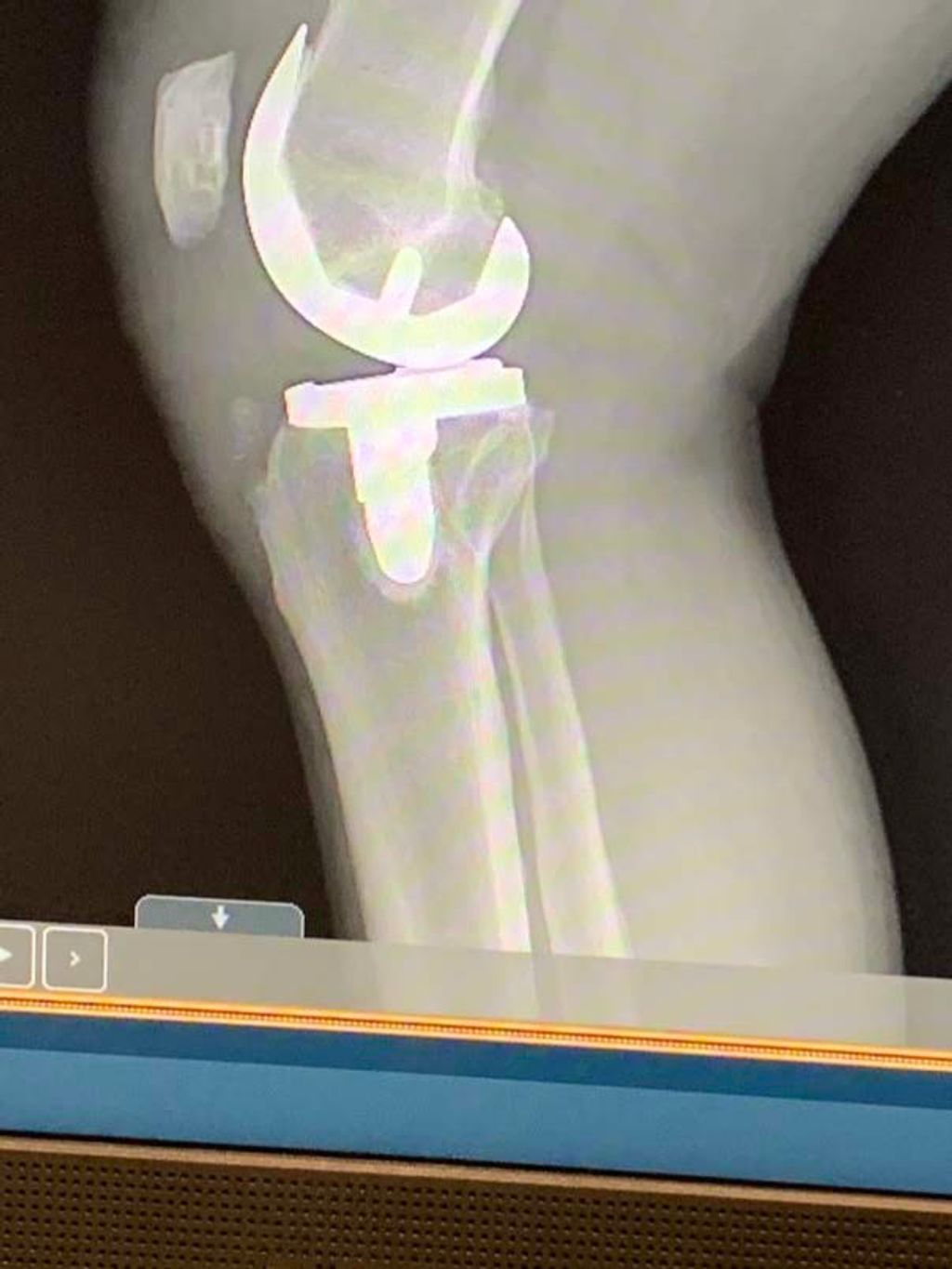
Are there surgical options for treating severe osteoarthritis knee pain?
In cases of severe osteoarthritis knee pain that does not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options such as knee replacement surgery or arthroscopic surgery may be recommended by orthopedic surgeons after thorough evaluation and consideration of individual health factors.