Hypermobile knees can present unique challenges and require specific management strategies to maintain mobility and reduce the risk of injury. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hypermobile knees is essential for individuals dealing with this condition. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of managing hypermobile knees and provide valuable insights into preventive measures and lifestyle changes.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the definition and characteristics of hypermobile knees is crucial for effective management.
- Conservative treatments such as bracing and taping can provide support and stability for hypermobile knees.
- Physical therapy and targeted exercise programs can help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and improve stability.
- Surgical interventions may be considered for severe cases of hypermobile knees, but they should be carefully evaluated and discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Joint protection techniques, proper nutrition, and exercise modifications play a vital role in preventing injuries and maintaining knee health.
Understanding Hypermobile Knees
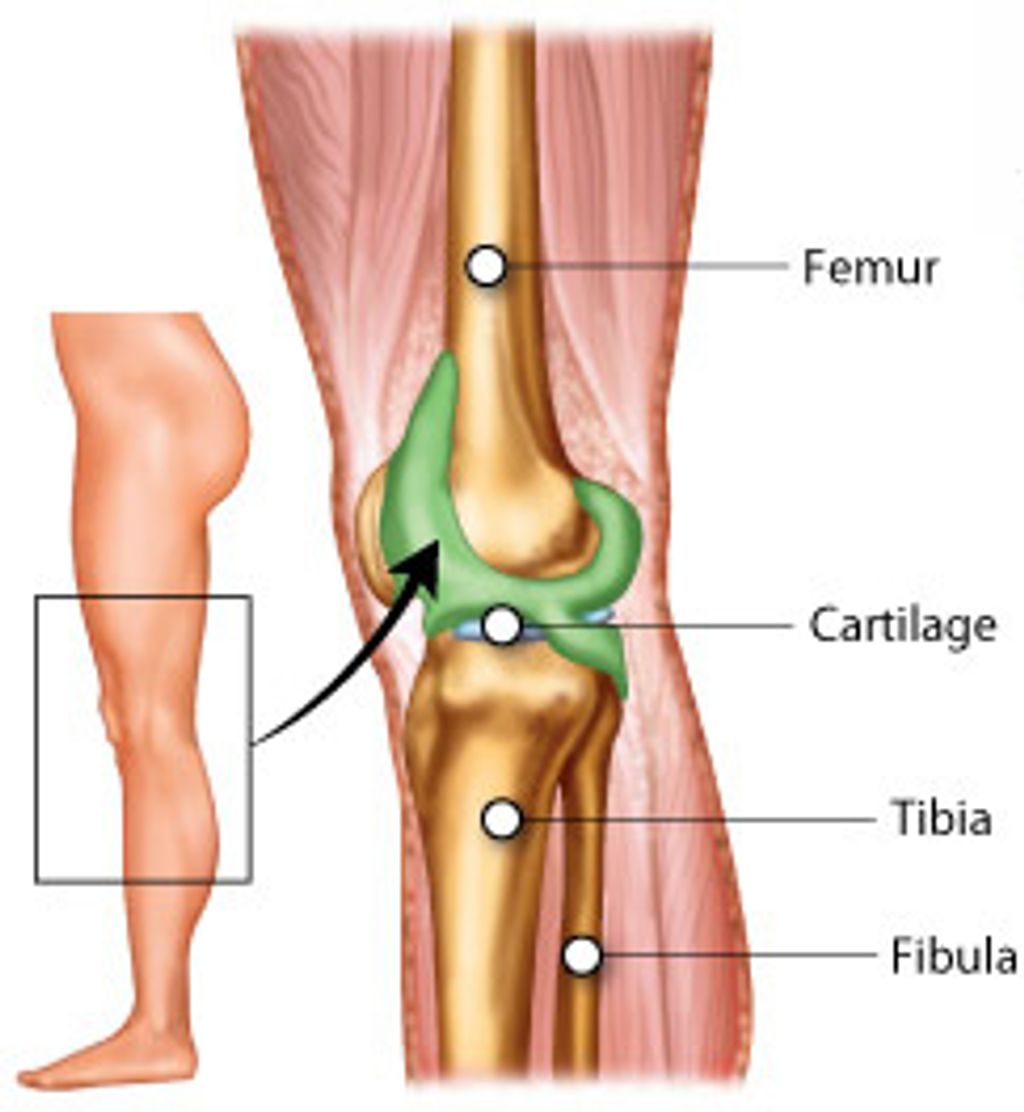
Definition and Characteristics
Hypermobile knees, also known as loose joints, are characterized by an excessive range of motion in the knee joint. This condition can lead to instability and increased susceptibility to injuries. Individuals with hypermobile knees may experience discomfort during physical activities and may be at a higher risk of developing knee-related complications. Understanding the causes and symptoms of hypermobile knees is crucial for effective management and treatment.
One common cause of hypermobile knees is ligament laxity, which can be a result of genetic factors or connective tissue disorders. Additionally, repetitive stress on the knee joint, such as from sports activities, can contribute to the development of hypermobility. Diagnosis of hypermobile knees involves a thorough physical examination, including assessing the degree of joint laxity and evaluating any associated symptoms.
It is important to note that hypermobile knees vary in severity, and the management approach should be tailored to each individual’s specific condition. Here is a table summarizing the characteristics of hypermobile knees:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Range of Motion | Excessive and unrestricted movement in the knee |
| Instability | Increased vulnerability to joint dislocation |
| Susceptibility | Higher risk of knee injuries and complications |
In addition to the table, here are some key points to consider when managing hypermobile knees:
- Implement joint protection techniques to minimize strain on the knee joint.
- Maintain a balanced diet and proper nutrition to support joint health.
- Modify exercise routines to avoid excessive stress on the knees.
Seeking professional guidance and support is essential for effectively managing hypermobile knees and minimizing associated discomfort and risks.
Causes of Hypermobile Knees
Hypermobile knees are primarily caused by ligament laxity, which refers to the excessive looseness of the ligaments surrounding the knee joint. This can be due to genetic factors, connective tissue disorders, or repetitive stress on the knee joint. It is important to note that hypermobile knees can lead to increased risk of injury and joint instability.
- It is crucial to maintain a balance between rest and physical activity to prevent overuse injuries.
- Implement joint protection techniques, such as using supportive braces during physical activities.
Tip: Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help improve knee stability and reduce the risk of injury.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Hypermobile knees can present with a range of symptoms, including instability, pain, and swelling. Diagnosis is typically based on a thorough physical examination, assessment of joint laxity, and may involve imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI scans. Additionally, a detailed medical history and evaluation of functional limitations are essential for accurate diagnosis. It’s important to note that symptoms may vary widely among individuals with hypermobile knees, and a personalized approach to diagnosis and management is crucial.
- Symptoms of Hypermobile Knees
- Instability
- Pain
- Swelling
Tip: Engaging in low-impact exercises and avoiding high-impact activities can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of injury. Regular monitoring and communication with a healthcare professional are key to effectively managing hypermobile knees.
Treatment Options for Hypermobile Knees
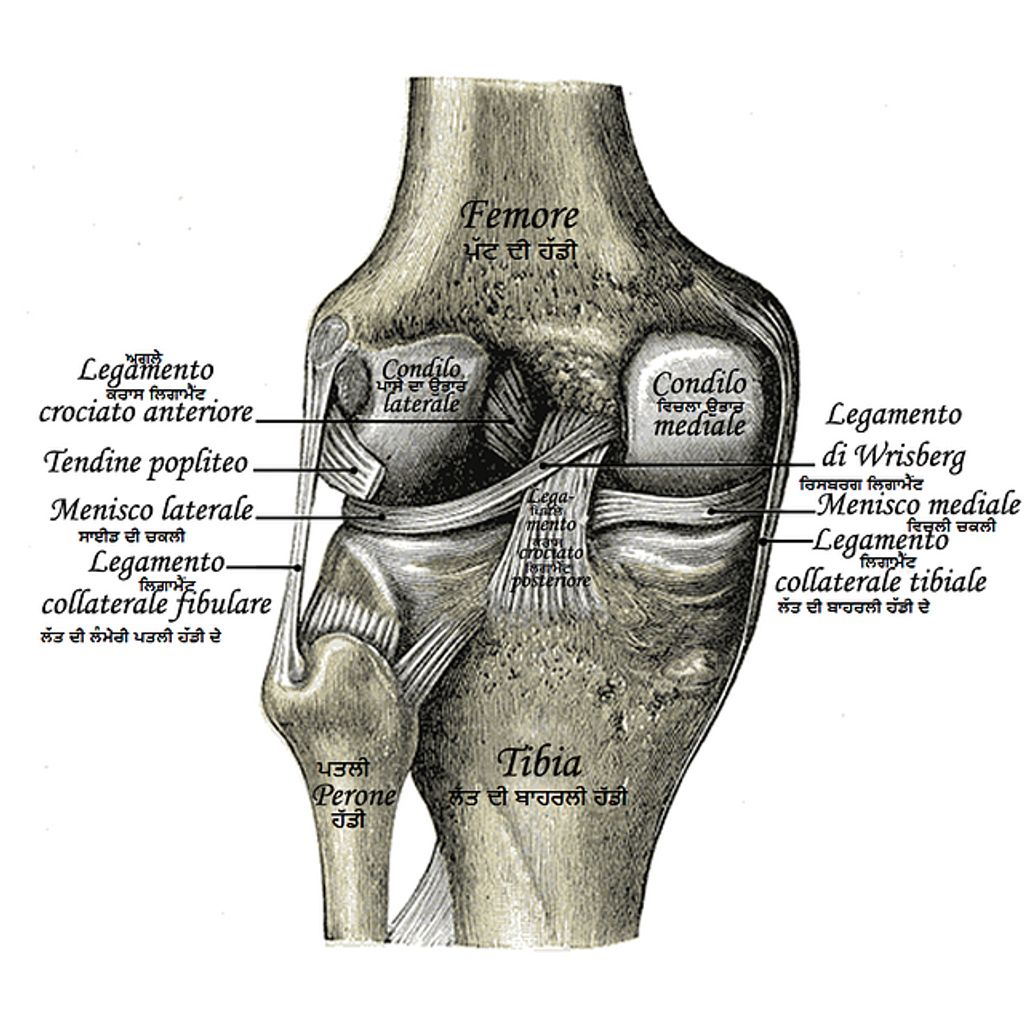
Conservative Treatments
When considering conservative treatments for hypermobile knees, it is important to focus on pain management and joint stability. This may involve a combination of physical therapy, bracing, and activity modification. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding high-impact activities can help reduce stress on the knees. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of individuals with hypermobile knees. Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can also contribute to overall joint health and function. Furthermore, incorporating joint protection techniques into daily activities can provide added support and minimize the risk of injury. It’s important to be mindful of posture and body mechanics to prevent unnecessary strain on the knees.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
In our journey to manage hypermobile knees, we recognize the pivotal role of physical therapy and exercise. Tailored exercise programs not only improve joint stability but also enhance muscle strength around the knee, which is crucial for joint support.
A typical physical therapy regimen may include:
- Strengthening exercises targeting the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
- Proprioception training to improve balance and joint position sense.
- Low-impact aerobic activities such as swimming or cycling to maintain cardiovascular fitness without overstressing the joints.
Tip: Always start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the difficulty under the guidance of a certified physical therapist.
It’s essential to maintain a consistent exercise routine, as sporadic efforts may lead to suboptimal results. We must also be mindful of our body’s signals; overexertion can exacerbate symptoms. Therefore, it’s important to strike a balance between activity and rest, ensuring that we do not push our knees beyond their capacity.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are considered when conservative treatments and physical therapy have not provided significant improvement in knee stability and function. These interventions may include procedures such as arthroscopic surgery, ligament reconstruction, or joint realignment. The decision to undergo surgical intervention is carefully evaluated based on the individual’s specific condition, severity of symptoms, and response to non-surgical treatments. It is important to consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of surgical options.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes

Joint Protection Techniques
When it comes to protecting our knees, proper alignment and body mechanics are crucial. We must also be mindful of our daily activities and make necessary adjustments to reduce strain on the joints. Additionally, incorporating supportive footwear and using assistive devices can further aid in minimizing the impact on our knees. It’s important to remember that small changes in our habits and routines can make a significant difference in preserving joint health and function.
Diet and Nutrition
When it comes to managing hypermobile knees, diet and nutrition play a crucial role in supporting overall joint health. Our dietary choices can impact inflammation levels and joint stability, affecting the symptoms associated with hypermobility. It’s important to focus on a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients, with an emphasis on foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are known to support bone health and may contribute to reducing joint discomfort and instability. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition can alleviate stress on the joints, potentially reducing the risk of injury and discomfort.
Exercise Modifications
Exercise modifications are an essential aspect of managing hypermobile knees. When engaging in physical activity, it is crucial to adapt exercises to minimize stress on the knee joints. This may involve reducing the range of motion in certain movements and incorporating low-impact activities. Additionally, focusing on strengthening the muscles around the knees through targeted exercises can provide significant benefits.
Incorporating a variety of exercises that promote stability and flexibility is key. This can include activities such as swimming, cycling, and modified yoga poses. These exercises help improve overall joint function and reduce the risk of injury. Furthermore, maintaining proper form and alignment during exercise is paramount for individuals with hypermobile knees.
For individuals with hypermobile knees, it is important to consult with a physical therapist or healthcare professional to develop a personalized exercise plan. This plan may include specific exercises, recommended frequency, and guidance on gradual progression. By working closely with a professional, individuals can ensure that their exercise routine is tailored to their unique needs and limitations.
It is important to note that exercise modifications should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a qualified professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of hypermobile knees requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses exercise, physical therapy, and joint protection. By understanding the challenges and implementing appropriate strategies, individuals with hypermobile knees can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Further research and clinical studies are needed to enhance our understanding of this complex condition and develop more targeted interventions for hypermobile knees.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are hypermobile knees?
Hypermobile knees are knees that have an excessive range of motion, often due to laxity in the ligaments and joint capsule.
What causes hypermobile knees?
Hypermobile knees can be caused by genetic factors, connective tissue disorders, or repetitive stress on the knee joint.
What are the common symptoms of hypermobile knees?
Common symptoms include knee instability, frequent joint dislocations, pain, and difficulty with activities that require stability.
How are hypermobile knees diagnosed?
Diagnosis is typically based on a physical examination, medical history, and possibly imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound.
What are the conservative treatment options for hypermobile knees?
Conservative treatments may include bracing, taping, activity modification, and orthotic devices to provide stability and support.
How can exercise be beneficial for hypermobile knees?
Specific exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve joint stability, and reduce the risk of injury for individuals with hypermobile knees.