Have you ever wondered why inner knee discomfort lingers despite rest or basic care? This guide dives into a common yet overlooked condition affecting athletes, active adults, and anyone experiencing persistent joint issues. We’ll uncover how a small, fluid-filled sac near your knee could hold answers to your mobility struggles.
Inflammation in this area often develops from repetitive motions or sudden strain. The result? Sharp aches during movement, tenderness when touched, and stiffness that limits daily activities. While these signs might seem vague, recognizing them early can prevent long-term complications.
Our focus combines insights from leading medical institutions with practical recovery strategies. You’ll learn how simple adjustments to exercise routines or targeted therapies can accelerate healing. We’ve prioritized clear, actionable steps to help you regain comfort without invasive procedures.
Key Takeaways
- Inner knee inflammation often stems from repetitive stress or improper movement patterns.
- Early intervention typically leads to faster recovery through conservative methods.
- Diagnosis combines physical exams with imaging to rule out similar conditions.
- Effective management blends rest, targeted exercises, and anti-inflammatory approaches.
- Trusted medical resources form the foundation of our recommended strategies.
Let’s explore how understanding this condition’s nuances can transform your approach to joint health. From identifying warning signs to implementing proven relief methods, we’ll walk through each phase of recovery together.
Introduction to Pes Anserine Bursitis
A tiny sac near the knee can lead to significant mobility issues when inflamed. The pes anserine bursa sits just below the knee joint on the inner leg, cushioning tendons during movement. When irritated, this fluid-filled structure swells, creating friction that disrupts natural motion.

Repetitive strain from activities like running or climbing often triggers this condition. Poor training form and underlying issues such as osteoarthritis amplify risks. Athletes and active adults frequently report tenderness when bending or straightening the leg.
| Feature | Healthy Bursa | Inflamed Bursa |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Reduces friction | Creates painful friction |
| Pain Level | None | Sharp during activity |
| Mobility | Unrestricted | Stiffness after rest |
| Common Triggers | Normal use | Overuse or injury |
Proper diagnosis separates this issue from similar knee problems. Healthcare providers assess swelling patterns and pressure points while reviewing activity history. Early identification helps avoid prolonged discomfort and supports targeted recovery plans.
We’ll explore how strategic care restores function while preventing recurrence. Next sections detail practical steps to address root causes rather than just masking discomfort.
What is Pes Anserine Bursitis?
Imagine your knee’s shock absorber failing during routine movements. The pes anserine region houses a critical cushioning structure where three tendons converge near the shinbone. This bursa normally prevents bone-to-tendon friction during walking or climbing.

Anatomy and Function of the Bursa
Located two inches below the kneecap’s inner edge, this fluid-filled sac separates the tibia from connected hamstring tendons. It acts like biological Teflon® – reducing wear from repetitive motions. When functioning properly, you’ll never notice its presence.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Three primary elements trigger irritation in this sensitive area:
- Repetitive leg motions (running, squatting)
- Excessive body weight straining connective tissues
- Biomechanical issues like bowed legs or flat feet
Runners often develop issues after sudden mileage increases. Weekend warriors risk inflammation through inconsistent training. Tight thigh muscles compound these problems by pulling excessively on the bursa during activity.
Understanding these mechanisms helps create smarter recovery plans. Next, we’ll examine how professionals distinguish this condition from similar knee issues.
Pes anserine bursitis symptoms and treatment
Recognizing early warning signals of inner knee inflammation helps people seek care before limitations escalate. Many dismiss discomfort as normal soreness until simple tasks like rising from chairs become challenging.
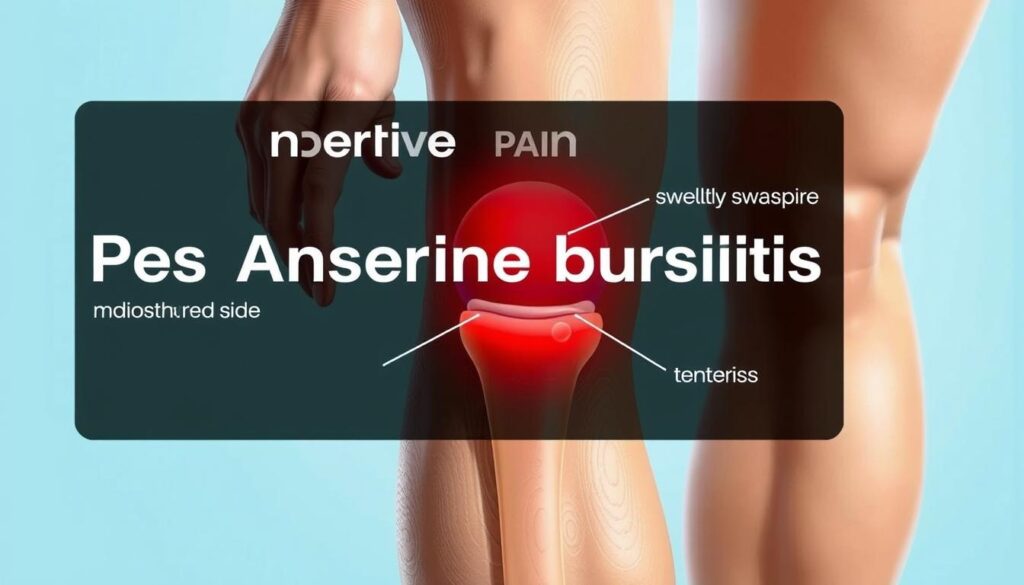
Recognizing the Symptoms
Three primary markers distinguish this condition from general joint strain:
- Persistent ache concentrated 2-3 inches below the kneecap
- Visible puffiness along the shinbone’s upper edge
- Sharp flares when bending or straightening the leg
Movement patterns often reveal hidden triggers. Climbing stairs or hills typically intensifies discomfort due to increased tendon friction. Nighttime stiffness after active days also signals irritated tissues.
| Diagnostic Method | Key Indicators | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Exam | Localized warmth, pressure sensitivity | Rule out meniscus tears |
| Activity Analysis | Pain patterns during specific motions | Identify movement triggers |
| Imaging | Bursa thickness, tendon alignment | Confirm fluid buildup |
Treatment Strategy Foundations
Initial care focuses on breaking the inflammation cycle. Rest reduces mechanical stress while ice application calms swollen tissues. Over-the-counter NSAIDs provide temporary relief but don’t address root causes.
Effective plans combine multiple approaches:
- Activity modifications to protect healing areas
- Targeted stretches improving tendon mobility
- Strengthening exercises stabilizing the joint
Medical professionals often recommend evidence-based non-surgical recovery plans first. Early intervention using these methods typically restores function within weeks while preventing chronic issues.
Diagnosing Pes Anserine Bursitis
Modern imaging tools reveal hidden causes of mobility challenges. Healthcare providers start with hands-on evaluations to map discomfort patterns. They press specific areas below the knee while observing reactions to identify tender zones linked to the pes anserinus region.
Confirming Inflammation Through Testing
Three-step verification ensures accurate results:
- Physical assessment: Checking for localized swelling along the upper tibia
- Movement analysis: Monitoring pain during stair climbing or leg rotations
- Imaging correlation: Matching symptoms with visual evidence
X-rays eliminate bone fractures, while ultrasound scans detect fluid buildup in soft tissues. MRI examinations provide detailed views of tendon alignment near the knee joint. These methods help distinguish this condition from meniscus injuries or osteoarthritis.
| Diagnostic Tool | Key Function | Accuracy Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Exam | Identifies pressure points | 78% |
| Ultrasound | Visualizes bursa thickness | 92% |
| MRI | Assesses surrounding structures | 95% |
Definitive diagnosis prevents mismanagement of similar knee issues. Providers combine test results with activity histories to create personalized recovery plans. This precision ensures therapies target the root problem rather than general discomfort.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Addressing tendon-related discomfort demands methods that target both symptoms and causes. Healthcare teams prioritize approaches that calm irritation while rebuilding strength. We’ll explore proven techniques ranging from basic self-care to advanced clinical interventions.
Non-Operative Approaches: Rest, Ice, and Medication
Initial care focuses on reducing strain. Short-term activity changes protect healing tissues – think swapping runs for swimming or cycling. Applying cold packs for 15-minute intervals lowers swelling effectively when done 3-4 times daily.
Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen ease discomfort temporarily. However, prolonged use requires medical supervision. Many find compression sleeves helpful during light activities to support the area without restricting blood flow.
| Approach | Key Actions | Average Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Rest & Activity Modification | Limit bending/squatting | 2-4 weeks |
| Ice Application | 15 mins, 3x/day | Immediate relief |
| Medication | NSAID regimen | 3-7 days |
Physical Therapy, Ultrasound, and Injection Therapies
Structured rehab programs restore mobility safely. Therapists guide patients through gentle stretches that loosen tight hamstrings and improve tendon glide. Ultrasound technology enhances blood flow to accelerate natural repair processes.
For persistent cases, corticosteroid injections deliver anti-inflammatory agents directly to the affected area. These are often paired with numbing agents for immediate comfort. Clinical studies show 80% of patients report significant improvement within 72 hours post-treatment.
Every plan adapts to individual needs. Providers monitor progress through follow-up assessments, adjusting techniques as healing advances. This personalized strategy ensures lasting results rather than temporary fixes.
Practical Exercises and Rehabilitation Guidance
What if targeted movements could speed up your recovery while protecting vulnerable tissues? Strategic movement plans rebuild strength without overloading healing areas. We focus on methods that restore flexibility while teaching your body safer movement patterns.
Effective Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Hamstring stretches reduce tension pulling on the inner knee. Try seated stretches with legs extended, reaching gently toward your toes. Hold for 20 seconds, repeating 3 times daily. Wall-assisted stretches let you control intensity while standing.
Strengthen supporting muscles with bridges and side-lying leg lifts. These low-impact exercises build stability without bending the knee excessively. Start with 2 sets of 10 reps, increasing gradually as discomfort decreases.
| Exercise Type | Frequency | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Seated Stretch | 3x daily | Improves tendon glide |
| Wall Push Stretch | 2x daily | Reduces muscle tightness |
| Bridging | 4x weekly | Strengthens glutes |
Recovery Tips and Activity Modifications
Modify daily activities to avoid reinjury. Use handrails on stairs and limit squatting motions during household chores. Swap high-impact workouts for swimming or cycling until symptoms improve.
Track progress with a simple journal. Note pain levels during specific movements and adjust your program accordingly. Many find compression sleeves helpful during light activity, providing support without restricting circulation.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Preventive Measures
Protecting joint health requires smart daily choices that outpace wear and tear. For those recovering from or prone to pes anserine issues, small habit shifts create lasting protection. We’ll explore practical ways to maintain mobility while reducing strain on vulnerable areas.
Building Sustainable Routines
Three adjustments significantly lower recurrence risks:
- Footwear upgrades: Choose shoes with arch support and shock absorption
- Movement pacing: Alternate high-impact sports with low-stress activities
- Pre-activity prep: Implement dynamic warm-ups targeting hamstrings
“Gradual progression in training intensity allows tissues to adapt without overload,” notes sports physical therapist Dr. Elena Martinez.
| Focus Area | Action Steps | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Footwear Selection | Replace worn shoes every 300-500 miles | Reduces knee torque by 18% |
| Training Modifications | Mix running with swimming or cycling | Cuts repetitive stress by 40% |
| Weight Management | Combine balanced nutrition with strength training | Lowers joint pressure 5x per pound lost |
Individuals with osteoarthritis management strategies should prioritize consistent strength programs. Focus on quadriceps and hip stabilizers during workouts – these muscles absorb impact before it reaches the knee.
Weekly activity plans balance challenge and recovery. Sample schedules might include two days of strength training, three days of moderate cardio, and dedicated flexibility sessions. Tracking progress helps identify patterns that trigger discomfort early.
Conclusion
Effective management of knee discomfort begins with understanding its origins. Early recognition of pes anserine bursitis allows for swift action, combining rest with targeted therapies to reduce inflammation. Diagnostic tools like ultrasound help confirm fluid buildup while ruling out other joint issues.
Successful recovery hinges on tailored plans addressing both symptoms and causes. Physical therapy strengthens surrounding muscles, while activity modifications prevent reinjury. Studies show structured exercise programs improve mobility in 89% of cases within six weeks.
Consult healthcare providers if inner-leg tenderness persists during daily movements. Accurate imaging and professional guidance create roadmaps for lasting relief. Preventive strategies like supportive footwear and gradual training progressions further protect vulnerable areas.
With proper care, most individuals regain full function without invasive procedures. Small, consistent changes in movement patterns and self-care routines make recovery achievable. Reach out to specialists to design a plan matching your unique needs and lifestyle.
FAQ
How does pes anserine bursitis differ from other knee conditions?
Unlike arthritis or ligament injuries, this condition specifically involves inflammation of the bursa near the hamstring tendons. Pain typically occurs 2–3 inches below the knee joint and worsens with activities like climbing stairs or prolonged sitting.
Can physical therapy exercises worsen the pain?
When guided by a licensed therapist, targeted stretches and strengthening routines often reduce discomfort. We recommend avoiding high-impact movements initially and focusing on low-stress exercises like seated leg lifts or gentle hamstring stretches to avoid aggravating the area.
Are corticosteroid injections safe for long-term use?
While effective for short-term relief, repeated injections may weaken nearby tissues. We prioritize combining them with rest, ice therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications to minimize risks. Always discuss treatment plans with your healthcare provider.
What daily habits contribute to flare-ups?
Repetitive motions like squatting, sudden increases in exercise intensity, or poor footwear choices often trigger inflammation. We suggest modifying workouts, using supportive shoes, and incorporating rest days to manage stress on the knee.
How long does recovery typically take?
Most people see improvement within 4–6 weeks with consistent treatment. Chronic cases linked to osteoarthritis or obesity may require longer rehab. Early diagnosis and a structured therapy program improve outcomes significantly.
Is ultrasound imaging necessary for diagnosis?
While MRI or ultrasound can confirm inflammation, many providers diagnose based on physical exams and symptom history. Imaging is usually reserved for unclear cases or to rule out tears in the tendons or meniscus.
Can ice packs replace prescription medications?
Ice reduces swelling effectively but doesn’t address underlying inflammation. We combine cryotherapy with NSAIDs like ibuprofen for comprehensive management. Always consult a doctor before starting new medications.
Are there sports to avoid during recovery?
High-impact activities like basketball or running often strain the knee. We recommend switching to swimming, cycling, or yoga until tenderness subsides. Gradually reintroduce sports under a therapist’s supervision.