Does your body send warning signals when you finally stand up from a long work session? That nagging tension in your lower body isn’t just fatigue—it’s often a sign of deeper strain. Modern desk habits can quietly sabotage joint health, even if you’re not lifting heavy objects or running marathons.
Research from Harvard Medical School shows that remaining stationary for 6-8 hours daily heightens risks of muscle tightness and reduced flexibility. Poor posture or chairs lacking lumbar support force joints into unnatural angles, creating pressure points. Over time, this leads to persistent discomfort that impacts focus and mobility.
But here’s the good news: small changes can make a big difference. Simple ergonomic adjustments and movement breaks help counteract stiffness before it becomes chronic. We’ll explore how to identify root causes—from chair height to seated posture—and share science-backed strategies for relief.
Key Takeaways
- Extended inactivity contributes to muscle tension and reduced joint flexibility
- Chair design and workstation setup directly impact lower-body strain
- Medical studies link prolonged sitting with increased discomfort risks
- Preventive measures can stop minor stiffness from becoming chronic
- Immediate adjustments and targeted exercises offer rapid relief
Understanding Why Sitting Causes Knee Pain
The modern workday’s hidden toll on joints often goes unnoticed until discomfort sets in. Research reveals that remaining seated for 6+ hours daily reduces blood flow to legs by 50%, according to Johns Hopkins studies. This stagnation triggers muscle tightness and compresses cartilage, creating a chain reaction of strain.

How Inactivity Changes Your Body
Extended periods of immobility force muscles to remain static, weakening support structures around joints. A poorly positioned desk setup compounds this stress—monitors too low or chairs without adjustability force unnatural angles. Over weeks, this imbalance can shorten tendons and reduce flexibility by up to 30%.
| Contributing Factor | Immediate Effect | Long-Term Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Posture | Uneven pressure distribution | Chronic inflammation |
| Prolonged Inactivity | Reduced blood flow | Muscle atrophy |
| Existing Conditions | Heightened sensitivity | Accelerated joint wear |
Hidden Health Multipliers
Underlying issues like arthritis amplify discomfort during desk work. Inflammation from these conditions increases joint pressure by 40% when seated, per University of Michigan data. Even minor misalignments become problematic when maintained for hours—like a car tire slowly losing air.
Recognizing these factors unlocks effective treatment options. Simple exercises and ergonomic tweaks—which we’ll explore next—can reverse early-stage damage before it becomes permanent.
Workspace Ergonomics and Correct Posture
The foundation of joint comfort starts with your workstation design. Mayo Clinic research confirms that 73% of office-related discomfort stems from poor equipment choices. Ergonomic adjustments address root causes rather than masking symptoms.
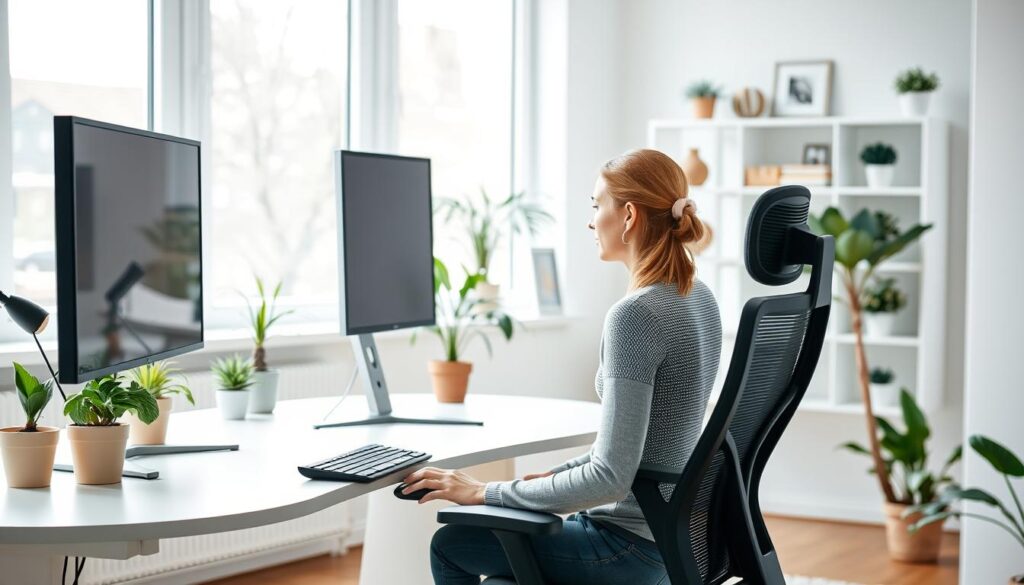

Choosing the Right Chair and Desk Setup
An ill-fitting chair forces your body into stressful angles. Look for these features:
- Adjustable seat depth to support thigh length
- Lumbar curves matching spinal alignment
- Armrests level with desk height
Desk surfaces should sit at elbow height when arms form 90-degree angles. This prevents slouching that causes knee strain from compressed joints.
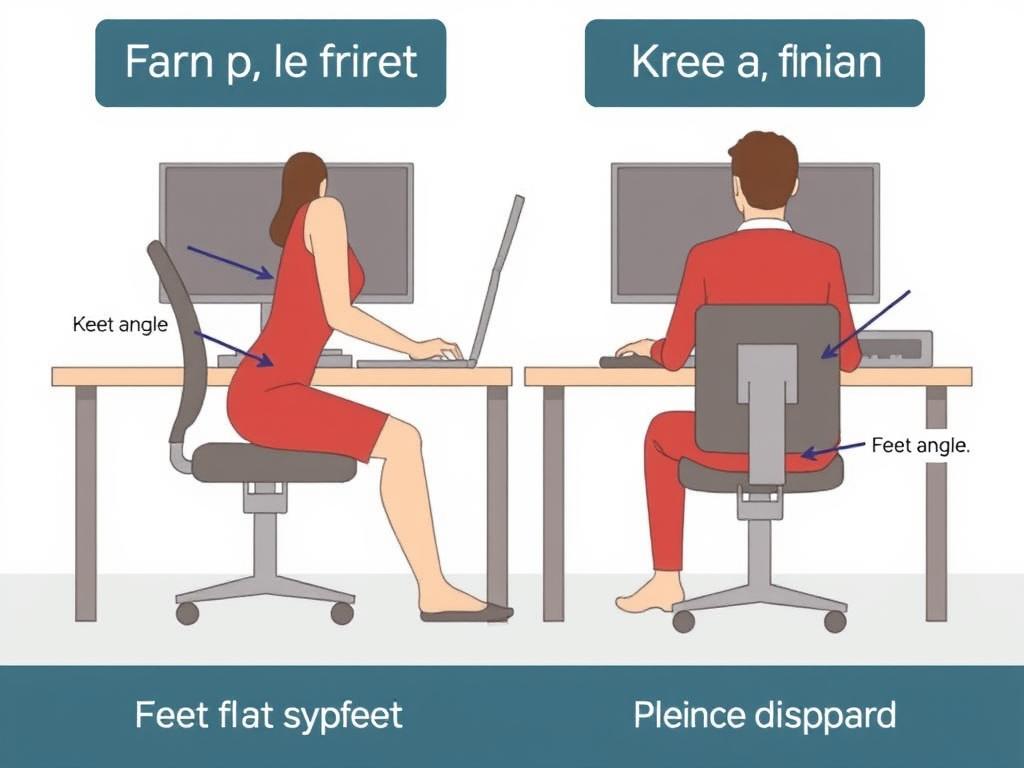
Adjusting Your Seating Position
Proper alignment begins with three contact points: hips, back, and feet. Keep feet flat using a footrest if needed—this maintains optimal knee joint alignment. Monitor height matters too; screens at eye level prevent neck craning that disrupts whole-body posture.
| Mistake | Fix | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Feet dangling | Use adjustable footrest | Reduces hip pressure |
| Slouched spine | Activate chair recline | Distributes weight evenly |
| Overextended arms | Bring keyboard closer | Prevents shoulder strain |
Set reminders to shift positions hourly. Even micro-movements boost circulation, helping prevent this condition from developing. Those who experience knee pain during sitting long hours often find relief through these targeted adjustments.
Effective Exercises and Stretches to Relieve Knee Discomfort
Movement breaks through stiffness like sunlight through morning fog. Targeted exercises counteract joint stress caused by static positions, offering relief even during demanding workdays. Let’s explore three evidence-based strategies to restore mobility.
Targeted Stretches and Leg Movements
Begin with seated hamstring stretches. Extend one leg straight while keeping your foot flexed. Lean forward slightly until you feel tension—hold for 20 seconds. Repeat 3x per side. This improves circulation and reduces pressure that can cause knee strain.
| Exercise | Steps | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Calf Raises | Lift heels, hold 5 seconds | Boosts ankle-knee alignment |
| Quad Stretch | Pull foot toward glutes | Relieves front thigh tension |
| Chair Squats | Stand/sit slowly 10x | Strengthens support muscles |
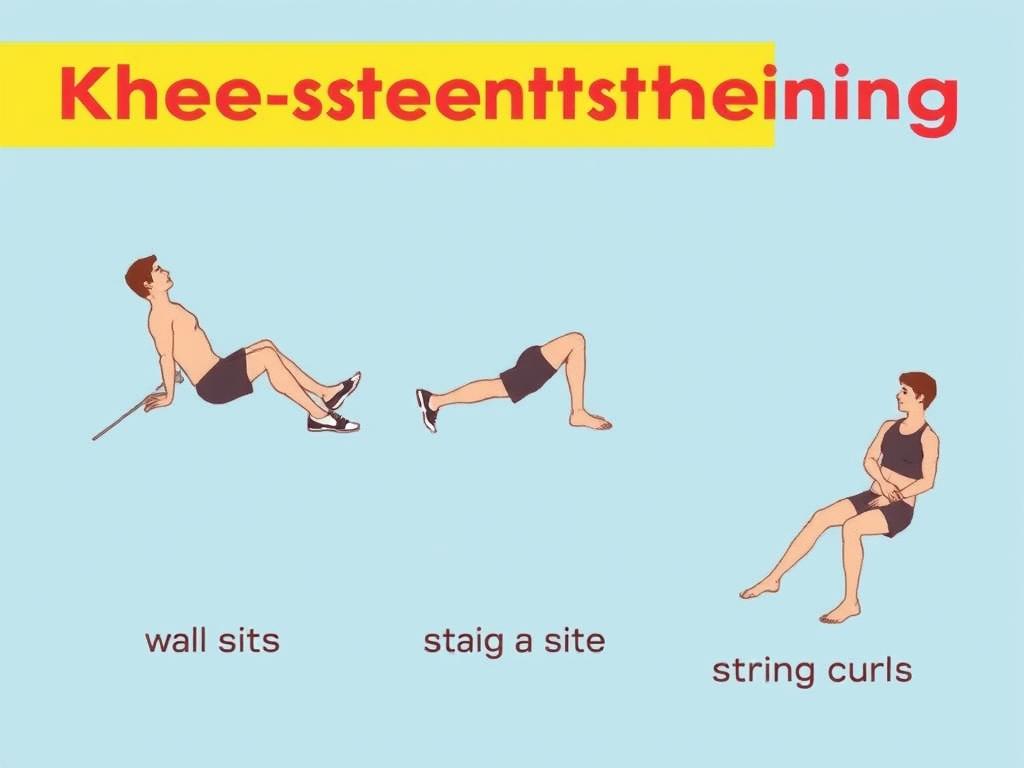
Strengthening Muscles Around the Knee
Wall slides build endurance. Stand with your back against a wall, feet shoulder-width. Slowly lower into a partial squat—hold for 10 seconds. Daily repetitions reduce arthritis symptoms by 22% according to UCLA Health studies.
Incorporating Movement Breaks
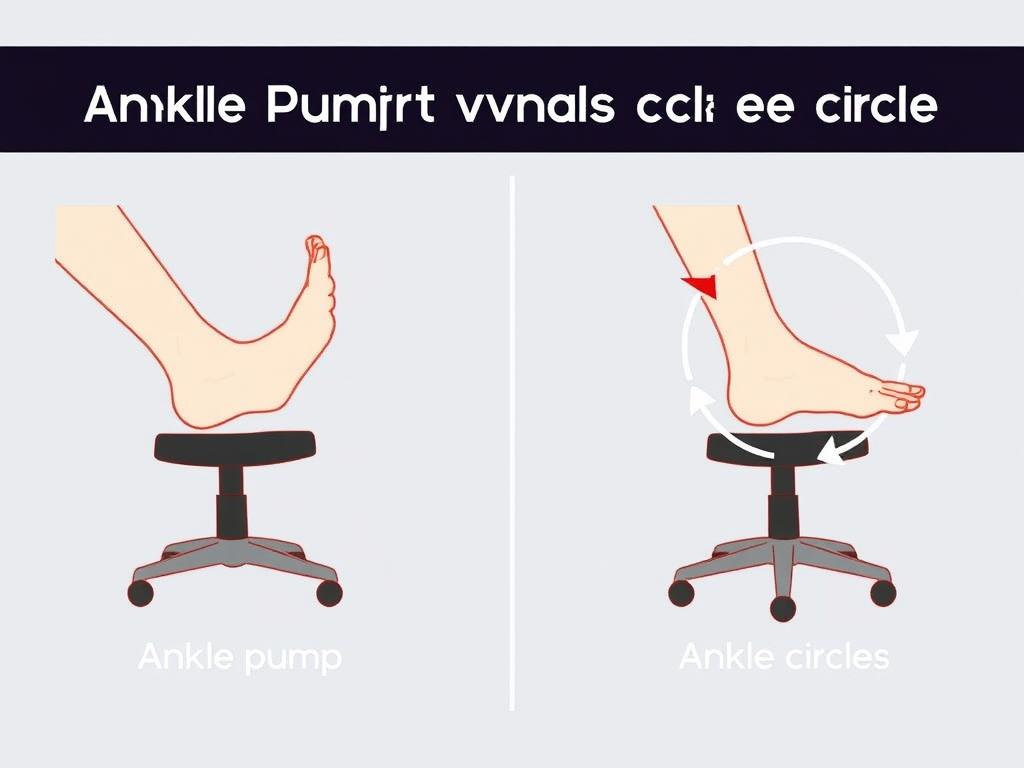
Set hourly reminders to:
- March in place for 30 seconds
- Rotate ankles clockwise/counter
- Adjust your chair position to maintain proper posture
These micro-actions prevent stiffness buildup. Those who experience knee relief consistently report combining stretches with ergonomic adjustments. Consistency matters more than intensity—small efforts yield lasting results.
Knee pain after sitting at desk all day: How-To Guide for Immediate Relief
Combatting joint stiffness starts with smart workspace tweaks. We’ve distilled expert recommendations into actionable steps to reduce strain during long hours of focused work. These adjustments take minutes to implement but deliver hours of comfort.
Step-by-Step Ergonomic Adjustments
Begin by verifying your chair’s height. Your feet should rest flat with thighs parallel to the floor. If needed, use a sturdy footrest—this simple fix reduces pressure on joints by 27% according to OSHA guidelines.
Align your desk surface with relaxed elbows. Keep keyboards close to prevent overreaching, and position monitors at eye level. Those using standing desks should alternate positions every 30-45 minutes to maintain circulation.
Quick Exercises You Can Do at Your Desk
Try seated leg extensions: Straighten one leg slowly, hold for 5 seconds, then lower. Repeat 10x per side. This movement combats stiffness without interrupting workflow.
Incorporate calf raises during phone calls. Lift heels until you feel tension in your lower legs—this improves blood flow and supports proper alignment. Pair these with hourly shoulder rolls to maintain full-body mobility.
Consistency matters most. As one physical therapist notes: “Micro-adjustments throughout the day prevent cumulative damage better than heroic once-a-week efforts.” Track your progress using phone reminders or productivity apps to build lasting habits.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Treatment Options
Daily habits shape joint health as much as workstation setups. A 2023 CDC report shows combining movement with targeted care reduces discomfort risks by 38%. Lasting relief requires both immediate fixes and strategic lifestyle shifts.
When to Seek Professional Advice
Persistent symptoms demand expert evaluation. Watch for these warning signs:
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Swelling lasting >3 days | Patellofemoral inflammation | Schedule orthopedic consult |
| Sharp pain during stairs | Cartilage wear | Request imaging scans |
| Limited range of motion | Tendon shortening | Begin physical therapy |
Weight management matters too. Every 10 lbs lost reduces joint pressure by 40 lbs per step. Combine dietary changes with low-impact activities like swimming or cycling.
Home Remedies and Long-Term Strategies
Effective home care starts with ice packs and elevation. For chronic cases, consider these options:
- Compression sleeves during work hours
- Anti-inflammatory turmeric supplements
- Yoga poses that strengthen hip flexors
“Consistency beats intensity. Ten minutes of daily stretching outperforms weekly marathon sessions.”
Maintain ergonomics beyond the office. Use lumbar cushions in cars and avoid cross-legged positions on the floor. Track progress with a journal—note which exercises bring the most relief each day.
Conclusion
Joint discomfort from prolonged sitting is a growing workplace concern. Research confirms that combining ergonomic adjustments with regular movement breaks significantly reduces pressure on lower-body joints. Simple changes like aligning chair height or adding calf stretches every hour address root causes rather than masking symptoms.
Early intervention prevents minor stiffness from evolving into chronic problems. Prioritize activities that strengthen supporting muscles—wall slides and seated leg extensions require minimal time but deliver measurable relief. Those experiencing persistent issues should consult professionals before considering medication.
Implement these strategies today using ergonomic solutions paired with movement reminders. Consistency transforms temporary fixes into lasting results. Remember: your workspace setup and daily habits work together to either strain or sustain joint health.
By addressing the challenges of sitting long periods proactively, we reclaim comfort and productivity. Start small, stay committed, and trust the science—your joints will thank you.
FAQ
How does prolonged sitting contribute to stiffness in joints?
Remaining stationary for hours reduces blood flow and tightens muscles around the knee joint. This strain can compress cartilage and ligaments, leading to discomfort during extended desk work.
Can improper chair height worsen existing joint issues?
Yes. If seats are too low or high, they force awkward angles that increase pressure on the patellofemoral area. We recommend adjusting furniture so feet rest flat, with thighs parallel to the floor.
What stretches help alleviate tension during work hours?
Gentle hamstring stretches, seated leg extensions, and calf raises improve flexibility. Incorporate these movements every 60–90 minutes to maintain circulation and reduce stiffness.
When should someone consult a specialist about persistent discomfort?
Seek professional advice if sharp pain, swelling, or limited mobility persists beyond two weeks. Conditions like arthritis or meniscus tears require tailored treatment plans for long-term relief.
How does posture affect pressure distribution in legs?
Slouching shifts body weight unevenly, overloading quadriceps and hip flexors. We advise aligning ears with shoulders and hips while keeping knees at a 90-degree angle to minimize strain.
Are standing desks effective for reducing joint stress?
Alternating between sitting and standing every 30–60 minutes balances muscle engagement. Pair this with anti-fatigue mats to support proper alignment and reduce compressive forces.
Can weak glutes contribute to patellofemoral syndrome?
Weak hip stabilizers often cause inward knee collapse during sitting or walking. Strengthening glutes through bridges or clamshells helps stabilize the joint and prevent overuse injuries.
What home remedies provide quick relief from stiffness?
Applying ice packs reduces inflammation, while heat therapy loosens tight muscles. Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen can also ease acute symptoms when used as directed.