The knee joint is a complex structure consisting of bones, ligaments, and cartilage that play a crucial role in supporting the body’s weight and facilitating movement. Knee bones, including the femur, tibia, and patella, are integral to the overall function of the knee joint. Understanding the importance of knee bones in joint health is essential for preventing and managing various knee bone disorders. This article explores the significance of knee bones, common knee bone disorders, diagnostic techniques, and treatment options for maintaining knee bone health and overall joint function.
Key Takeaways
- Knee bones play a vital role in weight bearing and movement of the knee joint.
- Common knee bone disorders include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and fractures.
- Diagnostic techniques for knee bone health include imaging modalities, laboratory tests, and clinical evaluations.
- Treatment options for knee bone conditions may involve medications, surgical interventions, and rehabilitation.
- Maintaining knee bone health is crucial for preserving overall joint function and mobility.
The Structure and Function of Knee Bones
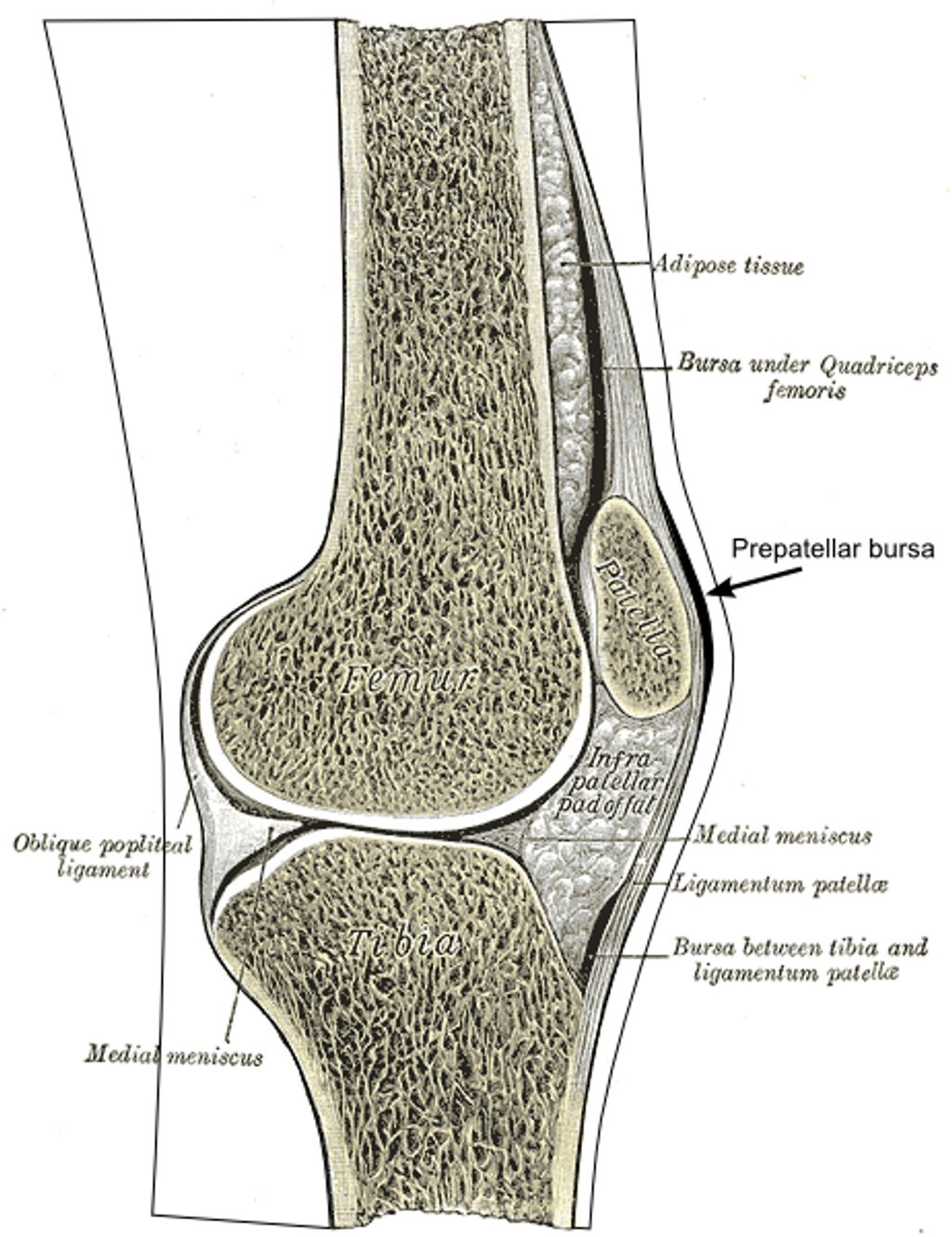
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
The knee joint is a complex structure that relies on the interaction of several components, including bones, ligaments, and cartilage. Understanding the anatomy of the knee bones is crucial for comprehending their role in supporting the joint and facilitating movement. Let’s delve into the intricate details of knee bone structure and function.
| Bone Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Femur | Weight bearing |
| Tibia | Stability and support |
| Patella | Protection and leverage |
In the knee joint, the femur, tibia, and patella work together to enable smooth and controlled movement. Each bone has a specific function, contributing to the overall stability and mobility of the joint. Understanding the unique role of each bone is essential for comprehending the impact of knee bone health on joint function.
Role of Knee Bones in Weight Bearing
We often take for granted the remarkable role our knee bones play in supporting the weight of our bodies. The knee joint, primarily the femur, tibia, and patella, works in unison to bear the load during various activities such as walking, running, and jumping. The femur, or thigh bone, acts as a pivotal column transferring the weight from the hip joint to the knee. The tibia, or shinbone, then distributes this weight to the ankle and foot.
Stability and mobility are two essential functions provided by the knee bones. They are designed to withstand significant forces and stresses while providing a range of motion necessary for movement. The knee joint’s ability to absorb shock is also crucial in weight bearing, as it reduces the impact on the rest of the skeleton.
- The femur distributes weight from the hip to the knee.
- The tibia transfers weight to the ankle and foot.
- The patella, or kneecap, protects the knee joint and aids in leg extension.
Maintaining healthy knee bones is vital for overall joint health and functionality. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and avoiding excessive strain can help preserve knee bone integrity.
Impact of Knee Bone Health on Joint Function
We must acknowledge the pivotal role that the health of our knee bones plays in the overall function of our joints. Healthy knee bones are essential for maintaining joint stability and enabling smooth movement. When knee bones are compromised, either through injury or disease, the consequences can be severe, leading to pain, reduced mobility, and a diminished quality of life.
Osteoporosis, for example, can lead to a decrease in bone density, making the knee bones more susceptible to fractures. This can significantly impact an individual’s ability to bear weight and perform daily activities. Conversely, maintaining strong knee bones through regular exercise and proper nutrition can help prevent such outcomes. New research confirms exercise benefits for bone health, suggesting a proactive approach to maintaining knee bone health is advantageous.
Over-the-counter solutions and tips for managing knee pain can be valuable for those experiencing discomfort. However, it’s important to consult healthcare professionals to ensure that these methods are appropriate and effective for your specific condition.
Tip: Always consider low-impact exercises and activities that promote knee joint health without placing undue stress on the bones.
Common Knee Bone Disorders
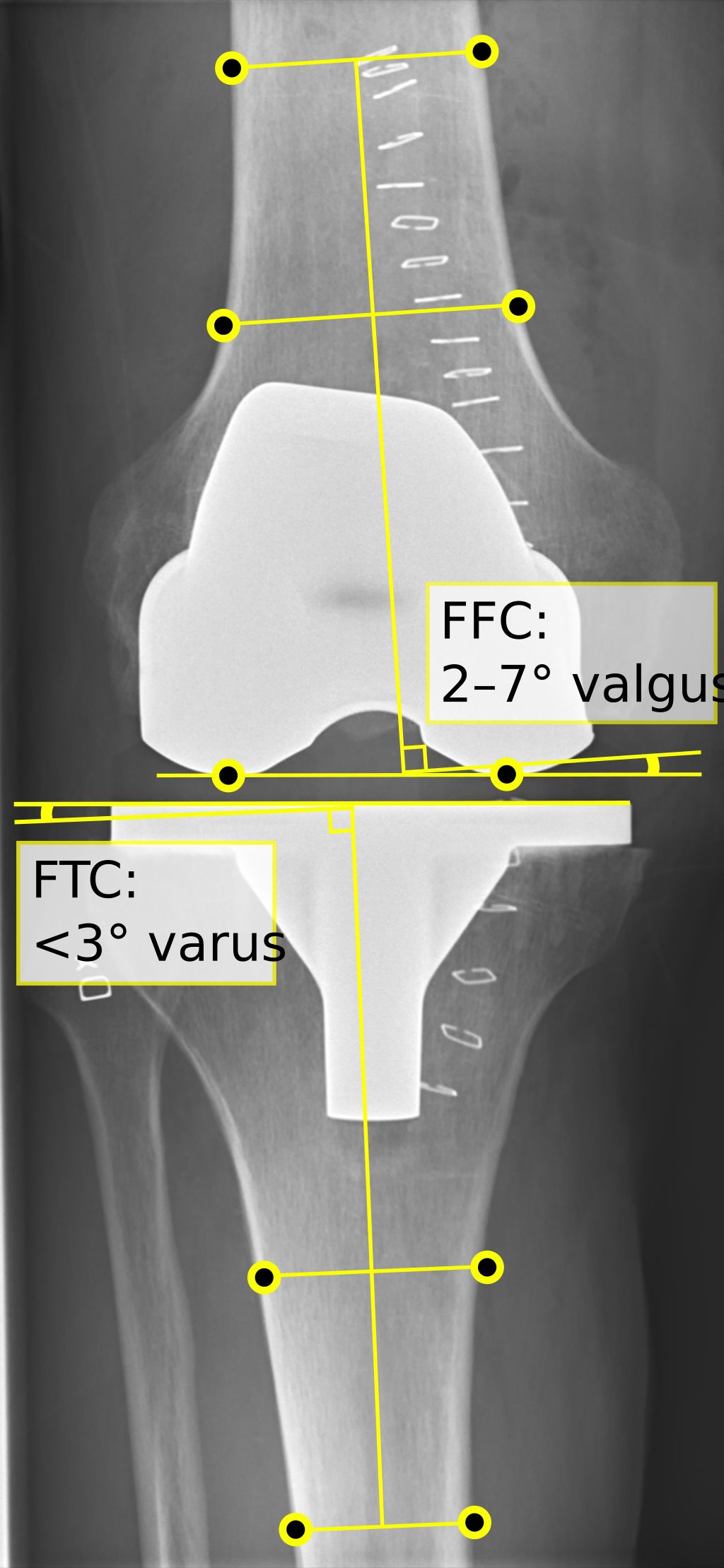
Osteoarthritis of the Knee
We recognize osteoarthritis as a prevalent knee bone disorder characterized by the gradual deterioration of cartilage. This degeneration leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the knee joint. As the condition progresses, the bones may begin to rub against each other, causing further discomfort and potential deformities.
The management of osteoarthritis involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and in some cases, surgery. We emphasize the importance of maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular, low-impact exercise to alleviate symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
- Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid might provide temporary relief.
- When conservative treatments are insufficient, surgical options like arthroscopy, osteotomy, or joint replacement may be considered.
Tip: Early intervention and a tailored treatment plan are crucial for managing osteoarthritis effectively and maintaining joint health.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Knee Bone Degeneration
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. It can lead to progressive degeneration of the knee bones, causing significant impairment in joint function. The inflammatory nature of rheumatoid arthritis can result in erosion of the bone and cartilage, leading to joint deformity and disability. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing the impact of rheumatoid arthritis on knee bone health. Here is a brief overview of the diagnostic techniques and treatment options for this condition:
- Imaging Modalities for Knee Bone Assessment
- Laboratory Tests for Bone Health
- Clinical Evaluation of Knee Bone Disorders
It is important to monitor the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and its effects on knee bone health through regular clinical assessments and imaging studies.
Fractures and Trauma to Knee Bones
We understand that fractures and trauma to the knee bones can significantly impair mobility and quality of life. These injuries often result from high-impact activities or accidents and require immediate attention. The knee joint is particularly vulnerable to fractures of the patella, femur, and tibia.
- Patellar fractures
- Femoral condyle fractures
- Tibial plateau fractures
Each type of fracture presents its own set of challenges and necessitates a tailored approach to treatment. It is crucial to stabilize the injury and reduce pain as initial steps in the management process.
Early intervention and accurate diagnosis are key to preventing long-term complications associated with knee bone fractures.
We advocate for a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, involving orthopedic specialists, physiotherapists, and, when necessary, surgical intervention. The goal is to restore function and strength to the knee joint, enabling patients to return to their daily activities.
Diagnostic Techniques for Knee Bone Health
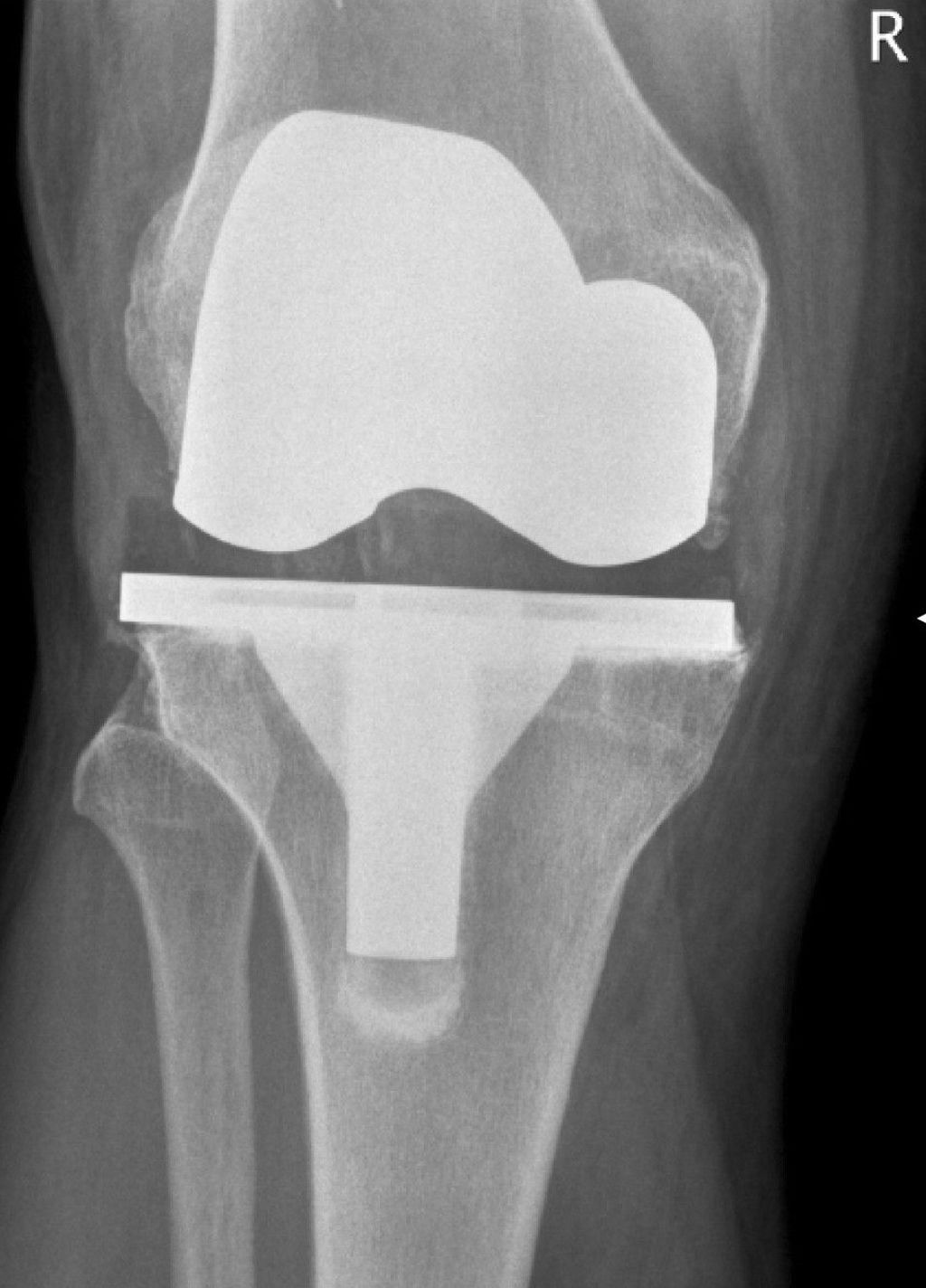
Imaging Modalities for Knee Bone Assessment
In our pursuit of understanding knee bone health, we recognize the critical role of imaging modalities. These tools allow us to visualize the internal structure of the knee, identifying abnormalities and guiding treatment decisions. Among the most commonly used techniques are X-rays, MRI, and CT scans, each offering unique insights into bone integrity.
- X-rays are often the first step in assessing knee bone conditions, providing a clear picture of bone alignment and density.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) offers a more detailed view, highlighting soft tissue and bone marrow changes that may not be visible on X-rays.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans combine multiple X-ray images to create a comprehensive three-dimensional representation of the knee structure.
Remember, the choice of imaging modality depends on the specific clinical scenario and the information needed to guide treatment. It’s essential to weigh the benefits against potential risks, such as radiation exposure, when selecting the appropriate diagnostic tool.
Laboratory Tests for Bone Health
Laboratory tests are a crucial component of bone health assessment. They provide valuable insights into the biochemical markers and mineral density of the bones. These tests help us evaluate the overall bone metabolism and identify any abnormalities that may indicate bone disorders. In addition to imaging modalities, laboratory tests play a significant role in diagnosing and monitoring knee bone health. Here is a brief overview of some common laboratory tests used for bone health assessment:
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Test: This test measures the mineral content and density of bones, providing quantitative data on bone strength and risk of fractures.
- Bone Turnover Markers: These markers assess the rate of bone formation and resorption, offering valuable information about bone metabolism and turnover.
- Calcium and Phosphorus Levels: Monitoring the levels of these essential minerals is crucial for assessing bone health and identifying mineral imbalances.
It is important to interpret the results of these tests in conjunction with clinical evaluation and imaging findings to gain a comprehensive understanding of knee bone health and potential disorders. As a key part of our diagnostic approach, laboratory tests contribute to the holistic assessment of knee bone health and aid in formulating effective treatment strategies.
Clinical Evaluation of Knee Bone Disorders
After discussing the various imaging modalities and laboratory tests for knee bone assessment, clinical evaluation becomes crucial in determining the severity of knee bone disorders. This evaluation involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and functional tests. Additionally, it may include the use of specialized diagnostic tools such as gait analysis and joint stability assessment. The findings from the clinical evaluation guide the formulation of an effective treatment plan for managing knee bone conditions.
Treatment and Management of Knee Bone Conditions
Medications for Knee Bone Disorders
When it comes to the treatment of knee bone disorders, medications play a crucial role in managing symptoms and slowing down the progression of the condition. Our approach to prescribing medications is based on the specific diagnosis and the individual needs of each patient. We prioritize the use of anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling, along with supplements to support bone health and aid in the healing process. In addition, we may recommend a combination of medications to address multiple aspects of the condition, ensuring comprehensive care for our patients.
Surgical Interventions for Knee Bone Injuries
In our pursuit of restoring knee joint functionality and alleviating pain, we often turn to surgical interventions when other treatments have not yielded the desired results. Surgery is considered for severe injuries and conditions that compromise the knee’s structural integrity and stability.
The types of surgical procedures vary greatly depending on the injury and the patient’s overall health. Common surgeries include:
- Arthroscopic surgery to repair ligaments or remove loose bone or cartilage.
- Osteotomy to realign bones and redistribute weight.
- Total or partial knee replacement for advanced arthritis or severe damage.
Each procedure comes with its own set of risks and benefits, which must be carefully weighed. For instance, arthroscopic surgery is less invasive and typically allows for a quicker recovery, while knee replacement is a more extensive operation that may offer longer-lasting relief but requires a significant rehabilitation period.
Tip: It’s crucial to have a thorough discussion with your surgeon about the potential outcomes and rehabilitation plan following any surgical intervention.
Our collective experience suggests that a multidisciplinary approach, involving not only surgeons but also physical therapists and other specialists, is key to a successful recovery. Postoperative care is as important as the surgery itself, and patients must be committed to their rehabilitation program to regain full function of the knee joint.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy for Knee Bone Health
In our pursuit of optimal knee bone health, we recognize the indispensable role of rehabilitation and physical therapy. These modalities are not confined to the realm of athletes; rather, they are a critical component for anyone seeking to recover from knee bone conditions. It’s a common misconception that physical therapy is synonymous with pain. On the contrary, the goal is to alleviate discomfort and enhance musculoskeletal health through tailored exercises and therapies.
A well-structured physical therapy program may include the following elements:
- Assessment of the individual’s current knee function and limitations.
- Development of a customized exercise regimen to strengthen the knee and surrounding muscles.
- Techniques to improve range of motion and flexibility.
- Education on proper body mechanics to prevent future injuries.
Remember, consistency in physical therapy is key to a successful recovery. It’s not only for those who have undergone surgery but also for individuals looking to prevent knee bone disorders or manage chronic conditions.
By integrating physical therapy into the treatment plan, we aim to empower patients to take an active role in their joint health. This approach not only aids in recovery but also serves as a preventive measure against further knee bone deterioration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the knee bones play a crucial role in maintaining overall joint health. Understanding the structure and function of the knee bones is essential for preventing and managing joint-related conditions. Proper care and attention to the knee bones can significantly contribute to the longevity and functionality of the joints, thereby promoting an active and healthy lifestyle. Further research and education in this area are imperative for advancing our knowledge of joint health and enhancing the quality of life for individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main knee bones and their functions?
The main knee bones are the femur, tibia, and patella. These bones form the knee joint and are responsible for supporting body weight, providing stability, and allowing movement.
How does knee bone health affect joint function?
Healthy knee bones are essential for proper joint function. They provide support, absorb shock, and facilitate smooth movement. Poor knee bone health can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
What are the common symptoms of knee bone disorders?
Common symptoms of knee bone disorders include pain, swelling, stiffness, limited range of motion, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected knee.
What imaging tests are used to assess knee bone health?
Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, and CT scans are commonly used to assess knee bone health and detect conditions such as fractures, arthritis, and degenerative changes.
What are the non-surgical treatment options for knee bone conditions?
Non-surgical treatment options for knee bone conditions include medications, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and assistive devices to support the knee joint.
How long does it take to recover from knee bone injuries?
Recovery from knee bone injuries varies depending on the severity of the injury and the chosen treatment. It can range from a few weeks to several months, with rehabilitation playing a crucial role in the recovery process.