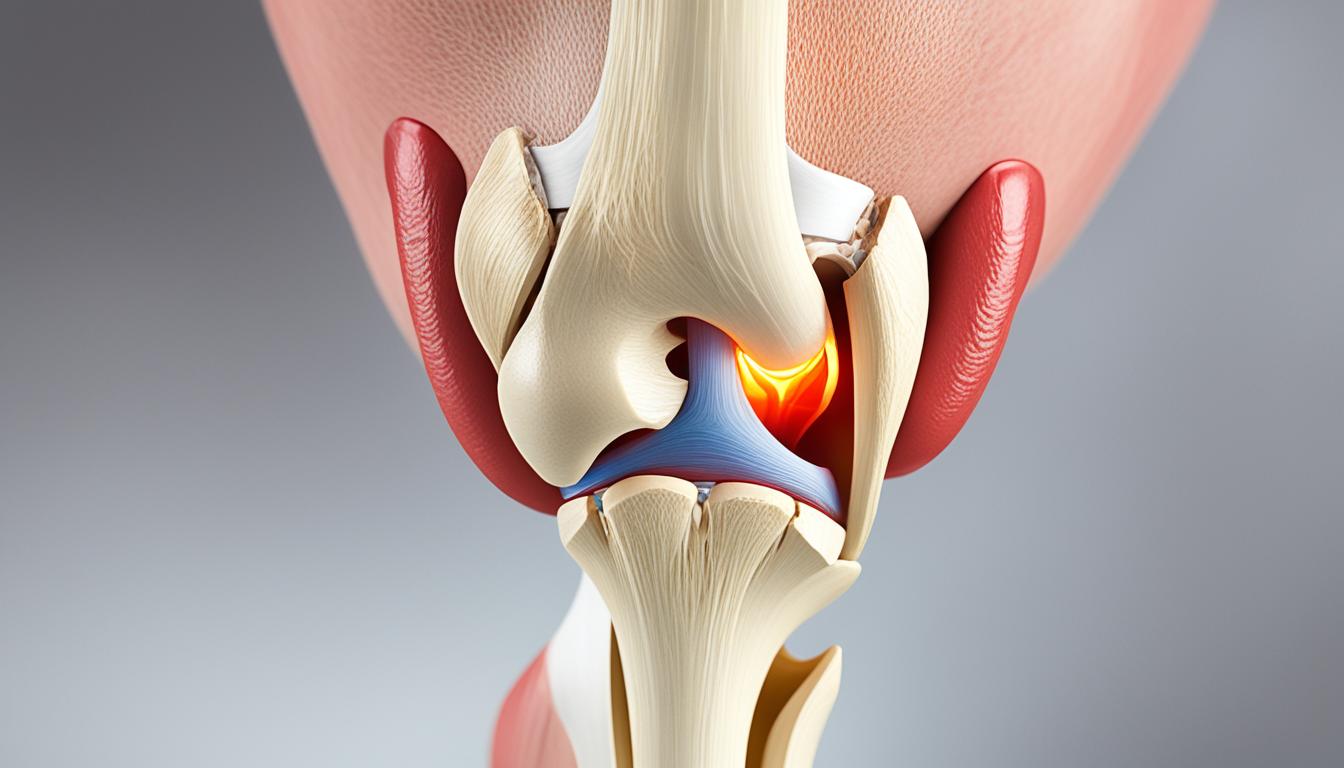
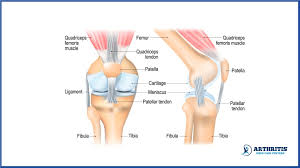
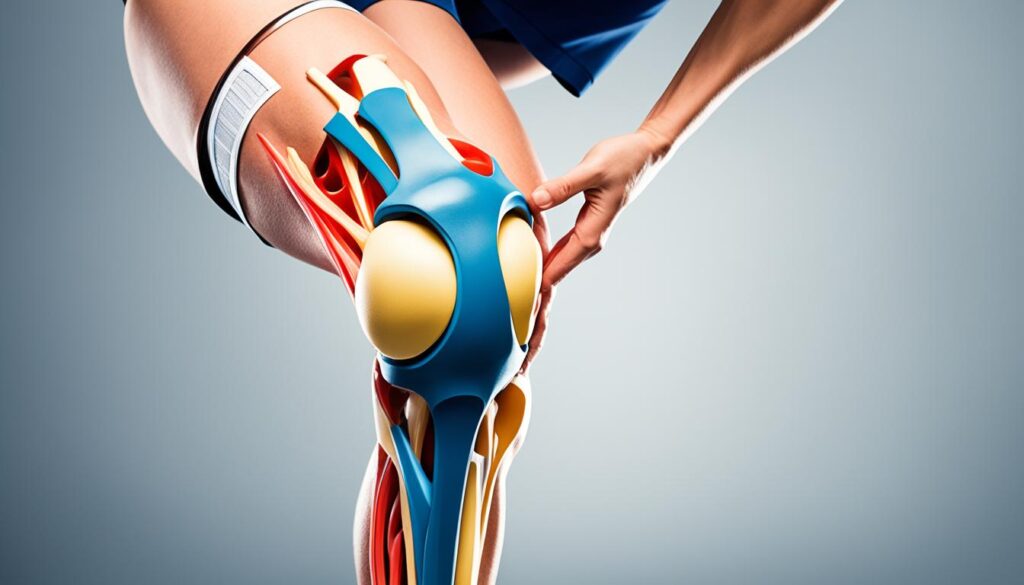
Did you know that your knee joint can produce various sounds, including clicks, pops, and grinding sensations, when you straighten your leg? These audible knee noises, known as patella pops, are more common than you might think and can be a normal occurrence for many individuals. However, they can also indicate underlying issues that require attention. In this article, we will explore the causes and implications of patella pops when straightening the leg, including knee popping sensations, knee crepitus, and patellofemoral syndrome. We will also discuss the importance of seeking medical evaluation and the benefits of physical therapy in managing this condition.
Common Causes of Knee Popping
Knee popping is a common phenomenon that can be attributed to various factors. Understanding these causes can help shed light on potential underlying issues and guide appropriate treatment. Some of the most common causes of knee popping include:
- Gas bubbles popping in the joint: The knee joint contains a small amount of fluid that helps with lubrication. Sometimes, gas bubbles can form within this fluid, leading to a popping sensation when they are released.
- Ligament and tendon snapping: The knee joint is supported by a network of ligaments and tendons. During movement, these structures may snap or shift over the joint, resulting in audible popping sounds.
- Injuries: Knee popping can be associated with various injuries, such as ligament tears and cartilage tears. These injuries can cause joint instability and result in clicking or popping sensations.
- Knee arthritis: Arthritis is a degenerative condition that affects the joints. In the knee, arthritis can lead to joint surface damage, causing grinding or popping sensations.
- Chondromalacia patella: Chondromalacia patella is a condition characterized by the softening and breakdown of the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap. This can cause irregular movement and contribute to knee popping.
- ACL and MCL injuries: Injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and medial collateral ligament (MCL) are common causes of both knee pain and popping. These injuries can destabilize the knee joint and lead to abnormal movement.
- Joint surface damage: Damage to the smooth surfaces of the knee joint, such as from wear and tear or trauma, can result in knee grinding or popping.
- Patellar instability: Patellar instability refers to the tendency of the kneecap to dislocate or move out of its normal position. This instability can cause clicking or popping sensations during movement.
It is important to note that the specific cause of knee popping should be determined through medical evaluation. A healthcare professional will be able to conduct a thorough examination, order any necessary imaging tests, and provide an accurate diagnosis.
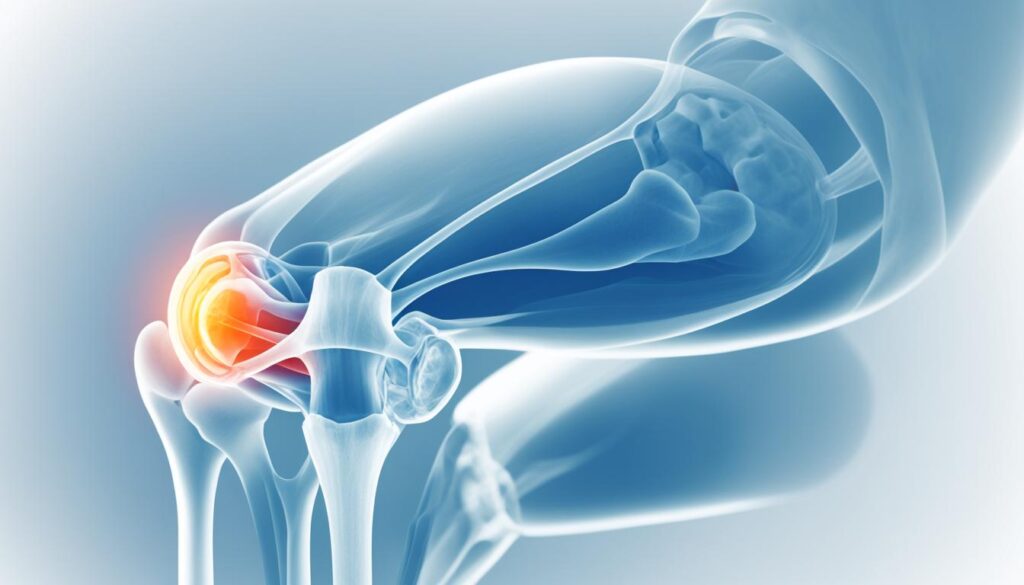
Signs and Symptoms of a Dislocated Patella
A dislocated patella is a condition that can cause significant discomfort and impair knee function. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a dislocated patella is crucial for prompt medical intervention and appropriate treatment. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
- Audible Pop: One of the telltale signs of a dislocated patella is an audible pop at the time of injury. This popping sensation is often accompanied by immediate pain and discomfort.
- Intense Pain: Dislocating the patella can cause excruciating pain in the knee. The severity of pain may vary depending on the extent of the dislocation and any associated injuries to the surrounding tissues.
- Sudden Swelling: Swelling is a common symptom of a dislocated patella. The knee may become visibly swollen shortly after the injury occurs.
- Bruising at the Knee: Another notable symptom is the presence of bruising around the knee joint. This discoloration typically occurs due to blood pooling beneath the skin as a result of the trauma.
- Locking of the Knee: In some cases, a dislocated patella may cause the knee joint to lock in a fixed position. This can make it challenging to extend or flex the leg normally.
- Visual Displacement of the Kneecap: A noticeable sign of a dislocated patella is the displacement of the kneecap from its usual position. The kneecap may appear visibly out of place or misaligned.
In addition to the above symptoms, individuals with a dislocated patella may experience difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected knee. However, it’s important to note that if the patella corrects itself spontaneously, there may be temporary relief from pain and improved mobility. Nonetheless, seeking medical attention is essential to assess any secondary injuries that may have occurred and to determine the most appropriate rehabilitation plan.
Rehabilitation is Key
Who is Affected by Patella Dislocation
Patella dislocation can affect anyone through injury, but certain individuals are more at risk. Athletes participating in high-impact sports and dancers who frequently pivot are prone to knee injuries and dislocations. Teenagers may be more susceptible due to the looseness of their joints and ligaments during the growth process. Women, particularly those with wider hips and looser ligaments, may experience lateral stress on the knee. Big and tall men may have increased pressure on their joints. Individuals with patellar instability, especially those who have previously dislocated their patella, are also more prone to dislocations.
To understand who is affected by patella dislocation, let’s take a closer look at the key factors:
- Athletes: Participating in high-impact sports puts a significant strain on the knees, increasing the risk of patella dislocation.
- Dancers: Frequent pivoting and sudden movements in dance routines can lead to knee injuries and dislocations.
- Teenagers: As teenagers go through the growth process, their joints and ligaments may be looser, making them more susceptible to patella dislocation.
- Women: Women, especially those with wider hips and looser ligaments, may experience lateral stress on the knee, making them more prone to dislocations.
- Big and tall men: Individuals who are larger in size may have increased pressure on their joints, making them more susceptible to knee injuries and dislocations.
- Patellar instability: Individuals who have previously dislocated their patella are at a higher risk of experiencing future dislocations.
It is important for individuals in these high-risk groups to take precautions and engage in appropriate strengthening exercises and preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of patella dislocation.
Below is a table summarizing the different categories of individuals who are more susceptible to patella dislocation:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Athletes | Participating in high-impact sports |
| Dancers | Frequent pivoting and sudden movements |
| Teenagers | Loose joints and ligaments during the growth process |
| Women | Wider hips and looser ligaments |
| Big and tall men | Increased pressure on joints |
| Patellar instability | Previous patella dislocation |
Being aware of the factors that increase the risk of patella dislocation can help individuals take proactive measures to protect their knees and prevent serious injuries.
Causes of Patella Dislocation
Patella dislocation can occur due to various factors, including acute dislocation caused by forceful impact or a sudden turn. Individuals with patellar instability are also at risk of experiencing patella dislocation. Additionally, there is a congenital form of patella dislocation that some individuals are born with.
Acute dislocation of the patella occurs when a forceful impact, such as a fall or collision, causes the kneecap to be forcefully knocked out of place. This sudden jolt can disrupt the normal alignment of the patella within the knee joint and lead to dislocation.
Another cause of patella dislocation is a sudden turn while the lower leg is firmly planted. This twisting motion can put excessive stress on the patella, causing it to dislocate. This often occurs during activities that involve pivoting or sudden changes in direction, such as sports or dancing.
Individuals with patellar instability have loose and unstable tendons and ligaments around the knee joint, making them more prone to patella dislocation. This instability can be congenital or may result from previous dislocations or other knee injuries.
Congenital patella dislocation is a condition that some individuals are born with. It is often associated with other developmental abnormalities and may have a genetic component. The exact cause of congenital patella dislocation is not fully understood, but it is believed to be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
| Causes of Patella Dislocation | Description |
|---|---|
| Acute Dislocation | Forceful impact or trauma that knocks the patella out of place. |
| Sudden Turn | A sharp twisting motion while the lower leg is planted, putting stress on the patella. |
| Patellar Instability | Loose and unstable tendons and ligaments around the knee, making the patella more prone to dislocation. |
| Congenital Patella Dislocation | A condition some individuals are born with, often associated with other developmental abnormalities and potentially influenced by genetics. |
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and implications of patella pops when straightening the leg is crucial for proper care and management. While knee popping can be a normal occurrence, it is important to seek medical attention if it is accompanied by pain or other issues. Physical therapy can help improve knee function and reduce the frequency of knee popping sensations.
There are various factors that can contribute to knee popping, including the presence of gas bubbles in the joints, ligament snapping, injuries, and underlying conditions like arthritis and patellar instability. These factors can lead to knee joint sounds such as knee crepitus, knee cracking, and knee clicking. However, with the right medical evaluation and treatment, the symptoms associated with dislocated patellas, including intense pain and other discomfort, can be effectively addressed.
By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals experiencing patella pops can receive the appropriate guidance and support to manage their condition. Whether it be through physical therapy exercises or other interventions, the goal is to improve knee function and reduce the grinding and popping sensations that can be associated with conditions like patellofemoral syndrome.
FAQ
What causes patella pops when straightening the leg?
Patella pops when straightening the leg can be caused by various factors, including gas bubbles popping in the joint, snapping of ligaments and tendons over the joint, injuries such as ligament tears and cartilage tears, and conditions like knee arthritis and chondromalacia patella. ACL and MCL injuries are also common causes of knee pain and popping.
Is knee popping normal?
Yes, knee popping is generally normal. The knee is a complex joint and noises like clicking can occur due to its intricacy and weight-bearing load. However, it is important to seek medical attention if the pops are accompanied by pain, discomfort, or mobility problems.
How can physical therapy help with knee popping?
Physical therapy can help improve knee function and reduce the frequency of clicking and popping noises. With targeted exercises, stretches, and strengthening techniques, physical therapy can address the underlying factors contributing to knee popping, such as muscle imbalances, tightness, and instability.
What are the signs and symptoms of a dislocated patella?
Signs and symptoms of a dislocated patella can include an audible pop, intense pain, sudden swelling, bruising at the knee, locking of the knee, and visual displacement of the kneecap. The severity of pain and mobility limitations may vary depending on the extent of the dislocation and potential injuries to surrounding tissues.
Who is more at risk for patella dislocation?
Certain individuals are more at risk for patella dislocation, including athletes participating in high-impact sports and dancers who frequently pivot. Teenagers may also be more susceptible due to the looseness of their joints and ligaments during the growth process. Women with wider hips and looser ligaments, as well as big and tall men who experience increased pressure on their joints, may also be at a higher risk. Individuals with patellar instability, especially those who have previously dislocated their patella, are also more prone to dislocations.
What causes patella dislocation?
Patella dislocation can be caused by forceful impact, such as a fall or collision, which knocks the kneecap out of place. It can also occur from a sudden turn that twists the knee while the lower leg is firmly planted. Individuals with patellar instability, characterized by loose and unstable tendons and ligaments, are prone to dislocations. Congenital patella dislocation, a condition some individuals are born with, may also be a cause, although the exact cause is not known.