This article explores the process of double knee replacement surgery, from understanding knee osteoarthritis to postoperative rehabilitation and recovery. Each section provides valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, preoperative preparation, surgical procedure, and postoperative care for double knee replacement surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Knee osteoarthritis is a leading cause of double knee replacement surgery.
- Preoperative preparation involves medical evaluation, physical therapy, and nutritional guidelines.
- The surgical procedure includes anesthesia, incision, and implantation of prosthetic knees.
- Postoperative rehabilitation focuses on physical therapy, pain management, and home care.
- Double knee replacement surgery significantly improves mobility and quality of life for patients.
Understanding Knee Osteoarthritis
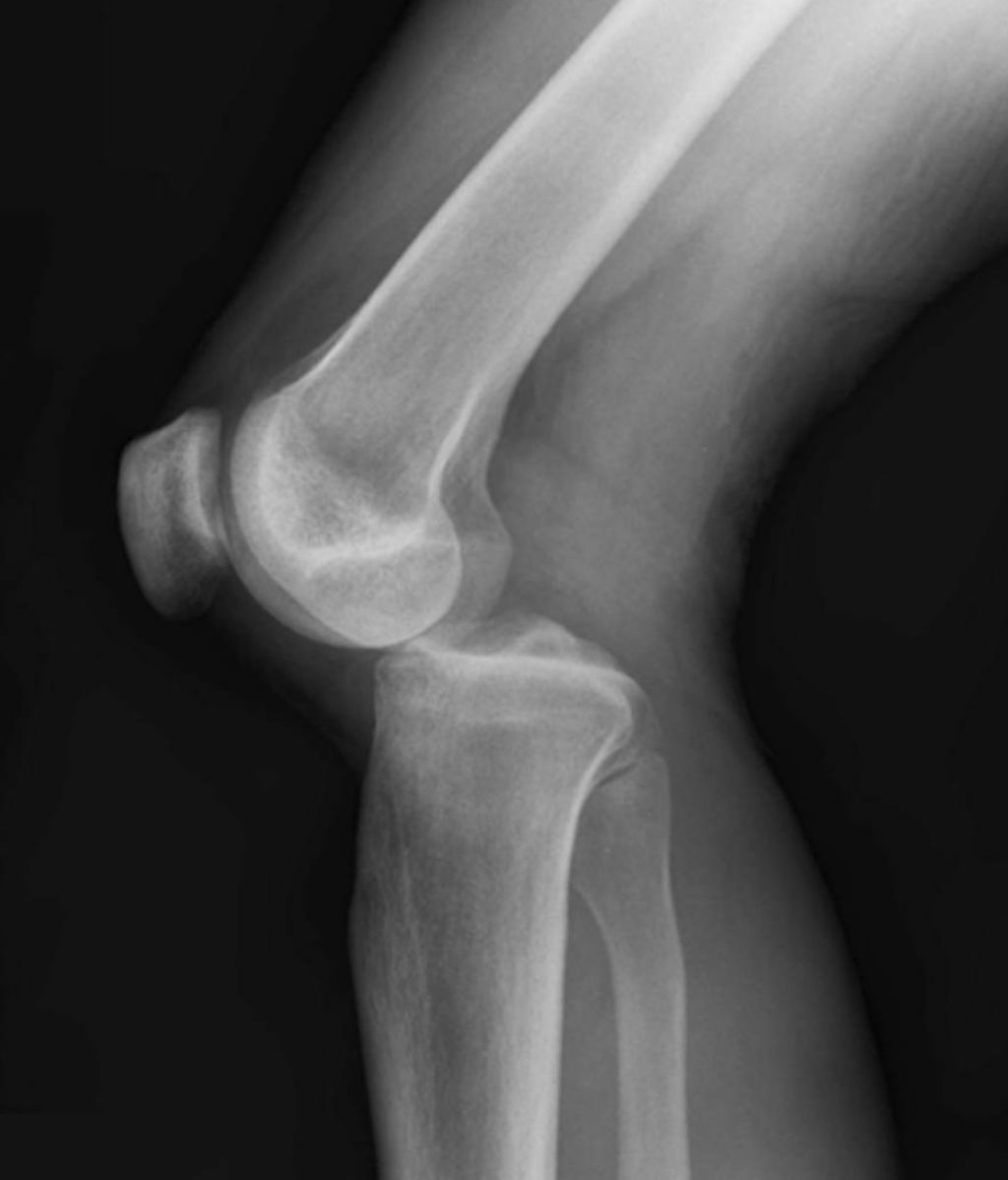
Causes of Knee Osteoarthritis
We recognize that knee osteoarthritis is a multifactorial disease, with a variety of factors contributing to its onset and progression. The primary cause is the degradation of cartilage in the knee joint, which can be attributed to several underlying factors. These include age-related wear and tear, obesity, which places extra stress on the joints, and previous knee injuries that may have caused damage to the cartilage or altered the mechanics of the knee.
Genetic predisposition also plays a role, as we see a higher incidence of knee osteoarthritis in certain families. Other contributing factors are occupational hazards, particularly those involving repetitive stress on the knees, and certain metabolic diseases.
- Age-related wear and tear
- Obesity
- Previous knee injuries
- Genetic predisposition
- Occupational hazards
- Metabolic diseases
Tip: Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular, low-impact exercise can help reduce the risk of developing knee osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Knee Osteoarthritis
As we delve into the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, it’s crucial to recognize the varied ways in which this condition can manifest. The primary symptom most individuals experience is pain during or after movement. This discomfort can range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation, often worsening after periods of inactivity or excessive use.
Stiffness is another common symptom, particularly noticeable upon waking or after sitting for extended periods. The affected joints may feel tight, making it difficult to achieve full range of motion. Swelling and tenderness around the knee joint are also prevalent, caused by inflammation within the joint capsule.
- Pain during or after movement
- Stiffness after inactivity
- Swelling and tenderness around the joint
- Reduced range of motion
- A grating sensation or crepitus when moving the knee
It’s important to pay attention to these symptoms, as early detection and treatment can significantly slow the progression of osteoarthritis and improve quality of life.
Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis
After observing the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis, we proceed to its diagnosis, which is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. We begin with a thorough medical history and a physical examination, focusing on the knee’s range of motion, stability, and strength. Radiographic tests, such as X-rays, are essential as they reveal the extent of joint damage and the presence of bone spurs.
To further assess the condition, we may also employ magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to visualize soft tissue structures, including cartilage, ligaments, and the meniscus. However, an MRI is not always necessary for diagnosis, as the clinical presentation and X-rays often suffice.
Blood tests are not typically used to diagnose osteoarthritis but may be conducted to rule out other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis. In some cases, a joint fluid analysis can help exclude gout or infection.
Remember, early and accurate diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis is key to managing symptoms and planning for potential surgical interventions, such as double knee replacement surgery.
Preoperative Preparation for Double Knee Replacement Surgery
Medical Evaluation for Surgery
Before undergoing the surgery, medical evaluation is crucial for assessing our overall health and identifying any potential risks. This evaluation involves a comprehensive review of our medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Additionally, we may need to undergo blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), and chest X-rays to ensure that we are in optimal condition for the procedure. Here is a brief table summarizing the key components of the medical evaluation:
| Test/Examination | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Medical history review | Identify pre-existing conditions |
| Physical examination | Assess joint function and mobility |
| Blood tests | Evaluate blood count and clotting ability |
| ECG | Assess heart function |
| Chest X-rays | Check for respiratory health |
It’s important to adhere to the guidelines provided by the healthcare team and to communicate any concerns or questions during this evaluation process. This ensures that we are well-prepared for the upcoming surgery and can minimize any potential complications. As we proceed with the evaluation, it’s essential to maintain open communication with our healthcare providers and follow their recommendations closely.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
After discussing the medical evaluation for surgery, physical therapy and exercise play a crucial role in preparing for double knee replacement. Our team emphasizes the importance of consistent exercise and rehabilitation to optimize the outcome of the surgery. It is essential to follow the prescribed exercise regimen to strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility in the knees. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet and proper nutrition is vital for overall health and recovery. Here is a brief overview of the recommended nutritional guidelines:
| Nutrient | Recommended Intake |
|---|---|
| Protein | 1.2-1.5 grams/kg |
| Vitamin C | 90 mg/day |
| Calcium | 1000-1200 mg/day |
It is important to consult with a nutritionist or healthcare provider to personalize the nutritional plan based on individual needs. Our team is dedicated to providing comprehensive support and guidance throughout the preoperative phase, ensuring that patients are well-prepared for the upcoming double knee replacement surgery.
Nutritional Guidelines
When it comes to nutritional guidelines, we emphasize the importance of a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients. Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in preparing our bodies for the upcoming surgery. It’s essential to focus on consuming foods that promote healing and support overall health. This includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Additionally, we recommend limiting the intake of processed foods and sugary beverages to optimize our nutritional status.
Furthermore, staying hydrated is paramount for our well-being. Adequate water intake aids in the body’s recovery process and helps prevent complications. We encourage maintaining a steady intake of water throughout the day to ensure proper hydration.
In addition to these dietary recommendations, it’s important to consult with our healthcare provider for personalized nutritional guidance based on our individual needs and medical history.
Surgical Procedure for Double Knee Replacement
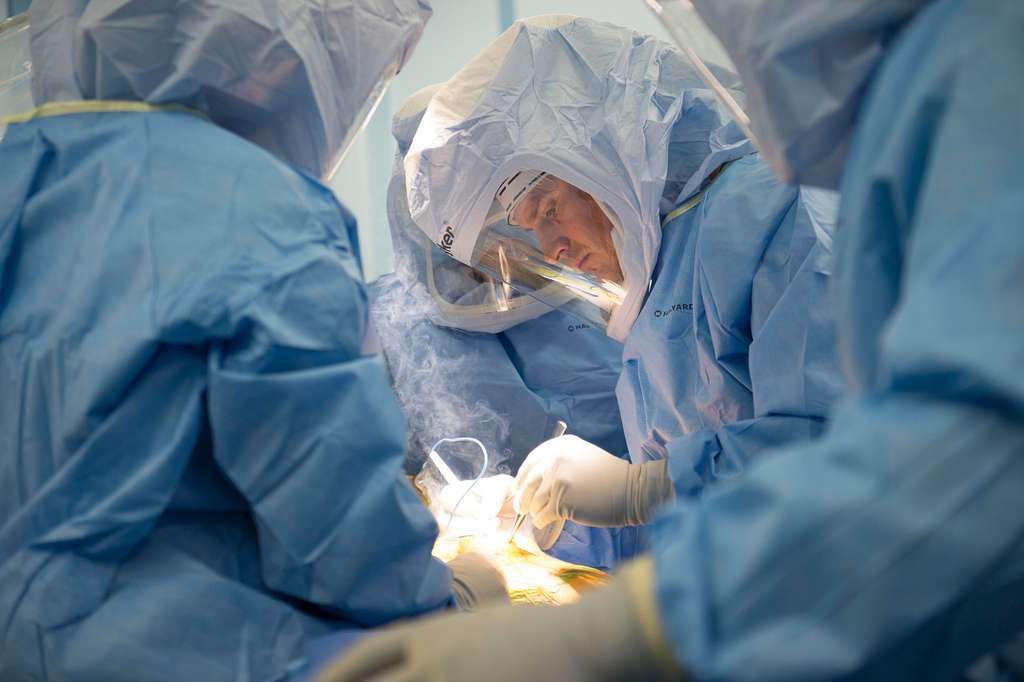
Anesthesia and Incision
Once we have ensured that our patient is comfortable and all preoperative checks are complete, we proceed with the administration of anesthesia. The type of anesthesia used is typically general, but in some cases, spinal or epidural anesthesia may be considered. The choice depends on various factors, including the patient’s health and the surgeon’s preference.
Following the onset of anesthesia, a careful and precise incision is made to expose the knee joint. This incision is typically 8 to 10 inches long and allows for the damaged surfaces of the knee joint to be fully accessible. It’s crucial that we maintain a sterile environment throughout the procedure to prevent infection.
Remember, the goal of the incision is not just access, but also to ensure minimal impact on surrounding tissues for a smoother recovery.
The incision is the first step in a series of carefully orchestrated maneuvers that will lead to the implantation of the prosthetic knees. Here is a brief overview of the steps that follow the incision:
- Preparation of the bone surfaces
- Alignment and placement of the prosthetic components
- Testing the movement of the prosthetic joint
- Closure of the incision with sutures or staples
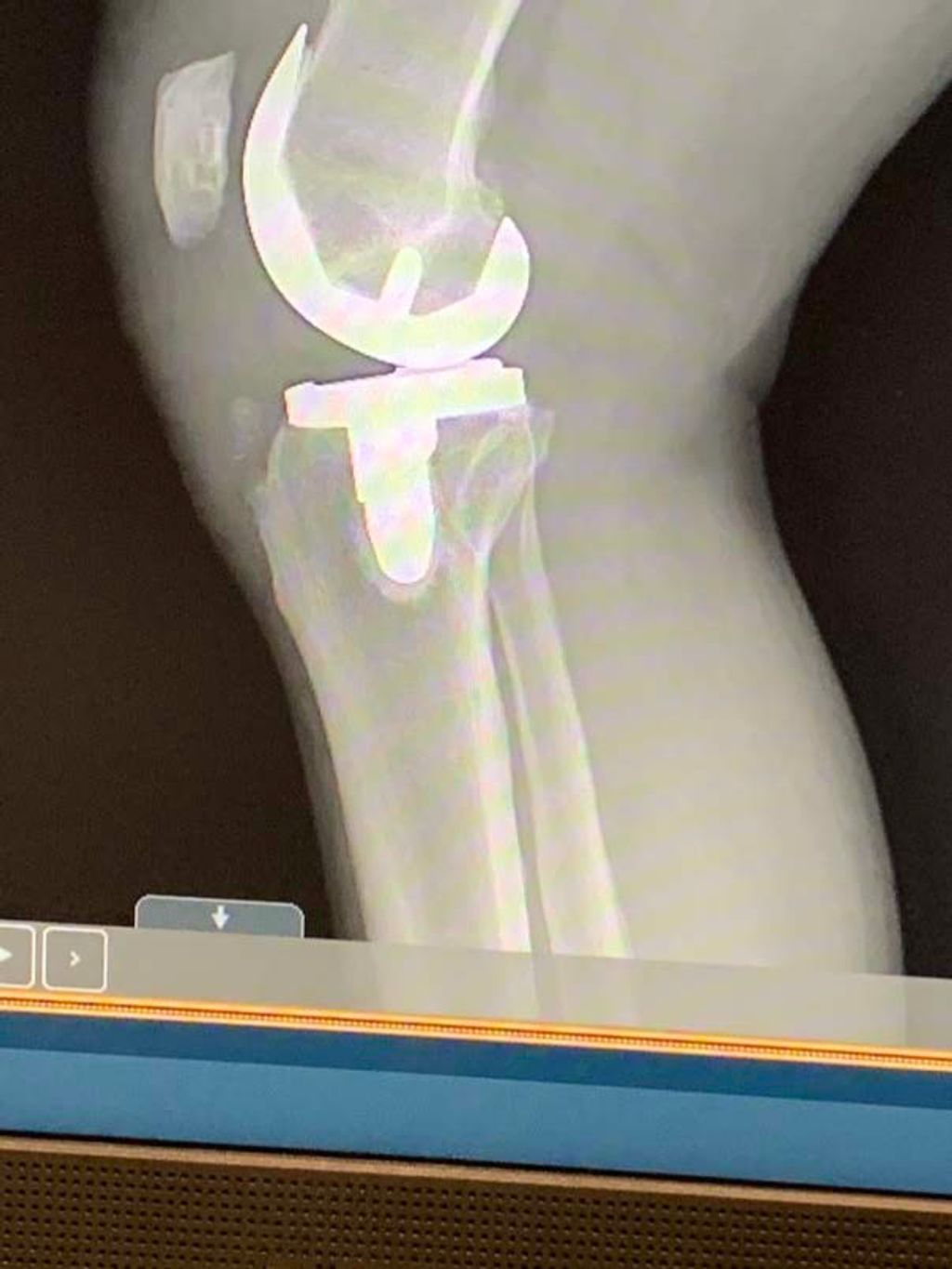
Implantation of Prosthetic Knees
Following the preparation of the knee area, we proceed with the implantation of the prosthetic knees. This critical phase involves the precise placement of the artificial components that will form the new joint surfaces. The components typically include a femoral piece, a tibial component, and a patellar part, which are designed to mimic the natural articulation of the knee.
Careful alignment is essential to ensure the longevity and functionality of the prosthetic knees. We use specialized instruments to measure and achieve the correct positioning. Once the components are secured, we test the range of motion and stability of the new joint.
It is crucial to maintain a sterile environment throughout the procedure to prevent infection.
The success of the surgery is not only dependent on the skill of the surgical team but also on the quality of the prosthetic materials used. Recent advancements in technology have led to the development of highly durable and biocompatible materials, contributing to improved patient outcomes.
Recovery Room Care
After the surgical procedure for double knee replacement, monitoring and care in the recovery room are crucial. Vital signs, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation, will be closely observed. Additionally, postoperative pain management will be initiated to ensure comfort and stability. Patients will receive detailed instructions for postoperative care and will be encouraged to engage in early mobilization and breathing exercises to promote optimal recovery. A comprehensive care plan will be tailored to each patient’s specific needs, addressing pain management, wound care, and early mobilization.
Postoperative Rehabilitation and Recovery

Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation Exercises
After completing the physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises, we focus on pain management strategies. This involves a combination of medication, ice therapy, and relaxation techniques to alleviate discomfort and promote healing. Additionally, we emphasize the importance of home care and assistance. This includes creating a safe and supportive environment at home, as well as arranging for help with daily activities and mobility. We understand that the recovery period can be challenging, and having the right support system in place is crucial for a successful rehabilitation journey.
Pain Management Strategies
After undergoing double knee replacement surgery, pain management is a crucial aspect of our recovery process. We focus on a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments to ensure that we manage pain effectively. It’s important to communicate any discomfort or changes in pain levels to our healthcare team to receive the appropriate support and adjustments to our pain management plan.
In addition, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for our recovery. Consuming foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties can aid in reducing postoperative pain and promoting healing. Our healthcare team will provide us with nutritional guidelines to support our recovery and overall well-being.
Furthermore, staying active and engaging in prescribed rehabilitation exercises is vital for regaining strength and mobility. Our physical therapist will guide us through a personalized exercise program that aligns with our recovery goals and ensures a smooth transition back to our daily activities.
Lastly, it’s important to create a supportive environment at home to facilitate our recovery. This may involve arranging assistance for daily tasks, ensuring a safe and accessible living space, and having open communication with our loved ones about our needs during the recovery period.
Home Care and Assistance
After undergoing double knee replacement surgery, recovery and rehabilitation are crucial for restoring mobility and regaining strength. Our home care and assistance plan is designed to provide comprehensive support during this phase. It includes a combination of physical therapy sessions, pain management strategies, and personalized care to ensure a smooth transition back to daily activities. Additionally, patients are encouraged to maintain a balanced diet and adhere to the prescribed medication schedule to facilitate the recovery process. Here is a brief overview of the postoperative care and assistance plan:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy Sessions | Regular sessions to improve mobility and strength |
| Pain Management Strategies | Medication, ice therapy, and relaxation techniques |
| Personalized Care | Assistance with daily activities and monitoring of progress |
It’s important to follow the postoperative care plan diligently to achieve optimal results and minimize the risk of complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of double knee replacement surgery has provided valuable insights into the intricacies of this medical procedure. The recovery process, surgical techniques, and patient outcomes have been examined in depth, shedding light on the complexities and considerations involved in this treatment. Further research in this area is essential to enhance our understanding and improve the efficacy of double knee replacement surgery for the benefit of patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the success rate of double knee replacement surgery?
The success rate of double knee replacement surgery is generally high, with most patients experiencing significant improvement in pain relief and mobility.
How long does it take to recover from double knee replacement surgery?
Recovery time can vary, but most patients can expect to see significant improvement in mobility and function within 3 to 6 months after surgery.
What are the potential risks and complications of double knee replacement surgery?
Potential risks and complications include infection, blood clots, implant failure, and nerve damage. Your surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the surgery.
Will I be able to resume normal activities after double knee replacement surgery?
Many patients are able to resume normal activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and low-impact exercises after fully recovering from double knee replacement surgery.
How long do the prosthetic knees last?
Prosthetic knees are designed to last for 15-20 years or more, depending on factors such as the patient’s activity level and overall health.
What lifestyle changes should I make after double knee replacement surgery?
After surgery, it’s important to maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular low-impact exercise, and avoid activities that put excessive strain on the knees to prolong the lifespan of the prosthetic knees.