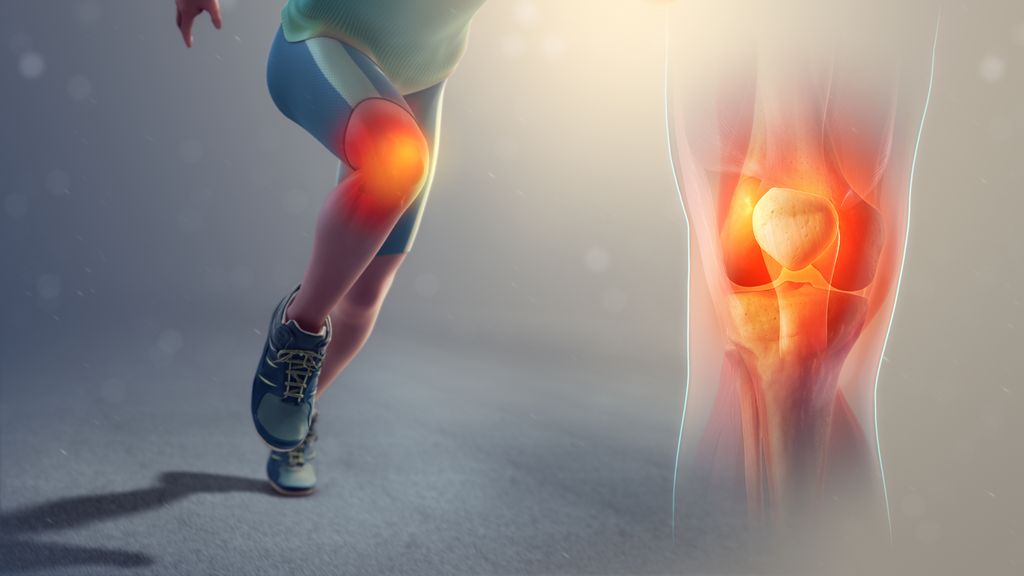
Knee pain is a common condition that can affect people of all ages. It can be caused by various factors, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, meniscus tear, or ACL injury. Diagnosing knee pain involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Treatment options for knee pain include medications, physical therapy, and surgery. To prevent knee pain, it is important to maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular exercise, and practice proper warm-up and cool-down techniques. Here are the key takeaways from understanding the diagnosis of knee pain:
Key Takeaways
- Common causes of knee pain include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, meniscus tear, and ACL injury.
- Diagnosing knee pain involves a medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Treatment options for knee pain include medications, physical therapy, and surgery.
- To prevent knee pain, maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular exercise, and practice proper warm-up and cool-down techniques.
- Understanding the diagnosis of knee pain is crucial for effective management and prevention of future complications.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a common cause of knee pain, especially in older adults. It is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage in the knee wears down over time. Pain, stiffness, and swelling are common symptoms of osteoarthritis. Risk factors for developing osteoarthritis include age, obesity, previous knee injuries, and genetics.
To diagnose osteoarthritis, a doctor will typically perform a physical examination of the knee and may order X-rays to assess the condition of the joint. Treatment options for osteoarthritis include medications to manage pain and inflammation, physical therapy to improve strength and flexibility, and in some cases, surgery to repair or replace damaged joint tissue.
It is important for individuals with osteoarthritis to maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint. Regular exercise can also help improve joint function and reduce pain. Proper warm-up and cool-down exercises before and after physical activity can help prevent further damage to the knee joint.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the joints. It is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may include joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and fatigue. The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
One of the diagnostic tests commonly used to confirm a diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is the rheumatoid factor blood test. This test measures the presence of antibodies that are often found in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Other tests, such as imaging studies and joint fluid analysis, may also be used to evaluate the extent of joint damage and inflammation.
Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis aims to reduce pain, inflammation, and joint damage, as well as improve overall function and quality of life. Medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), are often prescribed to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
It is important for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to engage in regular physical activity to maintain joint flexibility and strength. Physical therapy can also be beneficial in improving joint function and reducing pain. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding smoking, can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Meniscus Tear
A meniscus tear is a common injury that can cause knee pain. The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a cushion between the thighbone and the shinbone. It helps to stabilize the knee joint and absorb shock during movement.
When the meniscus is torn, it can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the knee. The tear can occur as a result of a sudden twisting or pivoting motion, or it can develop gradually over time due to wear and tear.
Treatment options for a meniscus tear depend on the severity of the injury. In some cases, conservative treatments such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) and physical therapy may be sufficient to relieve symptoms and promote healing. However, more severe tears may require surgical intervention, such as arthroscopic surgery to repair or remove the torn meniscus.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a meniscus tear, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve outcomes.
ACL Injury
An ACL injury, or anterior cruciate ligament injury, is a common cause of knee pain, especially among athletes. It occurs when the ACL, which is one of the major ligaments in the knee, gets stretched or torn. Symptoms of an ACL injury include pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty walking.
If you suspect an ACL injury, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis. The diagnosis of an ACL injury typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as an MRI.
Treatment options for an ACL injury may include physical therapy, bracing, or surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the injury and the individual’s activity level and goals.
Prevention of ACL injuries can be promoted through proper training techniques, strengthening exercises, and wearing protective gear during sports activities.
Diagnosing Knee Pain
Medical History
During the medical history evaluation, the healthcare provider will ask you questions about your knee pain and any related symptoms. Important information to provide includes the onset of the pain, any previous injuries or traumas to the knee, and any activities that worsen or alleviate the pain. Additionally, the healthcare provider may inquire about any underlying medical conditions that could contribute to knee pain, such as arthritis or gout.
It is important to be as detailed as possible when describing your knee pain, including the location, intensity, and any associated symptoms like swelling or stiffness. This information will help the healthcare provider in making an accurate diagnosis and determining the most appropriate treatment plan.
During the medical history evaluation, the healthcare provider may also ask about any medications you are currently taking, as certain medications can affect the joints and contribute to knee pain. Be sure to mention any over-the-counter pain relievers or supplements you are using.
Physical Examination
During the physical examination, the doctor will assess various aspects of the knee to help diagnose the cause of the pain. They will examine the range of motion, looking for any limitations or abnormalities. Swelling, tenderness, and warmth in specific areas may indicate inflammation or injury. The doctor may also perform specific tests, such as the Lachman test or the McMurray test, to evaluate the stability of the knee and check for ligament or meniscus tears.
In addition to the knee, the doctor may also examine the surrounding areas, such as the hips and ankles, to rule out any referred pain or underlying issues. Muscle strength and reflexes may be tested to assess overall lower limb function. It is important to communicate any discomfort or pain experienced during the examination to the doctor, as it can provide valuable clues for diagnosis and treatment.
Based on the findings from the physical examination, the doctor will be able to narrow down the possible causes of knee pain and determine the next steps in the diagnostic process.
Diagnostic Tests
After taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination, your healthcare provider may recommend several diagnostic tests to further evaluate your knee pain. These tests can help identify the underlying cause of your pain and guide treatment decisions.
X-rays are commonly used to assess the structure of the knee joint and detect any abnormalities, such as fractures or signs of osteoarthritis. They provide a clear image of the bones and can help determine if additional imaging tests are necessary.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be ordered to obtain more detailed information about the soft tissues in and around the knee. This imaging technique can reveal injuries to the ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and other structures that may not be visible on an X-ray.
If your healthcare provider suspects an infection or inflammation in the knee joint, they may recommend a joint aspiration. This procedure involves removing a small sample of fluid from the knee joint for laboratory analysis.
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for diagnostic tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
Medications
When it comes to treating knee pain, medications can play a crucial role in managing symptoms and reducing inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to relieve pain and reduce swelling. These medications work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation. Over-the-counter NSAIDs such as ibuprofen and naproxen can be effective for mild to moderate knee pain, while prescription-strength NSAIDs may be necessary for more severe cases.
In addition to NSAIDs, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and provide short-term pain relief. These medications are typically administered through injections directly into the knee joint. While corticosteroids can provide immediate relief, their effects are temporary and repeated injections may be required.
It’s important to note that medications alone may not be sufficient to treat knee pain in the long term. They are often used in combination with other treatment options such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is an essential component of the treatment plan for knee pain. It focuses on improving strength, flexibility, and mobility in the affected knee. Exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can help reduce pain, improve joint stability, and enhance overall function.
In addition to exercises, physical therapy may also include other modalities such as manual therapy, electrical stimulation, and hot/cold therapy. These modalities can provide pain relief and aid in the healing process.
It is important to follow the guidance of a qualified physical therapist and adhere to the prescribed exercises and treatment plan. Consistency and commitment to physical therapy are key to achieving optimal results.
Tip: If you experience any increased pain or discomfort during physical therapy, it is important to communicate this to your physical therapist. They can make necessary adjustments to ensure your safety and progress.
Surgery
Surgery is often considered as a last resort for treating knee pain when other conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. It is typically recommended for severe cases or when there is significant damage to the knee joint. During surgery, the orthopedic surgeon may repair or replace damaged tissues such as the meniscus or the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The type of surgery will depend on the specific condition and the individual’s needs.
In some cases, a knee replacement surgery may be necessary, especially for individuals with advanced osteoarthritis. This procedure involves removing the damaged parts of the knee joint and replacing them with artificial components. Knee replacement surgery can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain.
It is important to note that surgery is not always the best option for everyone. Recovery from surgery can be lengthy and may require extensive rehabilitation. It is essential to discuss the potential risks, benefits, and alternatives with a healthcare professional before making a decision.
Preventing Knee Pain
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for preventing and managing knee pain. Excess weight puts added stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of joint damage and pain. Losing even a small amount of weight can have a significant impact on reducing knee pain and improving overall joint health.
To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, it is important to adopt a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting the intake of sugary drinks and processed foods.
Regular physical activity is also essential for weight management and knee health. Engaging in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or cycling can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing better support and reducing the risk of injury.
In addition to diet and exercise, it is important to monitor portion sizes and practice mindful eating. Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can help prevent overeating and promote weight maintenance.
Remember, maintaining a healthy weight is not only beneficial for your knees but also for your overall well-being.
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining the health and strength of the knees. Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling can help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and improve flexibility. It is important to start with low-impact exercises and gradually increase the intensity to avoid putting excessive strain on the knees.
In addition to cardiovascular exercises, specific exercises that target the muscles supporting the knees can be beneficial. These include quadriceps strengthening exercises, hamstring stretches, and calf raises. Working with a physical therapist can help develop a personalized exercise program that suits individual needs and goals.
Remember to listen to your body and avoid overexertion. If any exercise causes pain or discomfort, it is important to modify or stop the activity. Proper warm-up and cool-down routines should also be followed to reduce the risk of injury and promote recovery.
Proper Warm-up and Cool-down
Proper warm-up and cool-down are essential for preventing knee pain and reducing the risk of injury. Warm-up exercises help to increase blood flow to the muscles, loosen up the joints, and prepare the body for physical activity. It is important to include dynamic stretches, such as leg swings and lunges, to warm up the muscles and improve flexibility.
During the cool-down phase, it is important to gradually decrease the intensity of the activity and allow the body to return to its resting state. This can be done through static stretches, such as quad stretches and hamstring stretches, to help prevent muscle tightness and promote recovery.
To ensure a proper warm-up and cool-down, consider the following tips:
- Duration: Aim for at least 5-10 minutes of warm-up and cool-down exercises.
- Intensity: Start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the intensity.
- Variety: Include a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups.
- Consistency: Make warm-up and cool-down a regular part of your exercise routine.
Remember, taking the time to properly warm up and cool down can help prevent knee pain and improve overall performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the diagnosis of knee pain is crucial for effective treatment and management. By recognizing the various causes and symptoms of knee pain, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose the underlying condition and develop a personalized treatment plan. It is important for individuals experiencing knee pain to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further complications. With proper diagnosis and appropriate interventions, individuals can regain mobility and improve their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of knee pain?
The common causes of knee pain include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, meniscus tear, and ACL injury.
How is knee pain diagnosed?
Knee pain is diagnosed through medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
What are the treatment options for knee pain?
The treatment options for knee pain include medications, physical therapy, and surgery.
How can I prevent knee pain?
You can prevent knee pain by maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and performing proper warm-up and cool-down exercises.
Is knee pain a sign of arthritis?
Yes, knee pain can be a sign of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Can knee pain be treated without surgery?
Yes, knee pain can often be treated without surgery through conservative measures such as medications and physical therapy.