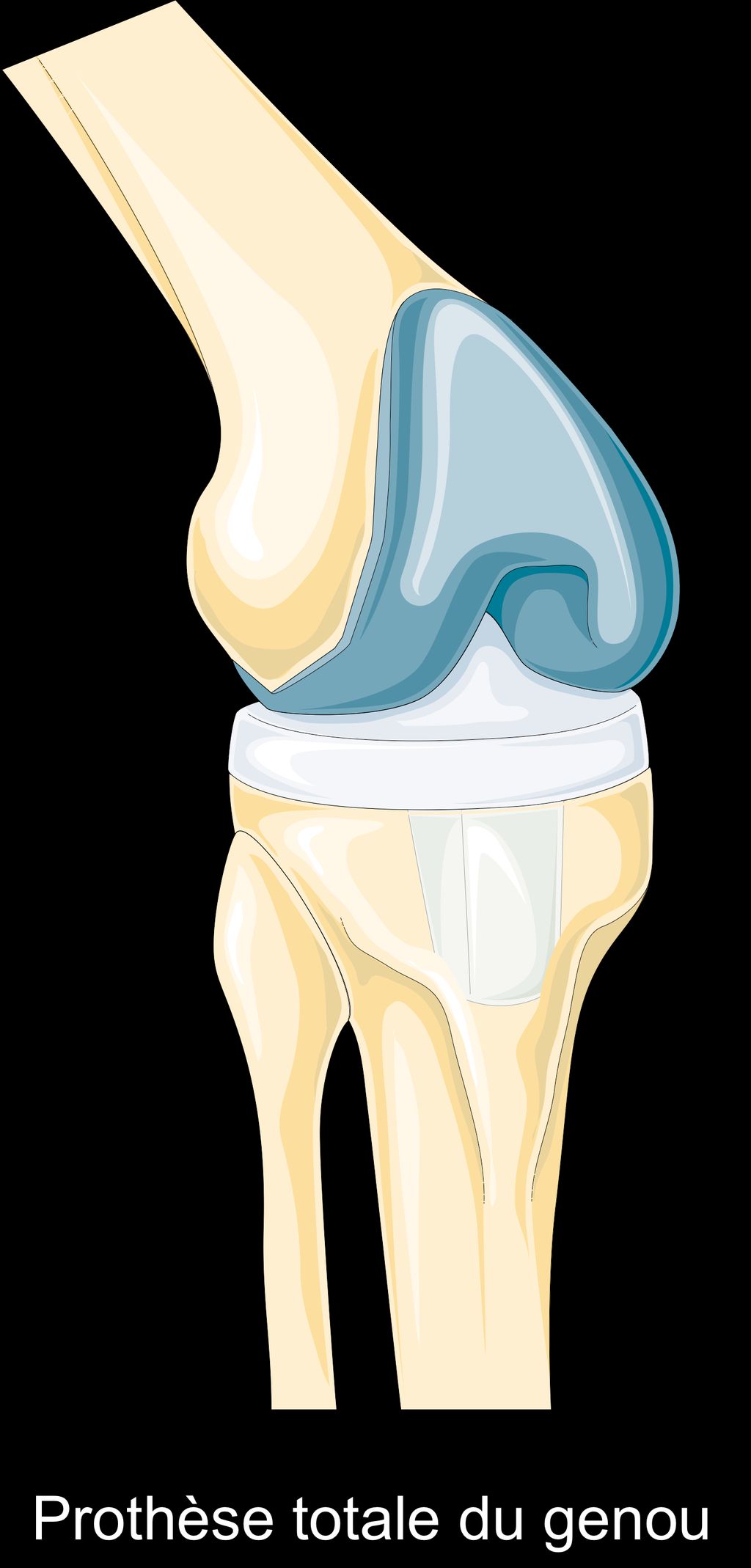
Titanium knee replacement surgery has revolutionized the field of joint health, offering a durable solution for individuals suffering from knee-related issues. With the evolution of knee replacement surgery, the use of titanium implants has significantly impacted the longevity and overall well-being of patients. This article explores the benefits, risks, surgical procedures, and lifestyle recommendations associated with titanium knee replacements, providing valuable insights into this innovative medical approach.
Key Takeaways
- Titanium knee replacements offer long-term durability and stability for joint health.
- Potential complications and risks of titanium knee replacements should be carefully evaluated and discussed with healthcare professionals.
- Comparative analysis reveals the advantages of titanium knee replacements over other materials, emphasizing their superior performance.
- Preoperative preparation, surgical techniques, and postoperative rehabilitation play crucial roles in the success of titanium knee replacement surgery.
- Following surgery, recipients of titanium knee replacements should adhere to physical activity guidelines and dietary considerations to maintain joint health and overall well-being.
The Evolution of Knee Replacement Surgery

Historical Background of Knee Replacement
Knee replacement surgery has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. Our understanding of joint health and surgical techniques has evolved significantly over the years, leading to the development of advanced materials and procedures. The introduction of titanium as a primary material for knee replacements marked a significant milestone in the field of orthopedic surgery. This transition to titanium implants revolutionized the durability and longevity of knee replacements, offering enhanced stability and reduced wear and tear over time. The use of titanium has reshaped the landscape of joint health and paved the way for improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
Advancements in Knee Replacement Materials
As we delve into the realm of knee replacement materials, it’s crucial to acknowledge the significant strides made in this field. The journey from early materials like stainless steel and polyethylene to the modern use of titanium has been transformative. Titanium stands out for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, making it an ideal choice for implants.
In our pursuit of improved patient outcomes, we’ve seen a shift towards materials that better mimic the natural behavior of bone. This is where titanium’s ability to osseointegrate, or bond with bone tissue, becomes a pivotal advantage. It’s not just about durability; it’s about creating a harmonious relationship between implant and body.
Consider the following points highlighting the evolution of materials used in knee replacements:
- Early materials included metals like stainless steel and cobalt-chromium alloys.
- Polyethylene was introduced for its cushioning effect but had wear issues.
- The introduction of titanium revolutionized the field with its durability and compatibility.
- Ongoing research focuses on surface treatments and coatings to enhance the performance of titanium implants.
Tip: Patients should discuss with their surgeons the type of material used in their knee implants to understand the implications for longevity and lifestyle.
Impact of Titanium Knee Replacements on Joint Health
The use of titanium in knee replacements has revolutionized the field of joint health. Its exceptional strength and biocompatibility make it an ideal material for ensuring long-term durability and stability of the implant. Moreover, the low incidence of adverse reactions and the ability to promote bone growth around the implant contribute to improved joint health and function.
Tip: Engaging in regular physical therapy and following a balanced exercise regimen can further enhance the benefits of titanium knee replacements, promoting flexibility and strength in the affected joint.
Benefits and Risks of Titanium Knee Replacement

Long-Term Durability of Titanium Implants
We recognize the significance of long-term outcomes in knee replacement surgeries, and it’s here that titanium implants truly shine. Their exceptional durability stems from titanium’s inherent properties, including its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. These characteristics ensure that titanium implants can withstand the rigors of daily activity while minimizing wear and tear.
- Titanium’s biocompatibility is another key factor contributing to its longevity. This compatibility with the human body reduces the risk of rejection and facilitates the integration of the implant with bone tissue. To illustrate the durability of titanium knee implants, consider the following data:
| Years Post-Surgery | Implant Success Rate |
|---|---|
| 5 | 95% |
| 10 | 93% |
| 15 | 90% |
| 20 | 85% |
Tip: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the condition of the implant and to address any potential issues early on.
When comparing titanium to other materials, it is evident that titanium implants offer a reliable solution for those seeking a long-term fix for knee pain. Their ability to maintain structural integrity over time is a testament to the material’s superiority in the realm of joint replacement.
Potential Complications and Risks
While we recognize the transformative impact of titanium knee replacements, it is our responsibility to acknowledge the potential complications and risks associated with the procedure. Infections, though rare, remain a concern and can occur at the site of the surgery. We also consider the possibility of implant failure, which, despite the durability of titanium, can arise from factors such as incorrect placement or the patient’s activity level.
Prosthesis wear and tear is another risk, albeit a long-term one, as even the sturdiest materials eventually degrade. Allergic reactions to the metal, though uncommon, are also a potential risk that must be monitored. It is crucial for patients to understand these risks to make informed decisions about their health care.
Tip: Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition of your titanium knee replacement and to address any concerns promptly.
To provide a clearer picture, here’s a list of potential risks associated with titanium knee replacements:
- Infection at the surgery site
- Implant failure
- Prosthesis wear and tear
- Allergic reactions to titanium
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Nerve damage around the knee area
Each of these risks carries its own set of challenges and requires careful consideration when opting for a titanium knee replacement.
Comparative Analysis of Titanium vs. Other Materials
When comparing titanium knee replacements with other materials, long-term durability is a key factor to consider. Titanium implants have demonstrated exceptional longevity and resistance to wear, making them a preferred choice for many patients. In addition, titanium’s compatibility with the body’s natural bone structure promotes osseointegration, leading to improved stability and reduced risk of implant loosening over time. This is further supported by clinical studies that have shown a significantly lower rate of revision surgeries for titanium knee replacements compared to alternative materials.
Surgical Procedure and Rehabilitation Process

Preoperative Preparation and Evaluation
Before undergoing the titanium knee replacement surgery, we must undergo a thorough preoperative evaluation to ensure that we are in optimal health for the procedure. This evaluation will include a comprehensive medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as X-rays and blood work. Additionally, we may need to make certain lifestyle adjustments and adhere to specific preoperative guidelines to enhance the success of the surgery.
Furthermore, it is important to maintain open communication with the surgical team and ask any questions or express concerns we may have. This collaborative approach will help us feel more confident and informed about the upcoming procedure.
As part of the preoperative preparation, we should also be aware of the potential risks and complications associated with the surgery. This awareness will allow us to make well-informed decisions and actively participate in the decision-making process alongside the healthcare professionals.
In addition, here is a brief overview of the preoperative preparation and evaluation process:
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Medical History Review | Comprehensive review of our medical history to assess overall health and potential risks. |
| Physical Examination | Thorough examination to evaluate the condition of the knee joint and overall physical health. |
| Diagnostic Tests | X-rays, blood work, and other tests to provide detailed information for surgical planning. |
| Lifestyle Adjustments and Guidelines | Recommendations for lifestyle modifications and preoperative preparations. |
Surgical Techniques for Titanium Knee Replacement
When undergoing surgical techniques for titanium knee replacement, meticulous precision is crucial for ensuring the proper alignment and stability of the implant. Our team emphasizes the use of advanced imaging technology to guide the placement of the titanium implant, resulting in improved postoperative outcomes. Additionally, the surgical process involves a comprehensive approach to soft tissue management, which is essential for promoting efficient healing and reducing the risk of complications. Furthermore, the integration of minimally invasive techniques allows for reduced tissue trauma and faster recovery times, contributing to an overall positive surgical experience for patients.
Postoperative Rehabilitation and Recovery
Following the surgical implantation of a titanium knee replacement, we place a significant emphasis on the postoperative rehabilitation and recovery process. This phase is crucial for ensuring the longevity of the implant and the overall success of the surgery.
-
Rehabilitation typically begins within 24 hours after surgery, aiming to reduce recovery time and improve functional outcomes. Patients are guided through a series of exercises designed to restore movement and strengthen the knee.
-
Recovery protocols are tailored to individual needs, but generally include a combination of physical therapy, pain management, and gradual return to activities. It’s important to monitor treatment effects and compare pre- and postoperative functional scores, such as the KOOS (Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score), to gauge progress.
Tip: Consistent physiotherapy sessions and adherence to prescribed exercises are key to a successful recovery. Utilizing tools like the Curovate app can help track rehabilitation milestones and ensure a structured recovery plan.
As patients navigate through the recovery journey, we continuously assess and adjust the rehabilitation program to align with their healing progress and personal goals.
Lifestyle and Activity Recommendations After Surgery

Physical Activity Guidelines for Titanium Knee Recipients
After undergoing titanium knee replacement surgery, regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining joint flexibility and strength. Our rehabilitation program emphasizes a gradual increase in activity levels, starting with low-impact exercises such as walking and swimming. As we progress, we incorporate strengthening exercises to improve muscle tone and support the knee joint. It’s important to consult with our healthcare team to develop a personalized exercise plan that aligns with our recovery goals and physical capabilities. Additionally, maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can further enhance the long-term success of the titanium knee replacement. Remember, consistency and patience are key to achieving optimal results in our recovery journey.
Dietary Considerations for Joint Health
Maintaining a balanced and nutrient-rich diet is crucial for supporting the long-term health of our titanium knee replacements. We emphasize the consumption of foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids to promote bone strength and overall joint function. Additionally, we recommend limiting the intake of processed foods and sugary beverages, as they can contribute to inflammation and joint discomfort.
Incorporating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into our diet provides essential antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, which can aid in reducing oxidative stress and supporting joint health. Furthermore, staying hydrated by consuming an adequate amount of water throughout the day is essential for maintaining the elasticity of connective tissues and lubricating the joints.
For a comprehensive overview of dietary considerations, please refer to the following table:
| Nutrient | Food Sources |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Dairy products, leafy greens, almonds |
| Vitamin D | Fatty fish, fortified dairy products |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Flaxseeds, walnuts, salmon |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to personalize dietary recommendations based on individual health needs and considerations.
Impact of Titanium Knee Replacement on Daily Activities
After undergoing titanium knee replacement surgery, we experienced a significant improvement in mobility and comfort. We were able to resume daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and standing for longer periods without experiencing discomfort or pain. Additionally, we found that engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming and cycling helped to further strengthen the knee and improve overall joint health.
Furthermore, we noticed that the titanium knee replacement allowed us to participate in activities that were previously challenging, such as gardening, light sports, and recreational activities. This enhanced our quality of life and provided a sense of normalcy in our daily routines.
We also found it beneficial to maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support joint health, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants. This, combined with regular physical activity, contributed to the long-term success of the titanium knee replacement.
It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before engaging in any new physical activities post-surgery, and to follow the recommended guidelines for a safe and effective recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the titanium knee replacement offers a durable and effective solution for improving joint health. With its remarkable strength and longevity, this advanced medical technology provides patients with the opportunity to regain mobility and enhance their quality of life. As research and innovation continue to drive advancements in orthopedic care, the titanium knee replacement stands as a testament to the ongoing pursuit of excellence in medical science and patient care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical lifespan of a titanium knee replacement?
The typical lifespan of a titanium knee replacement is around 15-20 years, but it can vary based on individual factors and activity level.
Are there any restrictions on physical activities after getting a titanium knee replacement?
While low-impact activities like walking and swimming are generally encouraged, high-impact activities like running and jumping may need to be limited to protect the implant.
What are the common complications associated with titanium knee replacements?
Common complications include infection, blood clots, implant loosening, and allergic reactions to the implant materials. However, these risks are relatively low.
Can a titanium knee replacement set off metal detectors at airports or security checkpoints?
Yes, titanium knee replacements can trigger metal detectors. Patients are advised to carry a medical alert card or inform security personnel about the implant.
How soon can I return to work after undergoing a titanium knee replacement surgery?
The timeline for returning to work varies, but most patients can resume light work duties within 4-6 weeks after surgery, with full recovery taking several months.
What dietary changes should I make to support the longevity of my titanium knee replacement?
A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and protein can support the health of the implant and surrounding tissues. Maintaining a healthy weight is also important for joint health.