
Does your joint ache flare up when climbing stairs or bending? This isn’t just random—it’s often a signal from your body. Identifying triggers behind discomfort in certain postures can unlock better solutions.
We’ve all experienced moments where movement feels restricted. Whether it’s stiffness after sitting or sharp twinges during exercise, pinpointing why it happens matters. Factors like muscle imbalances, joint wear, or inflammation often play hidden roles.
Solutions aren’t one-size-fits-all. Immediate relief might involve simple stretches or ice packs, but long-term care requires deeper understanding. Diagnosing the root issue ensures strategies align with your needs—not generic advice.
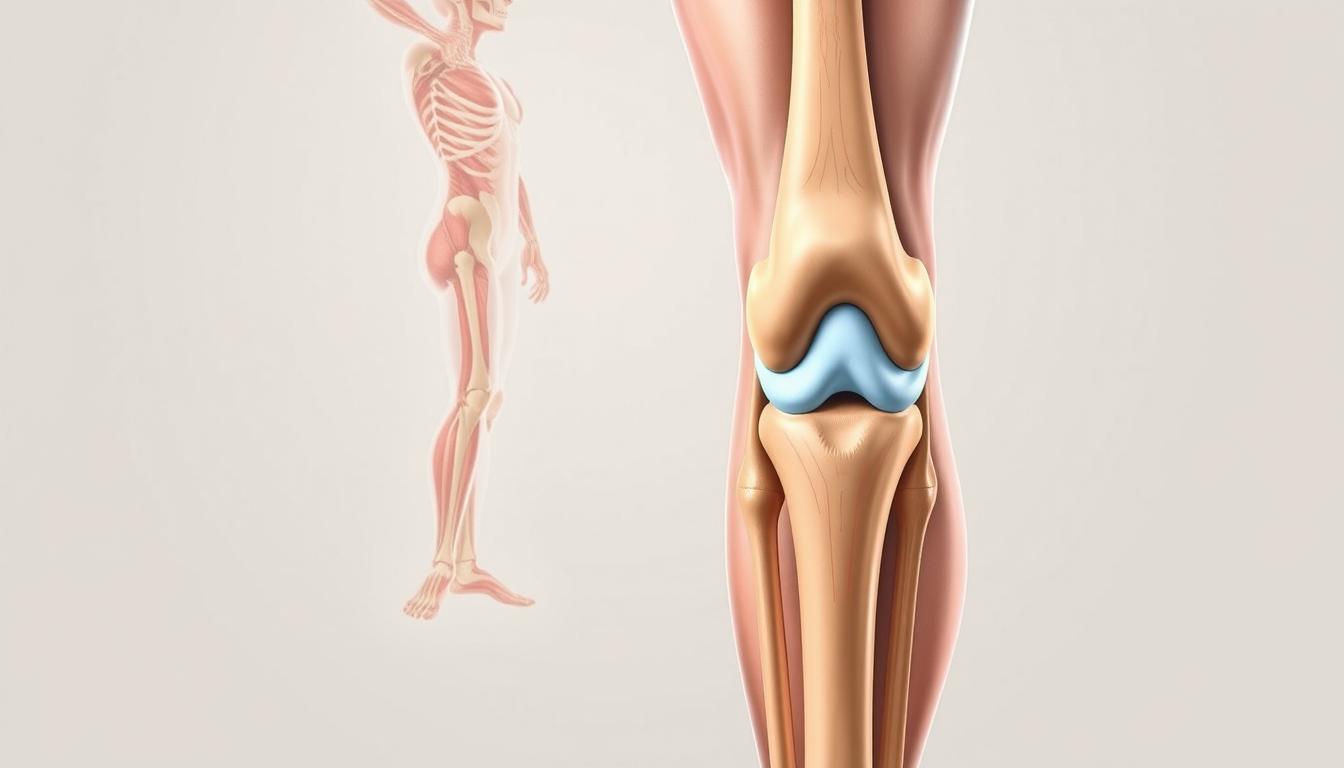
Your body’s largest joint acts like a precision hinge, balancing mobility with stability. To grasp why discomfort occurs, we’ll explore its design and common stressors.
Three bones meet here: the femur, tibia, and patella. Between them, cartilage cushions impacts while ligaments connect bone to bone. This synovial hinge joint allows bending and rotation, supported by muscles and tendons.

Acute trauma—like ACL tears—often stems from sudden twists. Repetitive stress, however, wears down cartilage over time. Conditions like arthritis gradually degrade joint surfaces, causing stiffness.
| Acute Injuries | Chronic Conditions | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Ligament tears | Osteoarthritis | High-impact sports |
| Meniscus damage | Rheumatoid arthritis | Excess body weight |
| Fractures | Tendonitis | Age-related wear |
As one orthopedic specialist notes:
“Minor injuries left untreated often become chronic issues. Early intervention preserves joint function.”
Understanding these patterns helps tailor prevention strategies. For example, strengthening quadriceps reduces strain during daily movements.
Ever wondered why discomfort strikes during simple movements like squatting? Where you feel it—above, around, or below the joint—often reveals the root issue. Let’s decode what these zones signal.
Aching above the joint often points to quadriceps tendon strain. This thick band connects muscles to the kneecap and weakens with overuse. Tenderness directly below? It might signal patellar tendonitis, common in runners.
Swelling around the entire area could mean bursitis—fluid-filled sacs becoming irritated. Cartilage wear, a hallmark of arthritis, often causes grinding sensations during bending. As one physiotherapist explains:
“Location-specific discomfort acts like a roadmap. It guides us toward tailored solutions.”
Persistent inflammation behind the joint warrants attention. This area houses crucial ligaments and could indicate a Baker’s cyst—a fluid buildup from cartilage damage. Morning stiffness that eases with movement? That’s classic arthritis behavior.
Redness or warmth alongside swelling suggests active inflammation. While tendonitis brings sharp twinges during activity, chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis cause symmetrical discomfort in both joints. Tracking these patterns helps professionals separate temporary strains from degenerative issues.
When stiffness strikes during routine activities, simple strategies can provide rapid relief. These approaches not only ease tension but also reveal clues about your joint health.
Rest and cold therapy remain gold standards for sudden flare-ups. Elevating the affected leg reduces swelling, while compression sleeves offer stability. Consider these steps:
Persistent soreness when standing from chairs often signals cartilage wear. Osteoarthritis frequently manifests this way, especially in those carrying excess weight. A physical therapist notes:
“How your body distributes pressure during motion directly impacts joint stress. Minor adjustments prevent major breakdowns.”
Morning stiffness that lingers beyond 30 minutes could indicate inflammatory conditions. Tracking when and where discomfort occurs helps professionals differentiate between temporary strains and chronic issues like rheumatoid arthritis.
While these methods provide short-term comfort, they’re stepping stones—not destinations. Recurring symptoms demand deeper investigation to address root causes rather than masking signals your body sends.
Does daily movement leave you wincing from discomfort? Immediate care at home can calm inflammation and create space for healing. Let’s explore practical steps to manage flare-ups while respecting your body’s recovery timeline.
Rest tops the list. Pause strenuous activities to prevent further strain on muscles and ligaments. Pair this with ice packs wrapped in cloth—15 minutes on, 30 minutes off—to numb sharp sensations.
Compression sleeves stabilize the joint without cutting off circulation. Elevate your leg above heart level when sitting or lying down. This combo reduces swelling around the kneecap by improving fluid drainage.
NSAIDs like ibuprofen tackle both inflammation and discomfort. Always follow dosage instructions and consult your doctor if using them longer than 10 days. For added stability during light activities, consider these options:
| Support Type | Purpose | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic bandage | Reduces swelling | Post-injury compression |
| Patellar strap | Relieves tendon stress | Running or jumping |
| Hinged brace | Limits side-to-side motion | Recovery from sprains |
Gentle exercises like seated leg lifts maintain strength without aggravating tissues. As one sports medicine specialist advises:
“Home care works best when combined with activity modification. Listen to your body’s signals—they guide smarter recovery choices.”
These strategies offer temporary relief while you monitor patterns. Persistent symptoms? That’s your cue to consult a professional for deeper solutions.
What happens when home remedies don’t resolve the ache? Persistent symptoms often mean it’s time to involve experts who specialize in joint health. Doctors use advanced tools to pinpoint issues affecting bones, tendons, or cartilage—ensuring treatments match your unique needs.
Schedule a consultation if discomfort lingers beyond two weeks or worsens during rest. Swelling that doesn’t improve with ice, or instability while standing, often signals deeper tissue damage. A qualified specialist might order MRI scans to check ligaments or X-rays to assess bone alignment.
Physical therapy strengthens muscles around the joint, improving stability. For patellar misalignment, braces redistribute pressure during movement. Severe cases may require surgery to repair torn tissues or replace damaged bone sections. Here’s how options compare:
| Treatment | Purpose | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Custom exercises | Restore mobility | Mild tendonitis |
| Support braces | Correct tracking issues | Patellar instability |
| Arthroscopy | Remove debris | Cartilage tears |
| Joint replacement | Address advanced disease | Bone-on-bone arthritis |
One orthopedic surgeon notes:
“Early intervention prevents irreversible damage. Surgery becomes necessary only when conservative methods fail.”
Ignoring chronic inflammation risks permanent tissue scarring. Professionals tailor plans using diagnostic data—whether that means adjusting your stride or scheduling minimally invasive procedures.
What if small daily choices could shield your joints from wear? Proactive habits build resilience against recurring issues while managing existing conditions like bursitis. Let’s explore sustainable strategies that protect mobility without drastic changes.
Low-impact activities maintain flexibility without straining tendons. Swimming or cycling strengthens muscles around joints, while yoga reduces morning stiffness. For those with rheumatoid arthritis, water aerobics minimizes pressure during motion.
Excess weight multiplies stress on load-bearing areas. Losing just 10 pounds relieves 40 pounds of force per step. A nutritionist explains:
“Sustainable weight loss isn’t about diets—it’s creating energy-balanced routines that fit your lifestyle.”
Overuse injuries like bursitis thrive on repetition. Alternate high-intensity workouts with gentler options—walk instead of run every third day. Proper warm-ups prepare tissues for strain, reducing microtears.
Ergonomic adjustments matter too. Use cushioned mats during floor exercises and avoid locked-knee postures. This table shows smart swaps:
| Risky Activity | Safer Alternative | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Deep squats | Wall sits | Reduces patellar pressure |
| Prolonged kneeling | Foam-padded stools | Prevents bursitis flare-ups |
| Running on pavement | Trail walking | Less tendon impact |
Consistency beats intensity. Daily stretches and posture checks create lasting protection against stiffness and inflammation.
Managing recurring discomfort requires consistent habits that address both symptoms and root issues. We’ll break down practical methods to maintain mobility while protecting vulnerable areas from strain.
Start mornings with gentle quad stretches to ease stiffness. Wall-assisted calf raises strengthen lower leg muscles without stressing sensitive tendons. For those managing patellofemoral pain, seated leg extensions with light resistance bands improve tracking.
Evening routines should focus on recovery. Use foam rollers on thigh muscles to release tension contributing to runner knee. Ice packs applied for 10-minute intervals reduce inflammation after prolonged activity.
Understanding what causes knee pain helps modify high-risk activities. Swap deep lunges for step-ups on stable platforms to minimize joint compression. This table shows smart adjustments:
| Original Activity | Modified Version | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pavement running | Elliptical training | Reduces impact on patellofemoral area |
| Basketball jumps | Swimming laps | Strengthens muscles without strain |
| Cross-legged sitting | Chair-supported posture | Prevents cartilage pressure |
A sports physiotherapist emphasizes:
“Alignment checks during squats or stairs prevent 60% of runner knee cases. Small form tweaks yield big protection.”
Consistency matters most. Weekly stability exercises build resilience against flare-ups. If discomfort persists despite these changes, consult a specialist to explore deeper causes knee issues might involve.
Understanding your body’s signals transforms how you approach joint care. By connecting symptoms like stiffness or swelling to their root causes, you can choose targeted solutions—whether that’s rest, therapy, or professional guidance.
Consistency matters. Over time, small daily habits strengthen muscles and reduce strain. Pairing home strategies with medical advice creates lasting results, especially when addressing issues early.
If you experience random discomfort episodes, don’t dismiss them. Tracking patterns helps identify whether it’s temporary stress or something needing expert attention.
We encourage prioritizing long-term health through preventive steps and timely check-ups. Thank you for exploring these strategies—may they guide you toward smoother movements and stronger joints every day.
Discover how to alleviate knee pain after sleeping on side with our expert guide. Learn…
Discover the causes and treatments for knee pain when bending but not swelling. We explore…
Knee pain relief for nurses is achievable. We share our expertise on managing knee pain,…
We provide a comprehensive guide on knee-friendly elliptical workouts, helping you achieve your fitness goals…
We outline the 15 acupuncture points for knee bursitis that are most effective. Find out…
Discover why we experience knee pain during ovulation and explore the underlying causes and potential…