Knee pain can really affect your life. At the University of Michigan Health System, we offer many non-surgical and surgical options. We aim to find out why you’re in pain and how we can help you1. We handle all kinds of knee issues, like ACL, LCL, MCL, and PCL injuries, meniscus tears, and more2.
Our team works together to create a treatment plan just for you. This approach has led to great success in treating knee pain.
Key Takeaways
- The University of Michigan Health System performs over 250 total knee replacements annually, with 90% still functional 15 years later1.
- Knee pain can stem from various causes, including arthritis, injuries, and structural issues2.
- Non-surgical options like physical therapy, injections, and bracing are often the first line of treatment before considering surgery2.
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight management and exercise, can help alleviate knee pain and prevent further injury1.
- The University of Michigan Health System’s personalized, multidisciplinary approach is key to successfully treating knee pain1.
Understanding Knee Pain and Its Causes
Knee problems are very common and affect many people. There are many reasons why someone might experience knee pain, from wear and tear to sudden injuries. Understanding the common causes of knee pain is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment approach.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Osteoarthritis is a common cause of knee pain, caused by the gradual wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the knee joint3. Rheumatoid arthritis is another cause, leading to swelling and cartilage destruction3. Injuries to the ligaments, like the ACL and PCL, can also cause a lot of pain3. Tendon injuries, from inflammation to tears, often happen from overuse or falls3. Damage to the cartilage, including softening or tearing, can also lead to pain3. Lastly, a broken kneecap, usually from a fall or direct blow, can be very painful and debilitating3.
Diagnosing Knee Pain
It’s important to figure out what’s causing knee pain to treat it right. This usually means a detailed check-up, looking at the patient’s characteristics, medical history, and physical exam to pinpoint the pain’s location and type4. Sometimes, imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs are needed to see any structural damage or issues5. Knowing what’s causing the pain helps doctors create a specific and effective treatment plan.
“Knee pain is a common complaint, and it’s crucial to accurately diagnose the underlying cause to ensure appropriate treatment.”
| Imaging Test | Diagnostic Value |
|---|---|
| X-ray | Helpful in detecting bone fractures and degenerative joint disease5 |
| CT Scan | Accurately identifies gout even when the joint is not inflamed5 |
| MRI | Particularly useful in revealing injuries to soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and muscles5 |
Knee pain treatment: pain relievers, physical therapy, injections, surgery
Managing knee pain offers many treatment options, each with its own pros and cons. We’ll look at both non-surgical and surgical ways to ease knee pain and improve movement.
The RICE method – rest, ice, compression, and elevation – is a common first step. Complementary therapies like massage, acupuncture, and meditation may also offer some relief.6
For ongoing or severe pain, injection therapy may be an option. This could be steroid or anti-inflammatory shots, giving relief for a few months6. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy also shows promise in helping the body heal itself6.
If non-surgical treatments don’t help enough, surgery might be considered. Total knee replacement surgery replaces damaged parts with artificial ones. Partial knee replacement focuses on a specific knee area6. Arthroscopic surgery is a less invasive method for diagnosing and treating knee problems6.
For those who are active and have wear and tear on one side, osteotomy could be an option. It aims to stop knee osteoarthritis from getting worse6.
| Treatment Option | Description | Typical Duration of Relief |
|---|---|---|
| Cortisone Shots | Injection of anti-inflammatory medication directly into the joint | Approximately 3 months7 |
| Gel Injections | Injections of hyaluronic acid to lubricate and cushion the joint | 6 to 12 months7 |
| Prolotherapy Injections | Injections that stimulate the body’s natural healing processes | Potential long-term benefits7 |
| Orthobiologic Injections | Injections of concentrated cells or tissues to promote healing | Potential long-term benefits7 |
The effectiveness and duration of these treatments can vary. Insurance coverage also affects the choice of treatment7. It’s key to talk to a healthcare professional to find the best treatment for you.
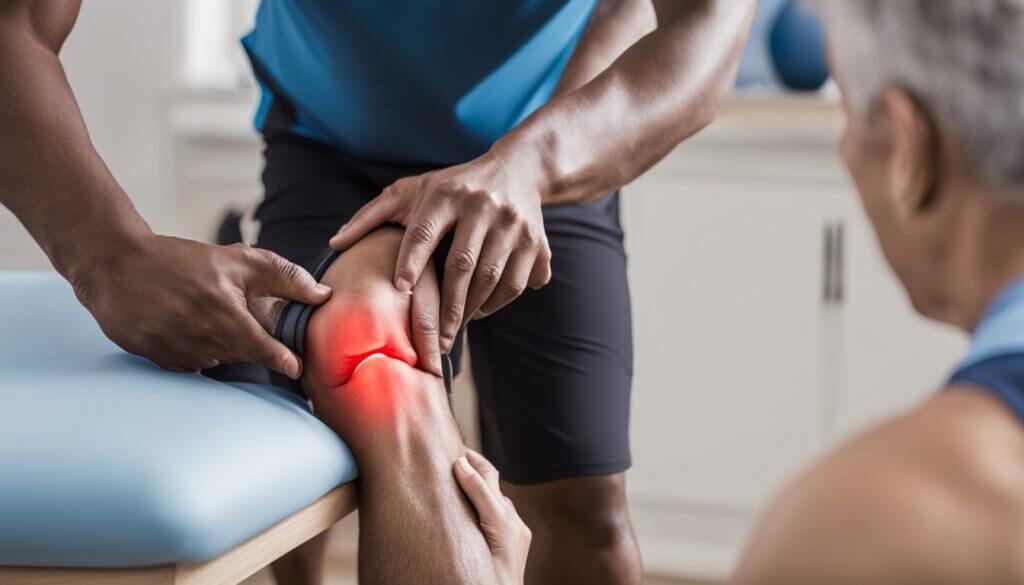
Knee pain can stem from injuries, past damage, or conditions like osteoarthritis8. Finding and treating the root cause is key to lasting relief.
“The goal of any knee pain treatment is to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further damage to the joint.”
Non-Surgical Approaches to Knee Pain Management
At our practice, we know that knee pain can really slow you down. We offer non-surgical treatments that work well9. Physical therapy is a top choice, helping to make your knee more flexible, strong, and stable10. We also use splinting or bracing to support and protect your knee while it heals.
We suggest anti-inflammatory medications and pain relievers to lessen inflammation and ease pain9. For quick relief, we have steroid injections that reduce inflammation10. We also offer gel shots and PRP therapy to tackle knee pain and speed up healing.
10 Gel injections might not help right away and could make your knee stiff at first. But, they can bring long-term benefits if you get insurance approval10. PRP injections try to grow new, healthy cartilage. But, they don’t always work as hoped10. PRP injections are not usually covered by insurance and can be expensive, costing from a few hundred to several thousand dollars per shot.
11 We also look at other options like cortisone injections, which you can have up to four times a year11. For younger patients with knee injuries and small cartilage damage, we might suggest autologous or stem cell injections. These are better for their situation.
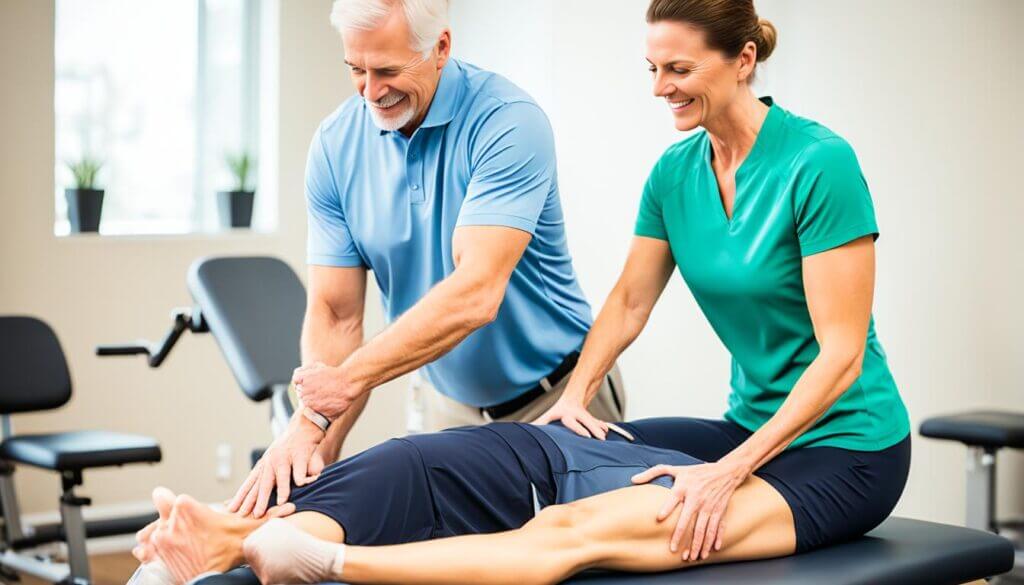

Our aim is to find the best non-surgical solution for each patient to relieve knee pain for good. By using proven treatments, we often help patients avoid more serious procedures.
Conclusion
Knee pain is a common issue that affects many people, especially as they get older12. Luckily, there’s a way to manage this pain effectively and improve your life. By using a mix of treatments, we can ease your pain, make moving easier, and help you enjoy activities again.
Our team will create a plan just for you to tackle the knee pain’s cause. This might include painkillers, physical therapy, and new treatments like corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP)12. These treatments help by reducing swelling, making the joint slippery, and helping tissues heal. They offer quick and lasting relief12. Studies also show they help with function, pain, and life quality for those with knee osteoarthritis and other joint issues13.
With a full approach to your knee pain, we aim to help you be independent again and live the active life you want. Using effective treatments and our support, we’re sure we can improve your mobility and life quality12. Let’s find the best solution for you and get you on the road to wellness.
FAQ
What are the common causes of knee pain?
How is knee pain diagnosed?
What are the treatment options for knee pain?
What are the non-surgical approaches to managing knee pain?
Source Links
- Knee Pain | University of Michigan Health – https://www.uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/cmc/knee/pain
- Noninvasive Treatments for Knee Pain: Orthopedic & Wellness : Pain Management – https://www.orthopedicwellness.com/blog/noninvasive-treatments-for-knee-pain
- Knee Pain – Causes & Treatment | Made for This Moment – https://www.asahq.org/madeforthismoment/pain-management/types-of-pain/knee-pain/
- An Overview of Knee Pain – https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/knee-pain/knee-pain-overview
- Knee pain – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic – https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20350855
- Knee Pain Treatment Options: Non-Surgical and Surgical – Orthopaedic Associates – https://oaidocs.com/2022/08/12/knee-pain-treatment-options-non-surgical-and-surgical/
- Types of Injections That Can Help With Joint Pain – https://www.massgeneralbrigham.org/en/about/newsroom/articles/types-of-injections-that-can-help-with-joint-pain
- Knee Pain Relief: Injections vs Surgery – https://posm.org/knee-pain-relief-injections-vs-surgery/
- Nonsurgical Management of Knee Pain in Adults – https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2015/1115/p875.html
- Nonsurgical Treatment Options for Knee Pain – https://phelpshealth.org/news/featured-stories/nonsurgical-treatment-options-knee-pain
- Nonsurgical and Minimally Invasive Knee Pain Treatments – https://www.memorialhermann.org/services/treatments/knee-pain-treatments/nonsurgical-and-minimally-invasive-treatments-for-knee-pain
- The Ultimate Guide to Knee Injections | Arthritis Knee Pain Centers – https://arthritiskneepain.com/wellness-blog/knee-injections/
- Intra-articular Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: from Anti-inflammatories to Products of Regenerative Medicine – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4932822/
Leave a Reply