Did you know that the human body contains approximately 206 bones?
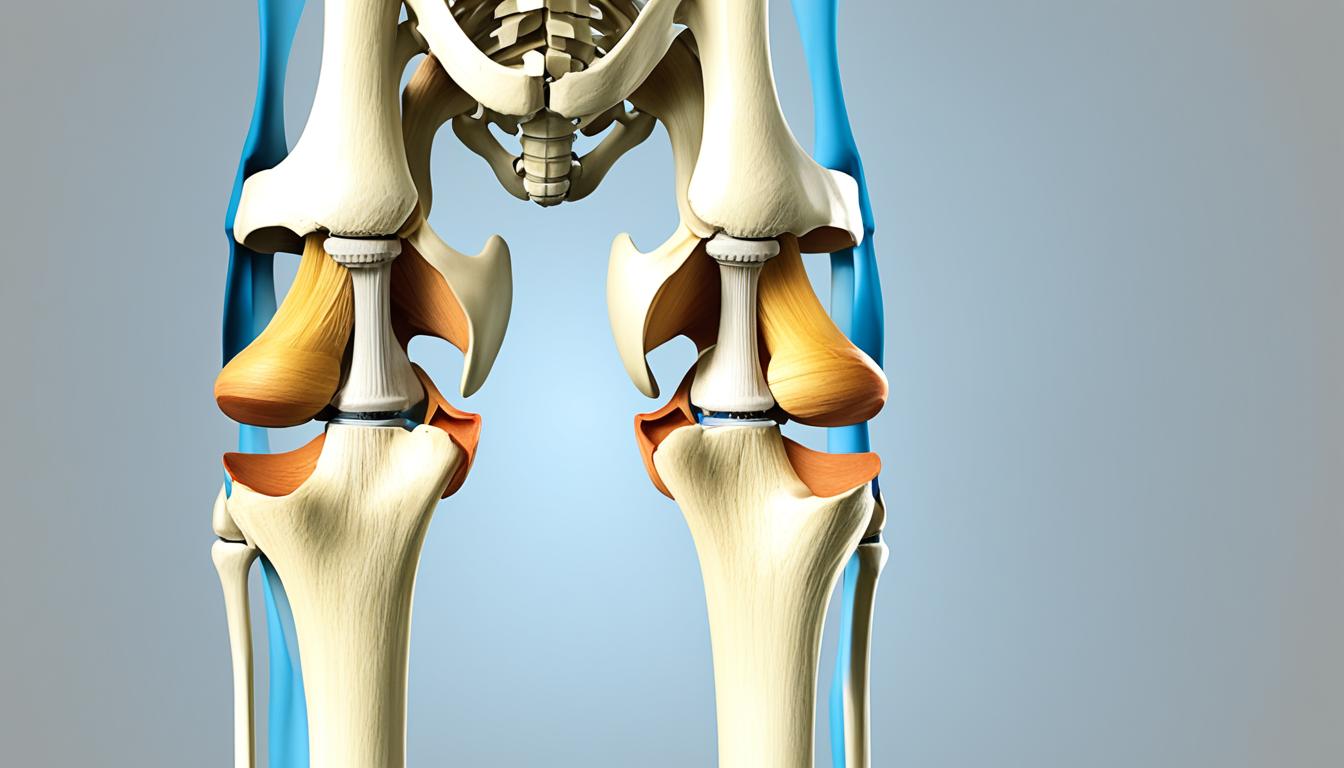
One of these bones, the patella, is a small but crucial component of the skeletal system. Also known as the kneecap, the patella plays a significant role in knee movement and stability.
Located in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle, the patella acts as an attachment point for the quadriceps tendon and patellar ligament, enhancing the efficiency of knee extension.
In addition to its role in movement, the patella serves as a protective shield for the deeper structures of the knee joint, safeguarding them from potential damage.
Understanding the anatomy of the patella is essential for comprehending the function and importance of the skeletal system, specifically in relation to knee movement and stability.
Join us as we delve deeper into the fascinating world of patella anatomy, unravel common conditions that affect this bone, explore tests and imaging techniques used for diagnosis, and discover the treatment options available for patella-related injuries and disorders.
Common Conditions and Disorders Affecting the Patella
The patella, or kneecap, is susceptible to various conditions and disorders that can cause knee pain and instability. It is important to understand these common ailments in order to seek appropriate medical attention and determine the most effective treatment plan.
Patellar Dislocation: One condition that affects the patella is patellar dislocation. This occurs when the patella completely moves out of its normal position, usually to the outer side of the knee joint. It can be a result of injury, trauma, or anatomical abnormalities. The sudden displacement can cause severe pain and discomfort, accompanied by visible deformity and difficulty in knee movement. Immediate medical attention is required to reduce the dislocation and prevent further damage.
Patellar Subluxation: Patellar subluxation is a milder form of dislocation where the patella partially moves out of its groove but doesn’t fully dislocate. It can cause similar symptoms of pain, instability, and difficulty in knee movement. However, unlike dislocation, the patella spontaneously relocates back into its normal position. Proper diagnosis is essential to differentiate between patellar subluxation and dislocation, as the treatment approaches may vary.
Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is a systemic bone disease characterized by low bone density, making the bones weak and susceptible to fractures. While osteoporosis primarily affects the spine, hips, and wrists, it can also impact the patella. Weakening of the patella due to osteoporosis increases the risk of fractures and exacerbates knee pain and instability. If you have osteoporosis and experience new symptoms in your knees or have difficulty walking or moving, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
“Understanding the common conditions and disorders affecting the patella is important for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Seeking medical attention for knee pain, instability, or any new symptoms can help prevent further damage and improve overall knee health.”
The Importance of Seeking Medical Attention
When experiencing knee pain, instability, or new symptoms in the knees, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of patella injuries and disorders can lead to worsening symptoms, complications, and long-term mobility issues.
By consulting a healthcare professional, you can receive an accurate diagnosis through a thorough physical examination, imaging tests, and other diagnostic procedures. This will help determine the specific condition affecting your patella and guide the most appropriate treatment plan for optimal recovery and improved knee function.
In the next section, we will explore the different tests and imaging techniques used to diagnose patella-related conditions, enabling effective treatment interventions.
Tests and Imaging for the Patella
When evaluating the health of the patella, healthcare providers utilize various tests and imaging techniques to diagnose injuries and fractures accurately. These diagnostic tools play a critical role in determining the extent of damage and formulating an appropriate treatment plan.
Patella Reflex Test
The patella reflex test is the most common evaluation performed on the patella. This test involves tapping the patellar tendon just below the kneecap, which triggers an involuntary reflex. The test assesses the functioning of the patellar reflex arc, involving the sensory and motor nerve pathways.
This reflex helps healthcare providers assess the integrity of the nerves and spinal cord and aids in the diagnosis of conditions affecting the patella. A normal response to the test indicates that the nerves and spinal cord are functioning properly.
Imaging Tests for Patellar Injuries and Fractures
In cases of patellar injuries or fractures, imaging tests are essential to evaluate the extent of the damage and guide appropriate treatment plans. X-rays are a commonly used imaging technique to assess fractures in the patella. They provide clear images of the bone structure, enabling healthcare providers to identify fractures and determine the severity of the injury.
Additional imaging tests, such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) or CT (Computerized Tomography) scans, may be ordered to further evaluate the soft tissues surrounding the patella. These tests can help identify ligamentous injuries or other possible damage that may affect treatment decisions.
By utilizing these tests and imaging techniques, healthcare providers can make accurate diagnoses and develop effective treatment plans for patella-related injuries and fractures.
Treatment Options for Patella Conditions
Treatment for patella conditions depends on the specific injury or disorder. Here, we explore various options that healthcare providers may recommend to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and restore knee function.
Conservative Measures:
- Wearing a brace can provide stability to the patella and support the knee joint during physical activities.
- Resting the knee is essential for reducing inflammation and allowing the damaged tissue to heal. Avoiding activities that exacerbate pain or stress on the patella is crucial for a successful recovery.
- Engaging in physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, increase flexibility, and improve overall knee stability. A trained physical therapist can guide individuals through specific exercises to target the affected area.
- Implementing at-home treatments such as icing the knee to reduce pain and swelling, and using over-the-counter pain relievers to manage discomfort can complement other conservative measures.
Surgical Interventions:
In more severe cases, such as complex fractures or patellar dislocations that cannot be addressed through conservative methods, surgery may be necessary. Surgical interventions can involve realigning the fractured bone, repositioning the patella, repairing the damaged ligaments or tendons, or removing loose fragments. Recovery from surgery may require a longer period of rest, physical therapy, and rehabilitation to regain full knee function.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment plan for a specific patella condition. A personalized approach based on the individual’s needs, severity of the injury or disorder, and overall health will contribute to the best possible outcome.
Treatment Comparison
| Treatment Method | Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Brace | Provides stability and support to the patella Reduces the risk of further injury during physical activities |
May limit mobility during certain movements May require adjustment and proper fitting |
| Rest | Reduces inflammation and promotes healing Prevents exacerbation of symptoms |
Requires avoiding activities that stress the knee May require modifications to daily routine |
| Physical Therapy | Strengthens muscles around the knee Improves flexibility and knee stability Guided exercises tailored to the individual’s needs |
Requires regular sessions with a trained physical therapist Commitment to exercises and rehabilitation |
| At-Home Treatments | Reduces pain and swelling Provides temporary relief |
May not address underlying causes Needs to be used in conjunction with other treatments |
| Surgery | Addresses complex fractures or dislocations Allows for precise realignment and repair |
Requires a more extended recovery period May carry risks associated with surgery |
Importance of Patella Fracture Treatment and Osteoporosis Management
Proper treatment for patella fractures is crucial for successful recovery and restoring normal function. Immobilization using a splint or cast is often necessary to ensure the fractured bone aligns correctly during the healing process. In more severe cases, surgery may be recommended to realign the patella and promote optimal healing.
It is important to follow the treatment plan provided by your healthcare provider or surgeon diligently. This includes adhering to weight-bearing restrictions, taking prescribed medications for pain management, and attending follow-up appointments. By actively participating in your treatment, you can enhance your chances of a full recovery and minimize the risk of complications.
Osteoporosis, a condition characterized by decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures, can also affect the patella. Managing osteoporosis is essential for preventing fractures and promoting overall bone health. Treatment options for osteoporosis may include a combination of lifestyle modifications, exercises to improve bone strength, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and prescription medications.
To facilitate early detection and diagnosis of osteoporosis, bone density tests are often conducted. These tests measure the density and strength of the bones, providing valuable information about the risk of fractures. Regular bone density tests can help identify osteoporosis at an early stage when interventions can be implemented to prevent further bone loss and reduce the risk of fractures.
Ensuring proper treatment for patella fractures and effectively managing osteoporosis are crucial steps in maintaining optimal bone health and preventing long-term complications. By working closely with healthcare professionals and following their recommendations, individuals can significantly improve their recovery outcomes and minimize the impact of these conditions on their daily lives.
Conclusion
The patella, as a vital component of the skeletal system, plays a crucial role in knee movement and stability. Understanding the anatomy and function of the patella is essential for identifying, treating, and preventing various patella-related conditions, including injuries and disorders.
When it comes to treatment options, there is a broad range available. Conservative measures such as bracing and physical therapy are often effective in managing patella injuries and promoting recovery. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary for optimal outcomes. It is important to seek appropriate medical care and follow recommended treatment plans to ensure the best possible results.
By prioritizing the well-being of our skeletal system and recognizing the significance of the patella’s anatomy, we can proactively maintain optimal knee health and function. Whether it’s engaging in preventive measures or seeking professional help for treatment options, taking proactive steps can help us effectively manage patella injuries and preserve the stability and movement of the knee.
FAQ
What is the function of the patella in the skeletal system?
The patella serves as an attachment point for the quadriceps tendon and patellar ligament, increasing the efficiency of knee extension. It also acts as a bony shield for deeper structures in the knee joint, protecting them from damage.
What conditions can affect the patella?
The patella can be affected by various conditions and disorders, including patellar dislocation, patellar subluxation, and osteoporosis.
What tests are performed on the patella?
The most common test performed on the patella is the patella reflex test, which involves tapping the knee to trigger an involuntary reflex. In cases of injury or fracture, imaging tests such as X-rays may be necessary.
What are the treatment options for patella conditions?
Treatment for patella conditions depends on the specific injury or disorder but may include wearing a brace, resting, engaging in physical therapy, and using at-home treatments like icing and over-the-counter pain relievers. Severe injuries or fractures may require surgery.
How are patella fractures treated?
Patella fractures may be treated through immobilization using a splint or cast. In some cases, surgery is necessary to realign the fractured bone.
How is osteoporosis managed to prevent patella fractures?
Osteoporosis, which can affect the patella, requires treatment to prevent fractures. Options may include exercise, vitamin and mineral supplements, prescription medications, and regular bone density tests for early diagnosis.
Leave a Reply