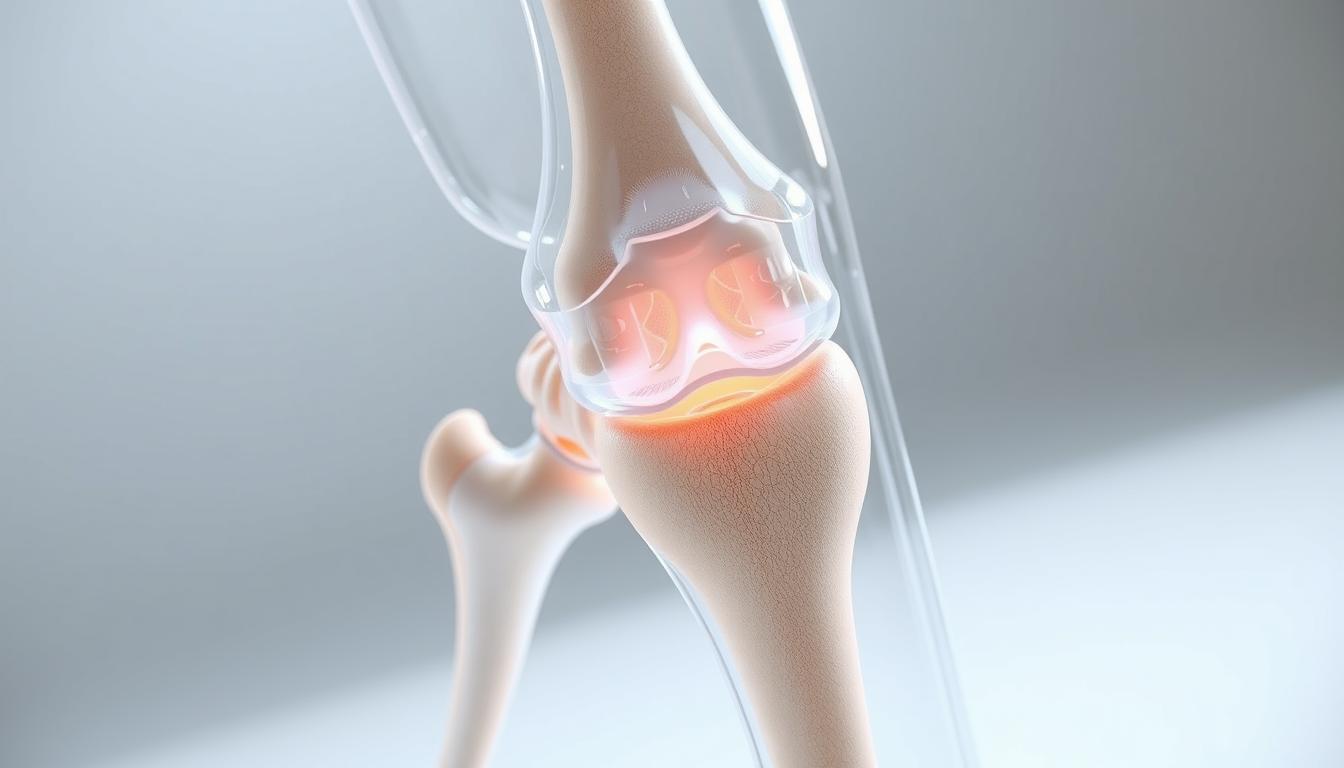
That faint crunching sound when bending your legs – is it a red flag for joint damage? Many people worry when they hear unusual noises from their bodies, especially around sensitive areas like the knee. Let’s explore what this common phenomenon really means.
Crepitus refers to crackling sensations or audible sounds during movement. While often linked to arthritis, research from VA studies shows many cases stem from harmless causes like air bubbles in synovial fluid. Our joints naturally change over time, and not every pop signals trouble.
We’ll break down how crepitus develops, when to seek medical advice, and practical ways to support joint health. You’ll discover current findings from trusted sources like Medical News Today, plus actionable strategies to stay active without fear.
Key Takeaways
- Crepitus describes noises like cracking or grinding during joint movement
- Multiple factors beyond arthritis can cause these sounds
- Age-related changes often contribute to harmless crepitus
- Persistent pain alongside noises warrants medical evaluation
- Preventive care helps maintain healthy joint function
Understanding your body’s signals empowers better health decisions. Let’s separate myths from facts about this widespread experience.
Understanding Knee Crepitus
That subtle crunch when standing up might make you pause, but it’s not always cause for alarm. Joint noises often come from everyday movements rather than serious damage. Let’s explore what’s happening beneath the surface.
What Creates Those Sounds?
Popping or crackling sensations during motion – medically termed crepitus – occur when tissues interact. Tendons may snap over bony ridges, while ligaments might rub during flexion. Research shows gas bubbles in synovial fluid can also collapse, creating harmless cracks.
Building Blocks of Movement
Three bones form the joint’s framework: the thigh’s femur, shin’s tibia, and kneecap (patella). Between them lies cartilage – a smooth tissue preventing bone friction. The crescent-shaped meniscus acts as a shock absorber during walking or jumping.
Synovial fluid lubricates these parts like oil in machinery. When cartilage wears thin or fluid levels drop, movements may feel rougher. This explains why some people notice grinding sensations as they age, even without injury or disease.
We’ll next examine specific triggers – from sports injuries to natural wear patterns – that affect these structures. Understanding normal anatomy helps distinguish routine noises from signs needing attention.
Exploring the Causes and Risk Factors
Hearing a snap while climbing stairs? Multiple factors could trigger joint noises. While often harmless, these sounds sometimes hint at underlying issues. Let’s unpack the key contributors – from weekend warrior mishaps to gradual wear patterns.

Injuries, Overuse, and Traumatic Events
Sports collisions or awkward landings can damage cartilage or ligaments. Medical News Today notes patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFS) often develops from repetitive stress. Even minor sprains may alter joint mechanics, creating audible friction during movement.
Active individuals face higher risks. A torn meniscus – common in sports like basketball – frequently causes grinding sensations. Research shows 40% of adults with past injuries report increased joint noises years later.
“Patients with persistent popping had 3x higher osteoarthritis risk over a decade.”
Underlying Conditions and Mechanical Stress
Cartilage thinning from osteoarthritis creates rough surfaces that grind during motion. Excess weight amplifies pressure – every 10 pounds adds 30-60 pounds of force per step. This accelerates wear, particularly in older adults.
| Cause | Description | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Traumatic Injury | Sudden impact damaging ligaments/meniscus | Contact sports, falls |
| Overuse | Repetitive strain on tendons/cartilage | Running, kneeling jobs |
| Osteoarthritis | Cartilage breakdown causing bone friction | Aging, obesity |
| Meniscus Tear | Torn shock-absorbing cartilage | Twisting motions, aging |
While occasional popping raises no red flags, pairing sounds with swelling or stiffness warrants evaluation. Early intervention helps prevent progressive damage.
Does knee crepitus always mean arthritis
A crunch during yoga poses or stairs often sparks concern. While joint sounds can indicate wear, they don’t automatically equal irreversible damage. Let’s unpack what research reveals about this connection.
The Link Between Noises and Joint Degeneration
Occasional popping rarely signals trouble. Persistent grinding with stiffness, however, might suggest cartilage thinning. A VA-led study tracking 3,000 adults found those with frequent noises had 50% higher osteoarthritis risk over 8 years.
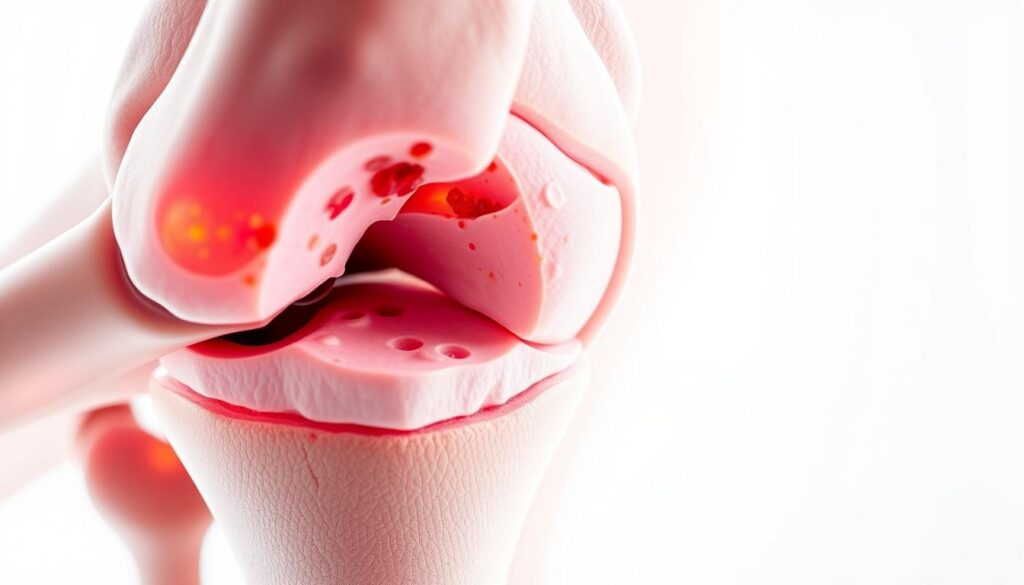
Decoding the Research
Data shows context matters. One-third of participants with audible sounds developed arthritis symptoms, while two-thirds remained pain-free. As one rheumatologist notes:
“Crepitus alone isn’t diagnostic – we assess swelling, mobility, and imaging together.”
Strengthening muscles around the joint helps reduce pressure. Low-impact activities like swimming maintain mobility without exacerbating wear. Monitoring changes in sound patterns helps identify when to seek evaluation.
| Frequency | Pain Present? | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Rare | No | Monitor |
| Daily | Mild | PT consult |
| Constant | Severe | Imaging needed |
Staying proactive allows us to address concerns early while avoiding unnecessary worry about every pop. Balance awareness with evidence-based care for lasting joint health.
Symptoms, Diagnosis, and When to Seek Medical Advice
Have you noticed new sensations while moving? While many joint noises are harmless, certain signs demand attention. Let’s identify key indicators that separate routine sounds from those needing professional evaluation.
Recognizing Pain, Swelling, and Stiffness
Three primary symptoms often accompany concerning joint changes:
- Pain that worsens with activity
- Visible swelling around the joint
- Morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes
These issues might develop gradually or appear suddenly after injury. Medical News Today reports 68% of osteoarthritis cases involve persistent discomfort during weight-bearing activities.
Diagnostic Tools and X-ray Findings
Doctors use multiple methods to assess joint health:
| Method | Purpose | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Exam | Check range of motion | 85% |
| X-ray | Detect bone changes | 90% |
| MRI | View soft tissue damage | 95% |
“X-rays reveal joint space narrowing – a key osteoarthritis marker – in 76% of symptomatic patients over 50.”
Seek medical advice if pain disrupts sleep or daily tasks. Early diagnosis helps manage conditions effectively through targeted therapies. Remember – awareness empowers better health decisions without unnecessary worry.
Managing Knee Crepitus with Lifestyle and Therapy
What if those joint sounds could become manageable through simple daily choices? Proactive care often makes the difference between discomfort and lasting mobility. Let’s explore practical strategies that address symptoms while supporting long-term joint function.
Effective Non-Surgical Approaches
Three pillars form the foundation of conservative treatment:
- RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) for acute flare-ups
- Anti-inflammatory medications for temporary pain relief
- Targeted physical therapy to strengthen supporting muscles
“Customized exercise plans improve joint stability in 89% of patients within 8 weeks.”
Smart Activity Modifications
Swapping high-impact exercises for joint-friendly alternatives maintains activity levels without strain. Consider this comparison:
| High-Impact | Low-Impact | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Running | Swimming | Reduces pressure by 75% |
| Basketball | Cycling | Maintains muscle tone |
| Jumping | Yoga | Improves flexibility |
Pair these changes with weight management and supportive footwear. Small lifestyle adjustments create cumulative benefits – like using a foam roller for 10 minutes daily to maintain tissue elasticity. Consistency matters more than intensity when preserving joint health.
Preventative Measures and Daily Care Strategies
Taking proactive steps today can help maintain joint flexibility tomorrow. Simple daily habits strengthen supporting muscles and reduce wear on vulnerable areas. Let’s explore practical ways to protect your body’s natural shock absorbers.
Movement as Medicine
Targeted exercises build stability without strain. The Cleveland Clinic recommends three foundational moves:
- Straight leg raises to engage quadriceps
- Wall sits for controlled muscle endurance
- Step-ups to improve balance and coordination
“Consistent strengthening routines reduce joint pressure by 40% in active adults.”
Weight Management & Smart Support
Every pound lost removes four pounds of force from lower joints during walking. Supportive footwear with proper arch cushioning distributes impact evenly. Consider these comparisons:
| Ideal Features | Avoid |
|---|---|
| Shock-absorbing soles | Flat sandals |
| Arch support | Worn-out treads |
| Proper width | Narrow toe boxes |
Hydration and anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish complement physical efforts. Monitoring symptoms helps adjust activities before minor irritation becomes persistent swelling. We can preserve mobility through mindful lifestyle choices that honor our body’s needs.
Conclusion
Joint sounds often spark questions about long-term health. Our analysis of recent studies shows most cases involve natural age-related changes rather than serious conditions. While occasional popping raises few concerns, persistent discomfort paired with grinding merits professional evaluation.
Three key insights guide our understanding:
Context determines significance: Gas bubbles and tendon movement frequently cause harmless noises. However, pain lasting weeks or visible swelling could signal cartilage wear requiring imaging.
Personalized care matters: Treatment plans should address individual causes – from sports injuries to mechanical stress. Many find relief through targeted exercises and effective treatment options before considering surgical solutions.
Proactive habits protect: Maintaining muscle strength and healthy weight reduces joint pressure significantly. Regular monitoring helps catch changes early, when conservative approaches work best.
We encourage readers to stay informed through trusted sources like VA research and Cleveland Clinic guidelines. While crepitus alone rarely predicts arthritis, combining awareness with timely action supports lasting mobility. Your joints deserve attention – not alarm – when navigating life’s daily movements.
FAQ
What causes cracking or grinding sounds in the knee?
Joint noises often result from gas bubbles popping, cartilage changes, or tendons moving over bones. While these sounds can occur without pain, persistent crepitus with discomfort may signal conditions like osteoarthritis, meniscus tears, or inflammation. Overuse, aging, or past injuries also increase risk.
How do I know if my knee noises are linked to arthritis?
Pain, swelling, or stiffness alongside crepitus often points to joint degeneration. Imaging like X-rays or MRIs can reveal cartilage loss or bone spurs common in osteoarthritis. Consult a doctor if symptoms interfere with daily activities or worsen over time.
Can exercises reduce knee grinding and popping?
Strengthening muscles around the joint improves stability and reduces strain. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling paired with physical therapy can minimize discomfort. Avoid high-stress movements like deep squats if they trigger pain.
Does being overweight worsen knee crepitus?
Excess weight stresses joints, accelerating cartilage wear. Losing even 5–10 pounds lowers pressure on knees during walking or climbing. Combining a balanced diet with joint-friendly workouts supports long-term joint health.
When should I consider surgery for chronic knee issues?
Surgery, like partial or total joint replacement, is typically a last resort after non-surgical options fail. Severe cartilage damage, unrelenting pain, or limited mobility may warrant it. Always discuss risks and recovery timelines with an orthopedic specialist.
Are there lifestyle changes to prevent worsening symptoms?
Wearing supportive footwear, avoiding repetitive impact, and warming up before exercise protect joints. Anti-inflammatory diets rich in omega-3s and vitamin D also help. Early intervention with therapies like RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation) can slow progression.