Ever step out of your car feeling like your leg transformed into a rusty hinge? That sudden stiffness or inability to move your joint freely isn’t just fatigue—it’s your body sounding an alarm. Drivers nationwide increasingly report this unsettling sensation, where their knees temporarily refuse to cooperate after prolonged time behind the wheel.
Modern vehicles confine us in positions that challenge natural movement. Sitting with knees bent at sharp angles for hours reduces blood flow and strains connective tissues. Over time, this can trigger inflammation, cartilage irritation, or even mechanical blockages within the joint. While occasional stiffness might resolve with stretching, recurring locking demands attention.
We’ve discovered three primary culprits behind this issue. Muscle imbalances from repetitive pedal motions create tension that pulls joints out of alignment. Pre-existing conditions like arthritis flare up under sustained pressure. Even minor swelling in the knee capsule can physically prevent smooth motion—like a door jamming in its frame.
Key Takeaways
- Driving positions strain knee joints through limited movement and sustained pressure
- Temporary stiffness differs from mechanical locking caused by cartilage or bone fragments
- Underlying conditions often worsen during long drives without proper support
- Early warning signs include clicking sounds and reduced range of motion
- Strategic stretching and seat adjustments can prevent most mild cases
Recognizing patterns in your discomfort helps determine next steps. Does the stiffness fade after walking, or persist for hours? Sharp pain accompanying the locking suggests different treatment needs than dull aches. We’ll break down how to distinguish between manageable irritation and signals demanding professional care.
Understanding Knee Lock: True vs. Pseudo Locked Knee
Not all joint restrictions are created equal. When movement suddenly stops, it’s critical to identify whether you’re dealing with a mechanical blockage or a protective response. This distinction guides everything from pain management to long-term recovery strategies.
Mechanical Blockage vs. Protective Response
True locked knee occurs when physical debris—like cartilage fragments or loose bone—jams the joint. Imagine a pebble lodged in a door hinge. The joint literally can’t straighten, even if you push through discomfort.
Pseudo locked knee mimics this immobility but stems from muscle spasms triggered by severe pain. Your body slams on the brakes to prevent further damage, creating stiffness that feels mechanical but isn’t.
Decoding Your Body’s Signals
True locking often involves sudden catching sensations or audible pops during movement. The joint stays fixed regardless of position changes. With pseudo locking, gentle shifts might temporarily ease stiffness, though pain persists.
Watch for swelling patterns. True cases frequently show localized puffiness near the obstruction. Pseudo locking may cause broader inflammation from strained muscles. Sharp, stabbing pain suggests mechanical issues, while deep throbbing often accompanies protective spasms.
Why does my knee lock up after driving? – Examining the Causes
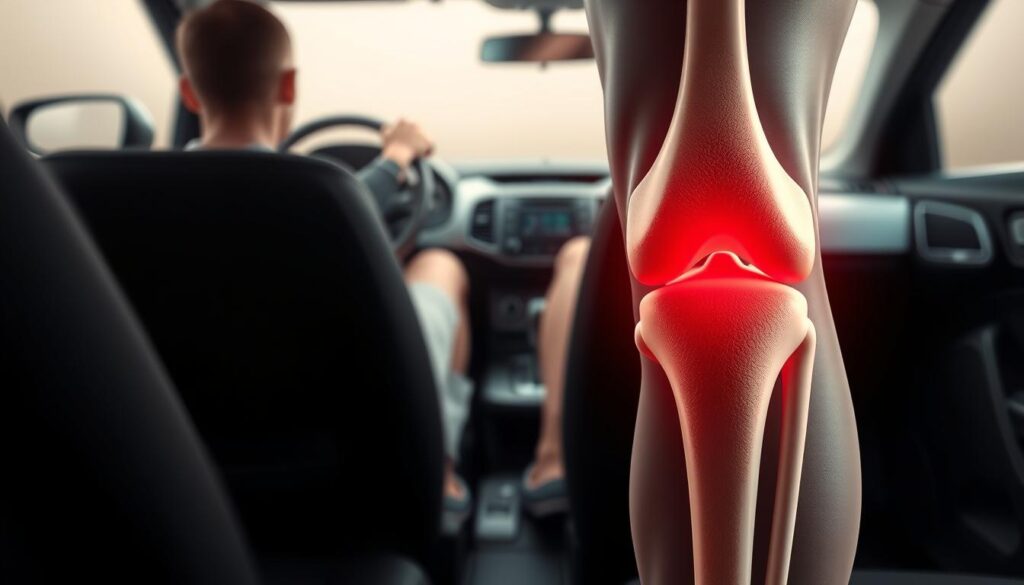
Drivers often overlook how their daily commute creates ideal conditions for joint stress. Extended periods in fixed positions compress blood vessels, starving knee tissues of oxygen. “The average driver’s seat becomes a biomechanical trap after 30 minutes,” notes automotive ergonomics researcher Dr. Ellen Voss. This compression cycle leads to stiffness that accumulates with each mile.
Repetitive pedal movements prove equally problematic. Accelerator pumps and brake taps engage the same muscle groups thousands of times per trip. These micro-motions strain tendons like overstretched rubber bands. Over weeks, this wear-and-tear can:
- Inflame the patellar tendon
- Weaken connective tissues
- Disrupt natural joint lubrication
Vehicle cabins amplify these issues through spatial constraints. Unlike office chairs that allow leg extensions, car seats force knees into perpetual 90-degree angles. This positioning:
“Chokes synovial fluid circulation – the joint’s natural shock absorber”
Individual factors like seat height and prior injuries determine your risk level. Those with arthritis often experience flare-ups from sustained pressure, while athletes might notice tendon irritation first. Even minor adjustments – raising seats 2 inches or using cruise control – can disrupt this damaging cycle.
Injury-Related Factors: Meniscus Tears, Ligament Damage, and Loose Bone Fragments
Hidden injuries turn routine drives into mobility challenges. Structural damage within the knee joint creates physical barriers that resist movement. Three mechanical disruptors commonly surface after extended driving sessions.
Cartilage Flaps That Block Motion
The c-shaped meniscus normally cushions your knee like a rubber gasket. A bucket handle tear splits this cartilage vertically, creating a flap that flips into the joint space. Drivers often notice:
- Sudden inability to straighten legs after exiting vehicles
- Audible pops when adjusting seating positions
- Persistent stiffness lasting hours post-drive
Ligament Failures and Joint Chaos
Damaged ligaments can’t stabilize the knee joint during repetitive pedal motions. As Dr. Lisa Tanaka, orthopedic surgeon, explains:
“ACL injuries create a domino effect – muscles overcompensate, tendons inflame, and protective locking becomes the body’s last defense”
This instability frequently worsens during highway merges or stop-and-go traffic.
Bone Debris: The Unseen Saboteurs
Loose fragments from past fractures or arthritis float like marbles in joint fluid. These joint mice:
| Cause | Symptoms | Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Osteochondral defects | Sudden locking during braking | Arthroscopic removal |
| Advanced arthritis | Grinding sensations | Synovial fluid therapy |
| Previous trauma | Catching pain when accelerating | Microfracture surgery |
True locked knee from bone fragments requires immediate care. Unlike muscle-related stiffness, this mechanical blockage won’t resolve with stretching alone. Early diagnosis prevents permanent cartilage damage.
Impact of Prolonged Driving and Ergonomic Factors
The road isn’t the only thing wearing down during long drives—your joints pay a price too. Hours spent pressing pedals and maintaining static positions create cumulative damage that manifests as driver’s knee syndrome. This repetitive stress injury affects 38% of commercial drivers and 21% of daily commuters according to recent occupational health studies.
Drivers Knee, Patellar Tendonitis, and Repetitive Strain
Known as gas pedal knee or trucker’s knee, this condition stems from excessive force on the patellar tendon. Each brake press generates impact equivalent to 1.5 times body weight. Over months, this leads to:
- Micro-tears in tendon fibers
- Reduced blood flow to knee tissues
- Inflammation that restricts movement
Without intervention, chronic strain can degrade cartilage beneath the kneecap. This progression to chondromalacia patella causes grinding sensations and sharp pain when straightening legs after driving.
Ergonomic Adjustments for Seat Position and Leg Alignment
Optimal seating setups combat mechanical stress. Start with these adjustments:
| Adjustment | Benefit | Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Seat height | Reduces hip angle strain | Knees level with hips |
| Pedal distance | Prevents overextension | Heel stays grounded |
| Backrest angle | Supports spinal alignment | 100-110 degrees |
Combine these changes with hourly posture breaks. Shift your leg position, perform seated calf raises, and rotate ankles to maintain circulation. Proper ergonomics reduce muscle fatigue by 47% according to automotive safety research.
Self-Care and Practical Tips to Reduce Knee Pain
Maintaining joint health requires proactive care, especially for frequent drivers. Simple adjustments to your routine can break the cycle of stiffness and discomfort. Let’s explore techniques that restore mobility while fitting seamlessly into your schedule.
Effective Stretches and Warm-Up Exercises
Target key muscle groups before starting your engine. Try this 5-minute routine:
- Quadriceps stretch: Hold each leg backward for 20 seconds
- Figure-8 leg swings: Improves hip and knee coordination
- Calf raises: Strengthens lower leg muscles during rest stops
Post-drive recovery matters just as much. Apply ice packs wrapped in towels for 15 minutes to reduce swelling. Follow with gentle heat therapy to relax tense muscles.
Daily Physical Therapy and Lifestyle Adjustments
Consistency transforms temporary relief into lasting results. Incorporate these habits:
| Strategy | Frequency | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hydration breaks | Every 90 minutes | Lubricates joints |
| Anti-inflammatory snacks | Daily | Redces tissue irritation |
| Leg elevation | Post-drive | Improves circulation |
Strengthen supporting muscles with wall sits and resistance band exercises. These activities build stability without straining joints. Remember – persistent symptoms lasting over 72 hours warrant professional evaluation.
Medical Treatments and When to Seek Professional Help
When home remedies fall short, targeted medical interventions become essential. Recognizing the tipping point between temporary discomfort and structural damage could save your joint from irreversible harm.
Non-Surgical Options: RICE, Medications, and Physical Therapy
Start with the RICE protocol – rest reduces inflammation, ice numbs acute pain, compression limits swelling, and elevation improves circulation. Combine this with:
- NSAIDs like ibuprofen for short-term relief
- Corticosteroid injections for stubborn inflammation
- Customized physical therapy to rebuild strength
“Movement therapy often resolves 70% of mild locking cases without scalpels,” notes sports medicine specialist Dr. Carla Ruiz. Eight-week programs typically focus on restoring range of motion through guided exercises.
Surgical Considerations for Persistent or Chronic Locking
Mechanical blockages demand precise solutions. Arthroscopic surgery removes loose bone fragments or repairs torn cartilage through two pencil-sized incisions. Common procedures include:
| Issue | Solution | Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Meniscus tear | Trimming or stitching | 4-6 weeks |
| Ligament damage | Reconstruction | 6-9 months |
| Advanced arthritis | Joint smoothing | 2-4 weeks |
Seek immediate care if you experience fever with joint warmth, inability to bear weight, or locking that lasts over 24 hours. Track symptom patterns in a driving journal – note pedal use duration, pain locations, and post-drive recovery time. This data helps doctors pinpoint underlying causes faster.
Conclusion
Many drivers discover their joint issues only after miles of discomfort. While locked knee episodes feel alarming, most stem from manageable causes. Recognizing whether stiffness results from mechanical blockages or protective muscle reactions guides effective responses.
True knee lock often signals debris in the joint space – torn cartilage or bone fragments needing professional care. Pseudo locking typically resolves with rest and targeted stretches. Both types demand attention, but their treatments differ sharply.
Simple adjustments break damaging cycles. Regular seat repositioning, hydration breaks, and pre-drive stretches maintain joint mobility. For persistent symptoms, early intervention prevents chronic conditions.
We’ve seen countless drivers regain comfort through proactive habits. Track your pain patterns, prioritize ergonomic tweaks, and consult specialists when stiffness lingers. Your knees weren’t designed for endless road trips – but with smart care, they’ll keep moving smoothly.
FAQ
What’s the difference between true locked knee and pseudo locked knee?
True locked knee occurs when a physical blockage—like a torn meniscus or loose bone fragment—prevents full joint movement. Pseudo locked knee involves muscle spasms or inflammation temporarily limiting mobility without structural obstruction.
Can driving worsen existing knee injuries?
Yes. Prolonged sitting with limited leg movement reduces blood flow, stiffens joints, and strains tendons. Existing issues like meniscus tears or patellar tendonitis may flare up due to repetitive pressure on the joint during braking or acceleration.
How do ergonomic factors contribute to knee locking?
Poor seat positioning forces awkward leg angles, compressing cartilage and straining ligaments. Adjusting seat height, using lumbar support, and maintaining proper leg alignment can reduce stress on the joint during long drives.
What immediate steps help relieve knee pain after driving?
Apply the RICE method: rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Gentle stretches for quadriceps and hamstrings improve flexibility, while over-the-counter anti-inflammatories like ibuprofen reduce swelling and discomfort.
When should someone seek medical help for a locked knee?
Persistent locking, severe swelling, or inability to bear weight warrants professional evaluation. Untreated meniscus tears or loose bodies may require arthroscopic surgery to restore mobility and prevent long-term damage.
Are meniscus tears the only cause of knee locking?
No. While meniscus injuries are common, ligament damage, cartilage wear, or conditions like osteoarthritis can also restrict movement. A thorough exam—including imaging—helps identify the root cause.
Can physical therapy prevent knee locking during drives?
Yes. Strengthening exercises for quadriceps and glutes stabilize the joint, while stretching routines enhance flexibility. Therapists may also recommend braces or taping techniques for added support during repetitive activities.




