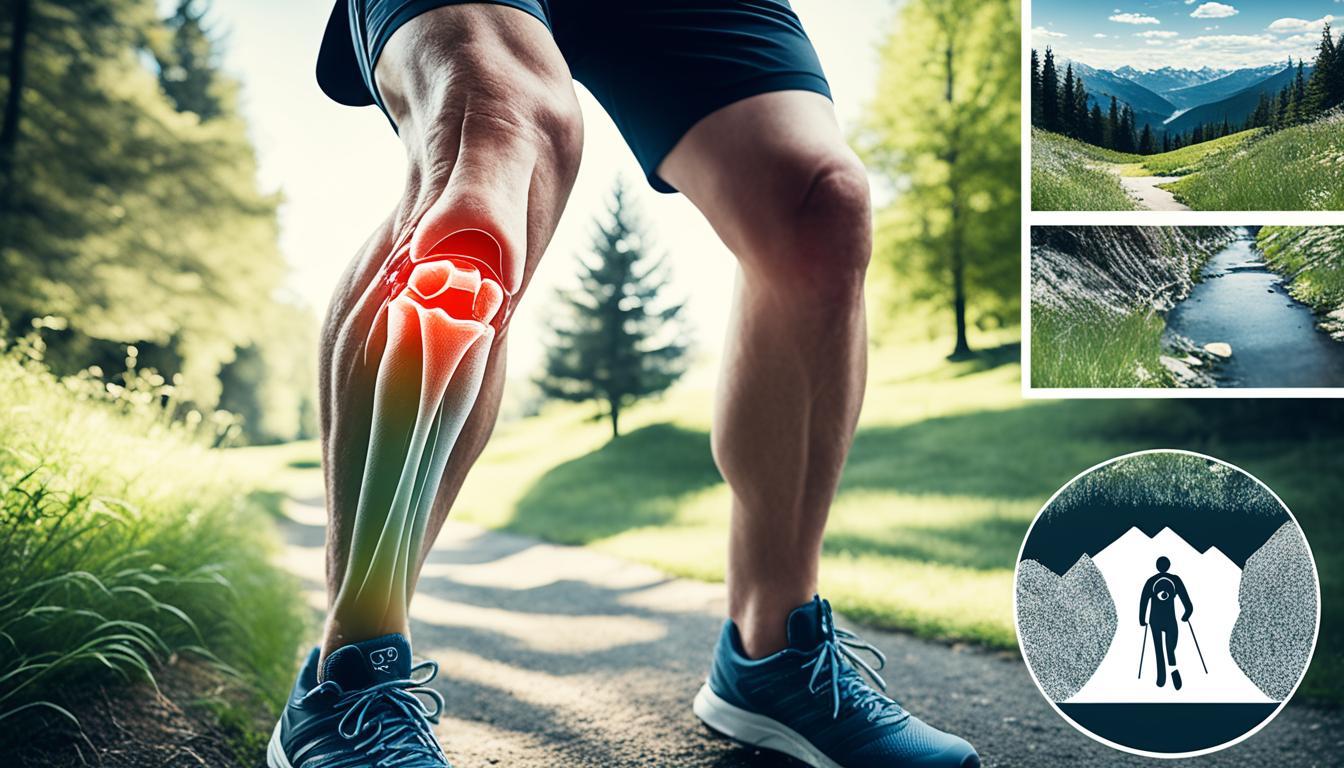
Did you know that knee injuries are a common occurrence when landing from a jump in various sports, including volleyball? Studies have shown that the knee, along with the ankle and shoulder, is one of the most frequently injured joints in volleyball.
Acute ankle sprains, patellar tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee), and overuse shoulder injuries are the most common types of knee injuries in volleyball players. These injuries can result from landing improperly, twisting too hard, or repetitive movements such as spiking and blocking.
It is essential to understand the factors that contribute to knee injuries during jump landing and take preventative measures to protect your joints.
Factors Contributing to Knee Injuries in Volleyball
When it comes to knee injuries in volleyball, there are several biomechanical factors that play a significant role. Research has shown that excessive knee valgus, which refers to the inward movement of the knee, can put immense stress on the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). This increased stress significantly elevates the risk of injury to the knee. Moreover, poor landing mechanics can also contribute to knee injuries. This includes landing with the knees in a flexed position and the ground reaction force not aligning with the center of mass. To reduce the risk of knee injuries, it is crucial to address these factors through proper training and technique.
One study observed that improper landing mechanics, including a flexed knee position and off-center ground reaction force, increased the likelihood of knee injuries in volleyball players. Another investigation found that excessive knee valgus during jump landing heightens the risk of ACL injuries. These findings highlight the importance of focusing on correct landing techniques, such as landing with soft knees and aligning the body’s center of mass with the ground reaction force.
By understanding and addressing these biomechanical factors, players can take proactive steps towards preventing knee injuries. This involves working on jump landing mechanics, maintaining proper knee alignment, and distributing force evenly across the lower extremity joints. Additionally, implementing specific exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, like squats and lunges, can help improve stability and reduce the risk of injury.
Proper coaching and guidance are crucial in ensuring that athletes develop optimal landing techniques and understand the importance of appropriate joint alignment. By incorporating these preventative measures into training programs, volleyball players can safeguard their knee health and minimize the risk of injuries.
Preventing Knee Injuries in Volleyball
To prevent knee injuries when landing from a jump in volleyball, it is crucial to focus on several key preventative measures. One of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of knee injuries is through proper jump landing technique. This includes landing with soft knees, distributing the force evenly through the lower extremity joints, and aligning the body’s center of mass with the ground reaction force.
Incorporating specific knee injury prevention exercises is also essential in strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving stability, and reducing the risk of injury. Exercises such as squats and lunges target the muscles responsible for supporting the knee joint and can help athletes maintain proper form during jump landings.
Proprioceptive training is another crucial component of knee injury prevention. This training focuses on improving an athlete’s balance, coordination, and body awareness to better control movement and reduce the risk of landing in an unstable position.
Additionally, incorporating plyometric exercises into a comprehensive training program can further enhance knee injury prevention. These exercises involve explosive movements and help improve an athlete’s ability to absorb and generate force during jump landings, improving overall landing mechanics and reducing the risk of injury.
| Preventive Measures | Description |
|---|---|
| Proper Jump Landing Technique | Landing with soft knees, distributing force evenly, and aligning body’s center of mass with ground reaction force. |
| Knee Injury Prevention Exercises | Strengthening the muscles around the knee through squats, lunges, and other targeted exercises. |
| Proprioceptive Training | Improving balance, coordination, and body awareness to control movement and maintain stability during landings. |
| Plyometric Exercises | Engaging in explosive movements to improve force absorption and generation during jump landings. |
By incorporating these preventative measures into training routines, volleyball players can significantly reduce the risk of knee injuries when landing from a jump. Taking proactive steps to ensure proper technique and strengthening the muscles around the knee will safeguard joint health and support long-term performance on the court.
Conclusion
Knee injuries are a common risk when landing from a jump in volleyball. However, with the right approach, these injuries can be prevented. By focusing on improving landing mechanics, incorporating knee injury prevention exercises, and implementing a comprehensive training program, athletes can reduce the risk of knee injuries and protect their joint health.
Proper jump landing technique is key to preventing knee injuries. Athletes should aim to land with soft knees, distributing the force evenly through the lower extremity joints. It’s also important to align the body’s center of mass with the ground reaction force. By practicing and refining these techniques, athletes can minimize the stress on their knees during landing and decrease the likelihood of injuries.
In addition to technique, strengthening the muscles around the knee is crucial in preventing knee injuries. Exercises such as squats and lunges can help improve stability and support the knee joint. By regularly incorporating these exercises into their training routine, athletes can enhance their lower body strength and reduce the risk of knee injuries associated with volleyball.
Ultimately, injury prevention should be a priority for volleyball players to ensure they can continue to participate in the sport and perform at their best. By understanding the causes of knee injuries, implementing preventative measures, and maintaining proper form and conditioning, athletes can safeguard their joint health and enjoy a successful and injury-free career in volleyball.
FAQ
Why are knee injuries common when landing from a jump in volleyball?
Knee injuries are common when landing from a jump in volleyball due to factors such as poor landing mechanics, excessive knee valgus, and repetitive movements like spiking and blocking. These factors can put stress on the knee joint and increase the risk of injury.
How can landing mechanics contribute to knee injuries?
Poor landing mechanics, such as landing with the knees in a flexed position and landing with the ground reaction force not aligned with the center of mass, can increase the risk of knee injuries. It is important to focus on proper jump landing technique to reduce the risk of injury.
What can I do to prevent knee injuries when landing from a jump in volleyball?
To prevent knee injuries, it is crucial to focus on proper jump landing technique. This includes landing with soft knees, distributing the force evenly through the lower extremity joints, and aligning the body’s center of mass with the ground reaction force. Strengthening the muscles around the knee through exercises like squats and lunges can also help improve stability and reduce the risk of injury.
Are there any specific exercises that can help prevent knee injuries?
Yes, exercises that target the muscles around the knee, such as squats, lunges, and step-ups, can help improve stability and reduce the risk of knee injuries. It is important to incorporate these exercises into a comprehensive training program that includes proprioceptive training and plyometric exercises for optimal injury prevention.
Why is knee injury prevention important in volleyball?
Knee injury prevention is crucial in volleyball to ensure the long-term health and performance of players. By prioritizing injury prevention through proper training, technique, and conditioning, athletes can reduce the risk of knee injuries and safeguard their joint health, allowing them to continue enjoying the sport and performing at their best.