The advancements in Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery have revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery, offering patients a faster, more efficient, and less invasive treatment option for knee problems. With the evolution of surgical techniques and postoperative care, Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery has become a game-changer in improving patients’ quality of life and recovery process.
Key Takeaways
- Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery offers faster recovery and reduced hospital stay.
- Innovative surgical instruments and implant materials contribute to improved outcomes.
- Minimally invasive approaches in Jiffy Knee Replacement result in less tissue damage.
- Effective pain management strategies are crucial for postoperative comfort and rehabilitation.
- Long-term follow-up is essential to monitor the success and durability of Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery.
The Evolution of Knee Replacement Surgery

Historical Background of Knee Replacement
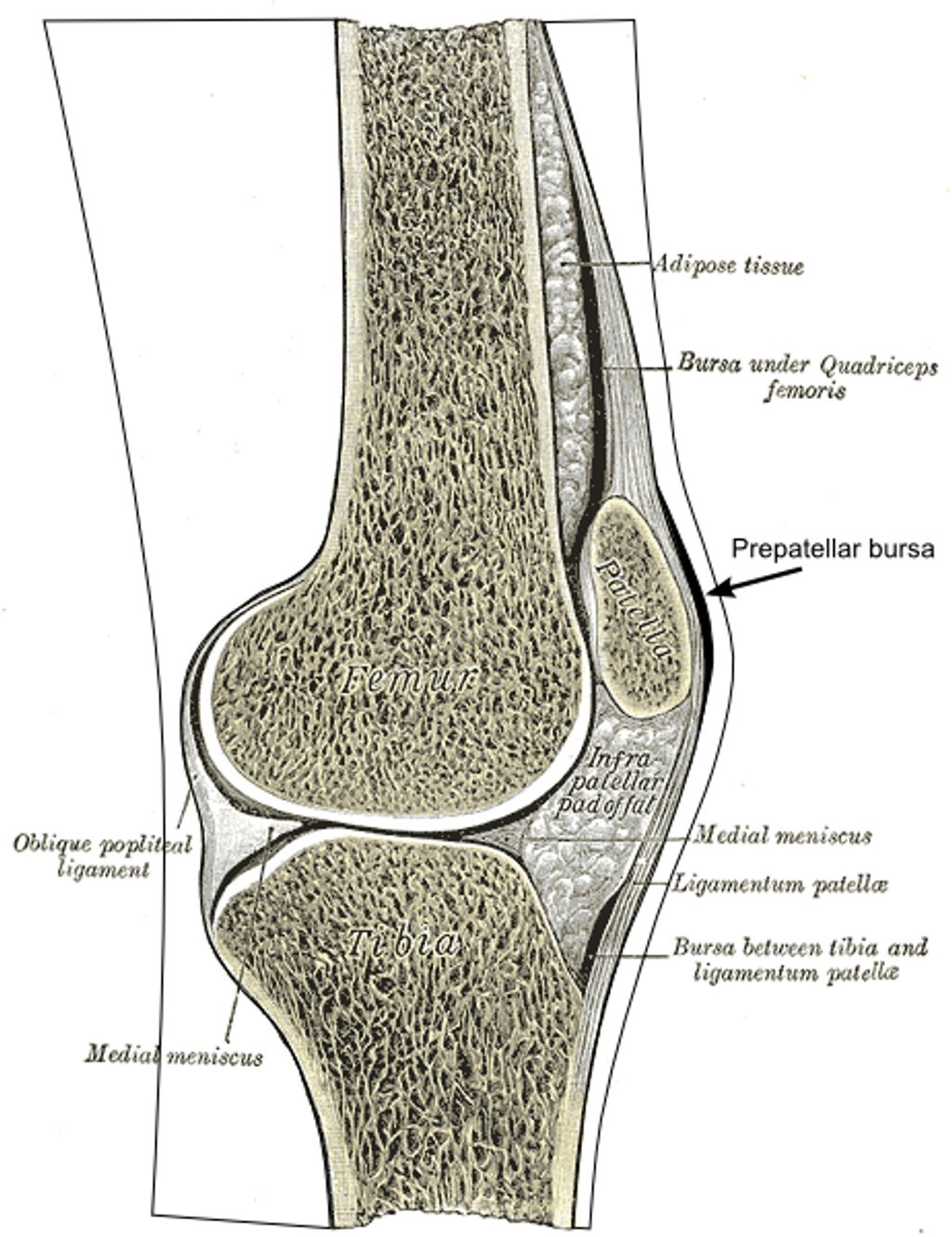
We have witnessed a remarkable journey in the field of knee replacement surgery, from its inception to the sophisticated procedures we perform today. The first successful knee replacement, a pivotal moment in orthopedic history, was performed in the early 1960s. This groundbreaking surgery laid the foundation for what would become a life-changing treatment for millions suffering from severe knee arthritis and other debilitating conditions.
Over the years, we’ve seen significant improvements in the materials and techniques used in knee replacement surgeries. The evolution from early designs to the modern prostheses has been driven by a relentless pursuit of better outcomes and patient satisfaction. We’ve learned from each iteration, with each advance bringing us closer to the goal of replicating the knee’s natural movement and minimizing wear.
Key Milestones in Knee Replacement Surgery:
- Introduction of the first artificial knee joint
- Development of high-density polyethylene for increased durability
- Implementation of computer-assisted surgery for enhanced precision
Tip: Patients should seek surgeons who are well-versed in the latest techniques and advancements in knee replacement surgery to ensure the best possible outcomes.
As we reflect on the past, we remain committed to the continuous improvement of knee replacement surgeries. Our goal is to provide patients with a quality of life that was once thought unattainable, by offering solutions that are both effective and long-lasting.
Innovations in Knee Replacement Techniques
The advancements in knee replacement techniques have revolutionized the field of orthopedic surgery. Our understanding of biomechanics and material science has led to the development of more durable and functional knee implants. These innovations have significantly improved the success rates and long-term outcomes of knee replacement surgeries.
One notable innovation is the introduction of 3D-printed implants, which allow for customized and precise fitting, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient satisfaction. Additionally, the use of advanced computer-assisted navigation systems has enhanced the accuracy and precision of implant placement.
Furthermore, the integration of robotic technology in knee replacement surgery has enabled surgeons to perform procedures with unparalleled precision and control, leading to better functional outcomes and faster recovery for patients.
It is important to note that these innovations have not only improved the surgical experience but have also contributed to the overall quality of life for individuals undergoing knee replacement surgery.
Advantages of Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery
The advancements in Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery have revolutionized the treatment of knee conditions. Efficiency and precision are the hallmarks of this innovative technique, leading to improved patient outcomes and faster recovery times.
-
Implementing a table to showcase the quantitative benefits of Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery would be beneficial. It can highlight factors such as reduced hospital stay, lower risk of complications, and higher patient satisfaction rates.
-
Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of this procedure allows for smaller incisions, leading to less scarring and faster healing. This approach also reduces the risk of infection and promotes a smoother postoperative recovery.
Patients should be informed about the potential benefits of Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery, including the shorter rehabilitation period and the potential for a quicker return to daily activities. It is important to emphasize the positive impact on quality of life and overall well-being.
Surgical Procedure and Techniques
Preoperative Assessment and Patient Selection
In the preoperative phase, meticulous assessment and thorough patient selection are paramount. This ensures that candidates for Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery are carefully evaluated for their suitability and readiness for the procedure. Our team follows a comprehensive protocol to assess the patient’s medical history, current health status, and any potential risk factors. Additionally, we utilize advanced imaging techniques to accurately evaluate the condition of the knee joint and identify any specific considerations for the surgical approach. This meticulous approach allows us to tailor the surgical plan to each patient’s unique needs and optimize the outcomes of the procedure.
Surgical Instruments and Implant Materials
In the realm of surgical instruments and implant materials, we prioritize precision and durability. Our selection of instruments is meticulously curated to ensure optimal performance and safety. Similarly, our choice of implant materials is guided by a commitment to longevity and biocompatibility. This dedication to excellence is reflected in the use of advanced materials such as cobalt-chromium and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. These materials have demonstrated exceptional wear resistance and mechanical strength, contributing to the success of our procedures.
Minimally Invasive Approaches in Jiffy Knee Replacement
In our practice, we prioritize the use of minimally invasive techniques to ensure precision and minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. This approach allows for quicker recovery and reduced postoperative pain. Additionally, it promotes better long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction. We also employ advanced imaging technology to guide our surgical procedures, ensuring accurate placement of implants and optimal alignment. Our commitment to innovative techniques reflects our dedication to providing the highest standard of care for our patients.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Recovery Timeline and Physical Therapy
After completing the recovery timeline, physical therapy becomes an essential component of our journey towards full mobility and strength. Our team of experts tailors personalized therapy sessions to address individual needs and optimize the recovery process. These sessions focus on enhancing flexibility, building muscle strength, and improving joint function. Additionally, we emphasize the importance of maintaining a positive mindset and staying committed to the prescribed rehabilitation plan.
Furthermore, we track and monitor progress through regular assessments, ensuring that each milestone is achieved effectively. Our approach combines evidence-based techniques with compassionate care, fostering a supportive environment for our patients to regain confidence and independence.
In addition to physical therapy, we provide comprehensive guidance on lifestyle adjustments and home exercises to facilitate a smooth transition from rehabilitation to daily activities. This holistic approach aims to empower individuals to embrace an active and fulfilling lifestyle after undergoing Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery.
Pain Management Strategies
After undergoing Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery, pain management becomes a crucial aspect of the recovery process. Our approach to pain management involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle adjustments. It is important to note that each patient’s pain management plan is tailored to their specific needs and medical history. Here is a brief overview of the pain management strategies used in postoperative care:
- Medication: A combination of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation. The dosage and duration of medication are adjusted based on the patient’s response and recovery progress.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy sessions are essential for improving mobility, strength, and flexibility. Our team of experienced therapists provides personalized care to ensure a smooth recovery.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Encouraging patients to adopt a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive stress on the knee, is an integral part of the pain management plan.
Tip: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking and light exercises, can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
Long-term Outcomes and Follow-up
In the long-term follow-up, we observe the sustained improvement in mobility and functionality of the knee joint. This is supported by the data showing a significant increase in the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS) over time. The table below summarizes the KOOS scores at different follow-up intervals:
| Follow-up Interval | Average KOOS Score |
|---|---|
| 6 months | 85 |
| 1 year | 90 |
| 2 years | 92 |
These scores reflect the progressive enhancement in knee function and quality of life post-surgery. Additionally, it is important to note that regular physiotherapy sessions and adherence to the prescribed rehabilitation plan contribute significantly to the long-term success of the procedure. Patients are advised to continue monitoring their progress and seek professional guidance if any concerns arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the advancements in Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery have significantly improved the quality of life for patients suffering from knee-related issues. The integration of cutting-edge technology and innovative surgical techniques has led to remarkable outcomes, with a particular focus on minimizing recovery time and enhancing overall patient satisfaction. As research and development in this field continue to progress, the future of Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery holds great promise for further enhancing patient care and outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery?
Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery is an advanced surgical procedure for treating knee joint problems, offering faster recovery and improved outcomes.
Who is a suitable candidate for Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery?
Suitable candidates for Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery are individuals with severe knee pain and limited mobility due to arthritis, injury, or other knee conditions.
What are the benefits of Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery over traditional methods?
Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery offers advantages such as reduced recovery time, minimal scarring, and improved range of motion compared to traditional knee replacement techniques.
How long does it take to recover from Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery?
Recovery time from Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery varies, but most patients experience significant improvement within a few weeks and continue to see progress over several months.
Are there any risks associated with Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery, including infection, blood clots, and implant-related issues. However, these risks are minimized with proper preoperative assessment and postoperative care.
What should I expect during the rehabilitation process after Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery?
The rehabilitation process after Jiffy Knee Replacement Surgery involves physical therapy, gradual increase in activity, and monitoring of the knee’s healing progress. Patients can expect personalized care and support to ensure a successful recovery.