Facing knee replacement surgery can feel overwhelming. The unfamiliar medical terminology, uncertainty about the procedure, and concerns about recovery can create anxiety. Educational knee replacement videos offer a powerful way to demystify the process, helping patients and caregivers understand what to expect before, during, and after surgery. This visual approach to learning about knee replacement surgery has been shown to reduce patient anxiety and improve recovery outcomes.
Benefits of Watching Knee Replacement Videos
Educational videos help patients understand the knee replacement procedure
Watching knee replacement videos before your surgery offers several important benefits. These visual resources can significantly reduce anxiety by showing you exactly what happens during the procedure. When you can see each step of the knee replacement surgery, the unknown becomes familiar, making the prospect of surgery less intimidating.
Educational knee replacement videos also help set realistic expectations about the recovery process. By seeing real patients progress through rehabilitation, you’ll gain a clearer understanding of the timeline and effort involved in recovery. This mental preparation is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes after surgery.
Medical professionals, including surgeons and physical therapists, often use these videos to explain complex concepts in simple terms. The visual nature of video content makes it easier to understand anatomical structures and surgical techniques that might be difficult to grasp from text descriptions alone.
Ready to See What Happens During Surgery?
Watch our comprehensive knee replacement video to understand the procedure step-by-step.
What You’ll Learn From Knee Replacement Videos
Educational knee replacement videos typically cover the entire journey from diagnosis to full recovery. They provide valuable insights into each phase of the process, helping you prepare mentally and physically for what lies ahead.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Videos show how to prepare your home for recovery, exercises to strengthen muscles before surgery, and what to expect during pre-operative appointments.
Surgical Procedure

Detailed animations and real surgical footage demonstrate how damaged bone and cartilage are removed and replaced with prosthetic components.
Recovery Process
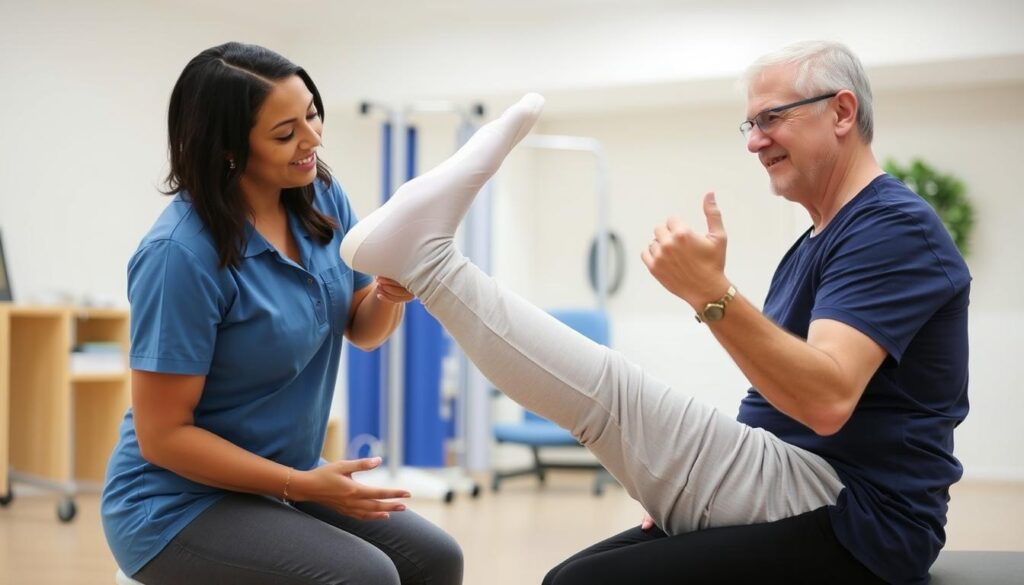
Videos show realistic timelines for recovery, physical therapy exercises, and milestones to expect during the rehabilitation process.
Key Topics Covered in Knee Replacement Videos
- Anatomy of the knee joint and how it functions
- Different types of knee replacements (total vs. partial)
- Step-by-step surgical procedure explanation
- Anesthesia options and pain management techniques
- Computer-assisted navigation systems used during surgery
- Physical therapy protocols and exercises
- Expected timeline for returning to daily activities
- Potential complications and how they’re addressed
- Patient testimonials and success stories
- Tips for optimizing recovery outcomes
Understanding the Knee Replacement Surgical Procedure

Surgeons use specialized instruments and prosthetic components during knee replacement
Knee replacement videos provide a clear visual understanding of what happens during surgery. The procedure typically begins with the surgeon making an incision at the front of the knee to access the joint. The damaged portions of the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone) are carefully removed using precision instruments.
Modern knee replacement surgery often utilizes computer navigation systems to ensure optimal alignment of the new joint components. These systems help surgeons achieve precise positioning, which is crucial for the long-term success of the implant. Educational videos often highlight this technology, showing how it improves surgical outcomes.
After preparing the bone surfaces, the surgeon places metal components on the femur and tibia, with a plastic spacer between them to allow smooth movement. In some cases, the back of the kneecap (patella) may also be resurfaced with a plastic component. The entire procedure typically takes 1-2 hours to complete.
“Watching a knee replacement video before my surgery helped me understand exactly what would happen. It made the whole process much less scary and gave me confidence in my decision to proceed with surgery.”
Have Questions About Knee Replacement?
Our orthopedic specialists can help determine if knee replacement is right for you.
Recovery After Knee Replacement Surgery

Physical therapy is essential for successful recovery after knee replacement
Educational knee replacement videos offer valuable insights into the recovery process, which typically takes several months to a year. Immediately after surgery, you’ll begin gentle exercises to restore movement and strengthen the muscles around your new knee joint. These early movements are crucial for preventing stiffness and promoting healing.
Most patients begin walking with assistance (walker or crutches) within 24 hours after surgery. Videos often demonstrate proper walking techniques and show how to safely navigate stairs and other daily challenges during early recovery. As strength improves, patients gradually transition to a cane and eventually walk independently.
Typical Recovery Timeline
| Recovery Phase | Timeline | Key Activities | Expected Progress |
| Hospital Stay | 1-3 days | Initial walking, basic exercises | Standing and walking with assistance |
| Early Home Recovery | Weeks 1-3 | Physical therapy 2-3 times weekly | Walking with walker or crutches |
| Intermediate Recovery | Weeks 4-6 | Advanced exercises, increased walking | Transition to cane, improved flexibility |
| Advanced Recovery | Weeks 7-12 | Strength training, balance exercises | Walking without assistance, stairs |
| Full Recovery | 3-12 months | Return to normal activities | Full function, minimal to no pain |
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in recovery, and knee replacement videos often demonstrate specific exercises that help restore range of motion and build strength. These visual guides are invaluable for ensuring proper form and understanding the progression of exercises throughout the rehabilitation process.

Patients typically experience significant improvement in mobility after recovery
Prepare for a Successful Recovery
Download our comprehensive guide to knee replacement recovery.
The Patient Experience: What to Expect

A comprehensive healthcare team supports patients throughout the knee replacement journey
Educational knee replacement videos often include patient testimonials that provide authentic perspectives on the surgery experience. These real-life accounts help set realistic expectations and offer reassurance that others have successfully navigated the same journey.
Benefits of Knee Replacement
- Significant reduction or elimination of knee pain
- Improved mobility and function
- Enhanced quality of life
- Return to most daily activities
- Long-lasting results (10-15+ years for most patients)
Challenges to Consider
- Recovery requires commitment to physical therapy
- Initial weeks involve some pain and discomfort
- Full recovery can take up to a year
- Some activities may remain restricted
- Small risk of complications (infection, blood clots)
Videos that show the entire patient journey help create a comprehensive understanding of what to expect at each stage. From the initial consultation and pre-operative preparation to the surgery itself and the rehabilitation process, these visual guides provide valuable context that written information alone cannot convey.
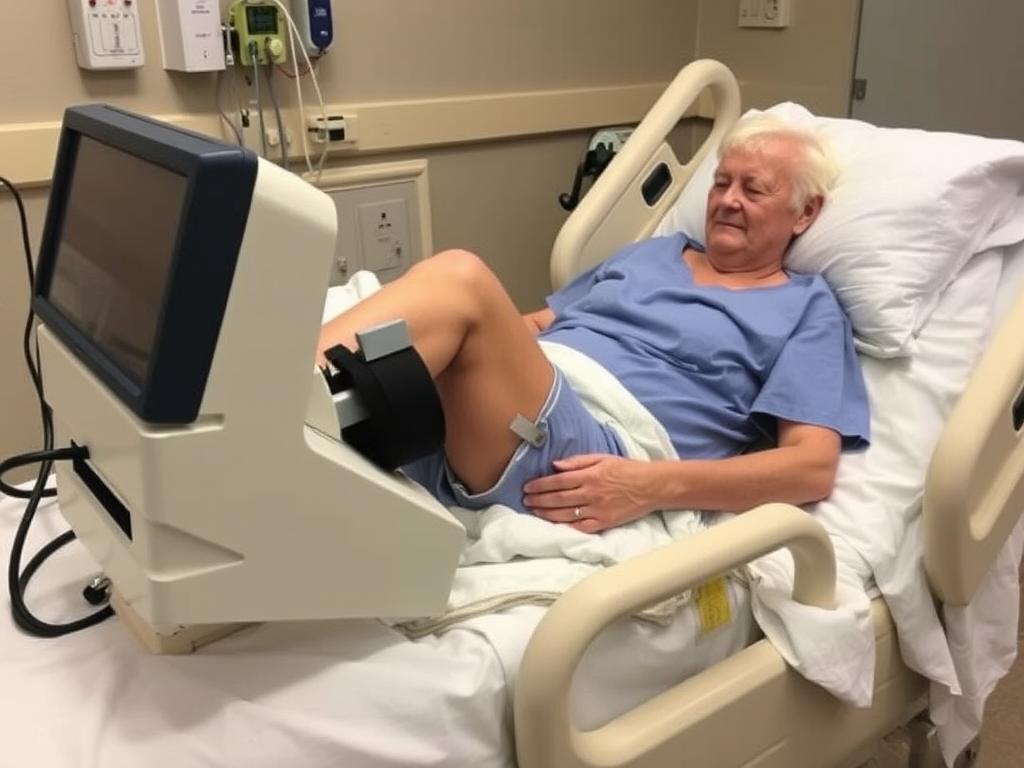
Continuous Passive Motion (CPM) machines are often used in early recovery
Many knee replacement videos also address common concerns and questions, such as pain management strategies, when to contact your doctor about potential complications, and tips for adapting your home environment for a safer recovery. This practical information helps patients feel more prepared and confident as they approach surgery.
Types of Knee Replacement Procedures
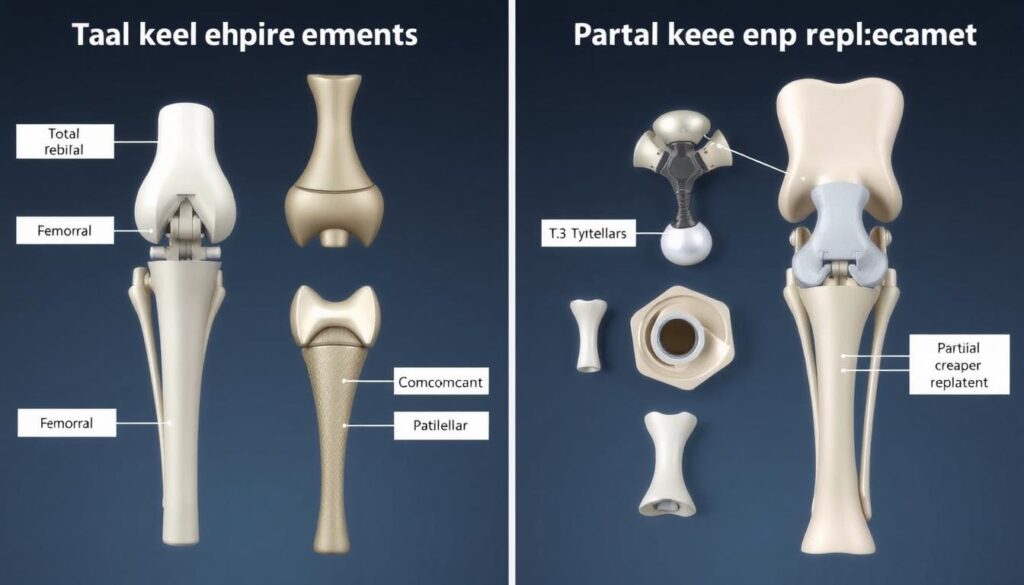
Total knee replacement (left) replaces all joint surfaces, while partial knee replacement (right) addresses only damaged areas
Educational videos often explain the different types of knee replacement procedures available. Understanding these options can help patients have more informed discussions with their surgeons about which approach might be best for their specific condition.
Total Knee Replacement
This is the most common type of knee replacement, where all three compartments of the knee joint are replaced with prosthetic components. The surgeon removes damaged cartilage and bone from the lower end of the femur, the upper end of the tibia, and often resurfaces the patella (kneecap). Metal components are placed on the femur and tibia with a plastic spacer between them to create a smooth, functional joint.
Partial Knee Replacement
Also called unicompartmental knee replacement, this procedure is an option when damage is limited to just one area of the knee. Only the damaged compartment is replaced, leaving healthy bone and tissue intact. This typically results in a smaller incision, less blood loss, faster recovery, and more natural knee motion. However, it’s only suitable for patients with damage limited to one compartment of the knee.
Videos that explain these different approaches often include animations showing how each procedure is performed and the types of prosthetic components used. This visual information helps patients understand why their surgeon might recommend one approach over another based on their specific condition.
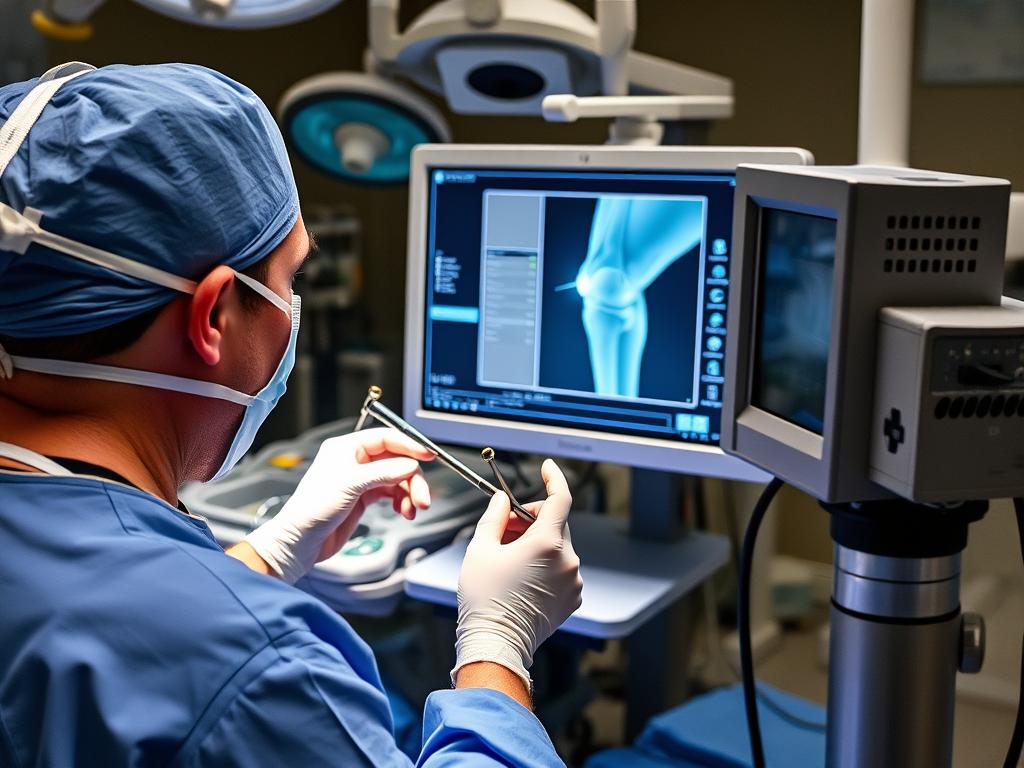
Modern knee replacement often utilizes computer navigation for precise alignment
Preparing for Your Knee Replacement Journey

Involving family in your preparation can provide valuable support during recovery
Educational knee replacement videos serve as powerful tools to help patients and their families prepare for surgery and recovery. By providing visual explanations of complex medical procedures, these resources demystify the process and help set realistic expectations for outcomes and recovery timelines.
When preparing for knee replacement surgery, take advantage of these visual resources alongside written materials and conversations with your healthcare team. The combination of different learning approaches will give you the most comprehensive understanding of what to expect and how to achieve the best possible outcome.
Remember that every patient’s experience is unique, and your surgeon will provide guidance specific to your individual needs and circumstances. Use educational videos as a supplement to—not a replacement for—personalized medical advice from your healthcare providers.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Schedule a consultation with a knee specialist to discuss if knee replacement is right for you.
Remember: Watching knee replacement videos is an excellent way to prepare, but always discuss any questions or concerns with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific medical situation.



