Did you know that the patella, or kneecap, is the largest sesamoid bone in the body? As surprising as it may seem, this small bone plays a vital role in our knee movement and stability, ensuring the proper functioning of this crucial joint. Let’s delve into the functions and importance of the patella, explore its structure, and understand why we have this unique bone in our knees.
The patella sits within the tendon of the quadriceps muscle and has bony landmarks and muscular attachments that contribute to its function. It is involved in various movements, including knee extension, and helps protect the knee joint from direct trauma. Understanding the purpose of the patella is not only essential for comprehending the mechanics of knee disorders but also for preventing and managing injuries.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the anatomical features of the patella, its muscular function, common pathologies and injuries associated with it, and the importance of physiotherapy in maintaining optimum patellar health. By gaining a deeper understanding of this remarkable bone, we can better appreciate the complexity of our own bodies and take proactive measures to keep our patellas healthy and functioning optimally. So, let’s dive in!
Anatomical Features of the Patella
When it comes to the knee joint, the patella is an integral part. Also known as the kneecap, the patella is a flat, triangular bone that is situated at the front of the knee. Its unique structure and bony landmarks contribute to its function and overall stability of the knee.
The patella consists of a base, an apex, and two articular surfaces that connect with the femur bone at the patellofemoral joint. The base of the patella is the widest part of the bone, providing a solid foundation for attachment to the surrounding structures. On the other hand, the apex of the patella is the thinnest part, tapering down to a point.
The bony landmarks of the patella are an essential aspect of its anatomy. At the superior pole of the patella, the quadriceps tendon attaches, allowing it to connect with the powerful quadriceps muscle. This attachment point is crucial for knee extension and movement. At the inferior pole of the patella, the patellar ligament originates, anchoring the patella to the tibia bone. These bony landmarks play a significant role in facilitating the movement and stability of the patella within the knee joint.
Furthermore, the patellar retinacula, located on the inner and outer sides of the patella, provide additional attachment points for ligaments and muscles. These structures help in maintaining the proper alignment and positioning of the patella during movement.
To visually appreciate the anatomical features of the patella, refer to the image below:
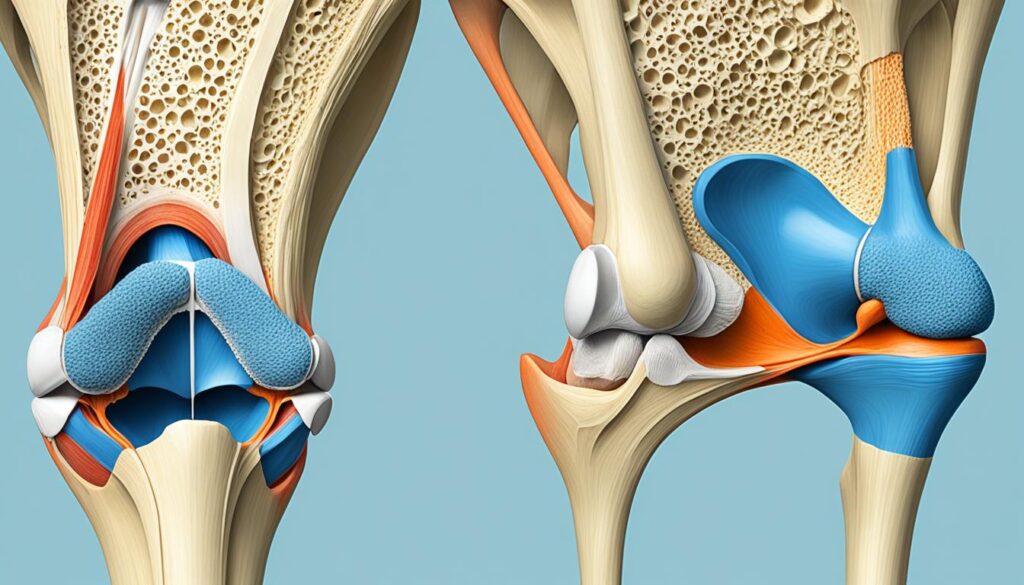
The anatomical features of the patella, including its triangular shape, bony landmarks, and muscular attachments, collectively contribute to its function in knee movement and stability. Understanding these aspects of the patella is crucial for comprehending the mechanics of the knee joint and its role in various activities and conditions.
Muscular Function of the Patella
When it comes to knee movement and stability, the patella plays a crucial role in conjunction with the quadriceps muscle. The quadriceps muscle, consisting of four separate muscle bellies, attaches to the patella through a common tendon that surrounds it.
The quadriceps muscle is primarily responsible for knee extension, which is essential for movements like walking, running, and jumping. This powerful muscle group generates force that allows us to extend our knees efficiently.
The patella acts as a fulcrum, enhancing the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps muscle during knee extension. It provides a leverage point for the quadriceps tendon, enabling it to produce a greater generation of force that results in effective knee extension.
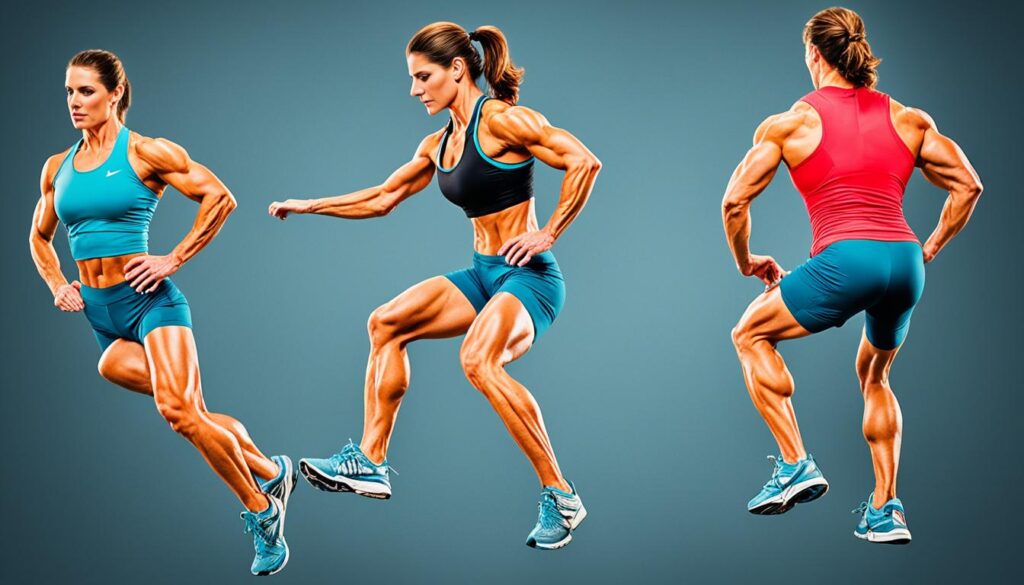

By distributing the force of the quadriceps muscle across the knee joint, the patella also helps to reduce stress on the patellofemoral joint. This distribution of force contributes to the overall stability of the knee.
The quadriceps muscle and the patella work synergistically to ensure smooth knee movement and stability. Understanding their relationship and function is essential for athletes, individuals recovering from knee injuries, and anyone interested in maintaining optimal knee health.
Muscles That Attach to the Patella
| Muscle | Attachment Point |
|---|---|
| Rectus Femoris | Superior part of the patella |
| Vastus Medialis | Medial side of the patella |
| Vastus Lateralis | Lateral side of the patella |
| Vastus Intermedius | Deep surface of the patella |
Common Patellar Pathologies and Injuries
The patella is prone to various injuries and pathologies. These conditions can result in significant pain and functional limitations. Understanding these common patellar pathologies is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Patella Fractures
Patella fractures occur when there is a break or crack in the kneecap bone. These fractures usually result from direct trauma or falls onto the knee. Common symptoms of patella fractures include severe pain, swelling, and difficulty straightening the knee.
Patella Dislocations
Patella dislocations happen when the kneecap is forced out of its normal position. This can occur due to sudden twisting motions, trauma, or congenital abnormalities. Symptoms of patella dislocations include intense pain, swelling, and visible deformity of the kneecap.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Patellofemoral pain syndrome, also known as runner’s knee, is a common condition characterized by pain around or behind the patella. It often arises from overuse, muscle imbalances, or abnormal patellar tracking. Symptoms of patellofemoral pain syndrome include a dull, aching pain under or around the kneecap during activities such as running, climbing stairs, or squatting.
Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis, or jumper’s knee, is an overuse injury that occurs when the patellar tendon becomes inflamed. It is commonly seen in athletes involved in activities that require repetitive jumping or explosive movements. Symptoms of patellar tendonitis include pain and tenderness just below the patella, stiffness, and difficulty performing activities that involve bending or straightening the knee.
Treatment approaches for these common patellar pathologies may vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help manage acute symptoms. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation process, focusing on strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving biomechanics, and addressing any contributing factors. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair fractures or correct structural abnormalities.
Seeking prompt medical attention and following appropriate treatment guidelines is crucial for optimal recovery and preventing long-term complications.
Importance of Physiotherapy in Patellar Health
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the management and rehabilitation of patellar injuries and conditions. Whether it’s a patellar fracture, dislocation, patellofemoral pain syndrome, or patellar tendonitis, physiotherapists can design personalized treatment plans to address specific needs and facilitate recovery.
One of the key benefits of physiotherapy for patella injuries is the emphasis on exercises that improve strength, flexibility, and mobility. These exercises are tailored to the individual’s condition and stage of recovery, helping to rebuild muscle strength, restore joint flexibility, and improve overall mobility in the knee.
In addition to exercise-based interventions, physiotherapists also play a crucial role in educating patients on proper biomechanics and movement patterns. By teaching individuals how to move correctly and avoid further injury, they help promote optimal patellar health and reduce the risk of reinjury or chronic conditions.
Physiotherapy interventions for patellar injuries may include a combination of manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, electrotherapy modalities, and functional training. Manual therapy techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue manipulation can help reduce pain, improve joint mobility, and promote tissue healing. Therapeutic exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee and improving overall joint stability. Electrotherapy modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation may also be used to manage pain and promote tissue healing. Functional training aims to restore normal functional movements, ensuring that patients can return to their daily activities or preferred sports.
By addressing both the physical and educational aspects of patellar rehabilitation, physiotherapy provides a comprehensive approach to recovery. Physiotherapists guide patients through each step of the rehabilitation process, monitoring progress and adjusting treatment plans as needed. Their expertise and personalized care help individuals regain confidence in their knee function, alleviate pain, and improve their overall quality of life.
| Benefits of Physiotherapy for the Patella | Role of Physiotherapy in Patellar Rehabilitation |
|---|---|
| 1. Improved muscle strength | 1. Personalized treatment plans |
| 2. Enhanced joint flexibility | 2. Education on proper biomechanics |
| 3. Increased mobility in the knee | 3. Utilization of manual therapy techniques |
| 4. Pain reduction | 4. Therapeutic exercises for muscle strengthening |
| 5. Tissue healing and recovery | 5. Application of electrotherapy modalities |
Conclusion
The patella, or kneecap, is a vital component of the knee joint, serving multiple functions in knee movement and stability. Understanding the purpose of the patella is essential for preventing and managing patellar injuries and conditions.
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of patellar injuries, helping individuals regain strength, flexibility, and function in the knee. By prioritizing patellar health and seeking appropriate care, individuals can maintain optimal knee function and overall well-being.
FAQ
What is the purpose of the patella?
The patella, or kneecap, serves multiple functions in knee movement and stability. It acts as a fulcrum for the quadriceps muscle, aids in knee extension, and helps distribute the force of the quadriceps muscle across the joint. Additionally, it helps protect the knee joint from direct trauma.
What are the anatomical features of the patella?
The patella is a flat, triangular bone located at the front of the knee joint. It has a base, apex, and two articular surfaces that connect with the femur bone at the patellofemoral joint. The patella has bony landmarks such as the superior and inferior poles, which serve as attachment points for the quadriceps tendon and patellar ligament, respectively. The patellar retinacula, located on the inner and outer sides of the patella, also provide attachment points for ligaments and muscles.
What is the muscular function of the patella?
The patella plays a crucial role in knee movement and stability through its interaction with the quadriceps muscle. The quadriceps muscle, which consists of four individual muscle bellies, merges into one common tendon that surrounds the patella. The patella acts as a fulcrum, allowing the quadriceps muscle to generate greater force and efficient extension of the knee joint. It also helps distribute the force across the joint, reducing stress on the patellofemoral joint.
What are common patellar pathologies and injuries?
Some common patellar pathologies and injuries include patellar fractures, patella dislocations, patellofemoral pain syndrome (runner’s knee), and patellar tendonitis (jumper’s knee). These conditions can occur due to trauma, repetitive stress on the knee, or biomechanical abnormalities. They may cause pain, instability, and reduced knee function.
What is the importance of physiotherapy in patellar health?
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the management and rehabilitation of patellar injuries and conditions. Physiotherapists can design personalized treatment plans that include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and mobility. They also provide education on proper biomechanics and movement patterns to prevent further injury and promote optimal patellar health. Physiotherapy interventions may include manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, electrotherapy modalities, and functional training to restore knee function and alleviate pain.
Why is understanding the purpose of the patella important?
Understanding the purpose of the patella is essential for preventing and managing patellar injuries and conditions. It allows individuals to make informed decisions about their knee health and seek appropriate care. The knowledge of the patella’s function and structure is also crucial for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating knee disorders effectively.
Leave a Reply