
Knee pain affects around 25% of adults. Experiencing knee pain when bending can disrupt daily activities and reduce quality of life. Understanding when to seek medical advice is crucial for effective management. Common causes include overuse injuries, traumatic injuries, and degenerative conditions.
Common Causes of Knee Pain When Bending
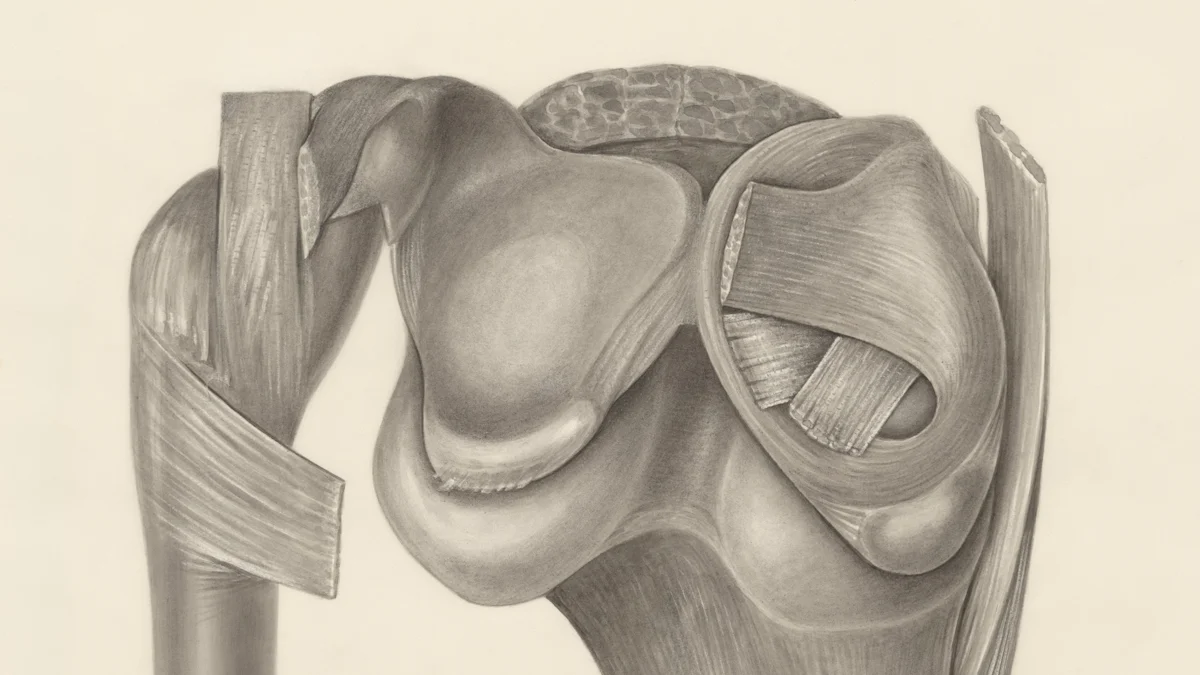
Overuse Injuries
Tendonitis
Tendonitis occurs when tendons around the knee become inflamed. Repetitive movements often cause this condition. Athletes frequently experience knee pain when bending due to tendonitis. Symptoms include pain and swelling around the knee joint.
Bursitis
Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint. Overuse or repetitive stress can lead to bursitis. This condition results in knee pain when bending and noticeable swelling. Rest and ice can help manage symptoms.
Traumatic Injuries
Ligament Tears
Ligament tears, such as ACL or MCL injuries, often result from sudden twists or impacts. These injuries cause severe knee pain when bending and instability. Immediate medical attention is necessary for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears occur when the cartilage in the knee joint gets damaged. This injury often happens during sports activities. Symptoms include knee pain when bending, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee. A healthcare provider can recommend appropriate treatment options.
Degenerative Conditions
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a common degenerative condition affecting the knee joint. The cartilage wears down over time, leading to knee pain when bending. This condition affects many adults, especially those over 50. Treatment focuses on managing pain and improving joint function.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the knee joint. This condition leads to knee pain when bending, swelling, and stiffness. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing joint damage.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Medical Attention
Severe Pain
Pain that limits daily activities
Severe knee pain when bending can disrupt daily routines. Pain that makes walking, climbing stairs, or standing difficult needs medical evaluation. Persistent pain can indicate an underlying issue that requires professional attention.
Pain that persists despite rest
Rest usually helps alleviate minor injuries. However, knee pain when bending that continues even after resting suggests a more serious problem. Consult a healthcare provider to identify the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Swelling and Redness
Swelling that doesn’t subside
Swelling often accompanies knee pain when bending. If swelling does not reduce with rest and ice, seek medical advice. Persistent swelling can signal inflammation or injury that needs further investigation.
Redness and warmth around the knee
Redness and warmth around the knee joint are signs of inflammation. Knee pain when bending combined with these symptoms may indicate an infection or other serious condition. Immediate medical attention ensures proper diagnosis and treatment.
Limited Range of Motion
Difficulty bending or straightening the knee
Limited range of motion affects daily activities. Difficulty bending or straightening the knee can result from various conditions. Knee pain when bending that restricts movement warrants a visit to a healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent further complications.
Stiffness that worsens over time
Stiffness in the knee that progressively worsens is a concern. Knee pain when bending accompanied by increasing stiffness may indicate degenerative conditions like arthritis. Consulting a healthcare professional can help manage symptoms and improve joint function.
Diagnostic Procedures
Physical Examination
Doctors use physical examinations to assess knee pain when bending. These exams help identify the cause of the pain.
Range of Motion Tests
Doctors perform range of motion tests to check how well the knee moves. These tests involve bending and straightening the knee. Limited movement can indicate issues like arthritis or ligament injuries.
Palpation for Tenderness
Palpation involves pressing on different parts of the knee. This helps locate areas of tenderness or swelling. Doctors use palpation to detect conditions like bursitis or tendonitis.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests provide detailed pictures of the knee’s internal structures. These tests help diagnose the cause of knee pain when bending.
X-rays
X-rays are often the first imaging test used. They show the bones and can reveal fractures or arthritis. According to the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, X-rays are effective for diagnosing knee pain in older patients.
MRI Scans
MRI scans use radio waves and a magnetic field to create detailed images of soft tissues. These scans can detect ligament tears, meniscus injuries, and other soft tissue problems. Although MRI scans are more expensive than X-rays, they provide more detailed information.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests can help identify underlying conditions causing knee pain when bending.
Blood Tests for Inflammation Markers
Blood tests can detect markers of inflammation. Elevated levels may indicate rheumatoid arthritis or an infection. Doctors use these tests to guide treatment decisions.
Joint Fluid Analysis
Joint fluid analysis involves extracting fluid from the knee joint. This test can identify infections or gout. Analyzing the fluid helps doctors determine the appropriate treatment for knee pain when bending.
Treatment Options
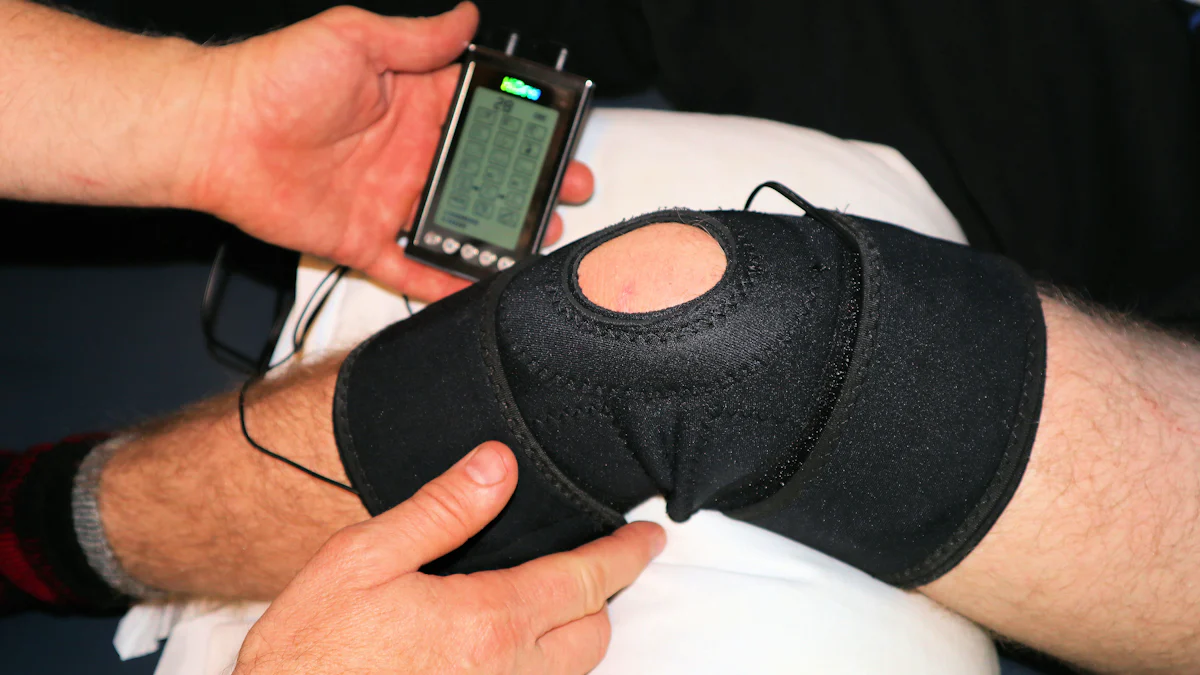
Non-Surgical Treatments
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help manage knee pain when bending. Therapists design exercises to strengthen muscles around the knee. Stronger muscles support the joint and reduce pain. Regular sessions improve flexibility and range of motion. According to the American Family Physician, nonsurgical management is effective for conditions like osteoarthritis and ligament injuries.
Medications
Medications provide relief from knee pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen reduce inflammation. Doctors may prescribe stronger medications for severe pain. Topical creams and gels also help alleviate discomfort. Consistent use of medications can improve daily function and quality of life.
Surgical Treatments
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgery. Surgeons insert a small camera into the knee joint. This procedure allows doctors to diagnose and treat problems inside the knee. Arthroscopy can repair torn ligaments or remove damaged cartilage. Recovery time is shorter compared to traditional surgery.
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement involves replacing damaged parts of the knee with artificial components. This surgery is recommended for severe arthritis or extensive joint damage. Patients experience significant pain relief and improved mobility after recovery. Knee replacement can restore the ability to perform daily activities without pain.
Knee pain when bending can stem from various causes, including overuse injuries, traumatic injuries, and degenerative conditions. Severe or persistent knee pain requires professional medical evaluation. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. A doctor can determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatments. Always prioritize your health and seek medical attention when necessary.
Leave a Reply