Knee Pain Weakness While Climbing Stairs
If walking around on flat surfaces feels fine but your knees start to ache as soon as you start climbing stairs, you might be wondering what’s going on. While your knees are designed to withstand a lot of pressure, stepping onto a staircase engages different muscles and makes you move at an angle while working against gravity. As you climb, your knees may end up bearing a force that’s anywhere from three to six times your body weight. That extra pressure alone shouldn’t hurt, but if you’ve been doing a lot of stair climbing, have an underlying health condition, or even just turn the wrong way you might find that taking the stairs is suddenly painful. Feeling an ache or twinge isn’t a cause for alarm, and it doesn’t mean you should stop moving, either. But it is a sign that something might be amiss and that you could benefit from building strength in and around your knees. Here, learn more about what causes knee pain when climbing stairs and how to prevent and treat it — especially with exercises from our Hinge Health physical therapists.
Key Takeaways:
- Knee pain while climbing stairs can be a sign of an underlying issue or muscle weakness.
- Understanding the anatomy of the knee and common conditions that can cause pain is crucial for effective treatment.
- Proper diagnosis through physical examination and imaging tests can help in determining the specific cause of knee pain when climbing stairs.
- Treatment options include targeted exercises, modifications to walking technique, and physical therapy.
- Consult with a healthcare professional to create a personalized treatment plan for managing and relieving knee pain when climbing stairs.
Understanding Knee Anatomy and Common Conditions
In order to understand knee pain when climbing stairs, it helps to know some basics about what comprises your knee and how this important joint works. The knee is made up of bones (patella, femur, and tibia), ligaments, tendons, cartilage, menisci, bursae, muscles, and nerves.
Common conditions that can cause knee pain when climbing stairs include:
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome: This is a broad term used to describe pain at the front of the knee, often due to issues with how the patella (kneecap) moves.
- Meniscus tear: A tear in the rubbery cartilage that cushions the knee joint, often resulting from sudden twisting or direct impact.
- Chondromalacia patella: Also known as runner’s knee, this condition involves the softening and wearing down of the cartilage on the underside of the patella, leading to pain and discomfort.
- IT band syndrome: The iliotibial band, a thick band of tissue that runs along the outside of the thigh, can become tight and irritated, causing pain on the outer side of the knee.
- Muscle imbalance: Weakness or imbalance in the muscles around the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, can result in abnormal forces on the knee joint during stair climbing, leading to pain.
Understanding these common knee conditions can help you identify potential causes of your knee pain when climbing stairs. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Diagnosing Knee Pain When Climbing Stairs
When experiencing knee pain while climbing stairs, it’s important to get a proper diagnosis to understand the underlying cause. Identifying the specific cause of your knee pain will help guide the appropriate treatment plan.
“Proper diagnosis is essential in managing knee pain when climbing stairs. Understanding the root cause of the pain enables us to create an effective and personalized treatment plan for each individual.”
There are several common diagnostic methods used to evaluate knee pain:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the affected knee is performed, assessing range of motion, stability, and signs of inflammation.
- Medical History Evaluation: Gathering information about prior injuries, activities, and any underlying health conditions that may contribute to the knee pain.
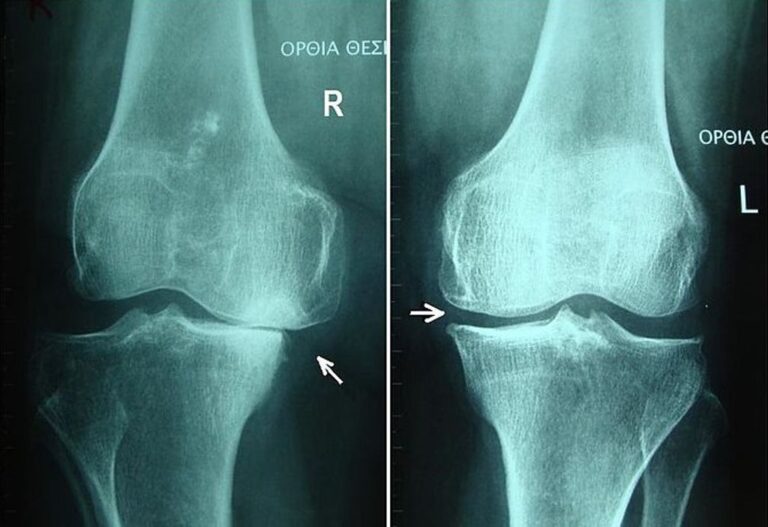
- Imaging Tests: X-ray and MRI scans can provide detailed images of the knee joint, helping identify structural abnormalities or damage.
- Specialized Tests: In certain cases, an ultrasound may be used to visualize soft tissues and detect any abnormalities.
By utilizing these diagnostic methods, healthcare professionals can determine the appropriate course of action for effective knee pain relief and treatment.
Differentiating Knee Pain Causes
It is crucial to distinguish between different causes of knee pain to develop an accurate diagnosis, such as:
| Cause | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome | Anterior knee pain, worsens with activities such as climbing stairs | Physical therapy, strengthening exercises, pain management |
| Meniscus Tear | Knee pain, swelling, locking, difficulty fully extending the knee | Arthroscopic surgery, physical therapy, pain management |
| Chondromalacia Patella | Frontal knee pain, worsens with stair climbing and prolonged sitting | Physical therapy, quadriceps strengthening, pain management |
| IT Band Syndrome | Outer knee pain, worsens with repetitive activities like climbing stairs | Physical therapy, stretching exercises, pain management |
| Muscle Imbalance | Imbalanced strength in the muscles surrounding the knee joint | Physical therapy, targeted exercises to correct muscle imbalance |
By accurately identifying the cause of knee pain, healthcare professionals can provide appropriate treatment options and lifestyle adjustments for long-term relief and management.
Treating and Managing Knee Pain When Climbing Stairs
When it comes to knee pain while climbing stairs, there are several treatment options available to alleviate discomfort and improve mobility. A comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes of knee pain is essential for effective management and long-term relief. In this section, we will explore various strategies and techniques that can help individuals with knee pain when navigating staircases.
Targeted Exercises for Knee Pain Relief
One of the key components of treating knee pain is incorporating targeted exercises to strengthen the knee and surrounding muscles. These exercises aim to improve stability, flexibility, and overall knee function. By engaging in a regular exercise routine, individuals can reduce pain and enhance their ability to climb stairs without discomfort. Some effective knee pain exercises include:
- Straight leg raises: This exercise focuses on strengthening the quadriceps muscles, which play a crucial role in maintaining knee stability.
- Hamstring curls: By targeting the hamstring muscles, this exercise helps to balance the strength of the muscles around the knee.
- Step-ups: This exercise mimics the motion of climbing stairs and can help individuals build strength and endurance in the knee and leg muscles.
- Wall squats: By performing squats against a wall, individuals can develop strength in the quadriceps and gluteal muscles, providing stability and support to the knee joint.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise program to ensure that the exercises are suitable for your specific condition and are performed correctly.
Body Awareness Techniques
In addition to targeted exercises, body awareness techniques can be beneficial in managing knee pain while climbing stairs. These techniques focus on improving posture, body mechanics, and movement patterns to reduce strain on the knee joint. By learning to move and distribute weight properly, individuals can alleviate stress on the knees and minimize discomfort. Some body awareness techniques that may be helpful include:
- Postural alignment: Practicing proper posture while climbing stairs can help distribute weight evenly, reducing pressure on the knees.
- Balance training: Enhancing balance and stability can improve knee control and minimize the risk of injury while climbing stairs.
- Gait analysis: Analyzing your walking pattern can help identify any irregularities or imbalances that may contribute to knee pain. Making adjustments to your gait can alleviate stress on the knees.
Assistive Devices and Modifications
Assistive devices, such as knee braces or orthotics, can provide support and stability to the knee joint, reducing pain and preventing further damage. Depending on the underlying cause of the knee pain, healthcare professionals may recommend specific devices or modifications to alleviate discomfort while climbing stairs. These may include:
“Assistive devices can serve as valuable tools in managing knee pain when climbing stairs.”
Other modifications to consider include using handrails for support, taking smaller steps, or using elevators or ramps whenever possible. These adjustments can help minimize strain on the knees and make stair climbing more manageable.
Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation
For individuals with persistent or severe knee pain, physiotherapy can be an effective approach to treatment and management. A qualified physical therapist can evaluate your condition, develop a personalized treatment plan, and guide you through exercises and therapies designed to alleviate knee pain and improve function. Physiotherapy may include a combination of manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or cold therapy to relieve pain and promote healing.
Surgical Intervention
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying cause of knee pain when climbing stairs. Surgical procedures, such as arthroscopy, meniscus repair, or knee replacement, may be recommended by a healthcare professional to alleviate pain, correct structural abnormalities, or repair damaged tissues. Only a qualified orthopedic surgeon can determine if surgery is the right option for your specific condition.
NOTE: Surgical intervention is usually considered when conservative treatment methods have failed to provide relief or when the condition is severe.
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional
When it comes to treating and managing knee pain when climbing stairs, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist, physiotherapist, or sports medicine physician. They can provide an accurate diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and guide you through an individualized plan based on your specific needs and goals.
By implementing the right combination of targeted exercises, body awareness techniques, assistive devices, and other treatment modalities, individuals can effectively manage knee pain and regain their ability to climb stairs with confidence.
| Treatment Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Targeted exercises | Exercises focused on strengthening the knee and surrounding muscles to improve stability and function. |
| Body awareness techniques | Techniques that promote proper posture, balance, and movement patterns to alleviate strain on the knee joint. |
| Assistive devices and modifications | Devices such as knee braces or orthotics, and modifications to reduce strain on the knee while climbing stairs. |
| Physiotherapy and rehabilitation | Professional guidance through exercises and therapies to relieve pain and improve knee function. |
| Surgical intervention | Surgery may be necessary in severe cases or when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. |
Conclusion
Knee pain when climbing stairs can be a frustrating and limiting experience, but it is important to understand that there are solutions available to provide relief and improve your quality of life. Identifying the underlying cause of your knee pain, such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tear, chondromalacia patella, or muscle imbalance, is the first step in developing an effective treatment plan.
Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help you manage and prevent knee pain when climbing stairs. Incorporating targeted exercises that strengthen the muscles around your knees, modifying your walking technique, and utilizing assistive devices, such as knee braces or orthotics, can all contribute to reducing pain and improving your ability to climb stairs comfortably.
However, it is important to remember that every individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and treatment options tailored to your specific needs. They can help you navigate the best course of action to alleviate your knee pain and prevent further discomfort in the future.
Don’t let knee pain hinder your daily activities. Take control of your knee health by seeking professional guidance, incorporating targeted exercises, and implementing preventive measures. With the right approach, you can find relief, manage your knee pain, and continue to live an active and fulfilling life.
FAQ
What causes knee pain when climbing stairs?
Knee pain when climbing stairs can be caused by various factors, including conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tear, chondromalacia patella, and muscle imbalance.
How can I prevent and treat knee pain when climbing stairs?
To prevent and treat knee pain when climbing stairs, you can try targeted exercises to strengthen the knee and surrounding muscles, modify your walking technique, and utilize assistive devices. Physical therapy can also be beneficial in managing and relieving knee pain.
What are some common knee conditions that can cause pain when climbing stairs?
Common knee conditions that can cause pain when climbing stairs include patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tear, chondromalacia patella, IT band syndrome, and muscle imbalance.
How is knee pain diagnosed when climbing stairs?
Knee pain when climbing stairs is diagnosed through methods such as physical examination, evaluation of medical history, imaging tests (X-ray, MRI), and specialized tests (ultrasound) to identify the underlying cause.
What are the treatment options for knee pain when climbing stairs?
Treatment options for knee pain when climbing stairs include targeted exercises to strengthen the knee and surrounding muscles, body awareness techniques, modifications to walking technique, and utilizing assistive devices. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.