Knee Injury When Squatting: Causes & Prevention
Did you know that knee pain during squats affects a staggering 72% of individuals who regularly engage in this popular exercise? Knee injuries when squatting can be both debilitating and avoidable with the proper techniques and precautions. Whether you are a fitness enthusiast or an athlete, understanding the causes and prevention strategies for knee injury when squatting is essential to protect your knee health and maintain an active lifestyle.
In this article, we will delve into the ten most common causes of knee pain during squats, including cartilage tears, knee bursitis, and weak glutes. We will also explore the importance of practicing proper squatting technique and making necessary modifications to reduce the risk of knee injury. Additionally, we will discuss strengthening exercises that can help rehabilitate the knee and prevent future knee problems when squatting. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge and tools to prevent knee injuries and pain, allowing you to confidently perform squats and reap their numerous benefits.
Proper Technique for Knee-Friendly Squatting
Squatting with proper technique is crucial for maintaining knee health and preventing injury. When squatting, it is important to keep the knees, hips, and ankles in the correct position to avoid excessive stress on the knee joint. Here are some key elements of proper squatting technique:
- Place your feet shoulder-width apart to create a stable base.
- Maintain even weight distribution between both feet to avoid overloading one side.
- Ensure that your knees remain aligned with your toes throughout the movement.
- Avoid going too deep into the squat if it causes discomfort, as this can strain the knee joint.
- Keep your back straight and engage your core for proper alignment and stability.
- Use proper breathing techniques, inhaling as you lower into the squat and exhaling as you push back up.
Additionally, individuals with knee issues or pain can make modifications to their squatting technique to make it more knee-friendly. Some knee-friendly squat modifications include:
- Using a wider stance to reduce stress on the knee joint.
- Performing partial squats instead of going through the full range of motion.
- Using a stability ball against the wall for support and balance.
- Utilizing machines or resistance bands for added assistance in controlling movement.
By implementing proper technique and making necessary modifications, you can significantly reduce the risk of knee pain while squatting and maintain good knee health.
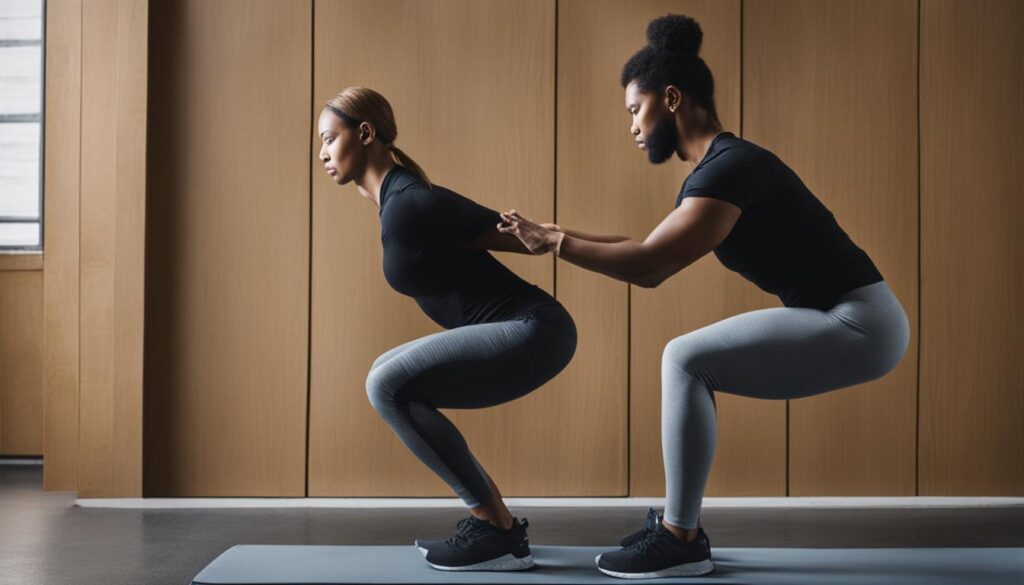

Expert Tip:
Remember to listen to your body and avoid any movements or positions that cause pain or discomfort. Proper form and modifications should always prioritize your individual needs and capabilities.
Strengthening Exercises for Knee Rehabilitation and Prevention
Strengthening the muscles around the knee is crucial for knee rehabilitation and injury prevention. By improving muscle strength, stability, and flexibility, these specific exercises can help reduce the risk of knee pain when squatting. Incorporating these knee rehabilitation and strengthening exercises into your routine can support your knee health and overall fitness goals.
1. Quadriceps Strengthening Exercises
Targeting the quadriceps muscles at the front of the thigh is essential for knee stability and function. Here are a few effective exercises:
- Leg extensions: Using a leg extension machine, sit down and extend your legs against the resistance.
- Squats with a resistance band: Place a resistance band around your thighs and perform squats with proper form.
2. Hamstring Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the hamstrings at the back of the thigh can help balance the muscles around the knee joint. Consider these exercises:
- Hamstring curls: Utilize a hamstring curl machine or resistance bands to perform this exercise effectively.
- Glute bridges: Lie on your back, bend your knees, and lift your hips off the ground while squeezing your glutes.
3. Hip Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the hips is crucial for promoting proper alignment and reducing stress on the knees. Incorporate these exercises into your routine:
- Hip abductions: Use a resistance band or hip abduction machine to perform outward leg movements.
- Clamshells: Lie on your side with your knees bent and feet together. Lift the top knee while keeping your feet together.
4. Calf Raises
Strengthening the calves is essential for ankle stability, which can indirectly support knee stability. Include calf raises in your routine:
- Perform standing calf raises by lifting your heels off the ground and rising onto your toes.
5. Balance and Stability Exercises
Improving balance and stability can help enhance overall knee control and reduce the risk of injuries. Try these exercises:
- Single-leg stands: Stand on one leg for 30 seconds, gradually increasing the duration as you develop balance.
- Bosu ball squats: Perform squats on a Bosu ball, engaging your core and focusing on balance.
6. Stretching Exercises
Improving flexibility can help alleviate tension in the knee joint and surrounding muscles. Consider these stretching exercises:
- Calf stretches: Perform calf stretches by placing your hands on a wall, extending one leg back, and leaning forward into the stretch.
- Quad stretches: Stand upright, bend one leg, and bring your foot towards your glutes. Use your hand to hold onto your foot and gently pull it closer.
Remember, consistency is key when it comes to strengthening and rehabilitating your knee. Start with exercises that suit your fitness level and gradually increase intensity and resistance over time. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for personalized guidance based on your specific needs and goals.
| Exercise | Description |
|---|---|
| Leg extensions | Using a leg extension machine, sit down and extend your legs against the resistance. |
| Squats with a resistance band | Place a resistance band around your thighs and perform squats with proper form. |
| Hamstring curls | Utilize a hamstring curl machine or resistance bands to perform this exercise effectively. |
| Glute bridges | Lie on your back, bend your knees, and lift your hips off the ground while squeezing your glutes. |
| Hip abductions | Use a resistance band or hip abduction machine to perform outward leg movements. |
| Clamshells | Lie on your side with your knees bent and feet together. Lift the top knee while keeping your feet together. |
| Calf raises | Perform standing calf raises by lifting your heels off the ground and rising onto your toes. |
| Single-leg stands | Stand on one leg for 30 seconds, gradually increasing the duration as you develop balance. |
| Bosu ball squats | Perform squats on a Bosu ball, engaging your core and focusing on balance. |
| Calf stretches | Perform calf stretches by placing your hands on a wall, extending one leg back, and leaning forward into the stretch. |
| Quad stretches | Stand upright, bend one leg, and bring your foot towards your glutes. Use your hand to hold onto your foot and gently pull it closer. |
Conclusion
Knee injury prevention is crucial when it comes to squatting. By following proper technique, making necessary modifications, and incorporating targeted knee strengthening exercises, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of knee injuries and pain during squats. It is important to address the underlying causes of knee pain, such as cartilage tears, knee bursitis, and weak glutes, in order to ensure knee health and injury prevention.
Knee-friendly squats involve maintaining the correct form and alignment of the knees, hips, and ankles. By keeping the knees aligned with the toes, using a shoulder-width stance, and focusing on breathing techniques, individuals can minimize stress on the knee joint. In cases where knee issues or pain persist, modifying the squatting technique by using wider stances, partial squats, or stability balls can further protect the knees.
In addition to proper technique and modifications, strengthening the muscles around the knee is essential for knee injury prevention. Quadriceps, hamstrings, hips, and calf muscles should be targeted through specific exercises that improve strength, stability, and flexibility. By regularly incorporating these exercises into a fitness routine and gradually increasing intensity, individuals can rehabilitate the knee, prevent future knee problems, and enjoy the benefits of squats without the risk of injury.
It is important to note that seeking professional guidance, such as consulting with a healthcare professional or physical therapist, is recommended for anyone experiencing persistent knee pain or uncertainty about proper squatting technique. These experts can provide personalized advice and ensure that individuals tailor their knee injury prevention and strengthening approach to their specific needs.
FAQ
What are the common causes of knee pain when squatting?
The common causes of knee pain when squatting include cartilage tear, knee bursitis, poor technique, weak glutes, runner’s knee, chondromalacia patella, patellar tendonitis, iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS), knee arthritis, and hamstring injuries.
How can knee injuries when squatting be prevented?
Knee injuries when squatting can be prevented by following proper technique, making necessary modifications, and strengthening the muscles around the knee. It is important to address the underlying causes of knee pain during squats, such as cartilage tears, knee bursitis, and weak glutes.
What is the proper technique for knee-friendly squatting?
The proper technique for knee-friendly squatting includes placing the feet shoulder-width apart, maintaining even weight distribution, ensuring the knees remain aligned with the toes, avoiding excessive depth in the squat if it causes discomfort, keeping the back straight and the core engaged, and using proper breathing techniques during the movement.
How can knee pain be avoided while squatting?
Knee pain can be avoided while squatting by using a wider stance, performing partial squats, using a stability ball against the wall for support, or using a machine or resistance bands for added assistance. These modifications can make squats more knee-friendly and reduce the risk of knee pain.
What are some exercises for knee rehabilitation and prevention?
Some exercises for knee rehabilitation and prevention include quadriceps strengthening exercises (e.g., leg extensions, squats with a resistance band), hamstring strengthening exercises (e.g., hamstring curls, glute bridges), hip strengthening exercises (e.g., hip abductions, clamshells), calf raises, balance and stability exercises (e.g., single-leg stands, bosu ball squats), and stretching exercises to improve flexibility (e.g., calf stretches, quad stretches).
How can knee injury prevention be achieved?
Knee injury prevention can be achieved by practicing proper squatting technique, making necessary modifications, and regularly performing exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee. It is also important to use the RICE treatment method (rest, ice, compression, elevation), take medication for pain relief and inflammation if necessary, and improve flexibility to reduce the risk of knee injuries.
When should I consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist for knee pain?
It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist if you experience persistent knee pain or are unsure about proper squatting technique. They can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend specific treatment options, and create a personalized plan for knee injury prevention and rehabilitation.