For millions of patients with chronic inflammatory conditions, long-term use of steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) presents a significant dilemma. While these medications effectively manage symptoms, their extended use often leads to serious side effects that can sometimes outweigh their benefits. Nanotechnology has emerged as a promising solution to this challenge, offering innovative approaches to drug delivery that could fundamentally transform how we manage chronic inflammation.
Recent advances in pharmaceutical nanotechnology are creating pathways to safer, more targeted treatments that maintain therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic exposure. This article explores how nanoscale drug delivery systems are being engineered to improve the safety profiles of steroids and NSAIDs, potentially revolutionizing treatment options for patients with arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and chronic pain conditions.
Current Risks of Long-Term Steroid and NSAID Use
Traditional delivery methods for steroids and NSAIDs present significant challenges for patients requiring ongoing treatment. These medications, while effective at controlling inflammation, come with substantial risks when used chronically.
Systemic Side Effects of Traditional Steroids
Corticosteroids, commonly prescribed for autoimmune conditions and severe inflammatory disorders, can cause widespread effects throughout the body. Long-term use often leads to bone density loss, increased susceptibility to infections, metabolic disturbances, and adrenal suppression. Patients may develop cushingoid features, hypertension, and glucose intolerance, significantly impacting quality of life.
Dr. Elena Mikhailov, rheumatologist at Northwestern University Medical Center, explains: “The therapeutic window for steroids is quite narrow. We’re constantly balancing inflammation control against potentially serious side effects. Many patients eventually develop complications that force us to discontinue treatment, even when the medication is effectively managing their primary condition.”
NSAID-Related Complications
NSAIDs present their own set of challenges with extended use. Gastrointestinal complications, including ulceration and bleeding, affect up to 25% of chronic NSAID users. Cardiovascular risks increase with duration of use, particularly in older patients and those with pre-existing conditions. Renal function can also become compromised, leading to fluid retention and potentially permanent kidney damage.
Benefits of Traditional NSAIDs/Steroids
- Effective inflammation control
- Well-established clinical protocols
- Relatively low cost
- Widely available
- Predictable pharmacokinetics
Risks of Long-Term Use
- Gastrointestinal bleeding and ulceration
- Increased cardiovascular events
- Renal function impairment
- Bone density loss (steroids)
- Metabolic disturbances
- Immunosuppression (steroids)
These limitations have driven the search for alternative delivery systems that can maintain therapeutic efficacy while reducing systemic exposure and associated risks. Nanotechnology offers promising approaches to address these challenges through targeted, controlled release of medications.
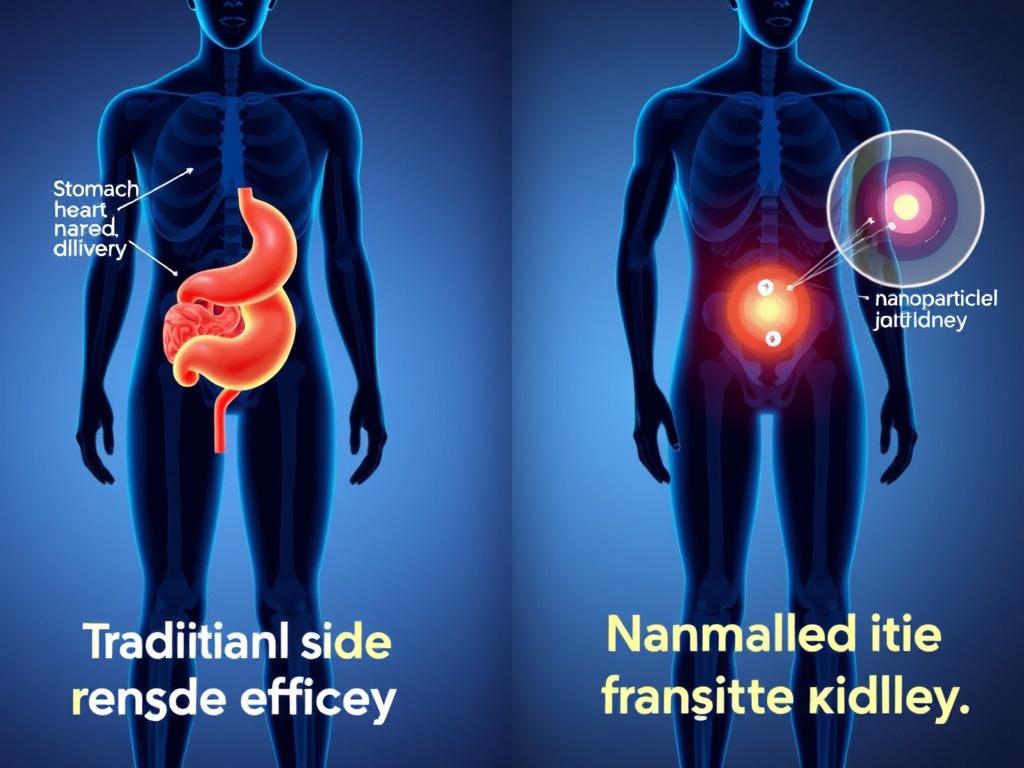
Fundamentals of Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery
Nanotechnology in pharmaceutical applications involves engineering structures and systems at the nanoscale (typically 1-100 nanometers) to enhance drug delivery. These tiny carriers can fundamentally change how medications interact with the body, offering unprecedented control over pharmacokinetics and biodistribution.
Key Principles of Nanopharmaceuticals
Nanocarriers leverage unique physical properties that emerge at the nanoscale. Their high surface-area-to-volume ratio allows for efficient drug loading, while their size enables them to penetrate biological barriers that larger particles cannot. Most importantly, they can be engineered with specific surface properties to control their interaction with biological systems.
“The revolutionary aspect of nanocarriers is their versatility,” notes Dr. James Chen, Professor of Nanomedicine at MIT. “We can design these systems to respond to specific biological triggers, releasing their payload only under predetermined conditions. This level of control was simply not possible with conventional formulations.”
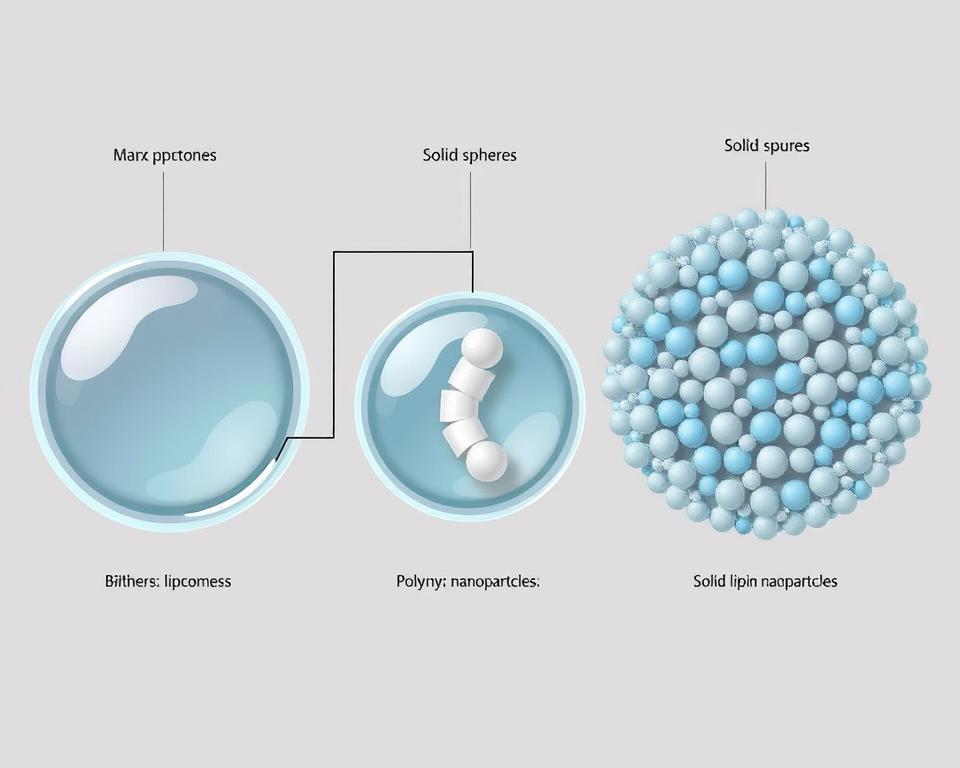
Common Nanocarrier Types for Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Liposomes
Spherical vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. Their structure mimics cell membranes, enhancing biocompatibility and reducing immunogenicity.
Polymeric Nanoparticles
Biodegradable polymer-based carriers that provide sustained drug release through matrix degradation. Their composition can be tailored to control release kinetics and target specific tissues.
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
Lipid-based carriers with solid cores that enhance stability of encapsulated drugs. They offer excellent biocompatibility and can significantly improve drug solubility and bioavailability.
These nanocarriers can be further functionalized with targeting ligands that recognize specific cell types or tissues, enabling precise delivery to sites of inflammation while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues. This targeted approach represents a paradigm shift in how we administer anti-inflammatory medications.
Want to learn more about nanocarrier technologies?
Download our comprehensive guide to pharmaceutical nanotechnology applications and discover how these innovations are transforming drug delivery.
Download Free Guide
Nano-Engineered Solutions for Safer Steroid Delivery
Steroids present particular challenges for long-term use due to their potent systemic effects. Nanotechnology approaches offer promising solutions by enabling targeted delivery and controlled release, potentially transforming how these medications are administered for chronic conditions.
Liposomal Steroid Formulations
Liposomal encapsulation represents one of the most advanced approaches for steroid delivery. These phospholipid vesicles can encapsulate steroid molecules within their aqueous core or lipid bilayer, depending on the drug’s properties. The resulting formulations demonstrate remarkable improvements in pharmacokinetics.
A landmark study by Avanti Biosciences demonstrated that liposomal dexamethasone maintained therapeutic concentrations in inflamed joints for up to 72 hours, compared to just 4-6 hours with conventional formulations. This extended residence time allowed for 80% dose reduction while maintaining equivalent anti-inflammatory effects.
| Nanocarrier Type |
Steroid Example |
Key Advantages |
Clinical Status |
| Liposomes |
Dexamethasone |
Extended joint residence time, reduced systemic exposure |
Phase II trials |
| PLGA Nanoparticles |
Prednisolone |
Sustained release over 2 weeks, biodegradable |
Preclinical |
| Solid Lipid Nanoparticles |
Betamethasone |
Enhanced stability, improved skin penetration |
Phase I trials |
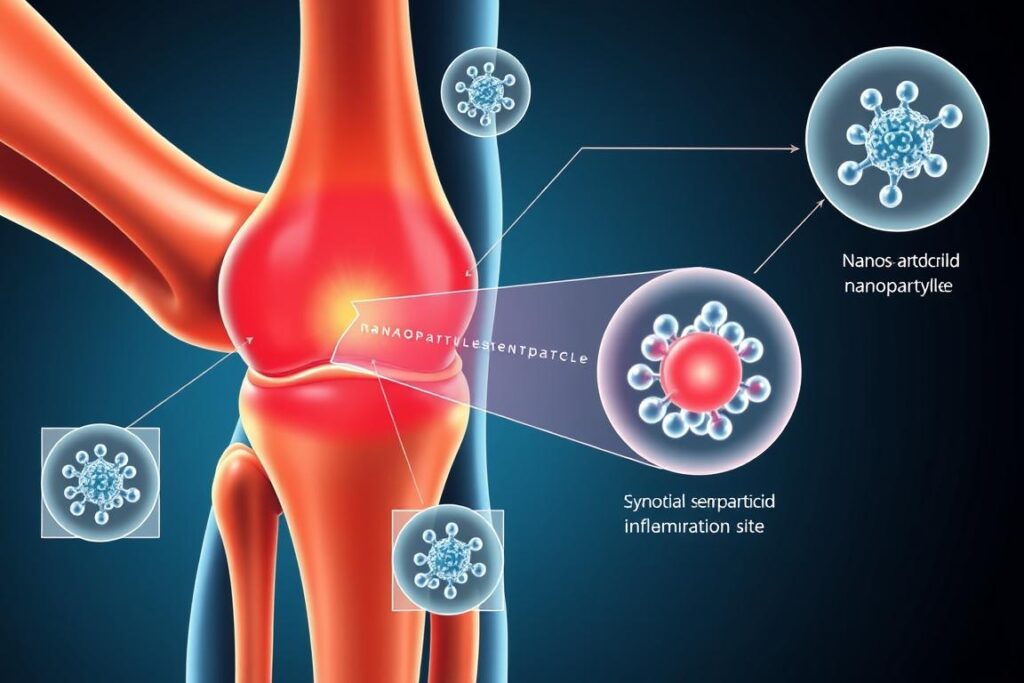
Case Study: NanoCore Betamethasone for Rheumatoid Arthritis
NanoCore Pharmaceuticals has developed a polymeric nanoparticle formulation of betamethasone that demonstrates remarkable targeting efficiency for inflamed synovial tissue. In preclinical models, these nanoparticles accumulated in arthritic joints at concentrations 8-fold higher than in healthy joints, leveraging the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect characteristic of inflamed tissues.
“What’s particularly exciting about this approach is the potential to completely reshape the side effect profile,” explains Dr. Sarah Johnson, lead researcher on the NanoCore project. “In our animal models, we’ve observed virtually no evidence of systemic steroid exposure, even after repeated administration. Blood glucose levels remained stable, and there was no evidence of bone density loss or immune suppression.”
This targeted approach could potentially allow patients to receive effective steroid therapy without the debilitating side effects that often force discontinuation of treatment. Phase I clinical trials are currently underway, with preliminary results expected by early next year.
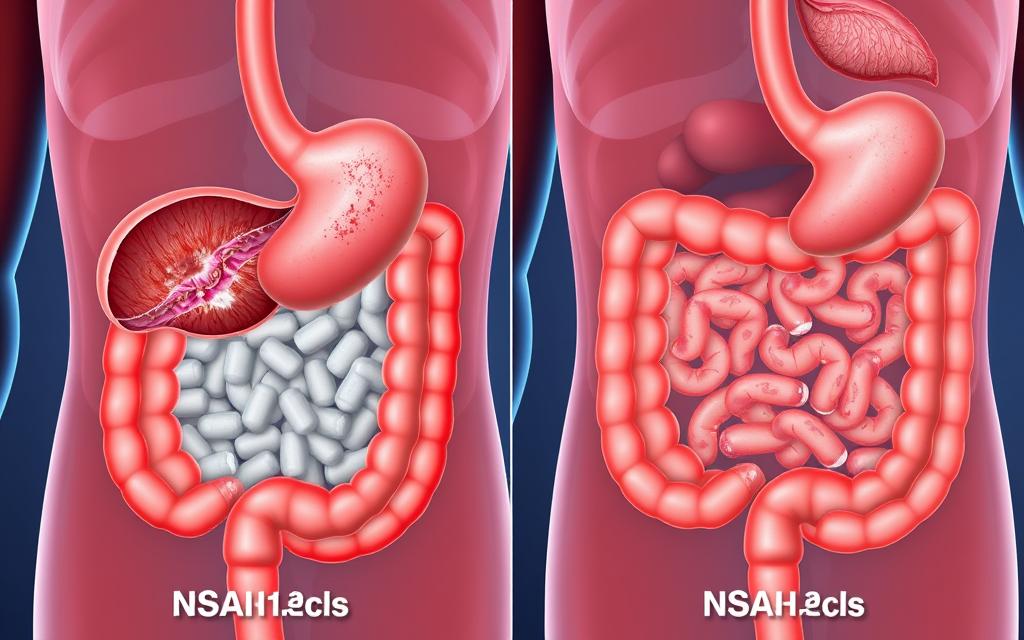
Nano-Formulations for NSAIDs: Enhancing Safety and Efficacy
NSAIDs represent one of the most widely used classes of anti-inflammatory medications, but their long-term use is limited by gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and renal toxicity. Nano-formulations offer innovative approaches to mitigate these risks while maintaining or even enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for NSAID Delivery
Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) have shown particular promise for NSAID delivery. These carriers consist of biocompatible lipids that form solid matrices at body temperature, providing excellent stability and controlled release properties.
A groundbreaking study published in Scientific Reports demonstrated that naproxen-loaded NLCs administered directly to the temporomandibular joint in rats maintained therapeutic effects for over a week, compared to just hours with conventional formulations. The researchers observed “significant reduction in leukocyte migration and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α)” throughout this extended period.
“The toxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is one of the major limitations to their long-term use in the treatment of chronic inflammatory conditions. Nanomedicine products can reduce toxicity and enhance the efficacy of certain encapsulated therapeutics.”
Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences
Case Study: Polymeric Ibuprofen Nanoparticles
Researchers at the University of Michigan have developed PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) nanoparticles encapsulating ibuprofen that demonstrate remarkable improvements in the drug’s safety profile. These biodegradable nanoparticles provide sustained release over 72 hours, maintaining therapeutic concentrations while significantly reducing peak plasma levels associated with side effects.
In animal models, these formulations showed 70% reduction in gastric ulceration compared to standard ibuprofen at equivalent doses. More remarkably, markers of renal stress remained at baseline levels, suggesting potential elimination of kidney-related complications.
Cyclodextrin Complexes for Enhanced Bioavailability
Another innovative approach involves cyclodextrin inclusion complexes, which can enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble NSAIDs. These ring-shaped oligosaccharides form host-guest complexes with drug molecules, protecting them from degradation and improving their pharmacokinetic properties.
Researchers at Pharma Nano Inc. have developed β-cyclodextrin complexes with diclofenac that demonstrate 3-fold higher bioavailability compared to conventional formulations. This enhanced efficiency allows for significant dose reduction while maintaining therapeutic efficacy, directly addressing the dose-dependent toxicity that limits traditional NSAID use.
Safety Improvements Demonstrated in Clinical and Preclinical Studies
The theoretical advantages of nano-formulated anti-inflammatory drugs are increasingly being validated through rigorous scientific investigation. Both animal studies and early human trials demonstrate significant improvements in safety profiles while maintaining or enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Reduced Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Gastrointestinal complications represent one of the most common and serious side effects of traditional NSAIDs. Multiple studies have demonstrated that nano-encapsulation can dramatically reduce these risks through several mechanisms:
- Physical protection of gastric mucosa from direct drug contact
- Bypass of upper GI absorption in favor of lymphatic uptake
- Targeted delivery to inflamed tissues, reducing required doses
- Modified release profiles that avoid concentration spikes
A comparative study in the Journal of Controlled Release demonstrated that rats receiving nano-encapsulated indomethacin showed 85% less gastric ulceration than those receiving standard formulations at equivalent doses. Histological examination revealed intact mucosal architecture in the nano-treatment group, while conventional treatment caused significant epithelial disruption.
Cardiovascular and Renal Safety Improvements
The cardiovascular and renal risks associated with long-term NSAID use represent serious concerns, particularly in elderly patients. Nano-formulations show promise in mitigating these risks through more favorable pharmacokinetic profiles.
Dr. Robert Langer of MIT explains: “By controlling the release kinetics and tissue distribution of these drugs, we can potentially eliminate the sustained COX-2 inhibition that contributes to cardiovascular risk, while maintaining effective tissue concentrations at inflammatory sites.”
A preclinical study with celecoxib-loaded polymeric nanoparticles demonstrated preservation of renal function in a 30-day administration protocol, while conventional celecoxib caused significant increases in serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen, indicating kidney stress.
Case Study: NanoNSAID Clinical Trial Results
One of the most promising clinical validations comes from a Phase II trial of NanoNSAID, a proprietary naproxen formulation using lipid nanocarriers. This 12-week study in patients with osteoarthritis compared the nano-formulation against standard naproxen and placebo.
78%
Reduction in GI Events
Renal Function Markers
68%
The results showed comparable pain relief between nano-formulated and standard naproxen, but the nano-formulation demonstrated a 78% reduction in gastrointestinal adverse events. Endoscopic evaluation revealed significantly less mucosal damage in the nano-treatment group, and markers of renal function remained stable throughout the treatment period.
Remaining Challenges in Nano-Pharmaceutical Development
Despite the promising advances in nano-formulated anti-inflammatory drugs, several significant challenges must be addressed before these technologies can achieve widespread clinical adoption. These hurdles span scientific, regulatory, and manufacturing domains.
Potential Nanotoxicity Concerns
While nanocarriers are designed to reduce drug toxicity, the carriers themselves may introduce new safety considerations. The unique properties that make nanomaterials effective delivery vehicles can also lead to unexpected biological interactions.
“We’re still developing our understanding of how these materials interact with biological systems over extended periods,” cautions Dr. Maria Rodriguez, toxicologist at the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “Particularly for chronic conditions requiring long-term treatment, we need comprehensive data on the fate of these nanocarriers after they deliver their payload.”
Key concerns include potential accumulation in tissues, interaction with the immune system, and long-term biodegradation pathways. These issues are being actively investigated through advanced imaging techniques and biomarker studies.
Manufacturing and Scale-Up Challenges
Transitioning from laboratory-scale production to commercial manufacturing represents a significant hurdle for many nano-pharmaceutical technologies. The precise control required to maintain consistent particle size, drug loading, and surface properties becomes increasingly challenging at larger scales.
Industry experts estimate that manufacturing costs for nano-formulated drugs currently run 3-5 times higher than conventional formulations, though this gap is expected to narrow as technologies mature and economies of scale develop.
Regulatory Pathways and Approval Processes
Regulatory agencies worldwide are still developing frameworks to evaluate the safety and efficacy of nanomedicines. The complex nature of these formulations often requires specialized testing protocols beyond those used for conventional drugs.
Key Regulatory Considerations for Nanopharmaceuticals:
- Physicochemical characterization requirements
- Specialized pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies
- Immunogenicity and hypersensitivity assessments
- Long-term stability under various storage conditions
- Manufacturing consistency and quality control metrics
The FDA has established the Nanotechnology Task Force to address these challenges, while the European Medicines Agency has published reflection papers on nanomedicine development. These initiatives aim to create clear pathways for bringing these innovative therapies to patients while ensuring appropriate safety standards.
Future Outlook for Nano-Pharmaceuticals in Chronic Pain Management
The field of nano-pharmaceuticals for anti-inflammatory applications stands at an exciting inflection point. With several formulations in advanced clinical trials and growing investment from major pharmaceutical companies, we are likely approaching a new era in how chronic inflammatory conditions are treated.
Emerging Technologies and Next-Generation Approaches
Beyond the current generation of nanocarriers, several cutting-edge technologies are showing promise for even more sophisticated drug delivery:
Stimuli-Responsive Nanocarriers
These “smart” delivery systems release their payload only in response to specific triggers such as pH changes, enzyme activity, or externally applied stimuli like ultrasound or magnetic fields. This approach could enable unprecedented precision in drug delivery, activating only at sites of active inflammation.
Biomimetic Nanoparticles
By coating nanoparticles with cell membranes derived from natural cells (such as red blood cells or leukocytes), researchers are creating delivery systems that can evade immune clearance and target specific tissues with remarkable precision. These “cloaked” nanoparticles demonstrate significantly longer circulation times and enhanced targeting efficiency.
Combination Nanotherapeutics
Next-generation formulations are exploring co-delivery of multiple therapeutic agents within a single nanocarrier. For example, combining an NSAID with an antioxidant or tissue-regenerative factor could simultaneously address inflammation while promoting healing of damaged tissues.
mRNA and Gene Therapy Approaches
Building on recent advances in mRNA delivery, researchers are exploring nanomedicine approaches to temporarily modulate the expression of inflammatory mediators at their source, potentially offering more fundamental control of inflammatory processes than conventional drugs.
Timeline for Clinical Implementation
Industry analysts project that the first wave of nano-formulated anti-inflammatory drugs will receive regulatory approval within the next 2-3 years, with several products currently in Phase III trials. These initial offerings will likely focus on well-established drugs reformulated with nanocarrier technology, leveraging the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway in the US for expedited approval.
More innovative approaches incorporating targeting ligands or stimuli-responsive features are expected to reach the market in the 5-7 year timeframe, while truly disruptive technologies like mRNA-based anti-inflammatory approaches may require 8-10 years for full clinical implementation.
Will nano-formulated anti-inflammatory drugs be more expensive than conventional medications?
Initially, these advanced formulations will likely command premium pricing due to higher manufacturing costs and development investments. However, their improved safety profiles may reduce overall healthcare costs by preventing complications and reducing hospitalization rates. As manufacturing scales and patents expire, more affordable options should become available.
How will patients receive these nano-formulated medications?
Administration routes will vary by formulation. Some will be available as oral preparations with enhanced bioavailability, while others may require less frequent injections directly into affected joints. Transdermal and topical nano-formulations are also in development for localized treatment of accessible inflammation sites.
Will these technologies completely replace conventional anti-inflammatory drugs?
Rather than complete replacement, we’re likely to see stratified treatment approaches. Conventional formulations may remain appropriate for acute, short-term use, while nano-formulations become the standard of care for chronic conditions requiring long-term management where safety profiles are particularly important.
Stay Informed About Nanomedicine Advances
Subscribe to our quarterly research digest to receive updates on the latest developments in nano-pharmaceutical technologies for chronic inflammatory conditions.
Subscribe to Research Updates
Practical Implications for Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
The emergence of nano-formulated anti-inflammatory medications holds particular significance for patients living with chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and other autoimmune disorders. These innovations could fundamentally change treatment approaches and quality of life outcomes.
Potential Benefits for Arthritis Patients
For the millions of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, nano-formulated medications offer several potential advantages:
- Reduced need for systemic steroids, minimizing metabolic and bone density complications
- Lower effective doses of NSAIDs, decreasing gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks
- Less frequent administration, improving treatment adherence and quality of life
- Potential for earlier intervention with safer medications, possibly slowing disease progression
- Combination with disease-modifying agents in targeted delivery systems
Janet Miller, a 58-year-old rheumatoid arthritis patient participating in a clinical trial of nano-formulated methotrexate, shares her experience: “After years of stomach problems with traditional medications, this new approach has been transformative. I’m getting the same relief without the constant worry about what the medication is doing to my stomach and liver.”
Implications for Chronic Pain Management
Beyond specific inflammatory conditions, nano-formulated medications could reshape approaches to chronic pain management more broadly. With growing concerns about opioid dependence, safer anti-inflammatory options could provide alternative pathways for long-term pain control.
Dr. William Thompson, pain management specialist at Cleveland Clinic, notes: “One of our greatest challenges is providing effective long-term pain relief without creating new health problems. Nano-formulated anti-inflammatories could help bridge this gap, particularly for patients with inflammatory components to their pain who currently rely on opioids because they can’t tolerate traditional NSAIDs.”
Patient Education and Shared Decision Making
As these new technologies enter clinical practice, patient education will be essential. Understanding the differences between conventional and nano-formulated medications—including potential benefits, limitations, and appropriate expectations—will be crucial for informed decision-making.
Healthcare providers will need resources to explain these complex technologies in accessible terms, while patients may benefit from support groups and educational materials specific to nanomedicine approaches for their conditions.

Conclusion: A New Horizon in Anti-Inflammatory Treatment
Nanotechnology applications in steroid and NSAID delivery represent one of the most promising frontiers in pharmaceutical science. By fundamentally reimagining how these medications interact with the body, researchers are creating pathways to overcome the limitations that have long constrained their use in chronic conditions.
The evidence from preclinical studies and early clinical trials suggests that these approaches can significantly improve safety profiles while maintaining or enhancing therapeutic efficacy. For patients who have struggled with the side effects of conventional anti-inflammatory medications, these innovations offer new hope for effective symptom management without the same risk of complications.
While challenges remain in manufacturing, regulation, and long-term safety assessment, the trajectory of development suggests that nano-formulated anti-inflammatory medications will become increasingly available in clinical practice over the coming years. As these technologies mature, they promise to expand treatment options and improve outcomes for millions of patients worldwide.
The convergence of nanotechnology and pharmaceutical science demonstrates how interdisciplinary approaches can address longstanding medical challenges. By continuing to invest in these innovative technologies and carefully evaluating their performance in clinical settings, we can work toward a future where chronic inflammatory conditions can be effectively managed without compromising patient safety.
Download Our Comprehensive Guide
Get our detailed report on nanotechnology applications in anti-inflammatory drug delivery, including case studies, comparison charts, and future developments.
Download Free Guide