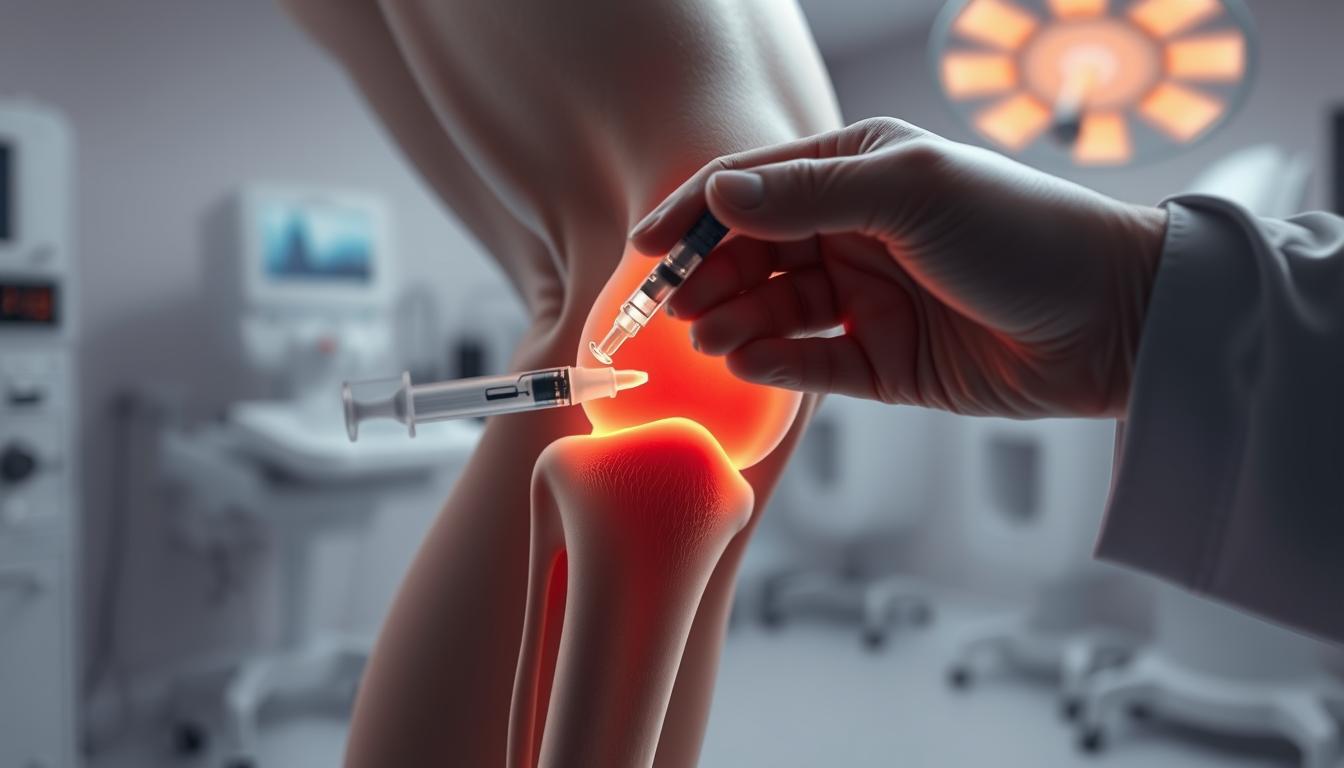
Are you one of the millions suffering from knee pain and seeking effective relief? The use of advanced technology in medical treatments has revolutionized the way we approach musculoskeletal issues.
Ultrasound-guided knee injections have emerged as a crucial treatment option, providing targeted pain relief and enabling individuals to progress with exercise therapy. By leveraging the precision of ultrasound technology, healthcare professionals can now administer injections with greater accuracy, ensuring that the medication reaches the exact area of need.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound-guided injections provide targeted pain relief for knee pain.
- This treatment enables individuals to engage in exercise therapy more effectively.
- The precision of ultrasound technology improves the accuracy of injections.
- Knee pain treatment has evolved with advancements in medical technology.
- Effective pain management is crucial for overall musculoskeletal health.
What Are Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections?
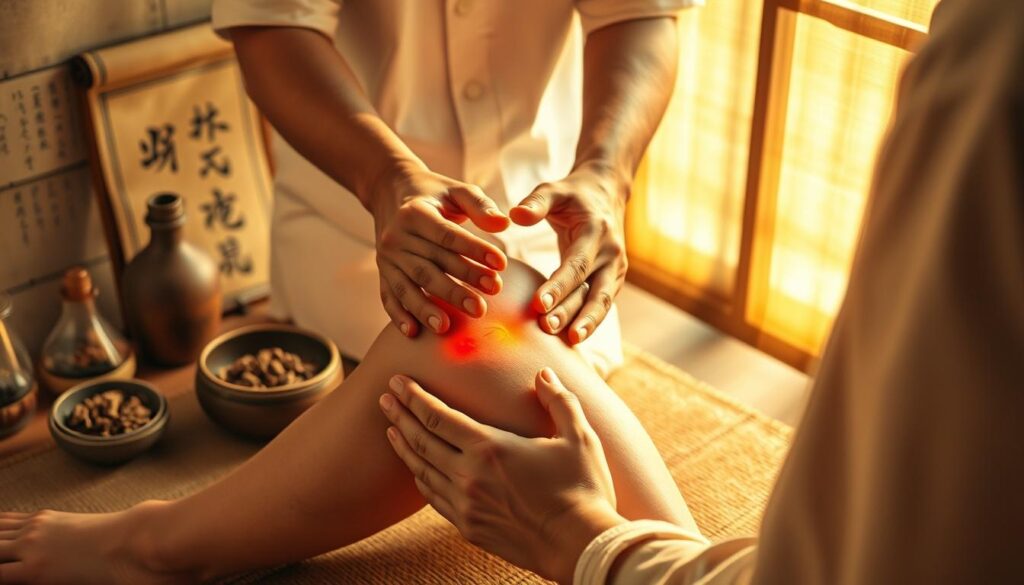
Ultrasound-guided knee injections represent a significant advancement in the treatment of knee disorders. These injections utilize ultrasound imaging to guide the needle to the precise location, enhancing the effectiveness of the treatment.
Definition of Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections
Ultrasound-guided knee injections involve the use of ultrasound imaging to visualize the knee joint and surrounding structures in real-time, allowing for the precise delivery of therapeutic agents, such as corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid, directly into the affected area.
Purpose and Benefits of This Procedure
The primary purpose of ultrasound-guided knee injections is to provide relief from pain and inflammation associated with various knee conditions. The benefits of this procedure include improved accuracy, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced effectiveness of the injected therapeutic agents.
Evidence suggests that using ultrasound improves the accuracy and effectiveness of injection therapy. Conditions such as knee arthritis benefit significantly from this precision.
| Characteristics | Traditional Knee Injections | Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Limited by anatomical landmarks | Enhanced by real-time ultrasound imaging |
| Risk of Complications | Higher due to potential misplacement | Lower due to precise needle placement |
| Effectiveness | Variable, dependent on injector skill | Improved due to accurate delivery |
How Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections Work
Ultrasound-guided knee injections represent a significant advancement in the treatment of knee-related conditions, offering a precise and minimally invasive solution. This procedure combines the benefits of ultrasound imaging with the therapeutic effects of injections to provide relief for patients suffering from various knee ailments.
The Role of Ultrasound in Guiding Injections
Ultrasound technology plays a crucial role in guiding the injection needle to the exact location within the knee joint. By providing real-time images, ultrasound allows healthcare providers to visualize the needle’s trajectory and placement, ensuring that the therapeutic agent is delivered precisely where it is needed. As noted by medical professionals,
“The use of ultrasound guidance has significantly improved the accuracy of knee injections, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing patient outcomes.”
The ultrasound-guided approach enables practitioners to avoid relying on landmark-based or palpation-guided techniques, which can be less accurate. This is particularly important in cases where the knee anatomy is complex or altered due to previous surgeries or conditions.

Steps Involved in the Injection Process
The process of receiving a minimally invasive knee injection typically begins with a thorough preparation of the knee area to minimize the risk of infection. The healthcare provider may clean the area with an antiseptic solution and may use a local anesthetic to numb the skin.
- The knee is prepared and cleaned to prevent infection.
- Ultrasound gel is applied to the skin to facilitate imaging.
- The healthcare provider uses ultrasound to identify the optimal injection site.
- The injection is administered, and the needle is guided in real-time using ultrasound.
- The procedure is typically quick, and patients can often resume normal activities shortly after.
In some cases, the healthcare provider may choose to aspirate excess joint fluid before administering the injection. This not only reduces swelling but also provides a clearer ultrasound image of the joint space, allowing for more accurate placement of the therapeutic agent.
By understanding the steps involved in knee injection therapy, patients can better appreciate the care and precision that goes into their treatment, ultimately leading to more effective relief from knee pain and associated conditions.
Conditions Treated with Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections
Knee conditions such as osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis can be effectively managed with ultrasound-guided injections. These conditions often result in significant knee pain and reduced mobility, impacting the quality of life.
Osteoarthritis and Joint Pain
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the knee to break down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Ultrasound-guided knee injections, particularly those using hyaluronic acid (viscosupplementation), can help restore joint lubrication, providing relief from osteoarthritis symptoms. For more information on knee pain, visit kneehurt.com.
The use of ultrasound guidance ensures that the injection is delivered precisely into the affected area, enhancing the effectiveness of the treatment. This approach is particularly beneficial for patients who have not responded well to other treatments.
Tendonitis and Bursitis
Tendonitis and bursitis are inflammatory conditions that can cause significant knee pain. Tendonitis involves inflammation of the tendons, while bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints. Ultrasound-guided injections can deliver corticosteroids directly to the inflamed area, reducing inflammation and pain.
By targeting the exact site of inflammation, these injections can provide rapid relief and help restore normal knee function. This targeted approach minimizes the risk of side effects associated with systemic corticosteroid use.
Other Common Knee Conditions
In addition to osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis, other knee conditions such as meniscal tears and ligament sprains can also benefit from ultrasound-guided injections. While these conditions may require additional treatments like physical therapy or surgery, injections can help manage pain and inflammation.
The versatility of ultrasound-guided knee injections makes them a valuable tool in the management of various knee disorders, offering patients a range of knee pain relief options and improving their overall quality of life.
Advantages of Ultrasound Guidance
One of the key advancements in knee pain management strategies is the utilization of ultrasound guidance during injections. This technique has significantly enhanced the effectiveness of knee injections by ensuring that the medication is delivered precisely to the targeted area.
Improved Precision and Accuracy
Ultrasound guidance allows healthcare providers to visualize the needle and the target area in real-time, ensuring that the injection is administered accurately. This precision is particularly important in complex knee anatomy, where the proximity of nerves, tendons, and blood vessels can complicate the injection process.
The accuracy provided by ultrasound guidance means that the medication, often cortisone, is delivered directly to the source of inflammation or pain, such as in cases of osteoarthritis or tendonitis. Cortisone is a potent anti-inflammatory medication that reduces inflammation and swelling in tendons and joints, providing relief to patients.
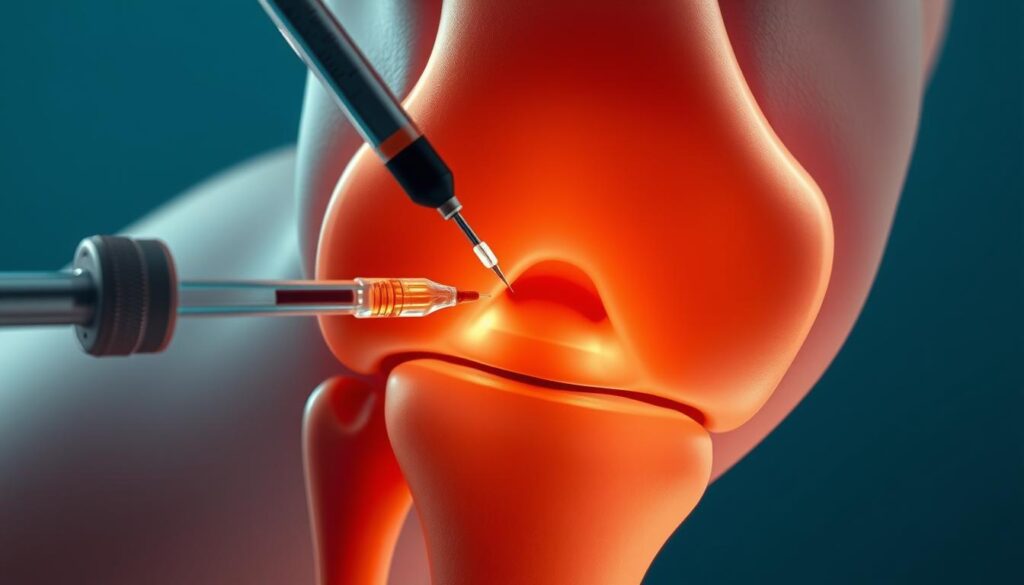
Reduced Risk of Complications
By using ultrasound to guide the needle, the risk of complications such as nerve damage or infection is significantly reduced. The real-time imaging allows for adjustments to be made during the procedure, ensuring the needle is placed correctly and avoiding potential complications.
| Benefits | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Precision | Real-time ultrasound guidance ensures accurate needle placement. | Effective delivery of medication to the target area. |
| Reduced Risk | Minimized risk of nerve damage and infection. | Safer procedure with fewer complications. |
| Enhanced Efficacy | Cortisone is delivered directly to the source of pain or inflammation. | Significant relief from pain and inflammation. |
What to Expect During the Procedure
When undergoing an ultrasound-guided knee injection, several steps are involved to ensure a safe and effective procedure.
Preparation Steps Before the Injection
Before the injection, the knee area is cleaned and prepared to minimize the risk of infection. Next, the joint is anesthetized using a local numbing agent like lidocaine to make the procedure more comfortable.
Preparation is key to a successful ultrasound-guided knee injection. The use of ultrasound imaging allows for real-time visualization, ensuring that the injection is delivered precisely to the targeted area.
The Injection Experience
Once the area is numb, the doctor will insert a needle into the knee joint, guided carefully by ultrasound imaging to ensure precise placement. Patients may feel a slight pinch or pressure during the injection, but this is typically minimal due to the local anesthesia.
The entire procedure is relatively quick, usually taking only a few minutes to complete. The precision of ultrasound guidance enhances the effectiveness of the knee joint injection procedure.
Aftercare Following Knee Injections
Post-procedure care is a vital component of knee pain relief options, including ultrasound-guided knee injections. Proper aftercare can significantly influence the effectiveness of the treatment and the patient’s recovery process.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After receiving knee injection therapy, patients may experience mild soreness, warmth, or swelling at the injection site. These symptoms are typically temporary and resolve within a day or two.
- Rest the knee and avoid strenuous activities for at least 24 to 48 hours.
- Apply ice to reduce swelling if necessary.
- Monitor the injection site for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pain.

Long-term Recovery Tips
For optimal recovery and to achieve the best results from knee injection therapy, consider the following long-term tips:
- Gradually resume normal activities and exercises as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint.
- Engage in physical therapy or exercises recommended by your healthcare provider to improve knee strength and flexibility.
By following these aftercare guidelines, patients can enhance their recovery and improve the overall effectiveness of their knee pain relief options.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While ultrasound-guided knee injections are considered safe, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with this procedure.
These injections, often used as a minimally invasive knee injections treatment for various knee conditions, including knee arthritis treatment, are generally well-tolerated. However, understanding the possible complications can help manage expectations and improve patient outcomes.
Common Side Effects to Anticipate
Most patients undergoing ultrasound-guided knee injections experience minimal side effects. Common issues may include:
- Temporary pain or discomfort at the injection site
- Mild swelling or redness
- A temporary flare-up of knee pain
These side effects are typically mild and resolve on their own within a few days.
Rare but Serious Complications
Serious adverse events are rare but can occur. These include:
- Allergic reactions to the injected medication
- Infections, which can be serious and require prompt medical attention
- Joint flare-ups characterized by increased pain, warmth, or swelling
- In very uncommon cases, a pseudoseptic reaction can happen, marked by significant redness and swelling that typically improves with rest and ice.
It’s crucial for patients to be aware of these potential complications and to seek medical help if they experience any severe or persistent symptoms.
By understanding the potential risks and side effects, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment. It’s also important to follow post-procedure care instructions to minimize the risk of complications.
Candidates for Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections
Identifying the right candidates for ultrasound-guided knee injections is crucial for effective knee pain management. This treatment is particularly beneficial for individuals who have not responded well to conservative treatments.
Who Can Benefit Most from This Treatment?
Patients with mild to moderate knee osteoarthritis are typically considered good candidates for ultrasound-guided knee injections, particularly those who have not achieved adequate relief from conservative treatments such as physical therapy, oral medications, or other non-surgical interventions. Hyaluronic acid injections, also known as viscosupplementation, are commonly used for these patients.
Age and Health Considerations
Age and overall health are significant factors in determining suitability for ultrasound-guided knee injections. While older adults with osteoarthritis may benefit significantly, younger patients with specific knee conditions may also be candidates. Healthcare providers assess each patient’s health status, including the presence of any comorbidities, to determine the appropriateness of this treatment.
For instance, patients with severe knee damage or certain health conditions may not be ideal candidates. Therefore, a thorough evaluation is necessary to ensure that the benefits of ultrasound-guided knee injections outweigh the potential risks.
Cost of Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections
For individuals considering knee joint injection procedures, understanding the associated costs is essential for making informed decisions. The cost of ultrasound-guided knee injections can vary based on several factors, including the location, healthcare provider, and specific requirements of the procedure.
Price Range in the United States
The cost of viscosupplementation, a common treatment involving ultrasound-guided knee injections, can range widely across the United States. On average, the price for a single injection can be between $300 to $1,000. However, the total cost may be higher when considering the series of injections often required for effective treatment.
Factors influencing the cost include:
- The expertise and fees of the healthcare provider
- Geographic location, with urban areas typically having higher costs
- The specific type of injection or medication used
Insurance Coverage and Options
Insurance coverage for ultrasound-guided knee injections varies among providers and policies. Some insurance plans may cover part or all of the procedure if deemed medically necessary, while others may not cover it at all. It’s crucial for patients to check their insurance coverage before undergoing the treatment.
Options for managing the cost include:
- Discussing financing options with the healthcare provider
- Exploring patient assistance programs if available
- Comparing prices among different providers
Understanding the financial aspects and exploring available options is crucial for patients considering this treatment. By being informed, patients can better navigate the costs associated with ultrasound-guided knee injections and make decisions that align with their financial situation and healthcare needs.
Finding a Qualified Provider
To ensure the best outcomes from ultrasound imaging for knee injections, it’s vital to find a skilled healthcare professional. The expertise of the provider can significantly impact the effectiveness of the treatment.
Questions to Ask Your Provider
Before undergoing the knee injection therapy, it’s essential to ask your provider a few critical questions to gauge their expertise and the quality of care you can expect.
- What experience do you have with ultrasound-guided knee injections?
- Can you explain the procedure and what I can expect during and after the injection?
- What are the potential risks and complications associated with this treatment?
- How will you ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the injection?
Asking these questions can help you understand the provider’s level of expertise and their approach to your care. As noted by a medical professional, “Precision is key when it comes to injections; it’s not just about injecting medication, but doing so with accuracy to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.”
Important Credentials to Look For
When searching for a provider, certain credentials can indicate a higher level of competence in administering ultrasound-guided knee injections. Look for providers who are:
- Board-certified in their specialty, such as orthopedics or physical medicine and rehabilitation.
- Experienced in performing ultrasound-guided procedures.
- Familiar with the latest techniques and technologies in knee injection therapy.
For more information on ultrasound-guided joint injections and to find a qualified provider, it’s advisable to consult reputable medical resources and professional directories.
Alternatives to Ultrasound-Guided Knee Injections
Not everyone may be suited for or prefer ultrasound-guided knee injections, making alternative treatments worth considering. For patients seeking knee pain relief options, there are various other treatments available.
Other Injection Techniques
Besides ultrasound-guided injections, other injection techniques can be considered for knee pain management. These include:
- Fluoroscopically guided injections, which use X-ray guidance to ensure accurate placement.
- Blind injections, although less accurate, may still offer relief for some patients.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, which involves injecting platelet-rich plasma derived from the patient’s own blood to stimulate healing.
As noted by medical professionals, “The choice of injection technique depends on the specific condition, patient preferences, and the expertise of the healthcare provider.”
“The key to successful treatment lies in selecting the most appropriate intervention based on a thorough assessment of the patient’s condition.”
Non-Injection Treatments for Knee Pain
For those who prefer to avoid injections or are not candidates for them, several minimally invasive knee injections alternatives and non-invasive treatments are available:
- Physical therapy to improve knee function and reduce pain.
- Medications such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids to manage pain and inflammation.
- Alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care.
- Lifestyle modifications, including weight loss and exercise, to reduce stress on the knee.
It’s essential for patients to discuss these options with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for their specific needs.
Conclusion: The Value of Ultrasound Guidance
Ultrasound-guided knee injections have emerged as a valuable treatment option for knee pain, particularly for individuals suffering from osteoarthritis. By leveraging the precision of ultrasound technology, healthcare providers can deliver injections with greater accuracy, enhancing the effectiveness of knee arthritis treatment.
Key Benefits and Effectiveness
The benefits of ultrasound-guided knee injections include improved precision, reduced risk of complications, and a favorable safety profile. These advantages make them an attractive choice for patients seeking knee pain management strategies.
Discussing Treatment Options with Healthcare Providers
Patients experiencing knee pain should discuss ultrasound-guided knee injections with their healthcare providers to determine if this treatment is suitable for their specific needs. By exploring this option, individuals can make informed decisions about their knee pain management strategies and potentially improve their quality of life.
FAQ
What is an ultrasound-guided knee injection?
An ultrasound-guided knee injection is a minimally invasive procedure that uses ultrasound imaging to guide the injection of medication into the knee joint, providing precise delivery of treatment for various knee conditions, including osteoarthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis.
How does ultrasound guidance improve the accuracy of knee injections?
Ultrasound guidance allows healthcare providers to visualize the needle and the target area in real-time, ensuring accurate placement of the medication and reducing the risk of complications, thereby improving the effectiveness of the treatment.
What are the benefits of using ultrasound-guided knee injections for osteoarthritis treatment?
The benefits include improved precision, reduced risk of complications, and enhanced effectiveness in managing osteoarthritis symptoms, such as pain and limited mobility, allowing patients to engage in exercise therapy and other rehabilitation programs.
What can I expect during an ultrasound-guided knee injection procedure?
You can expect the procedure to involve preparation steps, such as cleaning and numbing the area, followed by the injection itself, which is typically performed under local anesthesia, and the use of ultrasound imaging to guide the needle to the correct location.
How should I care for my knee after an ultrasound-guided injection?
After the procedure, it’s essential to follow immediate post-procedure care instructions, such as applying ice to reduce swelling, and long-term recovery tips, including gradually resuming normal activities and exercises, to ensure a smooth recovery and optimal pain relief.
What are the potential risks and side effects of ultrasound-guided knee injections?
Common side effects include temporary pain, swelling, or redness at the injection site, while rare but serious complications, such as infection or nerve damage, can occur; it’s crucial to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider.
Who is a suitable candidate for ultrasound-guided knee injections?
Suitable candidates include individuals with knee pain caused by osteoarthritis, tendonitis, or bursitis, who have not responded to conservative treatments or require a more targeted approach; age and overall health will be considered by your healthcare provider.
How much do ultrasound-guided knee injections cost in the United States?
The cost can vary depending on factors, such as location, provider, and insurance coverage; it’s essential to check with your insurance provider to determine the extent of coverage and any out-of-pocket expenses.
How can I find a qualified healthcare provider for ultrasound-guided knee injections?
To find a qualified provider, look for credentials, such as specialized training in musculoskeletal ultrasound and injection techniques, and ask questions, such as their experience with the procedure and their approach to patient care.
Are there alternatives to ultrasound-guided knee injections for knee pain management?
Yes, alternatives include other injection therapies, such as corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections, and non-injection treatments, such as physical therapy, bracing, or pain medications; your healthcare provider can help determine the best approach for your specific condition.
Can ultrasound-guided knee injections be used in conjunction with other treatments?
Yes, ultrasound-guided knee injections can be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, which may include other therapies, such as physical therapy, exercise programs, or pain management strategies, to achieve optimal pain relief and improved joint function.