Knee pain can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the common causes, types, and symptoms of knee pain is essential for effective management. Fortunately, there are several over-the-counter solutions available that can provide relief. This article explores the top solutions, including topical pain relief creams, oral pain medications, knee braces and supports, and physical therapy and exercise. Additionally, implementing preventive measures such as maintaining a healthy weight, wearing proper footwear, avoiding high-impact activities, and strengthening the muscles around the knee can help prevent knee pain. Here are the key takeaways:
Key Takeaways
- Topical pain relief creams can provide temporary relief for knee pain.
- Oral pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help reduce inflammation and alleviate knee pain.
- Knee braces and supports can provide stability and support to the knee joint, reducing pain and preventing further injury.
- Physical therapy and exercise can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and reduce knee pain.
- Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the stress on the knee joint and decrease the risk of knee pain.
Understanding Knee Pain
Common Causes of Knee Pain
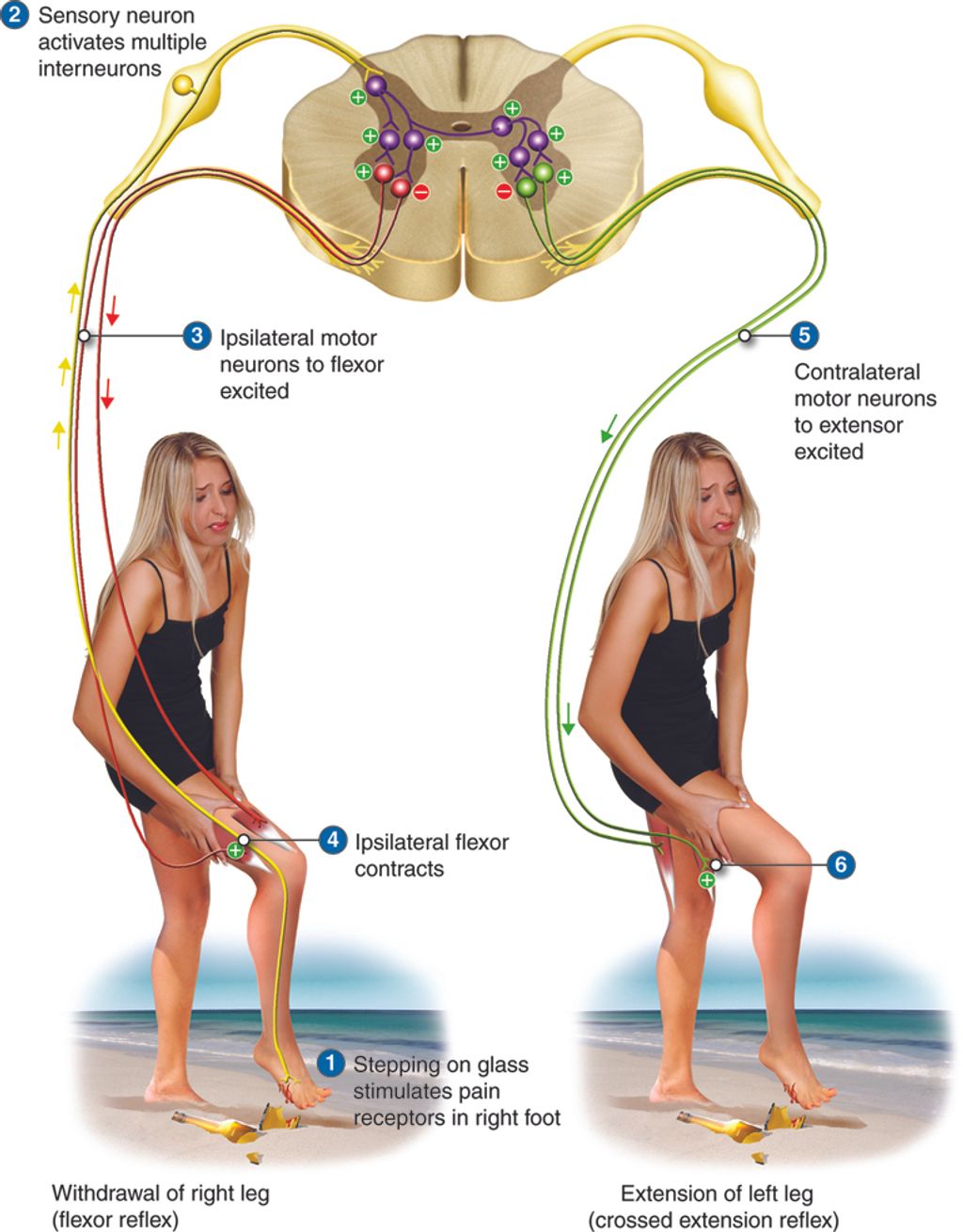
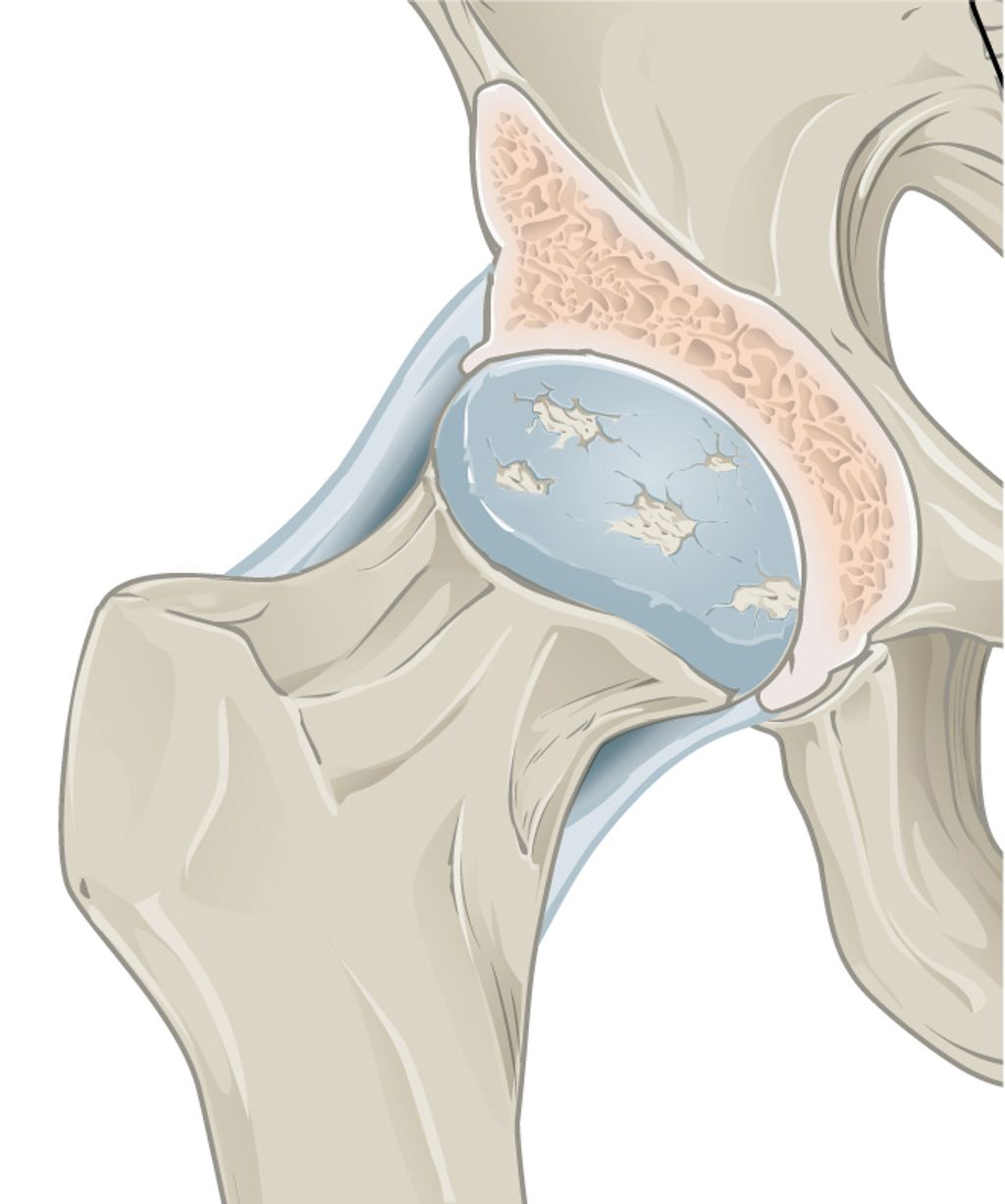
Knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, and medical conditions. Injuries such as sprains, strains, and tears to the ligaments and tendons surrounding the knee joint can result in pain and discomfort. Overuse of the knee joint, often seen in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive activities, can lead to inflammation and wear and tear on the joint. Additionally, certain medical conditions like arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis can cause chronic knee pain.
To better understand the cause of your knee pain, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Here are some common causes of knee pain:
- Injury: Sprains, strains, and tears to ligaments and tendons.
- Overuse: Repetitive activities and excessive strain on the knee joint.
- Medical conditions: Arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis.
Types of Knee Pain
Knee pain can manifest in various ways, depending on the underlying cause. Acute knee pain is sudden and often caused by an injury, such as a sprain or tear. This type of pain is usually sharp and intense. Chronic knee pain, on the other hand, persists over a longer period of time and is often associated with conditions like arthritis or overuse injuries.
It’s important to accurately identify the type of knee pain you’re experiencing in order to determine the most appropriate treatment approach. Here are some common types of knee pain:
- Patellofemoral pain syndrome: This is a common knee condition characterized by pain around or behind the kneecap. It is often caused by overuse, muscle imbalances, or improper tracking of the kneecap.
- Meniscal tears: These are tears in the cartilage that cushions the knee joint. They can cause pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Ligament injuries: Ligaments in the knee, such as the ACL or MCL, can be sprained or torn, resulting in pain and instability.
Understanding the specific type of knee pain you have can help guide your treatment decisions and improve your overall recovery.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Knee pain can manifest in various ways, with different individuals experiencing different symptoms. Common symptoms of knee pain include:
- Swelling: The knee may appear swollen and feel warm to the touch.
- Stiffness: The knee may feel stiff, making it difficult to fully bend or straighten the leg.
- Popping or clicking: Some individuals may experience a popping or clicking sensation in the knee joint.
- Weakness: The knee may feel weak or unstable, making it challenging to bear weight or engage in physical activities.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Ignoring knee pain can lead to further complications and hinder your daily activities.
Over-the-Counter Solutions for Knee Pain
Topical Pain Relief Creams
Topical pain relief creams are a popular over-the-counter solution for knee pain. These creams are applied directly to the skin and work by numbing the area and reducing inflammation. They can provide temporary relief from minor aches and pains caused by arthritis, muscle strains, or overuse.
One advantage of topical pain relief creams is that they can be easily applied and absorbed into the skin, targeting the source of the pain. They are available in different strengths and formulations, including those with menthol, camphor, or capsaicin. It’s important to follow the instructions and guidelines provided by the manufacturer when using these creams.
While topical pain relief creams can be effective for some individuals, they may not provide complete relief for everyone. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional if you have persistent or severe knee pain.
Oral Pain Medications
Oral pain medications are a common over-the-counter solution for knee pain. These medications can help to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the knee. They are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquids.
One popular type of oral pain medication is nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation and pain. Some common NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin.
It is important to follow the recommended dosage instructions when taking oral pain medications. Taking more than the recommended dose can lead to side effects such as stomach irritation or liver damage.
If you are unsure about which oral pain medication to take, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Knee Braces and Supports
Knee braces and supports are commonly used over-the-counter solutions for knee pain. Braces provide stability and support to the knee joint, helping to reduce pain and prevent further injury. They are often recommended for individuals with ligament injuries or osteoarthritis. Knee braces come in different types, including hinged braces, compression sleeves, and patellar stabilizers.
In addition to braces, there are also various types of knee supports available. These supports are designed to provide compression and mild support to the knee, helping to alleviate pain and discomfort. They are commonly used for conditions such as patellofemoral pain syndrome or runner’s knee.
When choosing a knee brace or support, it is important to consider the specific needs of the individual and consult with a healthcare professional if necessary. Proper fitting and usage instructions should be followed to ensure maximum effectiveness.
- Knee braces provide stability and support to the knee joint.
- Knee supports offer compression and mild support.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for proper fitting and usage instructions.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
Physical therapy and exercise are crucial components of managing knee pain. Physical therapy involves a combination of exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the knee joint. It can help reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further injury. Exercise is also important for maintaining overall knee health. Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, provide support to the joint, and improve stability.
In addition to physical therapy and exercise, there are other non-pharmacological approaches that can be beneficial for knee pain. These include hot and cold therapy, which can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. Weight management is also important, as excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joint. Maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate knee pain and prevent further damage.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercise or physical therapy program. They can provide guidance on the most appropriate exercises and techniques for your specific condition and help ensure you are performing them correctly to avoid further injury.
Preventing Knee Pain
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing stress on the knees and preventing knee pain. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the joints, leading to increased wear and tear. Losing even a small amount of weight can make a significant difference in relieving knee pain.
To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, consider the following:
- Balanced diet: Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Portion control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Use smaller plates and bowls to help control portion sizes.
- Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to burn calories and strengthen the muscles around the knee. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and walking are gentle on the joints.
Tip: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass, which can help support the knee joint and improve stability.
Proper Footwear and Orthotics
When it comes to managing knee pain, proper footwear and orthotics play a crucial role. Choosing the right shoes can help alleviate discomfort and provide support to the knees. Look for shoes that have cushioned soles and good arch support to reduce the impact on the knees. Additionally, orthotic inserts can be used to provide extra support and stability. These inserts can help correct any biomechanical issues that may be contributing to knee pain.
In addition to wearing the right footwear, there are a few other tips to keep in mind:
- Avoid high heels and shoes with minimal cushioning, as they can put extra strain on the knees.
- Replace worn-out shoes regularly to ensure proper support.
- Consider custom orthotics if you have specific foot or gait abnormalities.
Remember, taking care of your feet and wearing the right shoes can go a long way in preventing and managing knee pain.
Avoiding High-Impact Activities
Engaging in high-impact activities can put excessive strain on the knees and exacerbate knee pain. Running, jumping, and playing sports that involve quick and repetitive movements can increase the risk of knee injuries and worsen existing knee pain. It is important to modify your exercise routine to include low-impact activities that are gentler on the knees. Consider incorporating swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical machine as alternative forms of exercise. These activities provide cardiovascular benefits without subjecting the knees to excessive stress.
Additionally, it is advisable to avoid activities that require sudden changes in direction or involve twisting motions, as these movements can further strain the knee joints. Pivoting, sudden stops, and sharp turns should be minimized to prevent aggravating knee pain.
Remember, protecting your knees from high-impact activities is crucial in managing knee pain and preventing further damage.
Strengthening the Muscles around the Knee
Strengthening the muscles around the knee is crucial for maintaining knee stability and reducing the risk of injury. Regular exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can help improve overall knee strength. Here are some effective exercises to consider:
-
Squats: Squats are a great exercise for strengthening the muscles in the thighs and buttocks. Start with your feet shoulder-width apart, lower your body as if sitting back into a chair, and then return to a standing position.
-
Lunges: Lunges target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Take a step forward with one leg, lowering your body until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle, and then return to the starting position.
-
Step-ups: Step-ups are a simple yet effective exercise. Find a step or platform, step up with one leg, and then step back down. Repeat with the other leg.
Remember to start with light weights or no weights at all and gradually increase the intensity as your muscles get stronger.
Tip: It’s important to maintain proper form during these exercises to avoid putting unnecessary stress on the knee joints.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several effective over-the-counter solutions available for knee pain. These include topical creams, pain relievers, and supportive devices. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatment. With the right approach, individuals can find relief and manage their knee pain effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of knee pain?
Common causes of knee pain include arthritis, ligament injuries, meniscus tears, overuse or repetitive strain, and obesity.
How can I relieve knee pain using topical pain relief creams?
Topical pain relief creams containing ingredients like menthol or capsaicin can provide temporary relief by numbing the area and reducing inflammation.
Are oral pain medications effective for knee pain?
Oral pain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee.
Do knee braces and supports help with knee pain?
Knee braces and supports can provide stability, compression, and support to the knee joint, helping to alleviate pain and reduce the risk of further injury.
Can physical therapy and exercise help with knee pain?
Physical therapy and exercise can strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and reduce pain by promoting proper alignment and movement.
What are some tips for preventing knee pain?
Maintaining a healthy weight, wearing proper footwear and orthotics, avoiding high-impact activities, and regularly strengthening the muscles around the knee can help prevent knee pain.