Knee pain can be a debilitating condition that affects people of all ages. Whether you’re an athlete or someone who leads a sedentary lifestyle, finding exercises to relieve knee pain is essential for maintaining mobility and reducing discomfort. In this article, we will explore different types of knee pain, exercises for knee pain relief, how to find knee pain specialists, and tips for preventing knee pain. By understanding the causes and symptoms of knee pain, incorporating targeted exercises into your routine, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, you can take proactive steps towards improving your knee health.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of knee pain is crucial for effective treatment.
- Strengthening exercises can help improve knee stability and reduce pain.
- Stretching exercises can increase flexibility and alleviate knee tightness.
- Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, are gentle on the knees and can provide relief.
- Balance and stability exercises can enhance joint control and prevent future knee injuries.
Understanding Knee Pain
Causes of Knee Pain
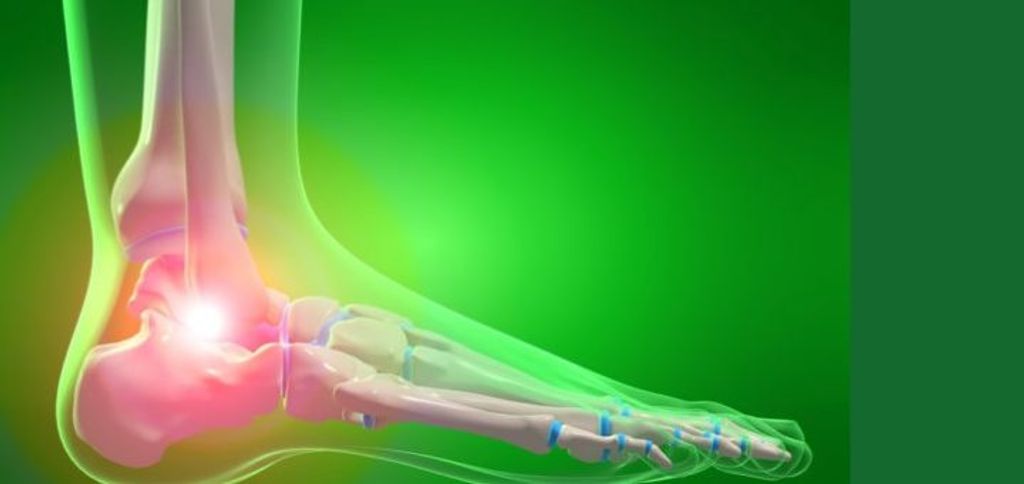
Knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, and medical conditions. Injuries such as sprains, strains, and tears to the ligaments or tendons surrounding the knee joint can lead to pain and discomfort. Overuse of the knee joint, often seen in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive activities, can also result in knee pain. Additionally, certain medical conditions like arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis can contribute to knee pain.
If you’re experiencing knee pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan. They may recommend a combination of rest, physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications to alleviate the pain and promote healing.
Here are some common causes of knee pain:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Injury | Sprains, strains, and tears to ligaments or tendons |
| Overuse | Repetitive activities or excessive strain on the knee joint |
| Arthritis | Inflammation of the joints |
| Bursitis | Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint |
| Tendonitis | Inflammation of the tendons |
Tip: If you’re unsure about the cause of your knee pain or if it persists despite self-care measures, seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Knee Pain
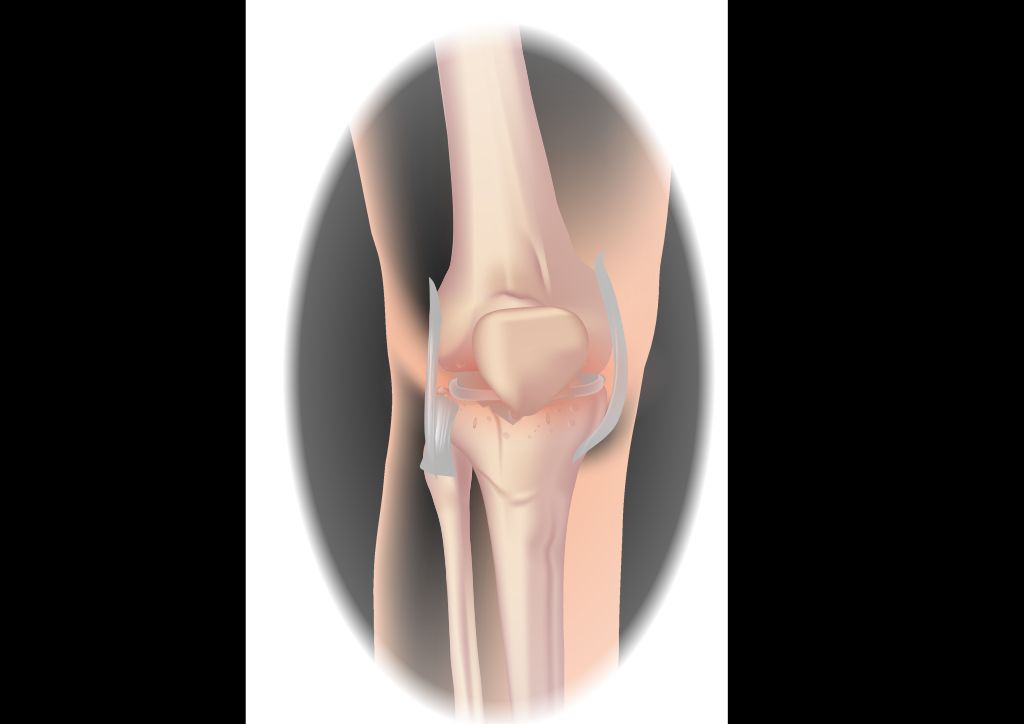
There are several types of knee pain that individuals may experience. Osteoarthritis is a common type of knee pain that occurs due to the breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint. This can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling. Patellofemoral pain syndrome is another type of knee pain that is characterized by pain around the kneecap. It is often caused by overuse or misalignment of the patella. Ligament injuries, such as an ACL tear or MCL sprain, can also cause knee pain. These injuries often occur during sports or activities that involve sudden changes in direction or impact.
To better understand the different types of knee pain, refer to the table below:
| Type of Knee Pain | Description |
|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | Breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling |
| Patellofemoral pain syndrome | Pain around the kneecap, often caused by overuse or misalignment of the patella |
| Ligament injuries | Injuries to the ligaments in the knee, such as ACL tears or MCL sprains |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to accurately diagnose the type of knee pain and determine the appropriate treatment plan. Each type of knee pain may require different exercises and interventions for relief.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Symptoms of knee pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the knee joint
- Swelling or inflammation around the knee
- Stiffness or limited range of motion
- Difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected knee
It is important to pay attention to these symptoms as they can indicate a more serious issue. If you experience persistent or worsening knee pain, it is recommended to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Tip: Applying ice to the affected knee and elevating it can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
Exercises for Knee Pain Relief
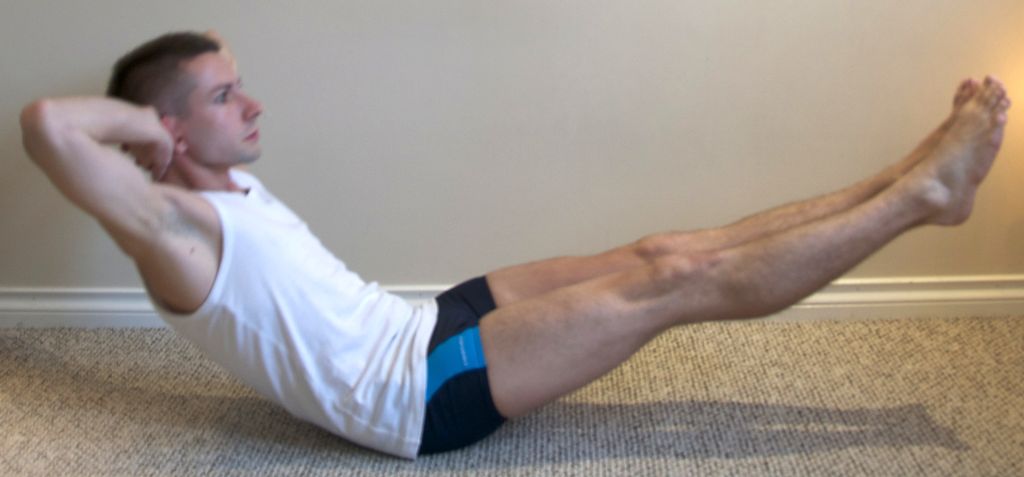
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises are an essential component of any knee pain relief program. These exercises help to build the muscles around the knee, providing support and stability. Squats and lunges are two effective strengthening exercises for the knees. They target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, which are important for knee stability. Leg presses and step-ups are also beneficial for strengthening the lower body.
In addition to these exercises, it is important to incorporate resistance training into your routine. This can be done using resistance bands or weights. Resistance training helps to increase muscle strength and endurance, which can alleviate knee pain.
Remember to start with light weights and gradually increase the intensity as your strength improves. It is also important to maintain proper form and technique while performing these exercises to avoid injury.
Tip: Consult with a physical therapist or fitness professional to ensure you are performing the exercises correctly and safely.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are an important component of any knee pain relief routine. They help improve flexibility and reduce muscle tightness, which can alleviate discomfort. Hamstring stretches are particularly beneficial for knee pain, as tight hamstrings can contribute to knee problems. Gentle quad stretches can also help relieve tension in the knee area.
In addition to these stretches, incorporating calf stretches into your routine can help improve overall lower body flexibility. This can be done by standing near a wall and placing one foot behind you, keeping the heel on the ground and leaning forward to stretch the calf muscles.
Remember to always warm up before stretching and to perform each stretch slowly and gently. It’s important to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard, as overstretching can lead to further injury. If you experience any pain or discomfort during stretching exercises, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance and modifications.
Table: Stretches for Knee Pain Relief
| Stretch | Description |
|---|---|
| Hamstring Stretch | Sit on the edge of a chair with one leg extended. Lean forward from the hips until you feel a stretch in the back of the thigh. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other leg. |
| Quad Stretch | Stand near a wall for support. Bend one knee and grab the ankle with the same side hand. Pull the heel towards the buttocks until you feel a stretch in the front of the thigh. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other leg. |
| Calf Stretch | Stand near a wall and place one foot behind you, keeping the heel on the ground. Lean forward to stretch the calf muscles. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other leg. |
Note: These stretches should be performed under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Low-Impact Exercises
Low-impact exercises are gentle on the joints and can help reduce knee pain. These exercises are suitable for individuals with knee pain or those recovering from knee injuries. Some examples of low-impact exercises include:
-
Swimming: Swimming is a great low-impact exercise that provides a full-body workout without putting stress on the knees. It helps improve cardiovascular fitness and strengthens the muscles around the knee.
-
Cycling: Cycling is another low-impact exercise that is easy on the knees. It helps improve leg strength and flexibility while minimizing the impact on the joints.
-
Tai Chi: Tai Chi is a gentle form of exercise that focuses on slow, controlled movements. It can help improve balance, flexibility, and strength, which are important for knee health.
-
Yoga: Yoga combines stretching, strength, and balance exercises. It can help improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen the muscles that support the knees.
Note: It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a physical therapist before starting any exercise program, especially if you have knee pain or a knee injury.
Balance and Stability Exercises
Balance and stability exercises are an important component of a comprehensive knee pain relief program. These exercises help improve proprioception, which is the body’s ability to sense its position in space. By enhancing proprioception, balance and stability exercises can help reduce the risk of falls and improve overall knee function.
One effective balance exercise is the single-leg stance. To perform this exercise, stand on one leg and try to maintain your balance for 30 seconds. Repeat on the other leg. This exercise can be made more challenging by closing your eyes or standing on an unstable surface, such as a foam pad.
Another beneficial exercise is the heel-to-toe walk. Start by placing the heel of one foot directly in front of the toes of the opposite foot. Take a step forward, placing the heel of the opposite foot in front of the toes of the first foot. Continue walking in a straight line, maintaining the heel-to-toe position. This exercise helps improve balance and coordination.
In addition to these exercises, incorporating a balance board or stability ball into your routine can further enhance your balance and stability. These tools provide an unstable surface, forcing your muscles to work harder to maintain stability. Start with simple exercises and gradually increase the difficulty as your balance improves.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have existing knee pain or injuries.
Finding Knee Pain Specialists
Orthopedic Surgeons
Orthopedic surgeons are medical doctors who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, including knee pain. They have extensive knowledge and experience in surgical procedures related to the knee, such as knee replacement surgery and arthroscopy. Orthopedic surgeons play a crucial role in the management of severe knee pain and injuries.
When considering an orthopedic surgeon for your knee pain, it is important to find a highly skilled and experienced professional. Here are some factors to consider when choosing an orthopedic surgeon:
- Board certification: Look for a surgeon who is board-certified in orthopedic surgery. This certification ensures that the surgeon has met the highest standards of knowledge, skill, and experience in the field.
- Specialization: Some orthopedic surgeons specialize in specific areas, such as sports medicine or joint replacement. Consider finding a surgeon who specializes in the type of knee pain or injury you have.
If you are experiencing severe knee pain or have a knee injury that requires surgical intervention, consulting with an orthopedic surgeon is essential. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, recommend appropriate treatment options, and perform necessary surgical procedures to alleviate your knee pain and improve your quality of life.
Physical Therapists
Physical therapists are healthcare professionals who specialize in treating musculoskeletal conditions, including knee pain. They are trained to assess and diagnose the underlying causes of knee pain and develop personalized treatment plans to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Benefits of working with a physical therapist
- Personalized treatment: Physical therapists will tailor exercises and therapies to your specific needs and goals.
- Expert guidance: They will teach you proper techniques and form to prevent further injury and maximize the effectiveness of your exercises.
- Rehabilitation support: Physical therapists can provide guidance and support during the recovery process, helping you regain strength and function.
Finding a physical therapist
When looking for a physical therapist, consider the following:
- Credentials: Ensure the therapist is licensed and has experience treating knee pain.
- Specialization: Look for therapists who specialize in orthopedics or sports medicine.
- Recommendations: Ask for recommendations from your primary care physician or friends who have had success with physical therapy.
Tip: It’s important to communicate openly with your physical therapist about your symptoms, goals, and any concerns you may have. This will help them develop the most effective treatment plan for you.
Sports Medicine Doctors
Sports medicine doctors specialize in the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and physical activity. They have extensive knowledge and experience in diagnosing and managing knee pain in athletes and active individuals. These doctors are trained to provide comprehensive care, including non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medications, and injections. They may also collaborate with orthopedic surgeons for more complex cases that require surgical intervention.
If you’re an athlete or someone who engages in regular physical activity, consulting a sports medicine doctor can be beneficial in managing and preventing knee pain. They can provide personalized treatment plans and recommendations based on your specific needs and goals.
Here are some key points to consider when seeking a sports medicine doctor:
- Look for a doctor who specializes in sports medicine and has experience treating knee injuries.
- Consider their credentials, including board certification and affiliations with sports medicine organizations.
- Ask about their treatment approach and philosophy, including their emphasis on conservative treatments before considering surgery.
- Inquire about their availability and accessibility for appointments and follow-up care.
Remember, early intervention and proper management of knee pain can help you recover faster and get back to your active lifestyle.
Preventing Knee Pain
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing knee pain. Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, leading to increased pain and discomfort. Losing weight can significantly reduce the pressure on the knees and improve overall joint health.
To achieve and maintain a healthy weight, it is important to follow a balanced diet and engage in regular physical activity. Eating a variety of nutritious foods and controlling portion sizes can help with weight management. Incorporating low-impact exercises into your routine, such as swimming or cycling, can also aid in weight loss while minimizing stress on the knees.
In addition to weight management, it is essential to avoid excessive sitting or standing for prolonged periods. Taking breaks and changing positions frequently can help prevent knee pain caused by prolonged pressure on the joints.
Remember, maintaining a healthy weight is not only beneficial for knee pain relief but also for overall well-being.
Wearing Proper Footwear
When it comes to managing knee pain, wearing the right footwear is crucial. Proper footwear can provide support and stability to the knees, reducing the risk of injury and discomfort. Here are some tips for choosing the right footwear:
- Arch support: Look for shoes with good arch support to help distribute weight evenly and reduce stress on the knees.
- Cushioning: Opt for shoes with adequate cushioning to absorb shock and minimize impact on the knees.
- Proper fit: Ensure that the shoes fit properly and provide enough room for the toes to move comfortably.
Tip: Avoid high heels and shoes with narrow toe boxes, as they can put excessive pressure on the knees and contribute to knee pain.
Remember, investing in the right footwear can make a significant difference in managing knee pain and maintaining overall knee health.
Using Correct Techniques
When performing exercises for knee pain relief, it is crucial to use correct techniques to avoid further injury and maximize the benefits. Here are some important tips to keep in mind:
-
Maintain proper form: Ensure that you are using the correct posture and alignment during each exercise. This will help target the right muscles and reduce strain on the knees.
-
Start slow and gradually increase intensity: It is important to start with low-impact exercises and gradually increase the intensity as your strength and flexibility improve. This will prevent overexertion and minimize the risk of aggravating knee pain.
-
Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain during the exercises. If you experience any sharp or persistent pain, it is important to stop and consult with a healthcare professional.
-
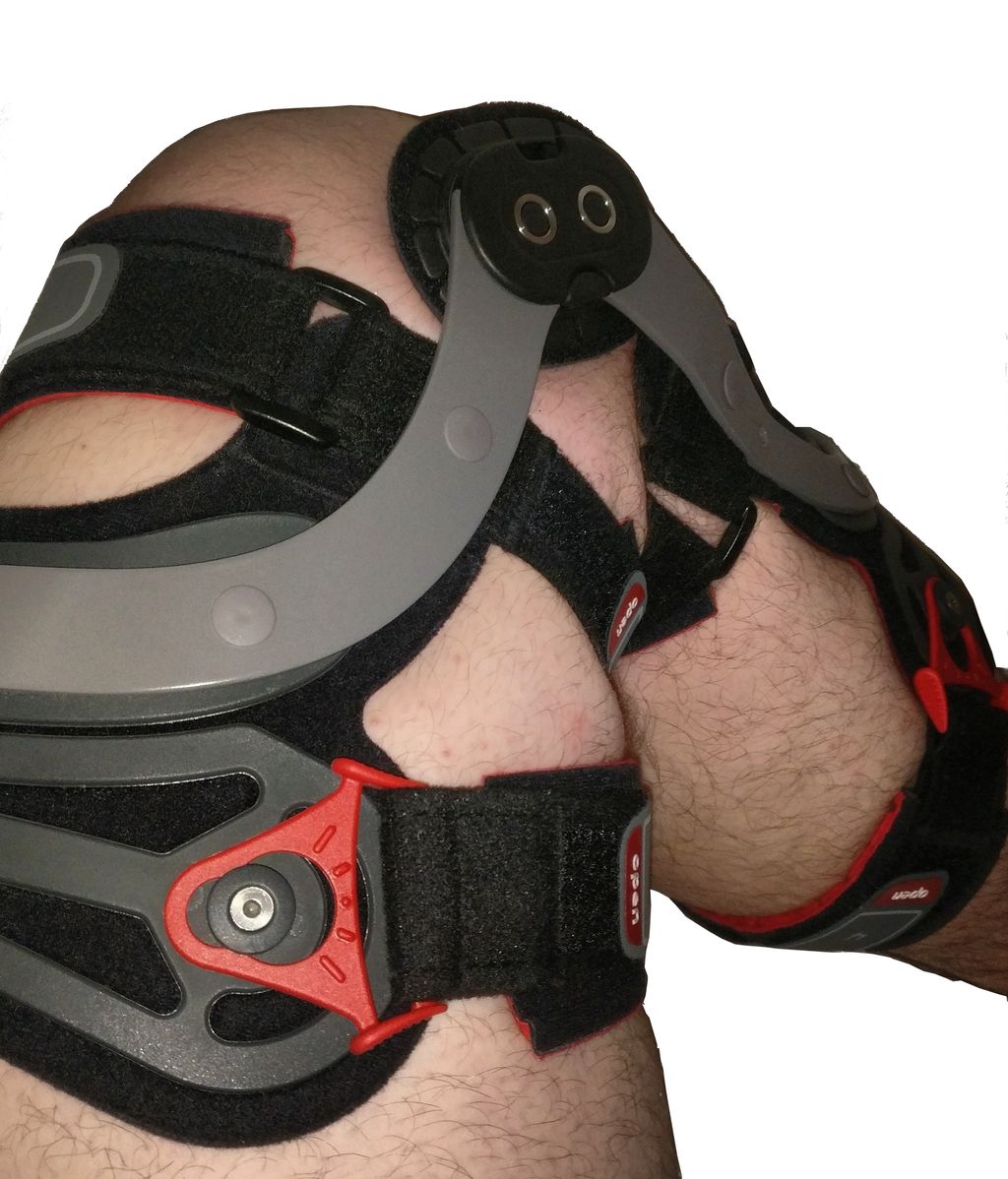
Use appropriate equipment: Make sure you have the right equipment, such as supportive shoes or knee braces, to provide stability and protect your knees.
Remember, using correct techniques is essential for a safe and effective knee pain relief exercise routine.
Avoiding Overuse
When it comes to preventing knee pain, avoiding overuse is crucial. Overuse can lead to inflammation and strain on the knee joint, exacerbating existing pain or causing new pain to develop. To avoid overuse, it’s important to listen to your body and pace yourself during physical activities. Moderation is key. Additionally, it’s important to incorporate rest days into your exercise routine to allow your knees to recover. Cross-training can also be beneficial, as it allows you to engage in different types of activities that put less stress on the knees. Remember, prevention is better than cure, so take steps to avoid overusing your knees and protect your joint health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding knee pain exercises near you is essential for managing and improving knee health. By incorporating specific exercises into your daily routine, you can alleviate pain, strengthen muscles, and improve flexibility. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have existing knee conditions. Take charge of your knee health today and start incorporating these exercises into your fitness regimen!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of knee pain?
The common causes of knee pain include injuries, arthritis, overuse, and obesity.
What are some exercises for knee pain relief?
Some exercises for knee pain relief include strengthening exercises, stretching exercises, low-impact exercises, and balance and stability exercises.
How can I find knee pain specialists near me?
You can find knee pain specialists near you by searching online directories, asking for referrals from your primary care physician, or contacting local hospitals and clinics.
What is the importance of maintaining a healthy weight for preventing knee pain?
Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the stress on your knees and can prevent or alleviate knee pain.
What types of footwear should I wear to prevent knee pain?
To prevent knee pain, it is recommended to wear supportive shoes with good cushioning and proper arch support.
Are there any techniques to avoid knee pain during exercise?
To avoid knee pain during exercise, make sure to warm up properly, use proper form and technique, and listen to your body to avoid overexertion.