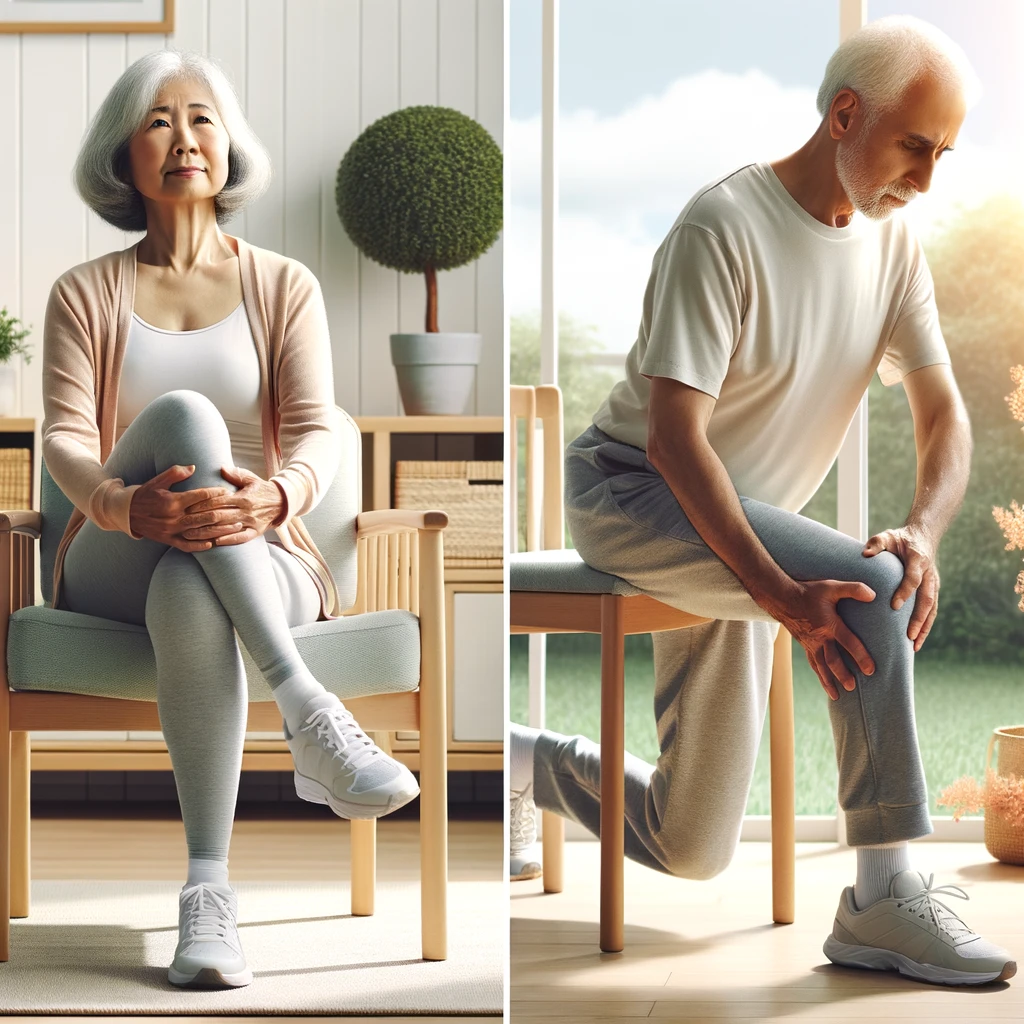
Knee pain is a common condition that affects many seniors. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including aging, arthritis, and injury. Knee pain can be debilitating, making it difficult for seniors to perform everyday tasks and enjoy their favorite activities. Fortunately, there are exercises that can help alleviate knee pain and improve mobility.

At our clinic, we recommend a variety of exercises to help seniors manage knee pain. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve flexibility, and reduce inflammation. They can be done at home or with the guidance of a physical therapist. It’s important to note that exercise is just one part of a comprehensive treatment plan for knee pain. Seniors should also work with their healthcare provider to address any underlying conditions that may be contributing to their knee pain.
As we age, it’s common to experience aches and pains in various parts of the body. However, knee pain can be particularly challenging, as it can limit mobility and impact overall quality of life. By incorporating targeted exercises into their daily routine, seniors can take an active role in managing their knee pain and improving their health and wellbeing.
Understanding Knee Pain in Seniors
As we age, our body undergoes changes that can lead to various health conditions, including knee pain. Knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, overuse, inflammation, and osteoarthritis. In this section, we will discuss the causes and risk factors of knee pain in seniors, as well as when to consult a doctor.
Causes and Risk Factors
Knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, overuse, inflammation, and osteoarthritis. Injuries such as meniscus tears, ligament sprains, and fractures can cause knee pain. Overuse injuries, such as tendinitis and bursitis, can also lead to knee pain. Inflammation caused by conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can also cause knee pain.
Osteoarthritis is a common cause of knee pain in seniors. It is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint wears away over time. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee joint.
Aging is also a risk factor for knee pain. As we age, our bones and joints become weaker and more prone to injury and wear and tear. This can lead to conditions such as osteoarthritis and other joint problems.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you are experiencing knee pain, it is important to consult a doctor. A doctor can help you determine the cause of your knee pain and recommend appropriate treatment options. Physical therapy, rehabilitation, and medication are common treatment options for knee pain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged knee joints.
An orthopedic surgeon or physician can provide medical advice and treatment options for knee pain. A physical therapist can also help with rehabilitation and physical therapy exercises to help improve knee function and reduce pain.
In conclusion, knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including injuries, overuse, inflammation, and osteoarthritis. If you are experiencing knee pain, it is important to consult a doctor to determine the cause of your pain and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Exercise Program for Knee Pain Relief
If you are experiencing knee pain, incorporating a regular exercise program can help reduce pain, improve flexibility, and increase strength. In this section, we will discuss low-impact exercises, strengthening and flexibility exercises, and exercise safety and techniques.
Low-Impact Exercises
Low-impact exercises are a great way to stay active while minimizing the stress on your knees. Some examples of low-impact exercises include cycling, swimming, water aerobics, and walking. These exercises can help improve cardiovascular health and increase range of motion without putting too much pressure on your knees.

Strengthening and Flexibility Exercises
Strengthening and flexibility exercises can help improve the muscles around your knee joint, providing more support and reducing pain. Some examples of strengthening exercises include squats, lunges, leg raises, and calf raises. For flexibility, try quadriceps, hamstring, and calf stretches. Additionally, exercises like clamshells, leg extensions, and hamstring curls can help target specific muscles like the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles.
Exercise Safety and Techniques
It’s important to warm up before any exercise program and to use proper technique to prevent injury. Stretching exercises, foam rolling, and myofascial release can help prepare your muscles for exercise. Resistance bands can also be used to add resistance to exercises like squats and lunges.
When starting an exercise program, start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Listen to your body and stop if you experience any pain or discomfort. Always wear proper footwear and use proper technique to prevent injury.
In summary, incorporating low-impact exercises, strengthening and flexibility exercises, and proper exercise safety and techniques can help reduce knee pain and improve overall knee health.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are effective seated knee strengthening exercises for older adults?
Seated knee strengthening exercises are beneficial for seniors with knee pain who may not be able to stand for long periods. Some effective seated knee strengthening exercises include:
- Seated leg extension: Lift one leg at a time and extend it straight out in front of you, hold for a few seconds, and lower it back down. Repeat with the other leg.
- Seated knee lift: Sit on a chair and lift one knee up towards your chest, hold for a few seconds, and lower it back down. Repeat with the other leg.
Which exercises should be avoided when experiencing knee pain?
High-impact exercises such as running and jumping should be avoided when experiencing knee pain. Exercises that put excessive strain on the knees, such as lunges and deep squats, should also be avoided. Instead, low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling are recommended.
How can knee osteoarthritis be managed with exercises for the elderly?
Knee osteoarthritis can be managed with exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee joint. Some effective exercises for knee osteoarthritis include:
- Straight leg raises: Lie on your back and lift one leg straight up towards the ceiling, hold for a few seconds, and lower it back down. Repeat with the other leg.
- Wall squats: Stand with your back against a wall and lower yourself down into a squatting position, hold for a few seconds, and stand back up.
Can you recommend knee strengthening exercises suitable for seniors to do at home?
Yes, there are many knee strengthening exercises that seniors can do at home. Some effective knee strengthening exercises for seniors include:
- Step-ups: Step up onto a low step with one foot, then step back down. Repeat with the other foot.
- Mini-squats: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and squat down slightly, hold for a few seconds, and stand back up.
What types of leg exercises are safe for seniors with knee issues?
Low-impact leg exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling are safe for seniors with knee issues. Strength training exercises that focus on the muscles around the knee joint, such as leg curls and leg presses, can also be beneficial.
What are the best practices for walking with knee pain?
When walking with knee pain, it’s important to wear comfortable, supportive shoes and to walk on flat, even surfaces. Start with short walks and gradually increase the distance over time. Use a walking aid, such as a cane or walker, if necessary. If the pain persists, consult a doctor or physical therapist for further guidance.