Have you ever wondered why discomfort strikes the inner area of your legs when lowering into a squat, even after perfecting your technique? This frustrating issue affects countless athletes and gym-goers, often leaving them questioning their form or fearing long-term damage.
Research from Medical News Today confirms that correctly executed squats shouldn’t strain your joints. Yet many still experience sharp twinges near the medial joint line during deep movements. The culprit often lies in subtle biomechanical flaws or pre-existing weaknesses rather than outright errors.
We’ll explore how factors like muscle imbalances, ligament stress, and joint alignment contribute to this problem. Understanding these elements helps explain why preventative strategies go beyond basic posture checks. From targeted strengthening exercises to recovery protocols, solutions exist for those willing to address root causes.
Key Takeaways
- Proper squat mechanics don’t always prevent medial joint discomfort
- Muscle imbalances and prior injuries often play hidden roles
- Medical studies validate the link between form breakdowns and symptoms
- Prevention requires addressing both technique and joint health
- Early intervention can stop temporary irritation from becoming chronic
Understanding Knee Pain and Its Impact During Squats
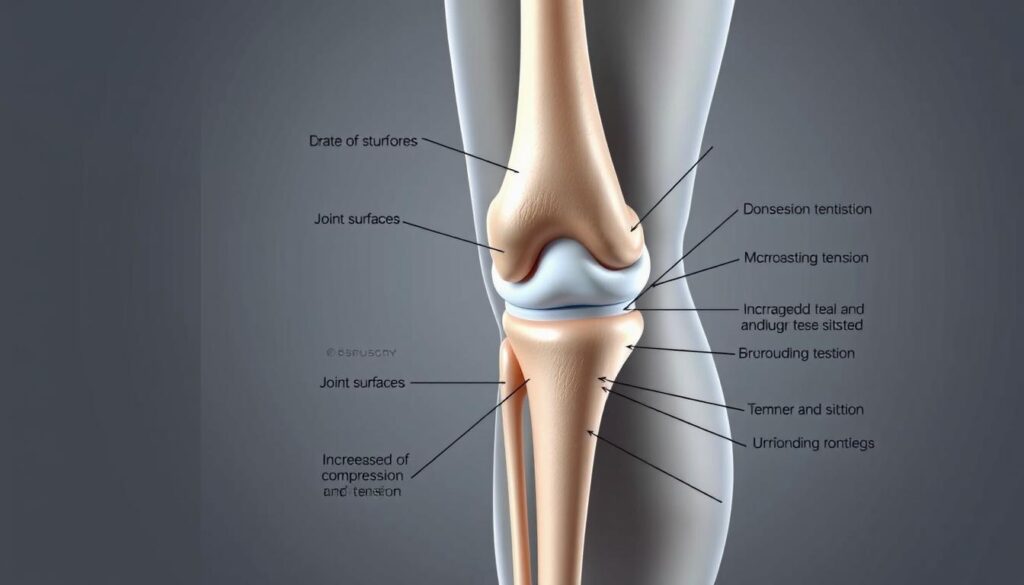
The human knee operates like a complex hinge, balancing stability with remarkable mobility. Three bones meet here—the femur, tibia, and patella—cushioned by cartilage and connected through a network of tendons and ligaments. This design allows smooth movement but creates vulnerability when forces exceed the joint’s capacity.
What Happens in the Knee Joint?
During flexion, pressure shifts across the joint surfaces. The medial compartment bears more load in deep positions, according to Hinge Health research. Cartilage acts as a shock absorber, while tendons like the patellar cord transfer muscle power. Ligaments prevent excessive sideways motion that could strain tissues.
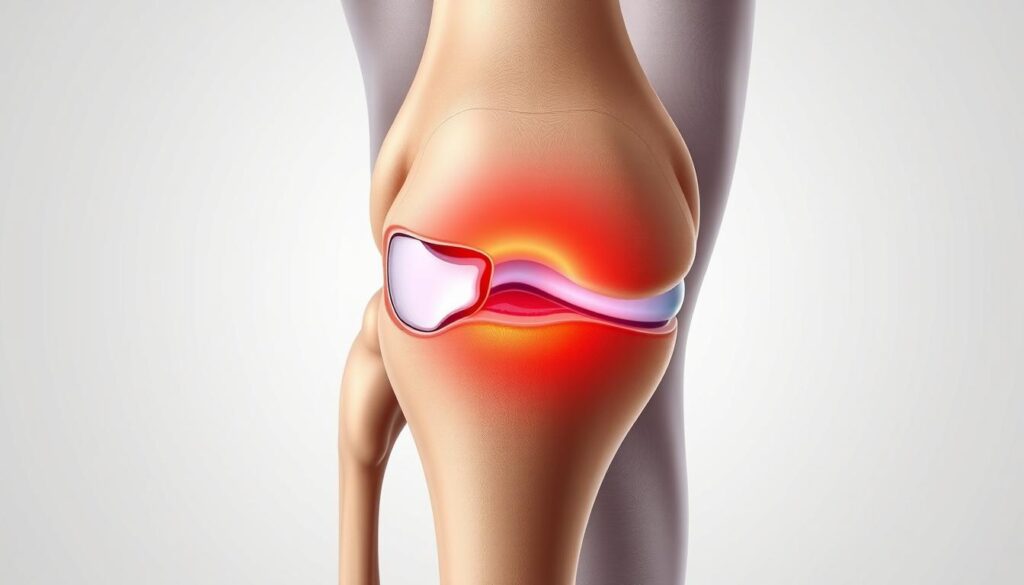
How Squatting Affects Knee Pressure
Biomechanics studies reveal squat depth dramatically changes force distribution. At 90 degrees, the patellofemoral joint experiences 7-8 times body weight. Deeper angles increase compression on the medial meniscus and collateral ligaments. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp twinges near the joint line
- Dull aches persisting after activity
- Stiffness when transitioning from bent to straight positions
“Proper form reduces but doesn’t eliminate stress,” notes a Medical News Today analysis. Foot positioning and hip mobility significantly influence where pressures concentrate. Those with prior injuries often feel discomfort earlier in the movement pattern, signaling compromised load management.
Inner knee pain only during deep squats: Causes and Contributing Factors
Medial joint stress during loaded movements often results from overlapping biomechanical and physiological factors. While proper form reduces risks, subtle flaws in movement patterns or underlying weaknesses frequently go unnoticed until discomfort appears.
Movement Mechanics and Tissue Coordination
Faulty hip-knee alignment during descent forces medial structures to absorb excessive force. A Journal of Orthopaedic Research study found quadriceps dominance increases patellar tendon strain by 18% compared to balanced glute engagement. Common technical errors include:
- Knees collapsing inward (valgus position)
- Limited ankle dorsiflexion altering weight distribution
- Premature heel lift shifting pressure forward
These misalignments strain the pes anserinus tendon group and medial collateral ligament. Over time, disproportionate loading can irritate cartilage or cause microtears.
Pre-Existing Vulnerabilities and Repetitive Stress
Prior ligament sprains or meniscus injuries often create lasting instability. Scar tissue formation reduces shock absorption capacity by up to 40%, per Sports Health journal data. Chronic overuse compounds these issues through:
- Inflammation weakening connective tissues
- Reduced blood flow to overworked muscles
- Gradual cartilage wear from repetitive compression
“The joint becomes less tolerant of deep flexion angles after trauma,” explains Dr. Alicia Tan, orthopedic specialist. This explains why symptoms may surface months after initial healing.
Understanding these root causes prepares athletes to address both immediate symptoms and long-term joint health. Our next sections explore practical strategies for sustainable training.
Common Underlying Knee Conditions
Persistent discomfort during squats often signals hidden issues within the joint’s complex structure. Medical News Today reports that 25% of active adults experience knee-related problems tied to specific conditions. Identifying these underlying factors helps tailor effective solutions.
Arthritis, Tendonitis, and Meniscus Issues
Osteoarthritis wears down protective cartilage between bones, creating friction during deep bends. Tendonitis inflames the tough cords connecting muscles to bones, while meniscus tears disrupt shock absorption. Mayo Clinic notes these conditions often manifest as:
- Swelling around the joint after activity
- Morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes
- Sudden instability when changing positions
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome and IT Band Syndrome
Often called “runner’s knee,” patellofemoral pain syndrome causes sharp sensations near the front of the joint. It frequently stems from muscle imbalances that misalign the kneecap. IT band syndrome tightens fibrous tissue along the outer thigh, pulling unevenly during squats.
Both conditions worsen with improper movement patterns. As one orthopedic specialist explains: “Poor hip stability forces the knee to compensate, accelerating tissue wear.” Those experiencing patella pain when squatting should assess their technique and recovery habits.
The Role of Correct Squat Form in Knee Health
What separates joint-friendly squats from harmful ones? Proper technique acts like a protective shield for your body’s most vulnerable hinge. Research from Hinge Health shows optimal alignment reduces strain by up to 35% compared to sloppy execution.

Proper Alignment and Movement Mechanics
Start with feet shoulder-width apart, toes angled slightly outward. The Arthritis Foundation emphasizes keeping knees aligned over toes during descent. Engage these checkpoints:
- Neutral spine – no rounding or over-arching
- Hips initiating movement, not knees
- Weight distributed through midfoot
Common errors like caving knees or lifting heels shift pressure to delicate tissues. “Even minor forward leans increase patellar tendon stress by 20%,” states a Hinge Health biomechanics report.
Adjustments for Individual Body Mechanics
Not everyone fits textbook form. Those with limited ankle mobility benefit from elevating heels on small plates. Narrower stances help people with hip impingement. Try these modifications:
- Box squats to control depth
- Resistance bands for tactile feedback
- Tempo variations to build control
Physical therapist Dr. Mark Ripple advises: “Film your squats from multiple angles. Small tweaks often yield dramatic relief.” Consistent practice with adjusted mechanics builds muscle memory while safeguarding joints.
Preventative Strategies for Knee-Friendly Squatting
Building joint resilience starts before the first rep. We prioritize smart preparation and structural reinforcement to maintain comfort during loaded movements. Experts at Hinge Health recommend a three-phase approach: dynamic preparation, targeted strengthening, and mindful recovery.
Warm-Up and Mobility Exercises
Start with dynamic movements that increase blood flow to the leg muscles. The Arthritis Foundation advocates 5-10 minutes of:
- Bodyweight lunges with torso rotations
- Ankle alphabet drills to improve dorsiflexion
- Controlled hip circles to enhance socket mobility
These drills lubricate joints and activate stabilizers. “Cold tissues are 40% more prone to microtears,” warns a Hinge Health mobility guide. Pair this with foam rolling tight quads or IT bands for better movement patterns.
Strengthening Muscles Around the Knee
Develop a bulletproof support system with these exercises:
- Step-ups focusing on slow eccentric lowering
- Clamshells with resistance bands for glute medius engagement
- Single-leg balance reaches to improve proprioception
Strengthening the posterior chain reduces strain on vulnerable areas. Physical therapist Dr. Ellen Cho notes: “Strong hips and ankles share the load that weak muscles dump onto joints.” Aim for 2-3 weekly sessions, gradually increasing resistance.
Consistency matters more than intensity. Integrate these strategies into existing routines – try mobility drills before workouts and strength exercises on rest days. Listen to your body; persistent discomfort signals needed adjustments. Pair these efforts with quality sleep and hydration for optimal tissue repair.
Effective Home Remedies and Recovery Techniques
Managing post-workout discomfort requires smart recovery practices that support your body’s healing process. We focus on methods proven to reduce inflammation while maintaining mobility.

The R.I.C.E. Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation
This four-step approach remains the gold standard for acute care:
| Component | Action | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rest | 48-hour activity modification | Prevents further tissue strain |
| Ice | 15-minute cold packs every 2 hours | Reduces swelling and numbs soreness |
| Compression | Elastic bandage application | Improves fluid drainage |
| Elevation | Legs above heart level | Decreases blood pooling |
Combine ice therapy with gentle ankle pumps to enhance circulation. Never apply ice directly to skin – use a thin cloth barrier. For compression, ensure wraps feel snug but don’t cut off circulation.
Supplement R.I.C.E. with these strategies:
- Perform seated hamstring stretches 2x daily
- Track swelling changes with a measuring tape
- Use NSAIDs sparingly for breakthrough discomfort
“Persistent stiffness lasting over 72 hours signals the need for professional evaluation,” advises Dr. Lisa Morrow, sports medicine specialist.
Maintain light activity like swimming or cycling if movements remain pain-free. This preserves joint lubrication without overloading healing tissues.
Incorporating Targeted Knee Exercises into Your Routine
Rebuilding strength starts with movements that respect your body’s current limits. Targeted exercises can restore function while protecting vulnerable areas from excessive pressure. Hinge Health research shows structured rehabilitation programs reduce discomfort by 62% in active individuals when performed consistently.
Low-Impact and Rehabilitation Exercises
Begin with these joint-friendly movements to enhance stability without straining tissues:
- Step-ups with tempo control: Use a 4-second lowering phase to build eccentric strength
- Wall sits with pelvic tilts: Maintain 60-degree knee bends while engaging core muscles
- Side-lying leg lifts: Strengthen hip abductors to prevent inward knee collapse
- Seated knee extensions: Improve quadriceps activation using light resistance bands
These activities distribute forces evenly across joints while promoting blood flow to cartilage. A Hinge Health study found participants who performed wall sits daily for six weeks reported 45% less stiffness during squats.
Focus on perfecting form before increasing intensity. Keep movements slow and controlled – rushing compromises alignment. “Quality repetitions matter more than quantity during rehab phases,” advises a Hinge Health mobility specialist. Track progress through pain-free range of motion improvements rather than weight lifted.
Consistency yields the best results. Start with 2-3 weekly sessions of 10-15 minutes, gradually increasing duration as tolerance improves. Pair these exercises with your existing warm-up routine for seamless integration.
When to Seek Professional Guidance
Persistent joint issues demand more than rest and ice. While minor soreness often resolves with self-care, certain warning signs require expert evaluation. Hinge Health reports 68% of athletes delay consultations until symptoms severely limit activity – a decision that often prolongs recovery.
Indicators for Physical Therapy
Physical therapists excel at identifying movement patterns that strain tissues. Schedule an assessment if you experience:
| Symptom | Recommended Action | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Discomfort lasting >72 hours post-activity | Biomechanical evaluation | Within 1 week |
| Swelling altering joint shape | Imaging studies | Immediately |
| Instability during daily tasks | Strength testing | Within 3 days |
“Ignoring instability often leads to secondary injuries,” warns a Hinge Health mobility specialist. Early intervention helps correct imbalances before they reshape cartilage or ligaments.
Consulting Healthcare Providers for Persistent Pain
Orthopedic experts recommend urgent care for these red flags:
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg
- Visible deformity around the joint area
- Locking or catching sensations during movement
Diagnostic tools like MRI scans reveal hidden issues – from meniscus tears to early-stage osteoarthritis. Dr. Sarah Lin, sports physician, notes: “Custom treatment plans reduce surgical needs by 42% when implemented early.” Pair medical advice with targeted exercises to address muscle weaknesses contributing to discomfort.
Proactive care preserves long-term joint function. Track symptom patterns using a pain diary, noting triggers like specific activities or weight shifts. This data helps clinicians design interventions that align with your body’s unique needs.
Adjusting Your Workout to Accommodate Knee Health
Smart training means adapting to your body’s needs while keeping progress on track. For those managing joint sensitivity, small modifications can maintain fitness gains without compromising recovery. Let’s explore practical adjustments backed by the Arthritis Foundation and rehabilitation specialists.
Exercise Modifications That Protect Joints
Swap high-impact movements with alternatives that build strength safely. Replace deep squats with step-ups using a 6-inch platform – this reduces flexion angles while targeting similar muscles. Wall sits at 45-degree angles maintain quad engagement without excessive pressure on tendons.
Consider these joint-friendly swaps:
- Lunges → Reverse sled drags (reduces deceleration forces)
- Box jumps → Resistance band lateral walks
- Burpees → Modified push-ups with knee taps
“Focus on controlled movements rather than depth,” advises a Hinge Health mobility coach. Pair these changes with proper warm-ups: dynamic leg swings and bodyweight glute bridges prepare tissues for activity. Cool down with foam rolling to prevent knee strain from tight muscles.
Phased Return to Full Intensity
Rebuild squat depth gradually using these milestones:
| Phase | Depth | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Partial range (60° bend) | 2-3 weeks |
| 2 | Parallel thighs to floor | 1-2 weeks |
| 3 | Controlled deep squats | Ongoing |
Monitor hip and ankle mobility throughout – restricted movement in these areas often shifts stress to vulnerable joints. Pair strength training with low-impact cardio like swimming or cycling to maintain endurance. Consistency with these strategies helps preserve long-term joint function while achieving fitness goals.
Conclusion
Addressing medial joint discomfort requires understanding its multifaceted origins. As we’ve explored, factors like muscle imbalances, prior injuries, and movement mechanics all influence how joints handle loaded positions. Experts from Hinge Health and Medical News Today emphasize that proper form serves as the foundation for protection—not a guaranteed solution.
Preventative strategies matter just as much as technique adjustments. Targeted exercises strengthen supporting muscles, while recovery protocols help maintain cartilage health. Early intervention proves critical; delaying treatment risks transforming temporary irritation into chronic issues.
Listen to your body’s signals. Persistent stiffness or swelling warrants professional evaluation to rule out conditions like osteoarthritis. Many find relief through modified training routines and evidence-based home care methods.
Commitment to joint-friendly habits pays long-term dividends. By prioritizing alignment, recovery, and gradual progression, athletes can maintain strong, resilient bones and tissues. Start implementing these strategies today—your future self will thank you.
FAQ
Why does my knee hurt only during deep squats?
Discomfort often stems from increased joint pressure or strain on tendons, ligaments, or cartilage when bending beyond 90 degrees. Misalignment, muscle weakness, or preexisting conditions like meniscus tears can amplify this stress.
Can poor squat form lead to long-term damage?
Yes. Repeated improper technique—like collapsing knees inward or shifting weight unevenly—places excessive strain on connective tissues. Over time, this may accelerate wear-and-tear or worsen conditions like osteoarthritis.
How do I know if my pain is from arthritis or an injury?
Arthritis typically causes gradual stiffness and swelling, worsening after inactivity. Injuries like ligament tears or tendonitis often involve sudden sharp pain, localized swelling, or instability. Imaging tests like MRIs provide definitive diagnoses.
What exercises strengthen muscles around the joint?
Focus on low-impact moves like step-ups, clamshells, or resistance band leg presses. Glute bridges and hamstring curls also build stability without overloading the joint. Always prioritize controlled motion over heavy weights.
Should I avoid squats entirely if I experience discomfort?
Not necessarily. Modify depth, stance width, or use box squats to reduce strain. Pair with mobility work for hips and ankles. If pain persists despite adjustments, consult a physical therapist for personalized guidance.
When should I use the R.I.C.E. method?
Apply rest, ice, compression, and elevation immediately after acute flare-ups or minor injuries. This reduces inflammation and swelling. Chronic issues may require targeted rehab exercises alongside these measures.
Can tight hips contribute to front knee pain?
Absolutely. Limited hip mobility forces the joint to compensate during squats, increasing stress on the patellar tendon or cartilage. Regular stretching for hip flexors and IT bands often alleviates this strain.
Are knee sleeves helpful for squatting?
Sleeves provide mild compression and warmth, improving proprioception. However, they’re not a substitute for proper form or strength training. Use them as a temporary aid while addressing underlying imbalances.