Knee pain clicking is a common issue that many people experience. It can be caused by various factors and can lead to discomfort and limited mobility. In this article, we will explore the causes and treatments for knee pain clicking, as well as ways to prevent it. Understanding the underlying causes and available treatment options can help individuals manage and alleviate their knee pain clicking symptoms. Here are the key takeaways from this article:
Key Takeaways
- Knee pain clicking can be caused by factors such as cartilage damage, ligament injuries, or muscle imbalances.
- Common symptoms of knee pain clicking include popping or clicking sounds, pain, swelling, and instability.
- Diagnosing knee pain clicking may involve a physical examination, imaging tests, and other diagnostic procedures.
- Treatment options for knee pain clicking include conservative treatments, medications, physical therapy, and surgical interventions.
- Preventing knee pain clicking can be achieved by maintaining a healthy weight, strengthening the muscles around the knee, and avoiding overuse and high-impact activities.
Understanding Knee Pain Clicking
What is Knee Pain Clicking?
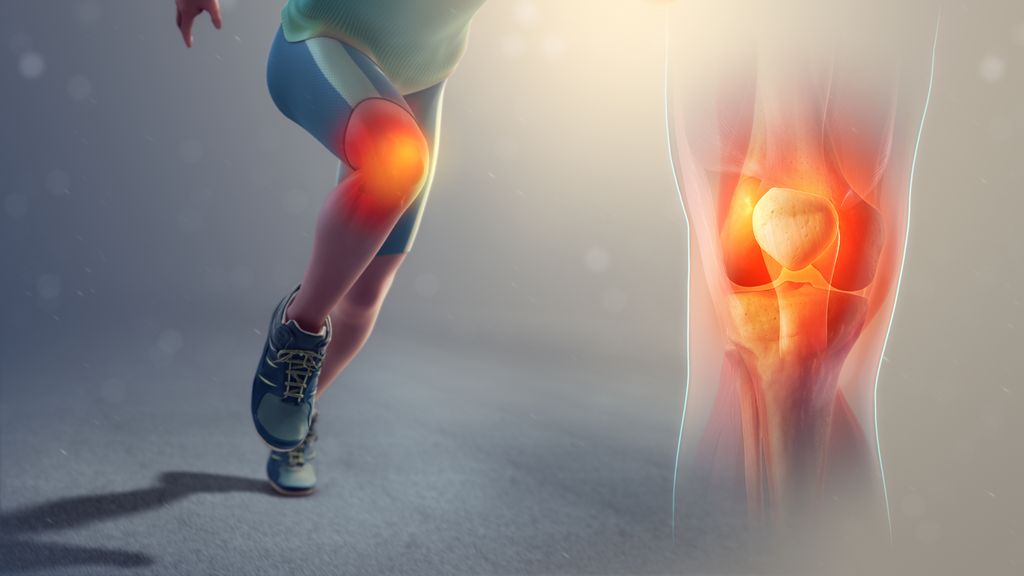
Knee pain clicking is a common symptom experienced by individuals with knee problems. It refers to a clicking or popping sound that occurs when the knee is in motion. The clicking sound is often accompanied by a sensation of the knee joint catching or locking. While knee pain clicking is not always a cause for concern, it can be indicative of an underlying issue with the knee joint or surrounding structures.
To better understand knee pain clicking, it is important to consider the anatomy of the knee joint. The knee is a complex joint that consists of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. When these structures are not functioning properly, they can cause the knee to click or pop during movement.
It is important to note that knee pain clicking can vary in severity and frequency. Some individuals may only experience occasional clicking, while others may have persistent clicking with every movement. If you are experiencing knee pain clicking, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Causes of Knee Pain Clicking
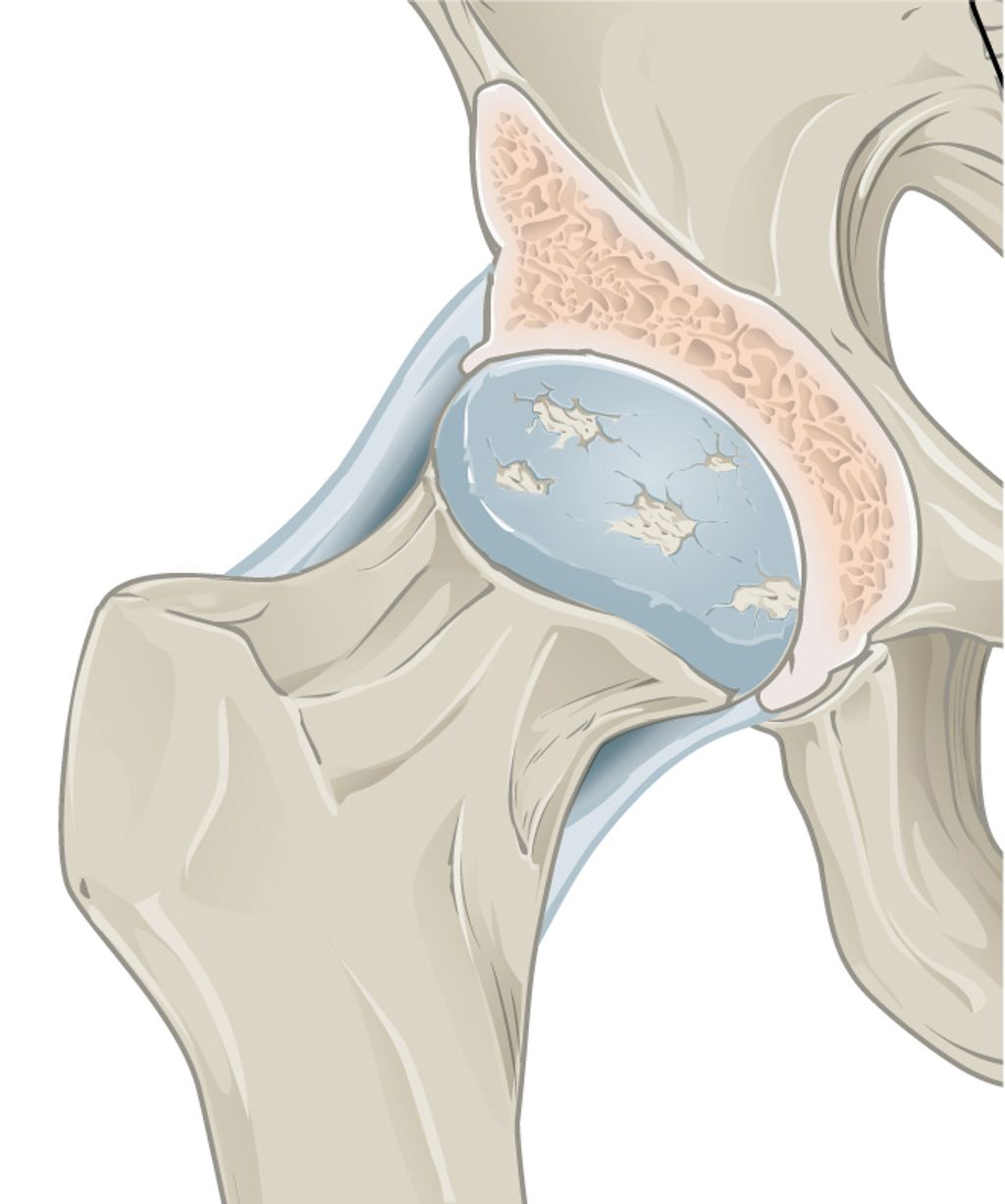
Knee pain clicking can be caused by a variety of factors. Joint misalignment, cartilage damage, and ligament injuries are common causes of this condition. Additionally, overuse and repetitive movements can contribute to the development of knee pain clicking. It is important to note that age and genetics can also play a role in the onset of this condition.
In some cases, knee pain clicking may be a result of meniscus tears or loose bodies within the joint. These structural abnormalities can cause the knee to click or pop during movement. Arthritis and inflammation in the knee joint can also lead to clicking sensations.
To determine the exact cause of knee pain clicking, a thorough physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be necessary. Other diagnostic procedures, such as arthroscopy, may also be performed to assess the condition of the knee joint.
Common Symptoms of Knee Pain Clicking
Knee pain clicking can be accompanied by a variety of symptoms that can vary in severity and frequency. Pain is one of the most common symptoms experienced by individuals with knee pain clicking. The pain may be sharp or dull and can occur during movement or at rest. Swelling is another common symptom, which is often accompanied by redness and warmth around the knee joint. Stiffness is also frequently reported, making it difficult to fully bend or straighten the knee. Other symptoms may include a grinding sensation when moving the knee, instability or a feeling that the knee may give way, and limited range of motion. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment options.
- Pain: Sharp or dull, during movement or at rest
- Swelling: Accompanied by redness and warmth
- Stiffness: Difficulty bending or straightening the knee
- Grinding sensation: When moving the knee
- Instability: Feeling that the knee may give way
- Limited range of motion
Tip: If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice to prevent further complications and ensure proper treatment.
Diagnosing Knee Pain Clicking
Physical Examination
During a physical examination for knee pain clicking, the healthcare provider will carefully assess the knee joint and surrounding structures. They will look for any visible signs of inflammation, swelling, or deformity. Range of motion of the knee will be tested to evaluate any limitations or abnormalities. The provider may also perform specific tests, such as the Lachman test or McMurray test, to assess the stability of the knee joint and identify any ligament or meniscus injuries.
In addition to the visual and manual examination, the healthcare provider may also ask the patient about their medical history, previous injuries, and any specific activities or movements that exacerbate the clicking sensation. This information helps in determining the possible causes and appropriate treatment options for the knee pain clicking.
It is important to note that a physical examination alone may not provide a definitive diagnosis. Additional imaging tests and diagnostic procedures may be necessary to confirm the underlying cause of the knee pain clicking.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests play a crucial role in diagnosing knee pain clicking. These tests allow healthcare professionals to get a detailed view of the internal structures of the knee joint. X-rays are commonly used to assess the bones and detect any abnormalities, such as fractures or bone spurs. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is another valuable tool that provides a more comprehensive evaluation of the soft tissues, including the ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. MRI can help identify issues like meniscal tears or ligament damage. Additionally, ultrasound may be used to examine the soft tissues and assess the movement of structures within the knee. It is a non-invasive and cost-effective imaging technique. Overall, these imaging tests aid in determining the underlying cause of knee pain clicking and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
Other Diagnostic Procedures
In addition to physical examination and imaging tests, there are other diagnostic procedures that can help identify the cause of knee pain clicking. These procedures may include:
-
Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera into the knee joint to visualize the structures and identify any abnormalities.
-
Joint aspiration: This procedure involves removing a small sample of fluid from the knee joint to analyze for signs of infection or inflammation.
-
Blood tests: Certain blood tests can help determine if there are any underlying conditions contributing to knee pain clicking.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine which diagnostic procedures are appropriate for your specific case of knee pain clicking.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain Clicking
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense for managing knee pain clicking. These treatments focus on non-invasive methods to reduce pain and improve function. Rest is an important component of conservative treatment, as it allows the knee joint to heal and reduces stress on the affected area. Ice therapy can also be beneficial in reducing inflammation and providing temporary pain relief.
In addition to rest and ice, physical therapy plays a crucial role in conservative treatment. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint stability. This can help alleviate clicking and prevent further damage.
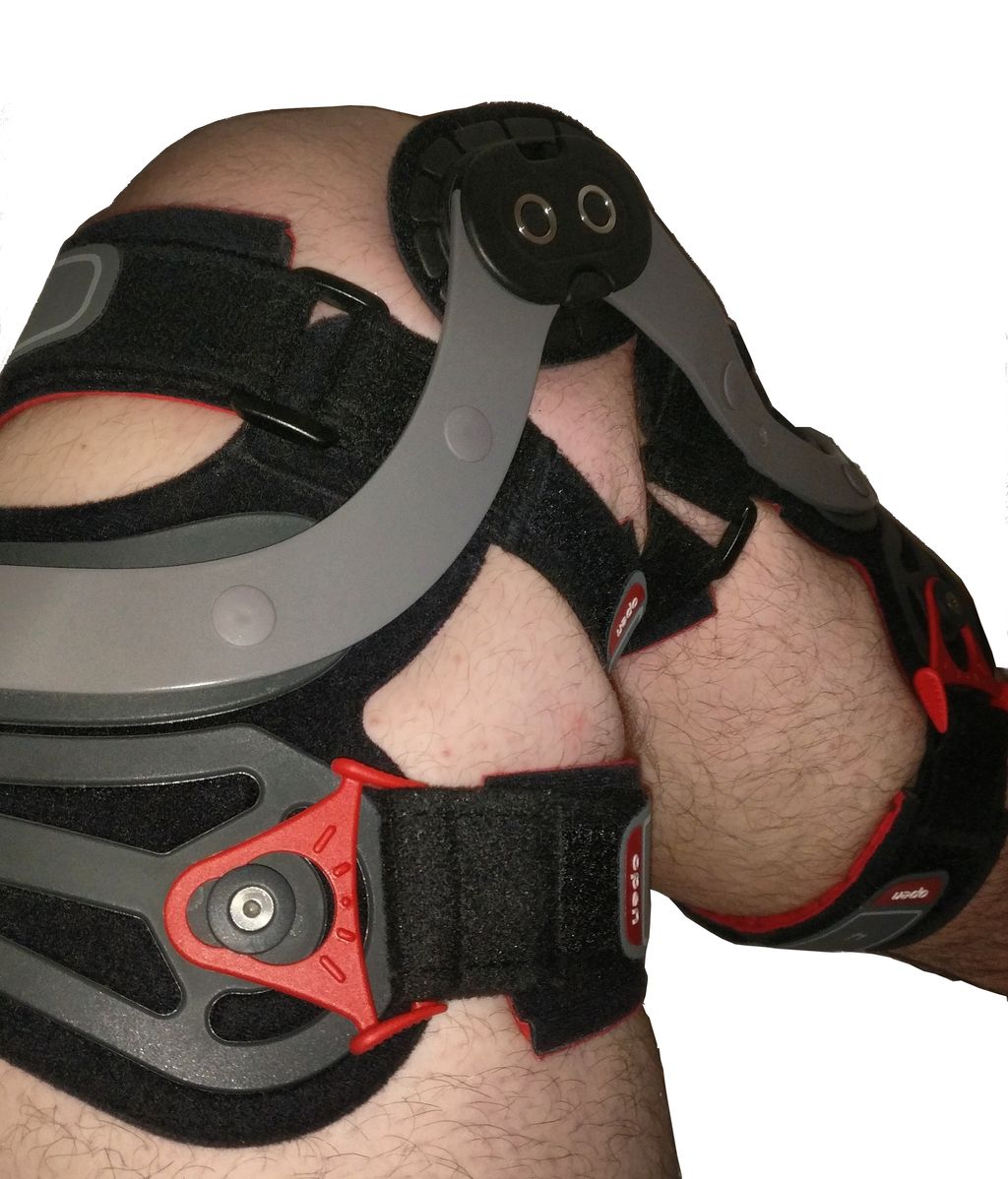
Bracing is another conservative treatment option that can provide support and stability to the knee joint. A knee brace can help reduce excessive movement and alleviate clicking during activities.
It’s important to note that conservative treatments may not completely eliminate knee pain clicking, but they can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life.
Medications
Medications can be an effective treatment option for managing knee pain clicking. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. These medications are available over-the-counter or by prescription. Corticosteroid injections may also be recommended to reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. However, it’s important to note that medications only provide temporary relief and do not address the underlying cause of knee pain clicking.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication regimen. They can assess your specific condition and recommend the most appropriate medication and dosage for your needs. Additionally, they can monitor your progress and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Important Tip: While medications can help manage knee pain clicking, it’s crucial to combine them with other treatment approaches, such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications, for optimal results.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a crucial component of the treatment plan for knee pain clicking. It focuses on improving the strength, flexibility, and stability of the muscles around the knee joint. Exercises that target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can help alleviate pain and reduce clicking sensations. Stretching exercises are also beneficial for improving joint mobility and reducing stiffness.
In addition to exercises, physical therapists may use manual therapy techniques to address any joint or soft tissue restrictions. These techniques can include joint mobilization, soft tissue massage, and stretching. Modalities such as heat or ice therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation may also be used to manage pain and inflammation.
A physical therapist will work closely with the patient to develop an individualized treatment plan based on their specific needs and goals. Regular sessions with a physical therapist can help improve knee function, reduce pain, and minimize clicking sensations.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are typically considered as a last resort for treating knee pain clicking. Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat knee problems. During arthroscopy, a small camera is inserted into the knee joint, allowing the surgeon to view and repair any damaged structures. In more severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary. This involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial joint. While surgical interventions can provide relief for some individuals, they come with risks and a longer recovery period. It is important to discuss the potential benefits and drawbacks with a healthcare professional before considering surgery.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that allows the surgeon to view and repair knee joint problems.
- Joint replacement surgery: Involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial joint.
Tip: Surgical interventions should only be considered after exhausting conservative treatments and non-invasive options.
Preventing Knee Pain Clicking
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing knee pain clicking. Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, which can worsen the clicking sensation and lead to further discomfort. Losing weight through a combination of healthy eating and regular exercise can help reduce the strain on the knees.
In addition to weight management, it is important to stay active and engage in low-impact exercises that promote joint flexibility and muscle strength. Activities such as swimming and cycling are gentle on the knees while still providing a good workout.
To support weight loss and overall joint health, it is recommended to include foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties in your diet. These include omega-3 fatty acids found in fish, turmeric, and ginger. These natural ingredients can help reduce inflammation and alleviate knee pain clicking.
Remember, maintaining a healthy weight is not only beneficial for managing knee pain clicking but also for overall well-being.
Strengthening the Muscles around the Knee
Strengthening the muscles around the knee is an important aspect of managing knee pain clicking. Regular exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can help improve the stability and support of the knee joint. Strength training exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg presses can be beneficial.
In addition to strength training, low-impact exercises like swimming and cycling can also help strengthen the muscles without putting excessive stress on the knee joint. These exercises can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of further injury.
It is important to start with light weights and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises. Proper form and technique should be maintained to avoid putting unnecessary strain on the knee.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercise program to ensure it is appropriate for your specific condition and needs.
Avoiding Overuse and High-Impact Activities
When it comes to preventing knee pain clicking, it is important to avoid overuse and high-impact activities. Overuse of the knee joint can lead to inflammation and irritation, which can contribute to the clicking sensation. Similarly, high-impact activities such as running or jumping can put excessive stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of clicking and discomfort.
To protect your knees and reduce the likelihood of clicking, consider the following tips:
- Modify your exercise routine: If you regularly engage in activities that involve repetitive knee movements, try incorporating low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling into your routine. This can help reduce the strain on your knees while still allowing you to stay active.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any discomfort or pain in your knees during or after physical activity. If you experience clicking or other symptoms, it may be a sign that you need to modify your activities or take a break.
- Use proper form: When participating in sports or exercises, make sure you use proper technique and form to minimize stress on your knees. This includes using appropriate footwear and equipment, as well as warming up and stretching before physical activity.
By following these tips and being mindful of your knee health, you can help prevent knee pain clicking and maintain the overall health and function of your knees.
Conclusion
In conclusion, knee pain clicking can be caused by various factors such as cartilage damage, ligament sprains, and meniscus tears. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent knee pain clicking, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further damage. Treatment options may include physical therapy, medications, and in severe cases, surgery. Remember to listen to your body and take necessary precautions to avoid knee injuries. With proper care and treatment, you can alleviate knee pain clicking and improve your overall knee health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is knee pain clicking?
Knee pain clicking is a condition where the knee joint produces clicking or popping sounds during movement.
What causes knee pain clicking?
Knee pain clicking can be caused by various factors such as cartilage damage, meniscus tears, ligament injuries, or joint misalignment.
What are the common symptoms of knee pain clicking?
Common symptoms of knee pain clicking include clicking or popping sounds, pain, swelling, instability, and limited range of motion.
How is knee pain clicking diagnosed?
Knee pain clicking can be diagnosed through a physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI, and other diagnostic procedures like arthroscopy.
What are the treatment options for knee pain clicking?
Treatment options for knee pain clicking include conservative treatments like rest and ice, medications, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical interventions.
How can knee pain clicking be prevented?
Knee pain clicking can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, strengthening the muscles around the knee through exercises, and avoiding overuse and high-impact activities.