Knee Stiffness: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Knee stiffness is a common complaint that affects people of all ages. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, and overuse. Knee stiffness can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires medical attention, or it may be a minor issue that can be managed with self-care.

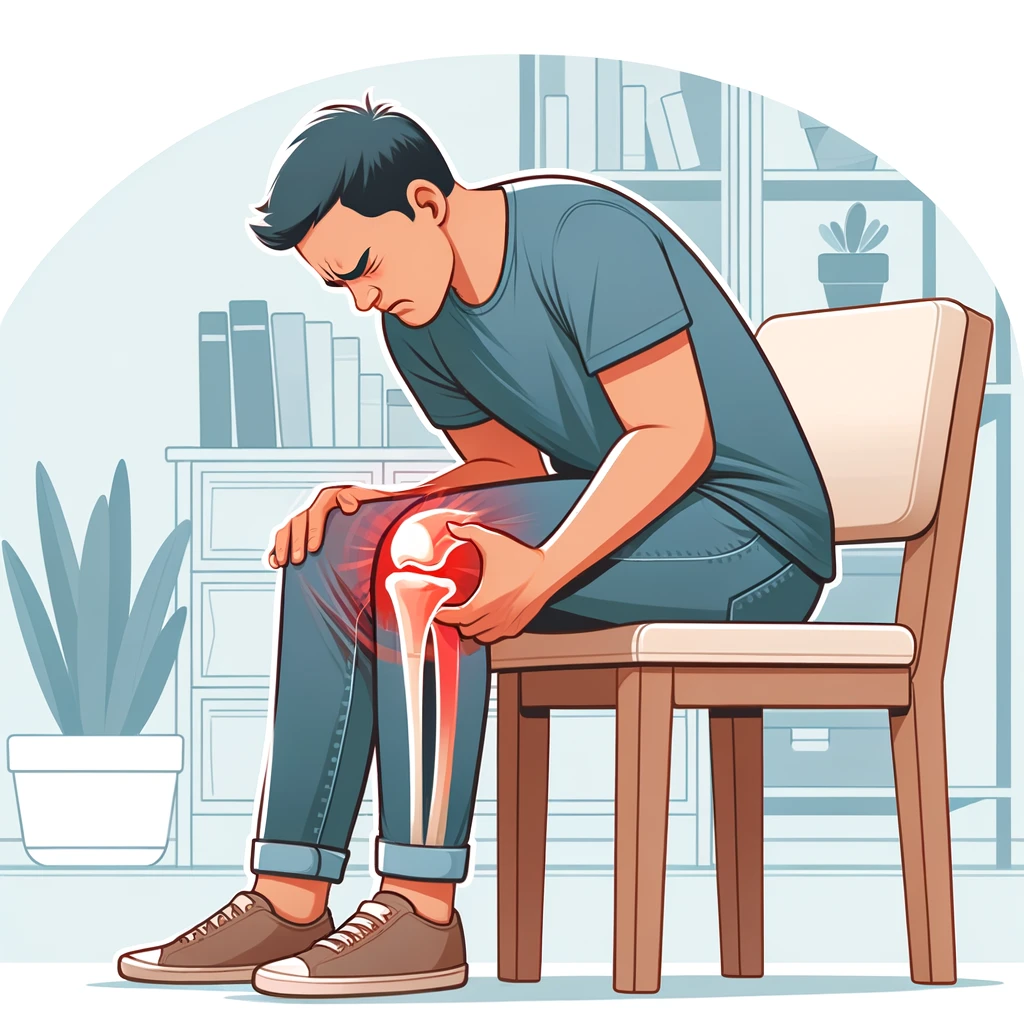
Understanding Knee Stiffness Knee stiffness is a feeling of tightness or restriction in the knee joint that makes it difficult to move the knee through its full range of motion. It can be accompanied by pain, swelling, and tenderness. Knee stiffness can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, and overuse. In some cases, knee stiffness may be a sign of an underlying condition that requires medical attention, such as a torn ligament or meniscus.
Common Causes of Knee Stiffness There are many different things that can cause knee stiffness, including injury, arthritis, and overuse. Injuries to the knee can cause swelling and inflammation, which can lead to stiffness. Arthritis is another common cause of knee stiffness, particularly in older adults. Overuse injuries, such as those that occur with repetitive activities like running or jumping, can also cause knee stiffness. Other causes of knee stiffness include obesity, muscle weakness, and poor flexibility.
Key Takeaways
- Knee stiffness is a feeling of tightness or restriction in the knee joint that can be caused by a variety of factors.
- Common causes of knee stiffness include injury, arthritis, and overuse.
- Treatment for knee stiffness depends on the underlying cause and may include self-care, medication, physical therapy, or surgery.
Understanding Knee Stiffness
Knee stiffness refers to a decreased range of motion in the knee joint, which can cause discomfort and limit movement. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, surgery, arthritis, and aging.
The knee joint is a complex joint that is made up of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. It is designed to provide stability and support while allowing for a wide range of movement. When the knee joint is stiff, it can be difficult to move the knee through its full range of motion.
Flexibility is an important factor in preventing knee stiffness. Regular stretching and exercise can help to improve flexibility and prevent stiffness from occurring. Maintaining a healthy weight can also help to reduce the risk of knee stiffness, as excess weight can put additional strain on the knee joint.
It is important to note that some degree of knee stiffness is normal, especially as we age. However, if knee stiffness is causing significant discomfort or limiting your ability to perform normal activities, it is important to seek medical attention.
In summary, knee stiffness can be caused by a variety of factors and can limit movement and cause discomfort. Regular exercise and stretching can help to prevent knee stiffness, while seeking medical attention is important if knee stiffness is causing significant discomfort or limiting normal activities.
Common Causes of Knee Stiffness
Knee stiffness can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, and overuse. In this section, we will explore some of the most common causes of knee stiffness and their associated symptoms.
Injury and Trauma
Injuries to the knee can cause stiffness, as well as pain and swelling. Common knee injuries include sprains, tears, and ruptures of the ligaments or meniscus. In some cases, knee stiffness may be the result of a fracture or dislocation. If you have recently suffered an injury to your knee and are experiencing stiffness, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the extent of the damage and receive appropriate treatment.
Arthritis and Autoimmune Conditions
Arthritis and other autoimmune conditions can also cause knee stiffness. Osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis, occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time, causing pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and joint damage throughout the body, including the knee. Other autoimmune conditions that can cause knee stiffness include lupus and psoriatic arthritis.
Age and Overuse
As we age, our joints can become stiffer and less flexible, making them more susceptible to injury and stiffness. Overuse of the knee joint can also cause stiffness, particularly in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive activities that put strain on the knee. In some cases, knee stiffness may be the result of wear and tear on the joint over time.
In summary, knee stiffness can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, and overuse. If you are experiencing knee stiffness, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Knee Stiffness

Knee stiffness can be a common problem that can limit a person’s mobility. It can occur due to a variety of reasons such as injury, overuse, or degenerative conditions. In this section, we will discuss the symptoms and diagnosis of knee stiffness.
Identifying Symptoms
The symptoms of knee stiffness can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain in the knee
- Swelling around the knee
- Stiffness in the knee joint
- Instability or weakness in the knee
- Warmth, tenderness, or redness around the knee joint
- Popping or cracking sounds when moving the knee joint
- Fever (in rare cases)
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a doctor.
Diagnostic Procedures
To diagnose knee stiffness, a doctor will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history. They may also order imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs to get a better view of the knee joint. These tests can help identify any underlying conditions such as arthritis, ligament tears, or cartilage damage.
In some cases, a doctor may also recommend a diagnostic arthroscopy. This is a minimally invasive procedure where a small camera is inserted into the knee joint to examine the tissues and structures.
It is important to identify the underlying cause of knee stiffness to determine the appropriate treatment plan. Some risk factors for knee stiffness include previous knee injuries, overuse, obesity, and muscle imbalances such as tight hamstrings.
In conclusion, identifying the symptoms and getting a proper diagnosis is crucial in treating knee stiffness. If you experience any symptoms, consult with a doctor to determine the underlying cause and the best course of treatment.
Treatment and Management of Knee Stiffness

When it comes to treating knee stiffness, there are a variety of options available. In this section, we will cover non-surgical treatments and surgical interventions.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Rest is a crucial component of treating knee stiffness. It is important to avoid activities that aggravate the injury and to take breaks when necessary. Cushioning the knee with a soft pad or pillow can also help alleviate discomfort.
Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility. Knee braces can provide additional support and stability, and compression and elevation can reduce swelling.
Medications such as corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation, and injections of hyaluronic acid can help lubricate the joint. Home remedies such as ice and heat therapy can also provide relief.
Surgical Interventions
If non-surgical treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgery may be necessary. Knee replacement surgery involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one. Torn meniscus and fractures may also require surgical intervention.
In some cases, gout or septic arthritis may cause knee stiffness. In these cases, lab tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the stiffness.
It is important to consult with an orthopedic surgeon to determine the best course of action for treating knee stiffness. Complications can arise from surgery, so it is important to weigh the risks and benefits carefully.
Overall, there are a variety of treatment options available for knee stiffness. With the right combination of rest, therapy, and possibly surgery, most cases can be effectively managed.
Frequently Asked Questions

How do you treat knee stiffness at home?
There are several ways to treat knee stiffness at home. Resting and elevating the affected knee can help reduce swelling and inflammation. Applying ice to the knee can also help relieve pain and stiffness. Gentle stretching exercises and light physical activity, such as walking, can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness over time.
What are the causes of knee stiffness?
Knee stiffness can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, arthritis, and other medical conditions. In some cases, knee stiffness may be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as a torn ligament or meniscus.
What are the symptoms of a stiff knee?
The most common symptom of a stiff knee is difficulty moving the joint. Other symptoms may include pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area. In some cases, the knee may also feel warm to the touch.
What is the best medicine for knee stiffness?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the best medicine for knee stiffness will depend on the underlying cause of the condition. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may be effective in reducing pain and inflammation. In some cases, prescription medications or injections may be necessary to manage more severe symptoms.
How can knee stiffness after sitting be prevented?
To prevent knee stiffness after sitting for extended periods of time, it is important to take frequent breaks and stretch your legs and knees regularly. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can also help reduce the risk of knee stiffness and related conditions.
At what age do knee problems commonly start?
Knee problems can occur at any age, but they are most common in older adults. As we age, the cartilage in our knees can begin to wear down, leading to stiffness, pain, and other symptoms. However, knee problems can also occur in younger adults and children as a result of injury or other medical conditions.