Knee Decreased Range of Motion: Causes and Treatment Options
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, including a decrease in joint mobility. Knee joint mobility, in particular, is crucial for performing daily activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. A decrease in knee range of motion can significantly impact our quality of life, making it difficult to perform even the simplest of tasks.

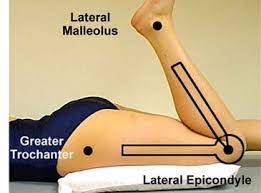
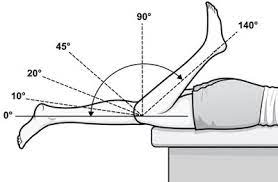
Understanding the knee joint and its range of motion is essential to identify the cause of decreased mobility. The knee joint is a complex hinge joint that connects the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone). It is made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that work together to provide stability and mobility. The normal range of motion for the knee joint is between 0-140 degrees, allowing for flexion and extension of the leg.
Common conditions leading to decreased knee range of motion include arthritis, injury, and surgery. Arthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes inflammation and pain in the knee joint, leading to decreased range of motion. Injury or trauma to the knee, such as a fracture or ligament tear, can also result in decreased mobility. Surgery, such as knee replacement or reconstruction, may cause temporary or permanent loss of knee range of motion.
Understanding Knee Joint and Its Range of Motion
The knee joint is a complex joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shinbone (tibia). It is a hinge joint that allows for movement in two directions: flexion (bending) and extension (straightening). The knee joint also has a small amount of rotation, which allows for twisting movements of the leg.
Normal Range of Motion
The normal range of motion (ROM) for the knee joint is between 0 and 135 degrees. This means that the knee can fully extend (straighten) to 0 degrees and can flex (bend) up to 135 degrees. The normal ROM of the knee joint is essential for daily activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Factors Affecting Range of Motion
Several factors can affect the ROM of the knee joint. These include:
- Age: As we age, the knee joint can become stiffer, reducing the ROM.
- Injury: An injury to the knee joint, such as a ligament tear, can limit the ROM.
- Surgery: Knee surgery can also limit the ROM of the joint.
- Arthritis: Arthritis can cause inflammation and damage to the knee joint, which can limit the ROM.
Maintaining good knee health is essential to ensure proper knee ROM. Regular exercise, stretching, and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve knee ROM.
In conclusion, understanding the knee joint and its ROM is crucial in maintaining good knee health. Knowing the normal ROM of the knee joint and the factors that can affect it can help individuals take steps to improve their knee health and prevent knee-related issues.
Common Conditions Leading to Decreased Knee Range of Motion

Decreased knee range of motion can be caused by a variety of conditions, including injuries and diseases, as well as degenerative conditions. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common conditions that can lead to decreased knee range of motion.
Injuries and Diseases
Injuries and diseases are some of the most common causes of decreased knee range of motion. Knee injuries, such as meniscus tears, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries, and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injuries, can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling, which can limit your range of motion. Infections, inflammation, and autoimmune conditions can also cause knee swelling and stiffness, leading to decreased range of motion.
Degenerative Conditions
Degenerative conditions, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can cause joint pain, inflammation, and stiffness, which can limit your range of motion. Arthrofibrosis, a condition where scar tissue forms in the knee joint, can also cause decreased range of motion. Bone spurs and osteophytes, which are bony growths that can develop in the knee joint, can also limit your range of motion.
Overall, there are many conditions that can cause decreased knee range of motion. If you are experiencing knee pain, stiffness, or swelling, it is important to see a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Decreased Knee Range of Motion
When a patient presents with decreased knee range of motion, we must first diagnose the underlying cause before selecting an appropriate treatment plan. Diagnosis methods typically involve a physical examination, X-rays, and the use of a goniometer to measure the degree of motion.
Diagnosis Methods
During a physical examination, we assess the patient’s knee for any visible deformities, swelling, or misalignment. We also check for signs of muscle weakness or tearing, strain, sprain, or rupture. X-rays are used to visualize any fractures or dislocations, while a goniometer is used to measure the degree of motion in the knee joint.
Treatment Options
Once the underlying cause has been identified, we can select an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment options may include physical therapy, surgery, or medication. Physical therapy is often used to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve alignment, and increase range of motion. Strengthening exercises can be used to improve muscle strength, while shock absorbers can be used to reduce impact on the knee joint during physical activity.
In more severe cases, knee surgeries such as knee replacement may be necessary. Medication may also be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. Rehabilitation is often required after surgery to aid in the healing process and restore full range of motion.
In conclusion, decreased knee range of motion can be caused by a variety of factors, from muscle weakness to fractures or dislocations. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for restoring full function to the knee joint. By utilizing a combination of physical therapy, surgery, and medication, we can effectively manage this condition and help patients regain their mobility.
Prevention and Rehabilitation

To prevent decreased range of motion in the knee, we recommend taking proactive steps to maintain knee health. This includes maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint and ensuring proper movement and alignment during physical activities.
Regular stretching and exercises to improve knee flexion and strengthen the muscles and tendons around the knee can also help prevent knee injuries and reduce the risk of decreased range of motion.
If you are experiencing reduced range of motion or knee instability, rehabilitation exercises can help improve knee stability and flexibility. This may include exercises to strengthen the thigh and shin muscles, improve muscle stiffness, and reduce restriction and wear and tear on the knee joint.
In addition to exercises, we may recommend the use of braces or other supportive devices to provide additional stability during physical activities. It is also important to avoid activities that exacerbate knee pain or instability, such as excessive bending or climbing stairs.
Overall, taking proactive steps to maintain knee health and seeking rehabilitation when necessary can help prevent and treat decreased range of motion in the knee.
Frequently Asked Questions

What limits the range of motion around a joint such that damage to the area is prevented?
The range of motion around a joint is limited by the surrounding ligaments, tendons, and muscles. These soft tissues provide stability to the joint and prevent damage to the area.
What are some of the most common causes of reduced range of motion?
Reduced range of motion can be caused by injury, inflammation, or degeneration of the joint. Other factors that can contribute to reduced range of motion include muscle weakness or stiffness, poor posture, and lack of physical activity.
How do I restore the range of motion in my knee?
Restoring range of motion in the knee can be achieved through a combination of stretching and strengthening exercises. Physical therapy can also be helpful in restoring range of motion.
What causes decreased knee flexion?
Decreased knee flexion can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, arthritis, or muscle weakness. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to restore knee flexion.
What are the best exercises for knee range of motion?
Some of the best exercises for knee range of motion include heel slides, knee extensions, and hamstring stretches. It is important to work with a physical therapist to develop an exercise program that is tailored to your specific needs.
How to increase range of motion in knee after surgery?
After knee surgery, it is important to follow a rehabilitation program that includes both stretching and strengthening exercises. Your physical therapist will work with you to develop a program that is appropriate for your specific needs and goals.
Leave a Reply