Did you know that knee injuries account for approximately 55% of all sports-related injuries? Whether you’re an athlete or not, knee injuries can happen to anyone, and taking the right actions immediately can make a significant difference in your recovery process.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide you with essential information on knee injury treatment options, self-care tips, recovery exercises, and more. We’ll equip you with the knowledge you need to take control of your knee injury, promote healing, and get back to your active lifestyle.
Understanding Knee Injuries
Knee injuries are a common concern for many individuals, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. The knee, being the largest joint in the body, is particularly susceptible to various types of injuries due to its complex structure.
Common knee injuries include:
- Sprains
- Torn ligaments (such as the ACL or PCL)
- Strains
- Damage to the cartilage
- Torn meniscus
- Irritation to the kneecap joint
Although less common, fractures, kneecap dislocations, and knee joint dislocations can also occur.
Being aware of the symptoms and causes of knee injuries is vital in seeking appropriate medical attention and ensuring proper treatment.
Here is a summarized table detailing knee injury types, symptoms, and causes:
| Knee Injury Type | Symptoms | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Sprains | Pain, swelling, instability | Sudden twist or impact |
| Torn Ligaments (ACL, PCL) | Pain, swelling, instability, popping sound | Sudden change in direction, trauma |
| Strains | Pain, muscle weakness, limited range of motion | Overstretching or overuse of muscles |
| Cartilage Damage | Pain, swelling, clicking or locking sensation | Wear and tear, trauma |
| Torn Meniscus | Pain, swelling, stiffness, catching or locking sensation | Twisting, squatting, lifting heavy objects |
| Kneecap Joint Irritation | Pain, grinding sensation, swelling | Overuse, misalignment |
| Fractures | Pain, swelling, inability to bear weight | High force impact |
| Kneecap Dislocations | Pain, visible deformity, inability to straighten the knee | Direct blow or trauma |
| Knee Joint Dislocations | Pain, swelling, visible deformity, inability to move the knee | High force impact or trauma |
Understanding the different types of knee injuries and their associated symptoms and causes can help individuals recognize and respond promptly to potential injuries. Seeking appropriate medical attention and following recommended treatment plans are crucial in ensuring optimal recovery.
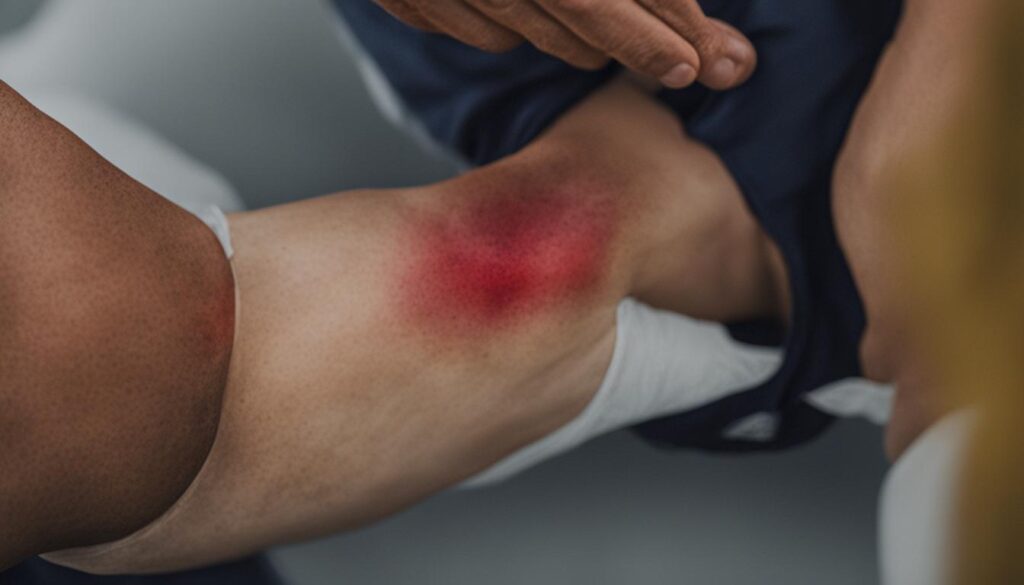
Immediate Care for Knee Injuries
When a knee injury occurs, it’s essential to provide immediate care to minimize pain and swelling. Prompt action can help alleviate discomfort and facilitate the healing process. One of the most widely recognized methods for initial treatment is the R.I.C.E. protocol, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
To properly execute the R.I.C.E. method, follow these steps:
- Rest: Avoid putting weight on the injured knee. Limit movement and activity to prevent further damage. Allow the joint to rest and heal.
- Ice: Apply ice packs or cold compresses to the injured area for approximately 20 minutes every 2 hours. Cold therapy helps reduce inflammation, swelling, and pain.
- Compression: Using a compression bandage or a knee brace, apply gentle pressure to the injured knee. Compression assists in restricting swelling, stabilizing the joint, and providing support during the recovery process.
- Elevation: Elevate the injured leg by propping it up with pillows or a cushion. Keep the knee elevated above the heart level to enhance blood flow and promote drainage, reducing swelling and pain.
It’s important to note that while waiting for medical assistance or evaluation, certain actions should be avoided to prevent worsening the injury. These include:
- Avoiding heat application to the injured knee, as it may exacerbate swelling.
- Refraining from indulging in vigorous activities or exercises that place stress on the injured knee.
- Avoiding alcohol consumption, as it can hinder the healing process and interact negatively with pain medications.
- Avoiding massaging the injured knee, as it can potentially aggravate the injury.
In addition to the R.I.C.E. method, over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can be taken to alleviate pain and discomfort. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any medication, as they can provide personalized advice and recommend the most suitable option for your specific situation.
Recovering from Knee Injuries
Immediate care sets the foundation for an effective recovery process, but it’s essential to continue managing your knee injury with appropriate measures. Depending on the severity of your injury, your healthcare provider may recommend additional treatment options, such as physiotherapy or guided rehabilitation programs.
In more severe cases, like an ACL or PCL rupture, surgical intervention might be necessary, which would require an extended period of rehabilitation. Sustaining ligament injuries may require a hinged knee brace and a carefully designed rehabilitation plan to ensure proper healing and restoration of joint functionality.
Throughout the recovery phase, it is important to strike a balance between rest and gentle exercise. Resting allows the body to heal, while specific exercises, as prescribed by a healthcare professional or physical therapist, promote strength, flexibility, and stability of the knee joint.
“Proper management and rehabilitation are crucial for a successful recovery from a knee injury.”
Hot and cold therapy can provide relief during the recovery process. Alternating between warm and cold compresses can help reduce pain and swelling, enhance circulation, and promote tissue healing. Additionally, topical pain relief gels like Voltaren gel can provide temporary acute pain relief when applied as directed.
Incorporating preventive measures into your lifestyle, such as maintaining a healthy weight, warming up and stretching before physical activities, and using proper form and protective gear, can significantly reduce the risk of sustaining knee injuries in the future.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan and to monitor your progress throughout your knee injury recovery journey. With the right care, commitment, and patience, you can restore the functionality of your knee and resume your daily activities pain-free.
Managing Knee Injuries and Recovery Tips
Proper management and rehabilitation are crucial for a successful recovery from a knee injury. When it comes to knee injury treatment, the approach depends on the severity of the injury. In most cases, physiotherapy and guided rehabilitation programs are recommended. These programs target the knee injury rehabilitation process and aim to restore strength, stability, and range of motion in the knee.
For more serious knee injuries such as ACL or PCL ruptures, knee injury surgery may be necessary. This can be followed by an extensive rehabilitation period lasting up to a year. Other ligament injuries may require wearing a hinged knee brace and undergoing rehabilitation exercises specific to the injury type.
Rest plays a crucial role in knee injury recovery. It allows the injured knee to heal and prevents aggravation of the injury. Alongside rest, exercises tailored to the individual’s condition and under the guidance of a healthcare professional are important for strengthening the muscles around the knee and promoting overall knee health. Stretching exercises also help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of future knee injuries.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight is important to minimize stress on the knee joints. Excess weight can contribute to knee pain and increase the likelihood of knee injuries. Hot and cold therapy techniques can provide relief from pain and reduce inflammation. Topical pain relief options like Voltaren gel can be used for temporary acute pain relief.
Remember, each knee injury is unique, and a personalized treatment plan is vital. Consulting with a healthcare professional who specializes in knee injuries is recommended. They can provide guidance, monitor your progress, and adjust the treatment plan as needed. By seeking proper knee injury treatment and following the recommended rehabilitation program, you can optimize your recovery and prevent future knee injuries.
FAQ
What should I do immediately after a knee injury?
The first step is to rest the injured joint. Apply ice packs for 20 minutes every 2 hours to reduce swelling. Compress the injury with a bandage and elevate your leg to further aid in reducing inflammation.
What is the R.I.C.E. method for knee injuries?
The R.I.C.E. method stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. It is a common approach to initial treatment for knee injuries. Rest the injured joint, apply ice packs, compress the injury with a bandage, and elevate the leg to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
What can I do to manage knee pain in the immediate aftermath of an injury?
While waiting for medical assistance, you can take over-the-counter pain relief medications as advised by a healthcare professional. Remember to avoid heat, massage, alcohol consumption, and activities that may aggravate the injury.
What are the common types of knee injuries?
Common knee injuries include sprains, torn ligaments (such as the ACL or PCL), strains, damage to the cartilage, torn meniscus, and irritation to the kneecap joint. Less common injuries include fractures, kneecap dislocations, and knee joint dislocations.
How are knee injuries managed and treated?
Depending on the severity of the injury, different treatment options may be recommended. Physiotherapy and guided rehabilitation programs are common for most knee injuries. More serious injuries like ACL or PCL ruptures may require surgery and an extensive rehabilitation period. Rest, exercises, stretching, and maintaining a healthy weight are important aspects of knee injury management.
How can I prevent knee injuries?
To prevent knee injuries, it’s important to maintain strong leg muscles through regular exercise. Avoid sudden movements or overexertion during physical activities. Using proper form and protective equipment during sports can also help prevent knee injuries.

Leave a Reply