Knee pain can be a debilitating condition that affects many individuals. Whether it is caused by an injury, overuse, or underlying medical conditions, managing knee pain is crucial for maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee pain. By understanding the underlying factors and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can effectively manage their knee pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the anatomy of the knee can help identify the source of knee pain.
- Common causes of knee pain include injuries, arthritis, and overuse.
- Risk factors for knee pain include age, obesity, and certain sports or activities.
- Symptoms of knee pain may include pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Diagnosing knee pain often involves physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests.
Understanding Knee Pain
Anatomy of the Knee
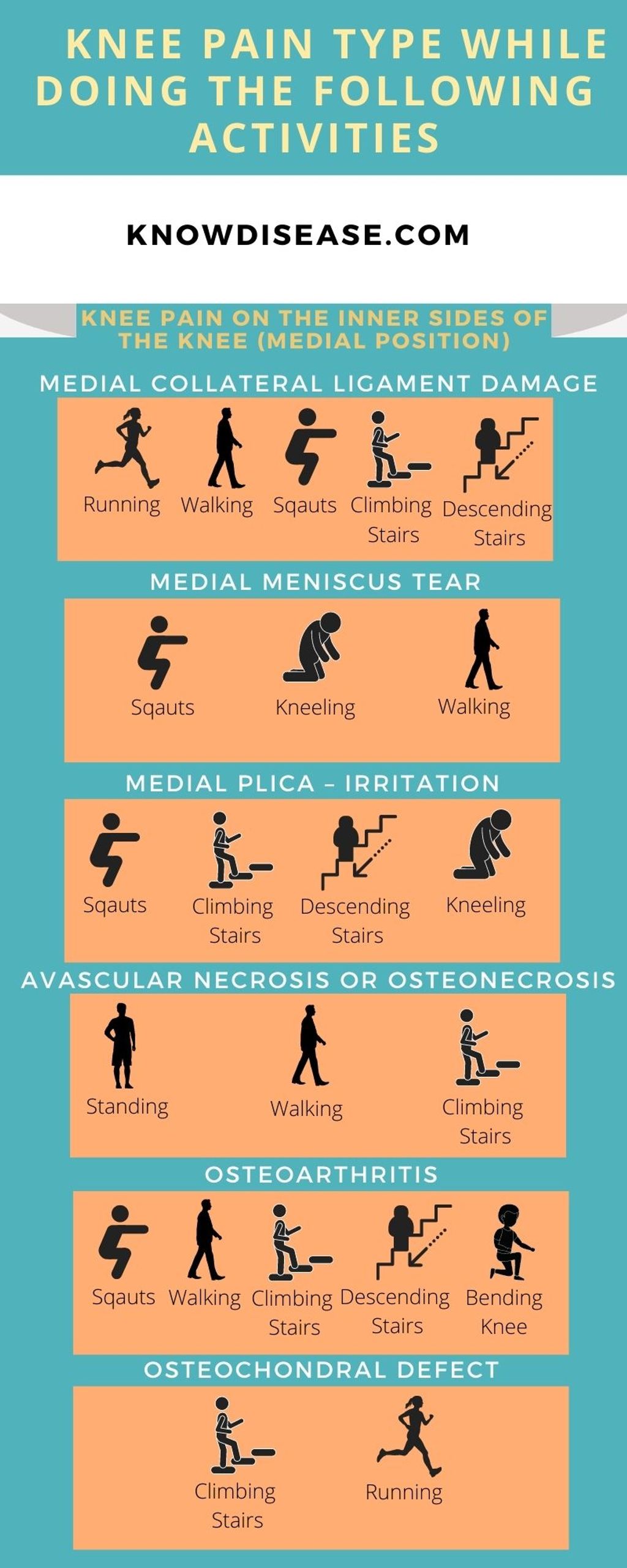
The knee is a complex joint that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). It is supported by ligaments, tendons, and muscles, which work together to provide stability and allow for movement. The knee joint is made up of three main components: the femur, the tibia, and the patella (kneecap). These components are cushioned by cartilage, which helps to absorb shock and prevent friction. The knee also contains synovial fluid, which lubricates the joint and reduces friction during movement.
In addition to its structural components, the knee also has several important structures, including the menisci, which are C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act as shock absorbers, and the cruciate ligaments, which provide stability and control the forward and backward movement of the knee. Understanding the anatomy of the knee is crucial in diagnosing and treating knee pain.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Knee pain can be caused by a variety of factors. Injury is one of the most common causes of knee pain. This can include sprains, strains, and fractures. Arthritis is another common cause of knee pain, particularly osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Other causes of knee pain include overuse, infection, and obesity.
It is important to note that knee pain can also be a symptom of an underlying condition or injury. If you are experiencing persistent or severe knee pain, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Here is a table summarizing the common causes of knee pain:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Injury | Sprains, strains, fractures |
| Arthritis | Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis |
| Overuse | Excessive use or repetitive movements |
| Infection | Bacterial or viral infection |
| Obesity | Excess weight and pressure on the knee |
Remember, proper diagnosis is key to effective treatment and management of knee pain.
Risk Factors for Knee Pain
While knee pain can occur in anyone, there are certain risk factors that may increase the likelihood of experiencing knee pain. These risk factors include:
- Age: As we age, the risk of developing knee pain increases. The wear and tear on the knee joint over time can lead to pain and discomfort.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of pain and inflammation.
- Previous Injuries: Individuals who have previously injured their knees, such as through sports or accidents, may be more prone to experiencing knee pain.
It is important to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to prevent or manage knee pain. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing proper knee care can help reduce the risk of developing knee pain.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Pain and Discomfort
Knee pain can manifest as a dull ache or sharp, stabbing pain in the knee joint. Pain is often the primary symptom experienced by individuals with knee problems. It can be localized to a specific area or radiate throughout the knee. Discomfort may worsen with movement, such as walking, running, or climbing stairs.
If you are experiencing knee pain, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Here are some common causes of knee pain:
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that causes the cartilage in the knee to wear away.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons that connect the muscles to the knee joint.
Tip: Applying ice to the affected area and resting the knee can help alleviate pain and discomfort. However, if the pain persists or worsens, seek medical attention for further evaluation and treatment options.
Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling and inflammation are common symptoms of knee pain. Swelling occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the knee joint, leading to a visible increase in size. This can make the knee feel tight and uncomfortable. Inflammation, on the other hand, refers to the body’s natural response to injury or irritation. It is characterized by redness, warmth, and tenderness around the knee. Inflammation can further contribute to swelling and pain.
To manage swelling and inflammation, it is important to follow the R.I.C.E. protocol:
- Rest: Avoid activities that put stress on the knee and worsen the swelling.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Compression: Use a compression bandage or knee brace to provide support and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Keep the affected leg elevated above the heart level to promote fluid drainage and reduce swelling.
Remember, if the swelling and inflammation persist or worsen, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment options.
Stiffness and Limited Range of Motion
Stiffness and limited range of motion are common symptoms of knee pain. Stiffness refers to a sensation of tightness or difficulty moving the knee joint. It can make it challenging to fully extend or flex the knee. Limited range of motion refers to a reduced ability to move the knee through its normal range of motion. This can make activities like walking, climbing stairs, or bending the knee more difficult.
To address stiffness and limited range of motion, it is important to incorporate gentle stretching exercises into your daily routine. These exercises can help improve flexibility and increase the range of motion in the knee joint. Additionally, physical therapy may be recommended to target specific muscle imbalances or weaknesses that contribute to stiffness and limited range of motion.
It is important to avoid activities that exacerbate the symptoms of stiffness and limited range of motion. Resting the knee and applying ice packs can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief. If the symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment options.
Diagnosing Knee Pain
Physical Examination
During a physical examination for knee pain, a healthcare professional will assess various aspects of the knee joint to determine the cause of the pain. This may involve evaluating the range of motion, checking for swelling or tenderness, and performing specific tests to assess ligament or meniscus injuries. The healthcare professional may also examine the surrounding muscles and joints to identify any contributing factors.
In addition to the physical examination, the healthcare professional may ask about the individual’s medical history, previous injuries, and any activities or movements that worsen the pain. This information helps in forming a comprehensive understanding of the knee pain and guides further diagnostic tests or treatment options.
It is important to communicate any specific concerns or symptoms experienced during the physical examination to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests play a crucial role in diagnosing knee pain. These tests allow healthcare professionals to get a detailed view of the internal structures of the knee, helping them identify any abnormalities or injuries. X-rays are commonly used to assess the bones and joints, providing valuable information about fractures, arthritis, or bone spurs. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is another commonly used imaging test that provides a more detailed view of the soft tissues, such as ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. It can help detect injuries like ligament tears or meniscus damage. Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of the knee. It is often used to evaluate soft tissue injuries, such as tendonitis or bursitis.
When interpreting the results of imaging tests, healthcare professionals consider the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and physical examination findings. It is important to note that imaging tests alone may not provide a definitive diagnosis, but they are valuable tools in the diagnostic process.
Here is a table summarizing the different imaging tests used for diagnosing knee pain:
| Imaging Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| X-ray | Assess bones and joints |
| MRI | Detailed view of soft tissues |
| Ultrasound | Evaluate soft tissue injuries |
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate imaging test based on individual circumstances and symptoms.
Tip: Imaging tests are useful in identifying the cause of knee pain, but they should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods for a comprehensive evaluation.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are an important tool in diagnosing knee pain. These tests help healthcare professionals identify underlying conditions or infections that may be causing the pain. Blood tests can detect signs of inflammation or infection, while joint fluid analysis can provide valuable information about the presence of certain diseases or conditions. Additionally, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs may be used to assess the structure of the knee joint and identify any abnormalities. It is important to note that laboratory tests alone may not provide a definitive diagnosis, but they are an essential part of the diagnostic process.
- Blood tests can detect signs of inflammation or infection.
- Joint fluid analysis can provide valuable information about the presence of certain diseases or conditions.
- Imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs may be used to assess the structure of the knee joint and identify any abnormalities.
Tip: Laboratory tests should always be interpreted in conjunction with a thorough physical examination and medical history to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
Medications
When it comes to managing knee pain, medications can play a crucial role in providing relief. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation in the knee. These medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help alleviate discomfort and improve mobility. Topical creams and ointments containing ingredients like menthol or capsaicin can also provide temporary relief by numbing the area or creating a warming sensation.
In addition to NSAIDs, corticosteroids may be prescribed for more severe cases of knee pain. These powerful anti-inflammatory medications can be injected directly into the knee joint to reduce swelling and pain. However, it’s important to note that corticosteroid injections should be used sparingly due to potential side effects.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication regimen for knee pain. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the individual’s specific condition and medical history.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a crucial component of the treatment plan for knee pain. It focuses on improving strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected knee. Exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing better support and stability. Additionally, stretching exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. Manual therapy techniques, such as joint mobilization and soft tissue massage, may also be used to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
In addition to exercises, physical therapists may also use modalities such as heat therapy or cold therapy to reduce pain and inflammation. These modalities can help promote healing and provide temporary relief. Electrical stimulation and ultrasound therapy are other techniques that may be used to manage knee pain.
It is important to follow the guidance of a qualified physical therapist and adhere to the prescribed exercises and treatment plan. Consistency and dedication to the physical therapy program can lead to significant improvements in knee pain and overall function.
Injections
Injections can be an effective treatment option for managing knee pain. Corticosteroid injections, also known as steroid injections, can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain. These injections are typically administered directly into the knee joint by a healthcare professional. Another type of injection that may be used is hyaluronic acid injections. Hyaluronic acid is a substance that occurs naturally in the body and helps lubricate the joints. These injections can help improve joint function and reduce pain. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of injections may vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause of knee pain.
When considering injections as a treatment option, it’s essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on whether injections are suitable for your specific condition and help determine the most appropriate type of injection. In some cases, a combination of different treatments, including injections, may be recommended to manage knee pain effectively.
Important Tips:
- Follow the healthcare professional’s instructions for post-injection care.
- Be aware of any potential side effects or complications associated with the injections.
- Keep track of any changes in symptoms or pain levels and communicate them to your healthcare provider.
Surgery
Surgery is considered as a last resort for treating knee pain when other conservative treatments have failed to provide relief. Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat knee problems. During this procedure, a small camera is inserted into the knee joint through a small incision, allowing the surgeon to view and repair any damage. In more severe cases, total knee replacement may be necessary. This involves removing the damaged knee joint and replacing it with an artificial joint. The decision to undergo surgery should be carefully considered and discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to diagnose and treat knee problems.
- Total knee replacement: A surgical procedure to replace the damaged knee joint with an artificial joint.
Tip: Surgery should only be considered after exhausting all other non-invasive treatment options and consulting with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing knee pain requires understanding the causes and symptoms and implementing appropriate treatments. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. By taking proactive steps, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and using proper techniques during physical activities, individuals can reduce the risk of knee pain and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, early intervention and self-care are key to managing knee pain effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of knee pain?
Common causes of knee pain include injuries, arthritis, overuse, and obesity.
How can I relieve knee pain at home?
You can try resting, applying ice or heat, taking over-the-counter pain medications, and doing gentle exercises.
When should I see a doctor for knee pain?
You should see a doctor if you experience severe pain, swelling, inability to bear weight, or if your knee pain persists for more than a few days.
What are the treatment options for knee arthritis?
Treatment options for knee arthritis include medications, physical therapy, injections, and in severe cases, surgery.
Can knee pain be prevented?
While not all knee pain can be prevented, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding excessive strain on the knees can help reduce the risk.
What exercises can I do to strengthen my knees?
Exercises such as leg raises, squats, lunges, and hamstring curls can help strengthen the muscles around the knees.
Leave a Reply