Welcome to our comprehensive guide on knee osteoarthritis and its impact on the whole body. Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a common condition, primarily affecting the elderly, and it can have a significant effect on joint health and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for knee OA, with a focus on addressing the whole body impact of this degenerative joint disease.
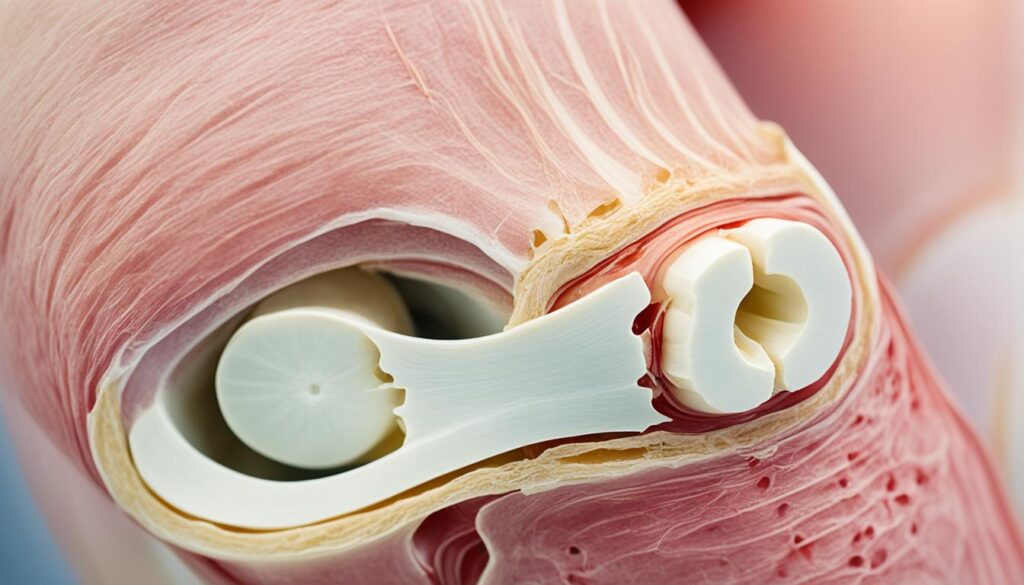
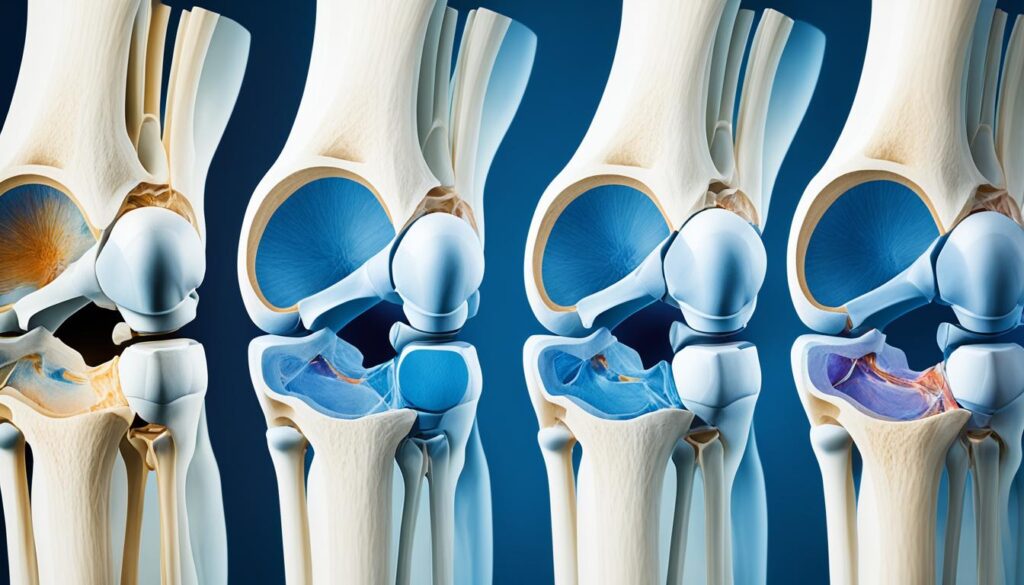
Knee osteoarthritis is characterized by the progressive loss of articular cartilage in the knee joint, leading to symptoms like knee pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility. While this condition primarily affects the knee joint, it can also have broader implications for the entire body. By understanding the whole body impact of knee OA, we can develop comprehensive strategies for managing symptoms, improving joint health, and finding effective knee pain relief.
In the sections to come, we will delve into the causes and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis, the symptoms and diagnosis process, as well as the various treatment options available. We will also explore how knee OA can have a ripple effect on other aspects of our physical and mental well-being. So, let’s embark on this journey to enhance our understanding of knee osteoarthritis and equip ourselves with valuable knowledge to better manage this condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) can have various causes and risk factors that contribute to its development and progression. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective prevention and early intervention strategies.
Primary and Secondary Causes
Knee OA can be classified into two main types: primary and secondary.
Primary knee OA occurs due to age-related degeneration and wear and tear on the joint over time. As we age, the cartilage in our knees naturally deteriorates, leading to the development of OA.
Secondary knee OA is caused by specific factors other than natural aging. These factors include previous joint injuries, obesity, repetitive stress on the knee joint, and certain metabolic diseases like diabetes and gout.
Risk Factors for Knee Osteoarthritis
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing knee OA:
- Older age: Knee OA becomes more common as we get older.
- Being female: Women are more likely to develop knee OA compared to men.
- Genetics: Certain genes can make individuals more susceptible to knee OA.
- Bone deformities: Structural abnormalities in the knee, such as bowed legs or abnormal knee joints, can increase the risk of OA.
Visually Appealing Table
| Risk Factors | Impact |
|---|---|
| Older Age | Increased likelihood of knee OA |
| Being Female | Higher risk of developing knee OA |
| Genetics | Increased susceptibility to knee OA |
| Bone Deformities | Higher risk of knee OA |
Understanding the causes and risk factors of knee OA enables individuals to take proactive measures to minimize their risk of developing the condition. It also emphasizes the importance of early intervention and targeted treatments for managing knee OA effectively.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis
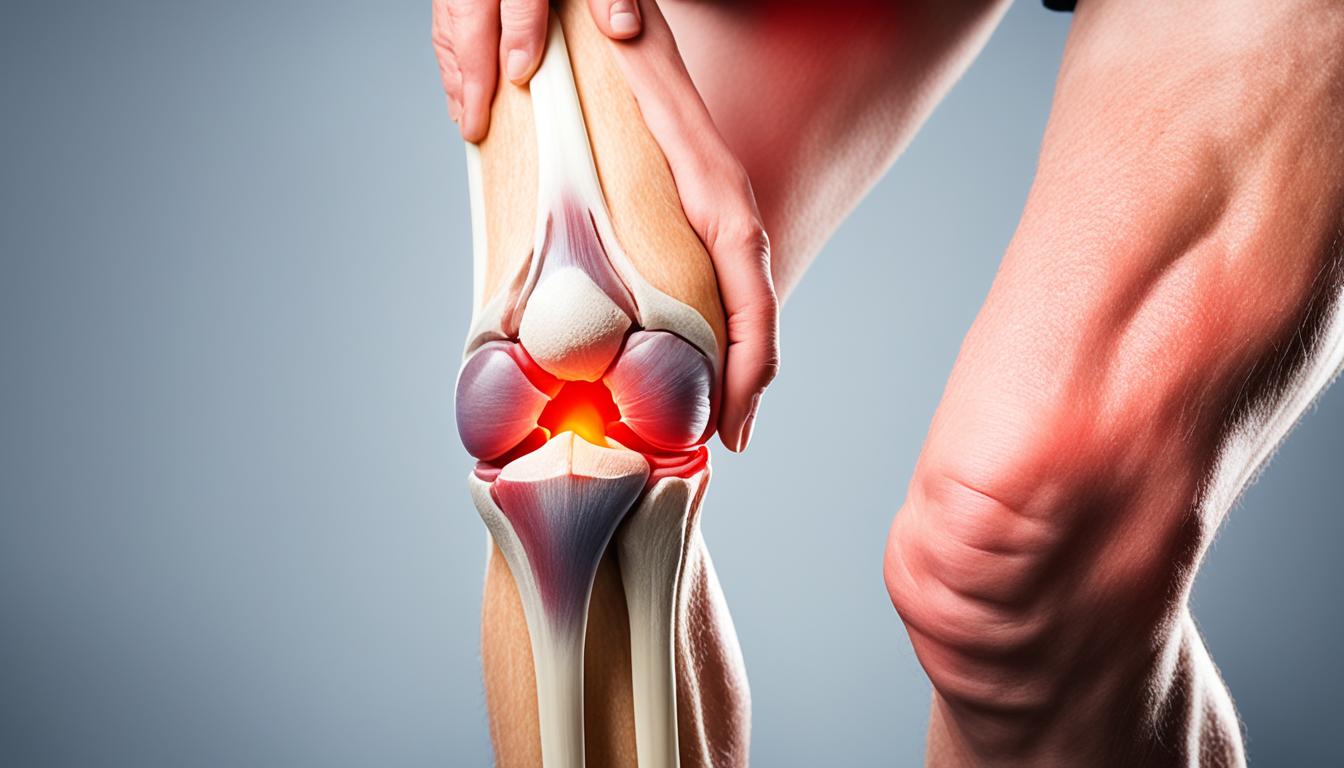
Knee osteoarthritis (OA) presents various symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective management. Common knee osteoarthritis symptoms include:
- Gradual onset knee pain: Individuals may experience knee pain that starts mildly and worsens over time.
- Pain worsens with activity: Engaging in physical activities such as walking or climbing stairs can exacerbate knee pain.
- Knee stiffness and swelling: Stiffness and swelling in the knee joint are common symptoms of knee OA.
- Pain after periods of rest or inactivity: Pain may intensify after prolonged periods of rest or inactivity, such as when waking up in the morning or after sitting for an extended period.
- Pain that worsens over time: Without appropriate treatment and management, knee OA pain may progressively worsen over time.
Proper diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis involves a comprehensive evaluation process, which typically includes:
- Clinical evaluation: A healthcare professional will assess the patient’s medical history, perform a physical examination of the knee joint, and inquire about the symptoms experienced.
- Medical history: Inquiring about the patient’s medical history helps identify any underlying conditions or factors that may contribute to knee OA.
- Imaging tests: X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans may be ordered to visualize the knee joint, assess the extent of cartilage damage, and rule out other potential causes of knee pain.
An accurate diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis is crucial for developing an appropriate treatment plan. It allows for targeted interventions and personalized knee joint care, aiming to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall joint health.

| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Gradual onset knee pain | Pain that starts mildly and worsens over time |
| Pain worsens with activity | Knee pain intensifies during physical activities |
| Knee stiffness and swelling | Stiffness and swelling of the knee joint |
| Pain after periods of rest or inactivity | Pain that increases after prolonged rest or inactivity |
| Pain that worsens over time | Persistent knee pain that progressively worsens |
Treatment Options for Knee Osteoarthritis
When it comes to managing knee osteoarthritis, there are various treatment options available to provide knee pain relief and improve joint function. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s specific needs. In this section, we will explore the different approaches to arthritis treatment and discuss the benefits they offer.
Lifestyle Modifications
One of the first steps in managing knee osteoarthritis is making lifestyle modifications. This may include maintaining a healthy weight, as excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints. Regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, can help strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve joint stability. Additionally, using assistive devices such as canes or knee braces can provide support and relieve pressure on the affected joint.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing knee osteoarthritis. A qualified physical therapist can design an individualized exercise program that focuses on knee-strengthening exercises and range of motion exercises. These exercises help improve joint function, reduce knee pain, and enhance overall mobility. The physical therapist may also use techniques such as manual therapy and hot or cold therapy to alleviate pain and inflammation.
Pain Medication
In some cases, over-the-counter or prescription pain medication may be necessary to manage knee pain caused by osteoarthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. However, it is important to use them as directed and to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medication.
Surgical Interventions
In situations where conservative treatments fail to provide sufficient relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, allows the surgeon to examine and treat damaged cartilage or meniscus tears. Joint replacement surgery, such as total knee replacement, may be recommended for individuals with severe knee osteoarthritis who have significant joint damage and debilitating symptoms. These surgical options can provide long-term pain relief and improve mobility.
| Treatment Option | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle Modifications | – Reduces joint stress – Improves overall joint health – Supports weight management |
| Physical Therapy | – Strengthens knee muscles – Enhances joint stability – Increases range of motion |
| Pain Medication | – Provides temporary pain relief – Reduces inflammation |
| Surgical Interventions | – Restores joint function – Long-term pain relief – Improves mobility |
It is crucial to individualize treatment plans based on the specific needs and symptoms of each patient. A healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist or rheumatologist, can assess the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options. Combining different approaches, such as lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, and medication, can often yield the best outcomes in managing knee osteoarthritis.
Next, we will delve into the whole-body impact of knee osteoarthritis and explore strategies for improving joint health and overall well-being.
Whole Body Impact of Knee Osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on the whole body. The chronic pain and limited mobility associated with knee osteoarthritis can lead to decreased physical activity, muscle weakness, and weight gain. This, in turn, can further exacerbate the symptoms and progression of the disease.
When individuals experience knee pain and find it difficult to move freely, they are more likely to reduce their physical activity. As a result, muscles that support the knee joint weaken, leading to decreased joint stability and increased stress on the remaining cartilage. This vicious cycle perpetuates the degenerative process in the knee, worsening the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis.
Moreover, reduced physical activity and mobility can also contribute to weight gain. Excess weight places additional pressure on the knee joint, accelerating the degeneration of cartilage and worsening knee pain and inflammation. It is essential to address these whole-body impacts of knee osteoarthritis to manage the condition effectively and improve joint health.
Impact on Mental Health
The whole-body impact of knee osteoarthritis extends beyond physical symptoms. The chronic pain and decreased mobility associated with the condition can take a toll on mental health as well. Individuals with knee osteoarthritis often experience increased levels of stress, anxiety, and depression.
The constant pain and limitation in daily activities can lead to frustration, feelings of helplessness, and a decline in overall well-being. Psychological distress can further exacerbate the perception of pain, disrupting sleep patterns and affecting mood and cognitive function. Addressing the impact of knee osteoarthritis on mental health is crucial for comprehensive arthritis treatment and promoting overall well-being.
Strategies for Managing Whole Body Impact
To manage the whole-body impact of knee osteoarthritis, a comprehensive approach is necessary. This involves addressing both physical and mental health aspects of the condition. Here are some strategies that can be incorporated:
- Regular low-impact exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee joint, improve joint stability, and promote weight management. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and tai chi can be beneficial for individuals with knee osteoarthritis.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the stress placed on the knee joint and slow down the progression of knee osteoarthritis. A balanced diet and portion control can aid in weight management.
- Physical therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help improve joint mobility, increase muscle strength, and enhance overall function. Physical therapy techniques can also provide pain relief through modalities such as heat or cold therapy and electrical stimulation.
- Supportive devices: Using assistive devices like knee braces or orthotic inserts can provide additional support to the knee joint and alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Mental health support: Seeking support from mental health professionals can help individuals manage the emotional impact of knee osteoarthritis. Techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) can be useful in reducing stress and anxiety.
| Treatment Approach | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle modifications | Allows individuals to take control of their knee osteoarthritis by making positive changes in diet, exercise, and daily activities |
| Medication | Provides pain relief and reduces inflammation, improving quality of life |
| Physical therapy | Helps improve joint flexibility, strength, and function, promoting joint health |
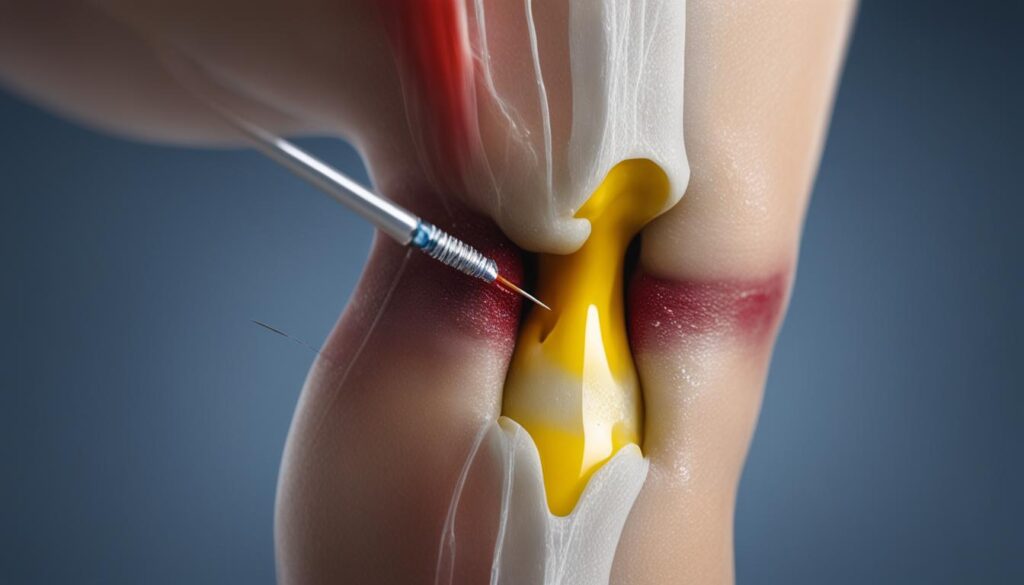
| Injections | Offers targeted pain relief and reduces inflammation in the knee joint |
| Surgery | Provides potential long-term relief for severe cases of knee osteoarthritis |
By addressing the whole-body impact of knee osteoarthritis and incorporating these strategies into arthritis treatment plans, individuals can effectively manage pain, improve joint health, and enhance their overall well-being.
Conclusion
Knee osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the elderly, can cause significant pain and limitations in mobility. Managing knee osteoarthritis requires a comprehensive approach that includes various strategies to improve joint health and overall well-being.
By implementing lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can reduce the impact of knee osteoarthritis and improve joint function. Physical therapy can also play a crucial role in strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, enhancing stability, and reducing pain.
In cases where conservative treatments are not sufficient, pain management techniques and surgical interventions can provide relief and restore joint functionality. However, it is important to individualize treatment plans based on the severity of symptoms and the patient’s specific needs.
By taking a proactive approach to managing knee osteoarthritis, individuals can achieve a better quality of life, with reduced pain and improved mobility. It is essential to prioritize joint health and follow the recommendations of healthcare professionals to effectively manage knee osteoarthritis and maintain overall well-being.
FAQ
What is knee osteoarthritis?
Knee osteoarthritis, also known as degenerative joint disease, is a common condition characterized by the progressive loss of articular cartilage in the knee joint. This leads to symptoms such as knee pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased mobility.
What are the causes and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis?
Knee osteoarthritis can be classified as primary or secondary. Primary knee OA is caused by age-related degeneration and wear and tear on the joint, while secondary knee OA can be caused by factors such as previous joint injuries, obesity, repetitive stress on the joint, and certain metabolic diseases. Other risk factors include older age, being female, genetics, and certain bone deformities.
What are the symptoms and how is knee osteoarthritis diagnosed?
The most common symptoms of knee osteoarthritis include gradual onset knee pain that worsens with activity, knee stiffness and swelling, pain after prolonged periods of rest or inactivity, and pain that worsens over time. Diagnosis of knee OA is typically based on a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI.
What are the treatment options for knee osteoarthritis?
The management of knee osteoarthritis begins with conservative treatments such as lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, weight management, and pain medication. Non-pharmacological interventions like exercise programs and knee-strengthening exercises can help improve joint function and reduce pain. In cases where conservative treatment fails, surgical options such as arthroscopy or joint replacement may be considered.
How does knee osteoarthritis impact the whole body?
Knee osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on the whole body. The chronic pain and limited mobility associated with knee OA can lead to decreased physical activity, muscle weakness, and weight gain. This can further exacerbate the symptoms and progression of the disease. The whole body impact of knee OA can also affect mental health, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and depression.