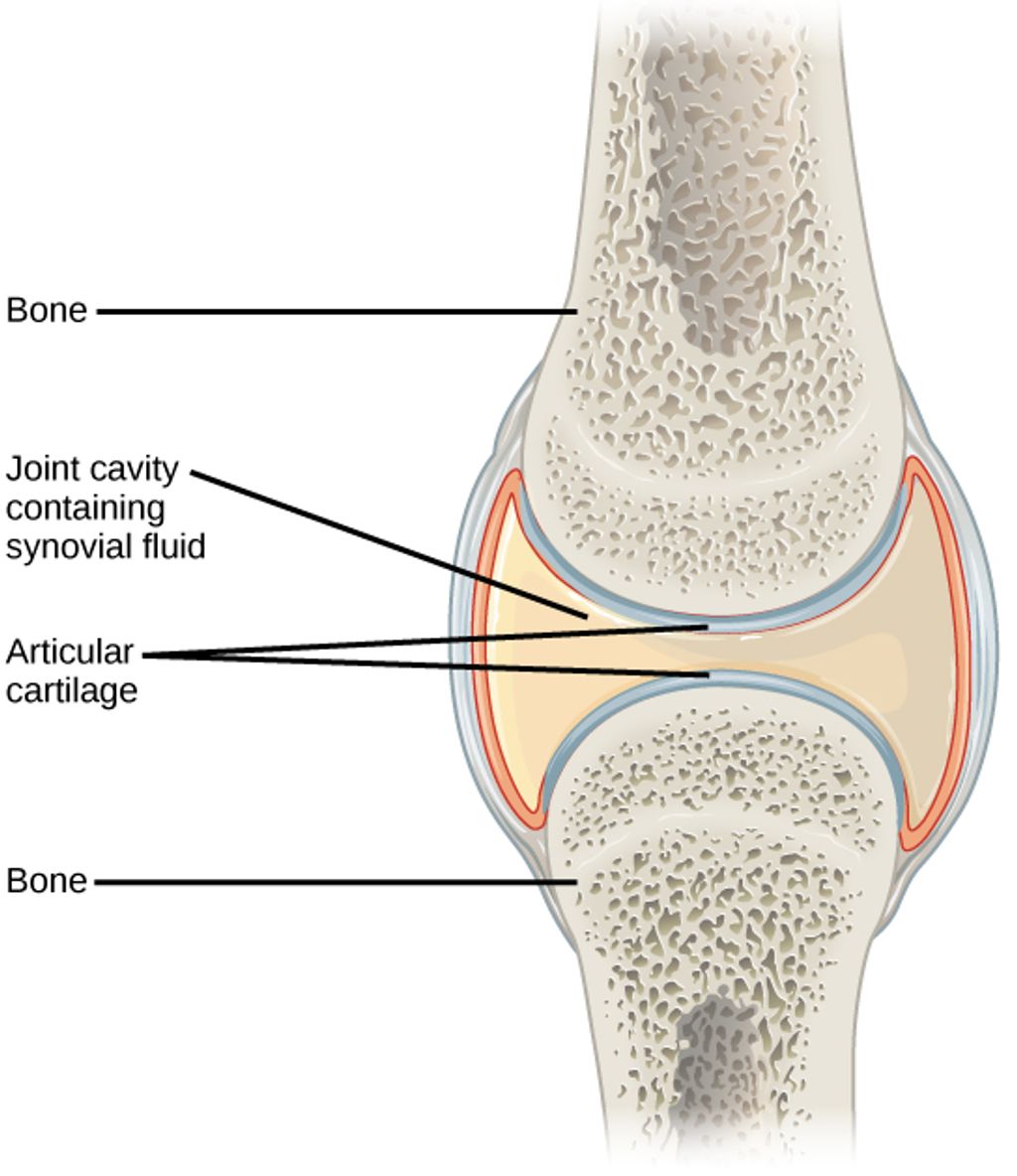
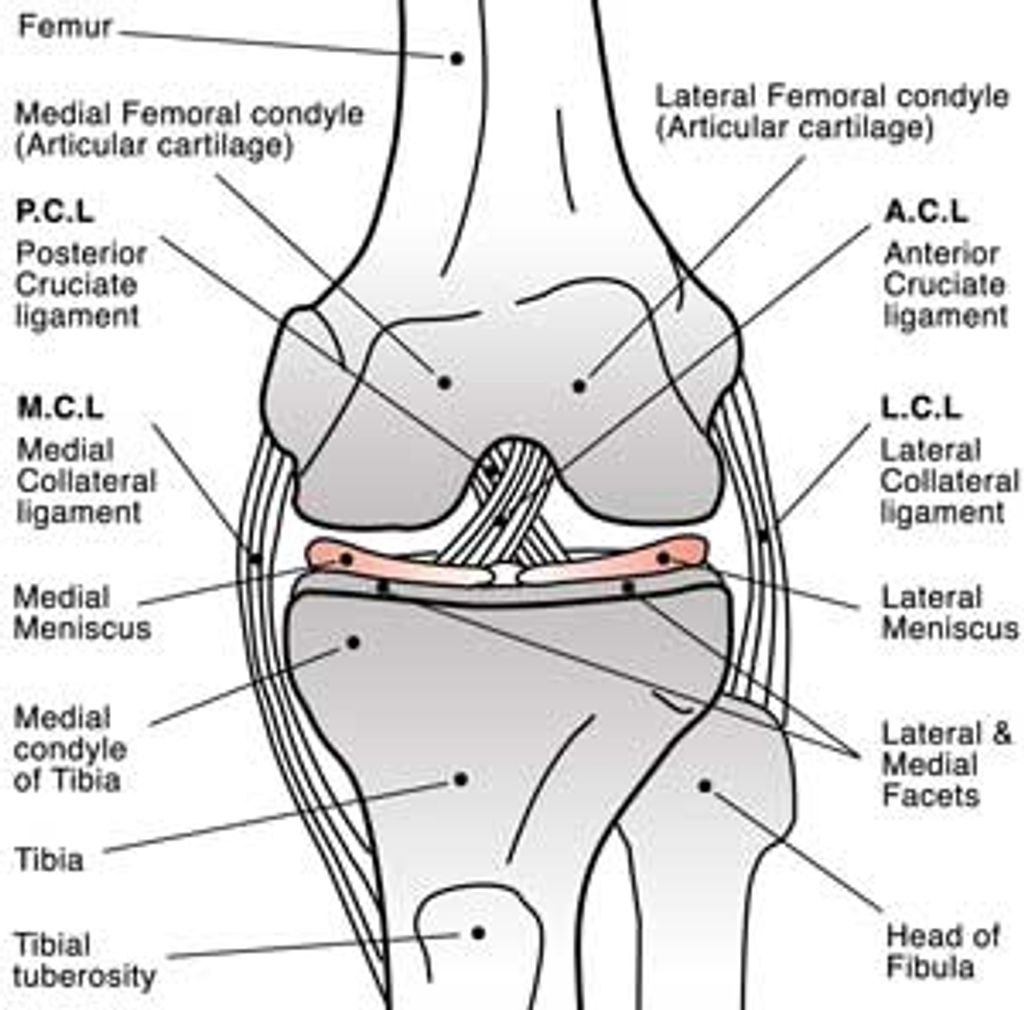
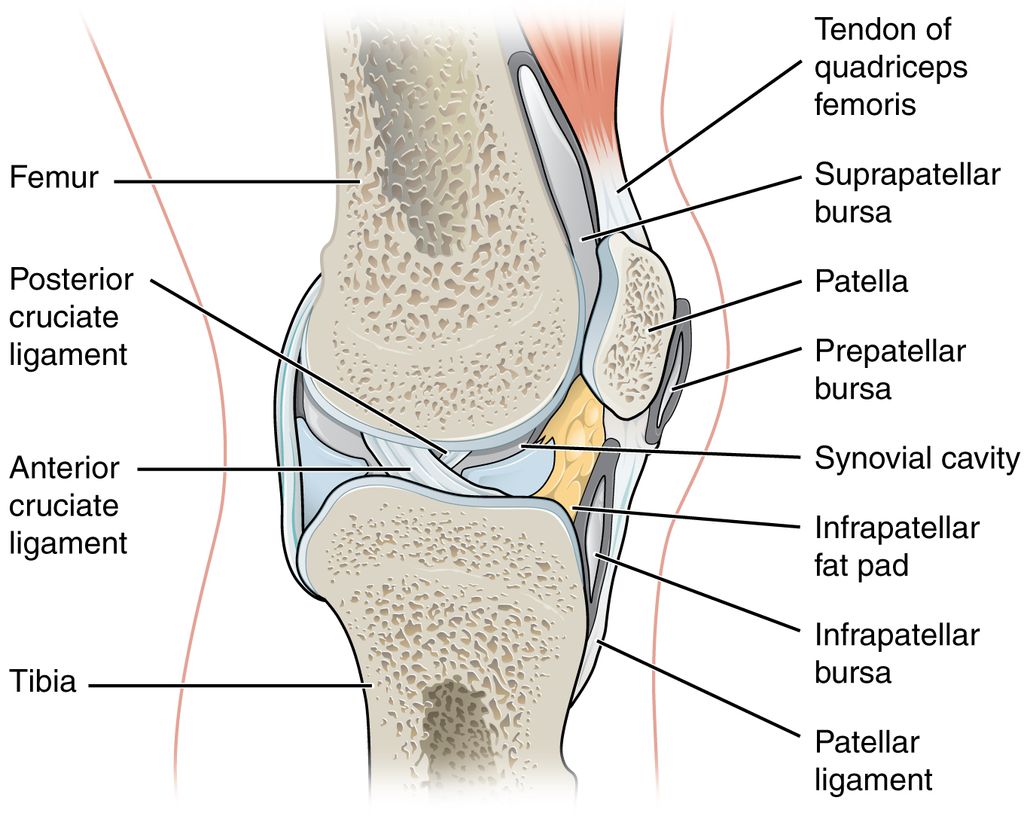
Knee pain under the kneecap can be a real problem for people of all ages. It can make everyday activities like walking, climbing stairs, or even sitting uncomfortable. This article will explore the common causes, symptoms, and treatments for this type of knee pain. We’ll also look at ways to prevent it and lifestyle changes that can help manage the pain.
Key Takeaways
- Knee pain under the kneecap can be caused by many things, including injuries and overuse.
- Symptoms to watch for include swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving the knee.
- Home remedies like rest, ice, and over-the-counter medications can help ease the pain.
- Seeing a doctor is important if the pain is severe or doesn’t go away with home treatment.
- Lifestyle changes like wearing proper footwear and maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent knee pain.
Understanding Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Common Causes
Knee pain under the kneecap, also known as patellofemoral pain, can stem from various sources. Overuse injuries are a frequent cause, often seen in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive activities like running or jumping. Other common causes include misalignment of the kneecap, weak thigh muscles, or direct trauma to the knee.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms early can help in managing the pain effectively. Common symptoms include a dull, aching pain under the kneecap, especially noticeable when climbing stairs, squatting, or sitting for long periods. Some people may also experience a grinding or clicking sensation in the knee.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to know when to seek medical advice. If the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by swelling, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you notice any deformity or inability to bear weight on the affected leg, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent further complications and help you return to your normal activities sooner.
Home Remedies for Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Rest and Ice
One of the simplest ways to ease knee pain is to rest and apply ice. Resting helps reduce stress on the knee, while ice can help decrease swelling and numb the pain. Try to keep your knee elevated when resting to further reduce swelling.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective in managing knee pain. These medications help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Always follow the dosage instructions on the package to avoid any side effects.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine can help improve knee function and reduce pain. Focus on exercises that target the muscles around the knee, such as quadriceps and hamstrings. Consistency is key, so try to make these exercises a regular part of your day.
Medical Treatments for Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often the first step in treating knee pain under the kneecap. A therapist will guide you through exercises that strengthen the muscles around your knee, improving stability and reducing pain. Consistency in these exercises is key to seeing improvement.
Prescription Medications
When over-the-counter medications aren’t enough, doctors may prescribe stronger pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications can help manage pain and reduce swelling, making it easier to perform daily activities.
Surgical Options
In severe cases, surgery might be necessary. Procedures can range from minimally invasive arthroscopy to more complex operations like knee replacement. Your doctor will discuss the best option based on the severity of your condition and your overall health.
If you’re experiencing severe or persistent knee pain, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to explore the best treatment options for you.
Preventing Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Proper Footwear
Wearing the right shoes can make a big difference in preventing knee pain. Supportive footwear helps to align your legs properly, reducing stress on your knees. Look for shoes with good arch support and cushioning.
Regular Exercise
Staying active is key to keeping your knees healthy. Focus on low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling to strengthen the muscles around your knees without putting too much pressure on them. Consistency is important; aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise most days of the week.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the strain on your knees. Extra weight increases the pressure on your knee joints, which can lead to pain and injury. Eating a balanced diet and staying active can help you keep your weight in check.
Keeping your knees healthy involves a combination of the right footwear, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Small changes in your daily routine can make a big difference in preventing knee pain.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Dietary Adjustments
Eating a balanced diet can help manage knee pain. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your knees. Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, to help reduce inflammation. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
Stress Management
Stress can make pain feel worse. Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These activities can help you stay calm and manage pain better. Finding time to relax is important for your overall health.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Making changes to your workspace can help reduce knee pain. Use a chair that supports your back and keeps your feet flat on the floor. Adjust your desk height so you don’t strain your knees. Small changes can make a big difference in how you feel.
Simple lifestyle changes can greatly improve your knee health and reduce pain. Start with one change at a time and see how it helps.
Alternative Therapies for Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. This method is believed to help reduce pain and improve healing by balancing the body’s energy flow. Many people find relief from knee pain through regular acupuncture sessions.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care focuses on diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders, especially those related to the spine. Chiropractors use hands-on spinal adjustments and other techniques to help alleviate knee pain. This approach can be particularly effective for those whose knee pain is linked to issues with their back or posture.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy involves manipulating the muscles and soft tissues to relieve pain and improve circulation. For knee pain under the kneecap, targeted massage can help reduce inflammation and improve mobility. Regular massage sessions can be a beneficial addition to your pain management plan.
Exploring alternative therapies can provide additional relief and complement traditional treatments for knee pain under the kneecap.
Understanding the Role of Biomechanics in Knee Pain Under the Kneecap
Gait Analysis
Gait analysis involves studying how you walk to identify any unusual patterns that might be causing knee pain. Correcting these patterns can help reduce pain and prevent further injury. Sometimes, small changes in how you move can make a big difference.
Orthotics
Orthotics are special shoe inserts designed to support your feet and improve your posture. They can help distribute weight more evenly across your knees, reducing stress on the kneecap. Custom orthotics are often recommended for the best results.
Posture Correction
Good posture is crucial for keeping your knees healthy. Poor posture can lead to uneven stress on your knees, causing pain under the kneecap. Simple exercises and mindful habits can help you maintain better posture and alleviate knee pain.
Paying attention to how you move and stand can make a significant difference in managing knee pain. Small adjustments can lead to big improvements in your comfort and mobility.
Conclusion
Knee pain under the kneecap can be a real bother, but with the right steps, you can manage it well. Remember to always listen to your body and avoid pushing through pain. Simple changes like wearing the right shoes, doing specific exercises, and taking breaks can make a big difference. If the pain doesn’t go away, it’s important to see a doctor. They can help you find the best treatment. Taking care of your knees now can help you stay active and healthy in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes pain under the kneecap?
Pain under the kneecap can be due to various reasons like overuse, injury, or conditions like patellar tendinitis or chondromalacia patella.
What are the symptoms of pain under the kneecap?
Common symptoms include aching, swelling, and difficulty in bending or straightening the knee.
When should I see a doctor for knee pain?
You should see a doctor if the pain is severe, if there is swelling that doesn’t go away, or if you have trouble moving your knee.
Can I treat knee pain at home?
Yes, you can try resting, applying ice, taking over-the-counter pain relievers, and doing gentle stretching exercises.
What medical treatments are available for knee pain?
Medical treatments include physical therapy, prescription medications, and in some cases, surgery.
How can I prevent knee pain under the kneecap?
Wearing proper footwear, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent knee pain.