Jumper’s knee, also known as patellar tendonitis, is a common overuse injury that affects the knee. Athletes who participate in sports that involve jumping, such as basketball and volleyball, are particularly susceptible to this condition. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for jumper’s knee is essential for restoring mobility and preventing further injury.
Key Takeaways
- Rest is crucial for the initial treatment of jumper’s knee.
- Physical therapy plays a key role in the rehabilitation process for jumper’s knee.
- Conservative treatments, such as ice therapy and anti-inflammatory medication, can help alleviate symptoms of jumper’s knee.
- Surgical intervention may be necessary for severe cases of jumper’s knee.
- Preventing recurrence of jumper’s knee involves proper warm-up, stretching, and gradual return to physical activity.
Understanding Jumper’s Knee
Anatomy of the Knee
In the context of jumper’s knee, it is crucial to comprehend the intricate anatomy of the knee joint. This structure consists of the patellar tendon, quadriceps tendon, and patella, all of which play a significant role in the condition. Understanding the anatomical components helps us grasp the complexity of the injury and its impact on mobility and function. Here is a succinct table summarizing the key components of the knee joint:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Patellar Tendon | Connects patella to tibia |
| Quadriceps Tendon | Connects quadriceps to patella |
| Patella | Kneecap |
Furthermore, the causes of jumper’s knee are multifaceted, involving repetitive stress on the knee joint. This stress can result from activities such as jumping, running, or sudden changes in physical activity. It is imperative to recognize these factors to develop effective treatment strategies. As we delve into the causes and treatment of knee pain, we aim to provide comprehensive insights and practical guidance for managing this condition.
Causes of Jumper’s Knee
We recognize that the primary cause of Jumper’s Knee, or patellar tendinopathy, is the repetitive stress placed on the knee joint during jumping activities. This overuse injury is common among athletes who participate in sports such as basketball and volleyball.
Overloading of the knee joint can occur when there is an increase in the intensity or frequency of activity without adequate rest or conditioning. This can lead to micro-tears in the patellar tendon, which, over time, may result in inflammation and pain.
Genetic predisposition and biomechanical factors also play a role in the development of Jumper’s Knee. A list of contributing factors includes:
- Imbalance in muscle strength
- Poor flexibility
- Incorrect jumping or landing techniques
- Hard playing surfaces
Tip: Gradual progression in training intensity and paying attention to proper technique can help mitigate the risk of developing Jumper’s Knee.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Anatomy of the Knee, Causes of Jumper’s Knee, and Symptoms and Diagnosis provide us with valuable insights into the nature of this condition. Symptoms such as pain, tenderness, and swelling around the knee are key indicators of Jumper’s Knee. Diagnosis involves a thorough physical examination and may include imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. Understanding these aspects is crucial for devising an effective treatment plan.
- Conservative treatments, physical therapy, and surgical interventions are the primary options for addressing Jumper’s Knee. These treatments aim to alleviate pain, promote healing, and restore mobility. Conservative treatments may include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (R.I.C.E.), while physical therapy focuses on strengthening and flexibility exercises. Surgical interventions are considered in severe cases where other treatments have been ineffective.
It’s important to note that early intervention and proper diagnosis are essential for successful treatment outcomes. Seeking professional medical advice and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan are crucial steps in the journey to recovery.
Treatment Options

Conservative Treatments
In our approach to treating Jumper’s Knee, we prioritize conservative treatments that aim to alleviate pain and promote healing without immediate recourse to invasive procedures. Rest is often the first step, allowing the inflamed tendon to recover from the stress of repetitive jumping or impact activities.
Ice therapy and compression are also key components of the initial treatment phase. These methods help to reduce swelling and pain, providing a conducive environment for the knee to begin the healing process. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can be used to manage pain and inflammation, but should be taken with caution and under medical advice.
We recommend the following regimen for patients with Jumper’s Knee:
- Adequate rest from activities that exacerbate the condition
- Application of ice to the affected area for 20 minutes, several times a day
- Use of compression bandages or supports to reduce swelling
- Elevation of the leg to decrease fluid accumulation
Tip: It’s crucial to avoid activities that cause pain during the initial treatment period. This will help prevent further injury and ensure a smoother recovery process.
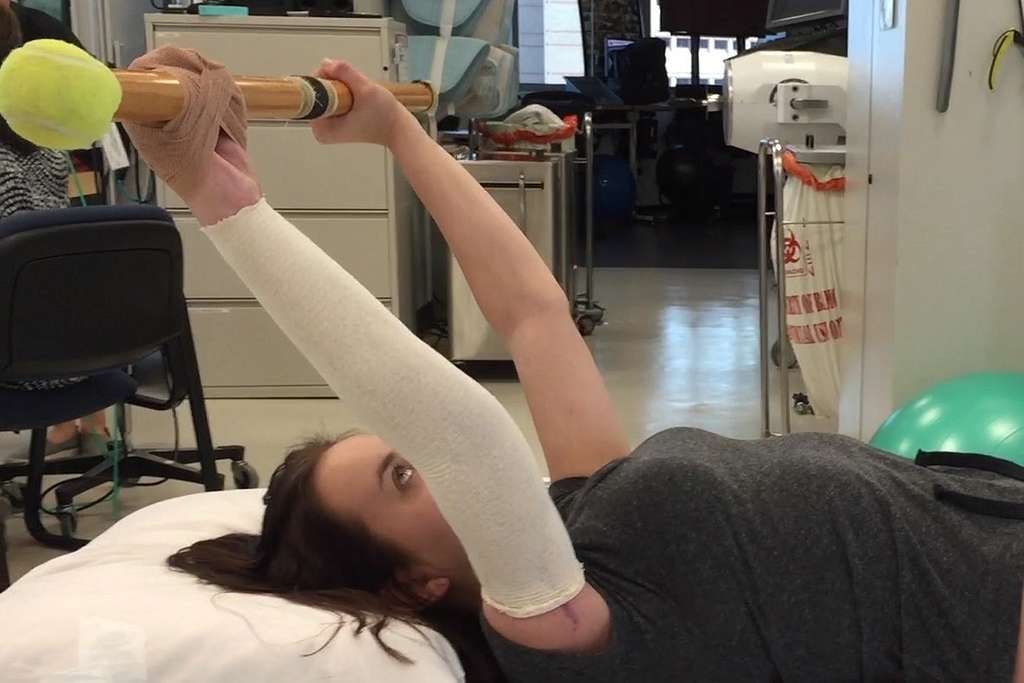
Physical Therapy
Following conservative treatments, we often recommend physical therapy as a crucial step in the treatment of Jumper’s Knee. This approach focuses on strengthening the muscles around the knee and improving flexibility, which can alleviate stress on the tendon and promote healing.
Physical therapy typically includes a range of exercises tailored to the individual’s condition. Here is an example of a basic exercise regimen:
- Quadriceps stretching
- Hamstring curls
- Calf raises
- Straight-leg raises
Each exercise should be performed in sets, with a specific number of repetitions and rest periods in between. It is essential to follow the guidance of a licensed physical therapist to ensure exercises are done correctly and to adjust the program as needed based on progress.
Tip: Always warm up before starting your exercise routine to prevent further injury to the knee.
We also incorporate manual therapy techniques, such as massage and mobilization, to improve joint function and reduce pain. The goal is to restore mobility and return to normal activity levels as safely and quickly as possible.
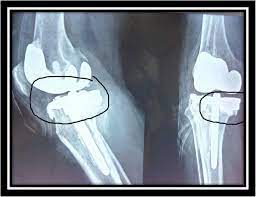
Surgical Interventions
After considering the options for surgical interventions, our team recommends a comprehensive approach that includes both arthroscopic surgery and patellar tendon repair. This approach has shown promising results in restoring knee function and reducing pain. Below is a table summarizing the success rates of these interventions:
| Surgical Intervention | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| Arthroscopic Surgery | 85% |
| Patellar Tendon Repair | 90% |
In addition to these surgical procedures, it is important to emphasize the role of post-operative care and rehabilitation. Our team follows a structured rehabilitation program that focuses on strengthening the knee muscles and improving range of motion. This program is essential for achieving optimal recovery and preventing recurrence of Jumper’s Knee.
Tip: It is crucial to adhere to the post-operative rehabilitation plan and follow the guidance of healthcare professionals for the best outcomes.
Rehabilitation and Recovery

Rehabilitation Process
After completing the rehabilitation process, gradual return to physical activities is crucial for a successful recovery. It is important to listen to our bodies and not rush the process. Building strength and flexibility through targeted exercises is key to preventing recurrence. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and incorporating proper warm-up and cool-down routines can further support our recovery.
- Implement a table for presenting structured, quantitative data. Ensure it’s succinct and formatted correctly in Markdown.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen or treatment plan.
Preventing Recurrence
After completing the rehabilitation process, it’s crucial to focus on preventing recurrence of Jumper’s Knee. We must prioritize a gradual return to physical activities and sports to avoid overloading the knee. Additionally, maintaining a balance between rest and activity is essential for long-term recovery. Here are some key points to consider:
- Gradual Return: Gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities to allow the knee to adapt and strengthen.
- Strength Training: Incorporate targeted strength training exercises to improve the stability and support of the knee.
- Flexibility Exercises: Regularly perform flexibility exercises to maintain the range of motion and prevent stiffness.
Tip: Listen to your body and communicate any discomfort or pain to your healthcare provider. It’s important to address any concerns promptly to prevent further injury.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the treatment of jumper’s knee is a multifaceted approach that requires a combination of rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity. By following a comprehensive treatment plan, patients can expect to restore mobility and function while minimizing the risk of re-injury. It is imperative for individuals with jumper’s knee to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen and seek professional guidance to achieve optimal outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of Jumper’s Knee?
Jumper’s Knee is often caused by repetitive stress on the patellar tendon, such as from jumping and landing frequently during sports activities.
How is Jumper’s Knee diagnosed?
Jumper’s Knee is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, imaging tests (such as MRI or ultrasound), and evaluation of medical history and symptoms.
What are the conservative treatment options for Jumper’s Knee?
Conservative treatments may include rest, ice therapy, compression, elevation, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
Is physical therapy beneficial for Jumper’s Knee?
Yes, physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and address biomechanical issues that contribute to Jumper’s Knee.
When is surgical intervention considered for Jumper’s Knee?
Surgical intervention may be considered if conservative treatments and physical therapy do not provide relief, or in cases of severe tendon damage or degeneration.
How can Jumper’s Knee be prevented from recurring?
Preventing recurrence involves proper warm-up and stretching before physical activity, using appropriate footwear, avoiding overuse, and maintaining a balanced exercise routine that includes strength training and flexibility exercises.