Did you know that knee replacement surgery is one of the most commonly performed orthopedic procedures in the United States? Approximately 600,000 knee replacement surgeries are performed each year, and the numbers continue to rise.
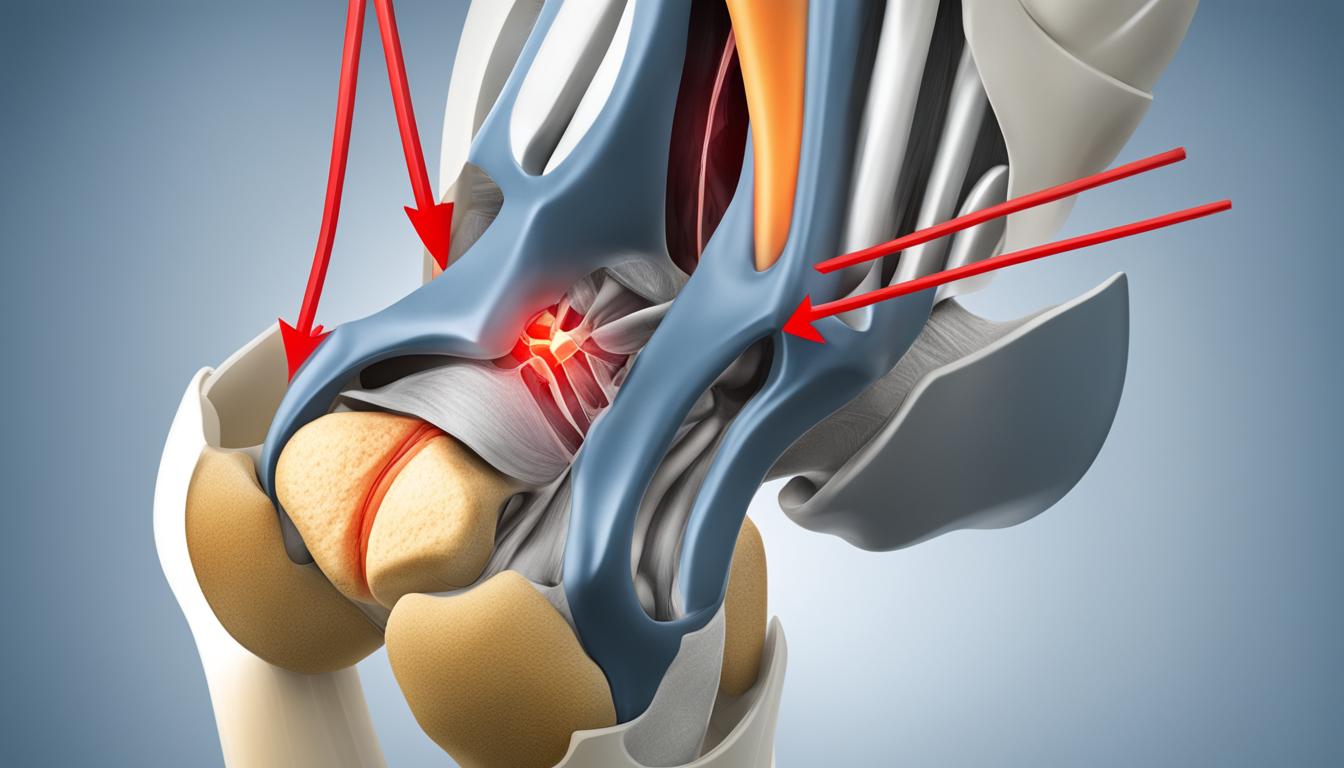
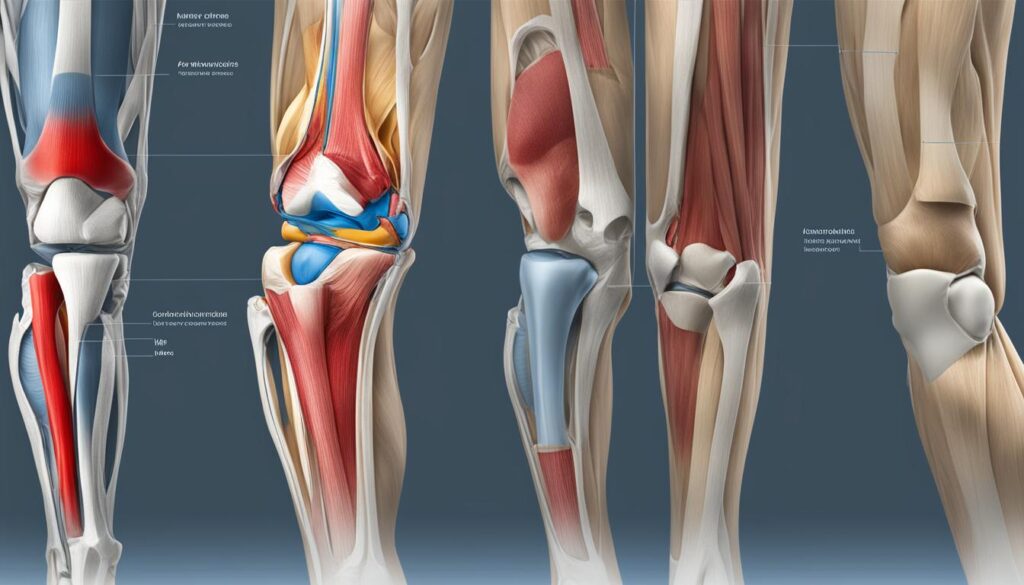
Knee surgery, specifically knee replacement surgery, is a procedure performed to resurface a knee that has been damaged by arthritis or severe injury. It involves the use of metal and plastic parts to cap the ends of the bones in the knee joint. The goal of knee replacement surgery is to relieve pain and improve mobility in patients who have not found relief from other treatments.
The most common reason for knee replacement surgery is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that causes the breakdown of joint cartilage. Other forms of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, as well as knee injuries, can also lead to the need for knee surgery.
The benefits of the procedure include pain relief, improved mobility, and a better quality of life for many patients. However, there are also risks involved, such as bleeding, infection, blood clots, and complications with the prosthesis. Recovery from knee surgery can vary, but physical therapy and rehabilitation are typically part of the recovery process. The cost of knee surgery can also vary depending on factors such as the type of procedure and insurance coverage.
Overall, knee surgery is a complex procedure with both benefits and risks. In the following sections, we will explore the different types of knee surgery, the procedure options available, and the risks and recovery involved.
Types of Knee Surgery and Procedure Options
When it comes to knee surgery, there are various types and procedure options available depending on the specific condition and needs of the patient. Understanding these options is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about the most suitable treatment approach. Let’s explore the two common types of knee surgery and other procedure options:
Knee Replacement Surgery
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is the most common type of knee surgery. This procedure involves replacing the damaged parts of the knee joint with artificial components made of metal and plastic. Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended for patients with severe arthritis or significant knee damage that causes chronic pain and limits mobility.
With advancements in surgical techniques and implant design, knee replacement surgery has become a highly effective treatment option for relieving pain and restoring knee function. The procedure aims to improve the patient’s quality of life by enabling them to engage in daily activities with reduced discomfort and improved mobility.
Arthroscopic Knee Surgery
Arthroscopic knee surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that utilizes a small camera, called an arthroscope, and specialized surgical tools to diagnose and treat various knee conditions. This procedure is commonly performed to address issues such as meniscus tears, ligament injuries, and cartilage damage.
The advantages of arthroscopic knee surgery include smaller incisions, reduced risk of infection, faster recovery time, and less post-operative pain compared to traditional open surgery. This technique allows for a more precise diagnosis and targeted treatment, minimizing trauma to the surrounding tissues.
Other Surgical Options
In addition to knee replacement and arthroscopic surgery, there are other surgical options available to address specific knee conditions. These may include procedures like cartilage repair or ligament reconstruction, which are tailored to the patient’s unique needs and circumstances.
Orthopedic surgeons assess various factors, such as the severity of the knee condition, the patient’s overall health, and their lifestyle requirements, to determine the most appropriate surgical option. The goal is to achieve optimal outcomes and improve the patient’s quality of life through customized treatment plans.
It’s crucial for patients to have open and honest discussions with their orthopedic surgeons about their knee surgery options. By understanding the benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of each procedure, patients can make well-informed decisions that align with their individual needs and goals.
“The right surgical option depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition, overall health, and lifestyle requirements.”
Risks and Recovery from Knee Surgery
When considering knee surgery, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks and complications that may arise. These can include bleeding, infection, blood clots, loosening or wearing out of the prosthesis, fracture, continued pain or stiffness, and nerve or blood vessel injury. It is crucial for patients to have open and honest discussions with their healthcare providers, asking any questions and seeking clarification regarding these potential risks. Understanding the risks of knee surgery is an important step in making an informed decision about your treatment plan.
Recovery from knee surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the type of procedure and the individual patient’s overall health condition. Physical therapy and rehabilitation are typically necessary components of the recovery process. Through these programs, patients can rebuild strength, regain mobility, and restore function to their knees. The recovery journey may include exercises, stretches, and other modalities designed to speed up the healing process and promote optimal outcomes. It is imperative to follow the guidance and recommendations provided by your healthcare team to ensure a successful recovery.
Before undergoing knee surgery, it’s important to consider the financial implications of the procedure. The cost of knee surgery can vary based on factors such as the type of procedure, the location of the facility, and the extent of insurance coverage. To avoid any unexpected financial burdens, patients should have open and transparent conversations with their healthcare providers and insurance companies. Understanding the cost and exploring available options can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment while minimizing the impact on their finances.
FAQ
Why is knee surgery performed?
Knee surgery, specifically knee replacement surgery, is performed to resurface a knee that has been damaged by arthritis or severe injury. The goal of knee replacement surgery is to relieve pain and improve mobility in patients who have not found relief from other treatments.
What are the benefits of knee surgery?
The benefits of knee surgery include pain relief, improved mobility, and a better quality of life for many patients.
What are the risks of knee surgery?
The risks of knee surgery include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and complications with the prosthetic joint.
How long does it take to recover from knee surgery?
The recovery time from knee surgery can vary, but physical therapy and rehabilitation are typically part of the recovery process.
What is knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is a common type of knee surgery where the damaged parts of the knee joint are replaced with artificial components made of metal and plastic.
What is arthroscopic knee surgery?
Arthroscopic knee surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a small camera and specialized tools to diagnose and treat various knee conditions, such as meniscus tears or ligament injuries.
What are the other surgical options for knee conditions?
Other surgical options for knee conditions include cartilage repair or ligament reconstruction, which are chosen based on the specific condition and needs of the patient.
What are some complications of knee surgery?
Complications of knee surgery can include bleeding, infection, blood clots, loosening or wearing out of the prosthesis, fracture, continued pain or stiffness, and nerve or blood vessel injury.
How much does knee surgery cost?
The cost of knee surgery can vary depending on factors such as the type of procedure, the location, and the patient’s insurance coverage.