Living with knee arthritis can be challenging, as it often causes pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. However, understanding the symptoms and treatment options can help individuals manage their condition effectively. This article provides an overview of knee arthritis, including its causes, symptoms, and various treatment approaches. It also explores alternative treatment options that can complement traditional medical interventions. By implementing lifestyle changes, exercises, and medications, individuals can alleviate pain and improve their quality of life. Additionally, alternative therapies such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and supplements may offer additional relief. Read on to learn more about living with knee arthritis and the strategies that can help individuals cope with this chronic condition.
Key Takeaways
- Knee arthritis causes pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Common symptoms include swelling, tenderness, and difficulty walking.
- Seek medical help if symptoms worsen or interfere with daily activities.
- Lifestyle changes such as weight management and low-impact exercises can reduce symptoms.
- Medications, physical therapy, acupuncture, and supplements are treatment options to consider.
Understanding Knee Arthritis
What is Knee Arthritis?
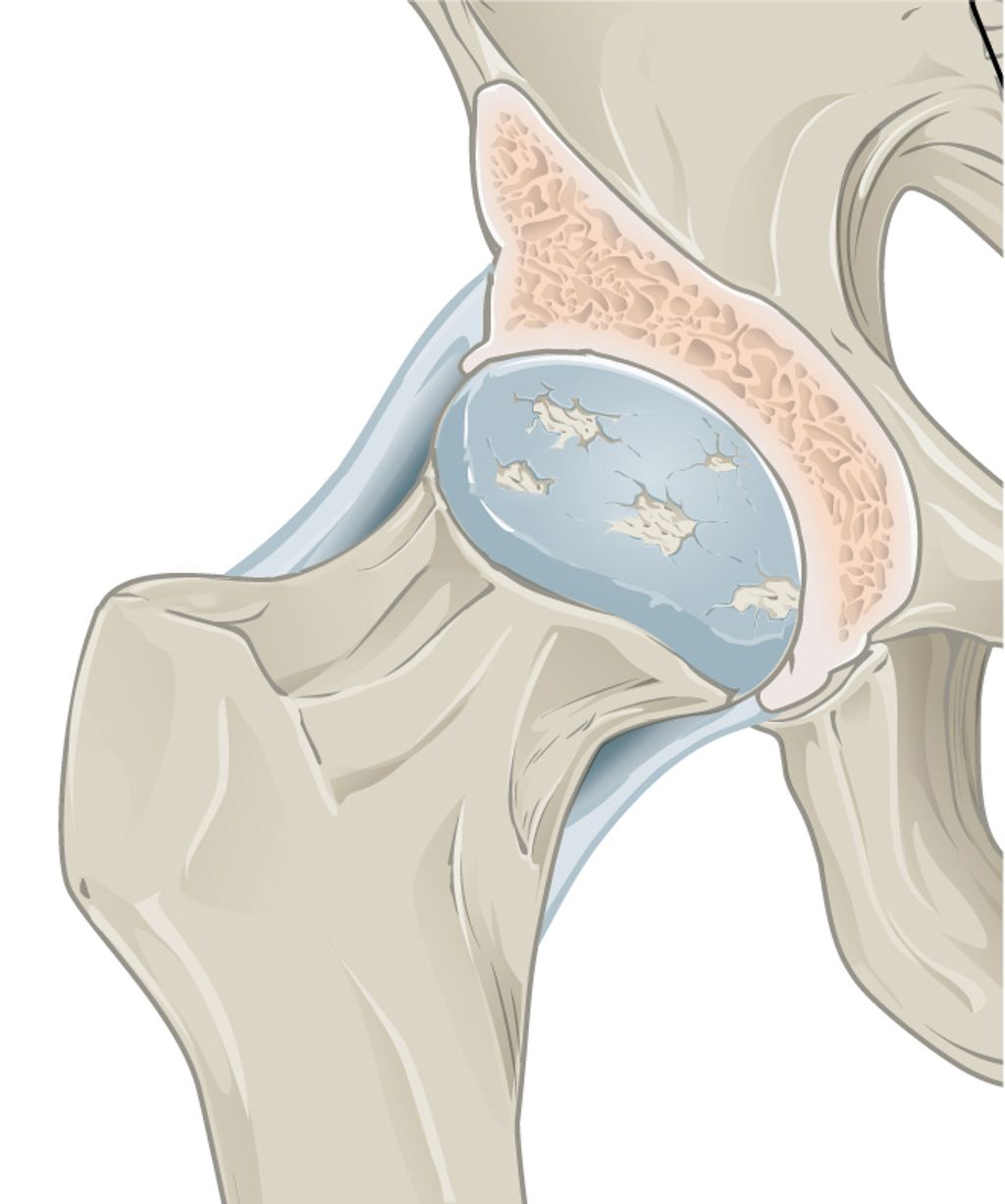
Knee arthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the knee joint. It is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, which leads to pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee. Arthritis can occur due to various factors, including age, injury, obesity, and genetics. There are different types of knee arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
In some cases, knee arthritis can be managed with lifestyle changes, exercises, and medications. However, it is important to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. If you experience persistent knee pain, it is advisable to seek medical help to prevent further damage and improve your quality of life.
Here are some common symptoms of knee arthritis:
- Pain in the knee joint
- Swelling and inflammation
- Stiffness and limited range of motion
- Cracking or popping sounds
Remember, early detection and proper management of knee arthritis can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall joint health.
Causes of Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis can be caused by a variety of factors. Age is a common risk factor, as the wear and tear on the knee joints over time can lead to arthritis. Obesity is another significant factor, as the excess weight puts added stress on the knee joints. Injury or trauma to the knee can also increase the risk of developing arthritis. Additionally, genetics can play a role, as certain genes may make individuals more susceptible to developing knee arthritis. It is important to note that while these factors can increase the risk, they do not guarantee the development of arthritis. It is a complex condition influenced by multiple factors.
Types of Knee Arthritis
There are several types of knee arthritis that can affect individuals. The most common types include:
-
Osteoarthritis: This is the most common form of knee arthritis and occurs when the protective cartilage in the knee joint wears down over time. It is often associated with aging and can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in the joints, including the knees. It can lead to joint deformity and severe pain.
-
Post-Traumatic Arthritis: This type of arthritis develops after a knee injury, such as a fracture or ligament tear. The damage to the knee joint can lead to the development of arthritis over time.
-
Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals build up in the joints, including the knees. It can cause sudden and severe pain, swelling, and redness.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific type of knee arthritis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Recognizing Symptoms
Common Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis can cause a range of symptoms that can vary in severity from person to person. Pain is the most common symptom experienced by individuals with knee arthritis. The pain may be localized to the knee joint or radiate to the surrounding areas. Stiffness is another common symptom, especially after periods of inactivity or prolonged sitting. This can make it difficult to bend or straighten the knee fully.
Other symptoms of knee arthritis include:
- Swelling and inflammation around the knee joint
- Limited range of motion in the knee
- Cracking or popping sounds when moving the knee
- Weakness in the knee joint
It’s important to note that not everyone with knee arthritis will experience all of these symptoms. The severity and combination of symptoms can vary. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical help for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Tip: Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular low-impact exercises can help alleviate symptoms and improve knee function.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you are experiencing persistent pain, swelling, or stiffness in your knee, it is important to seek medical help. These symptoms may indicate a more serious condition or progression of knee arthritis. Additionally, if you are unable to perform your daily activities or if your knee pain is interfering with your quality of life, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional.
In some cases, knee arthritis may lead to joint deformity or instability. If you notice any changes in the shape or alignment of your knee joint, or if you experience frequent episodes of your knee giving way, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Remember, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage knee arthritis effectively and prevent further damage to the joint.
Managing Knee Arthritis
Lifestyle Changes for Knee Arthritis
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage knee arthritis and reduce symptoms. Here are some recommendations:
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on the knees, so losing weight can help alleviate pain and improve mobility.
-
Stay active: Regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, can strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and improve flexibility.
-
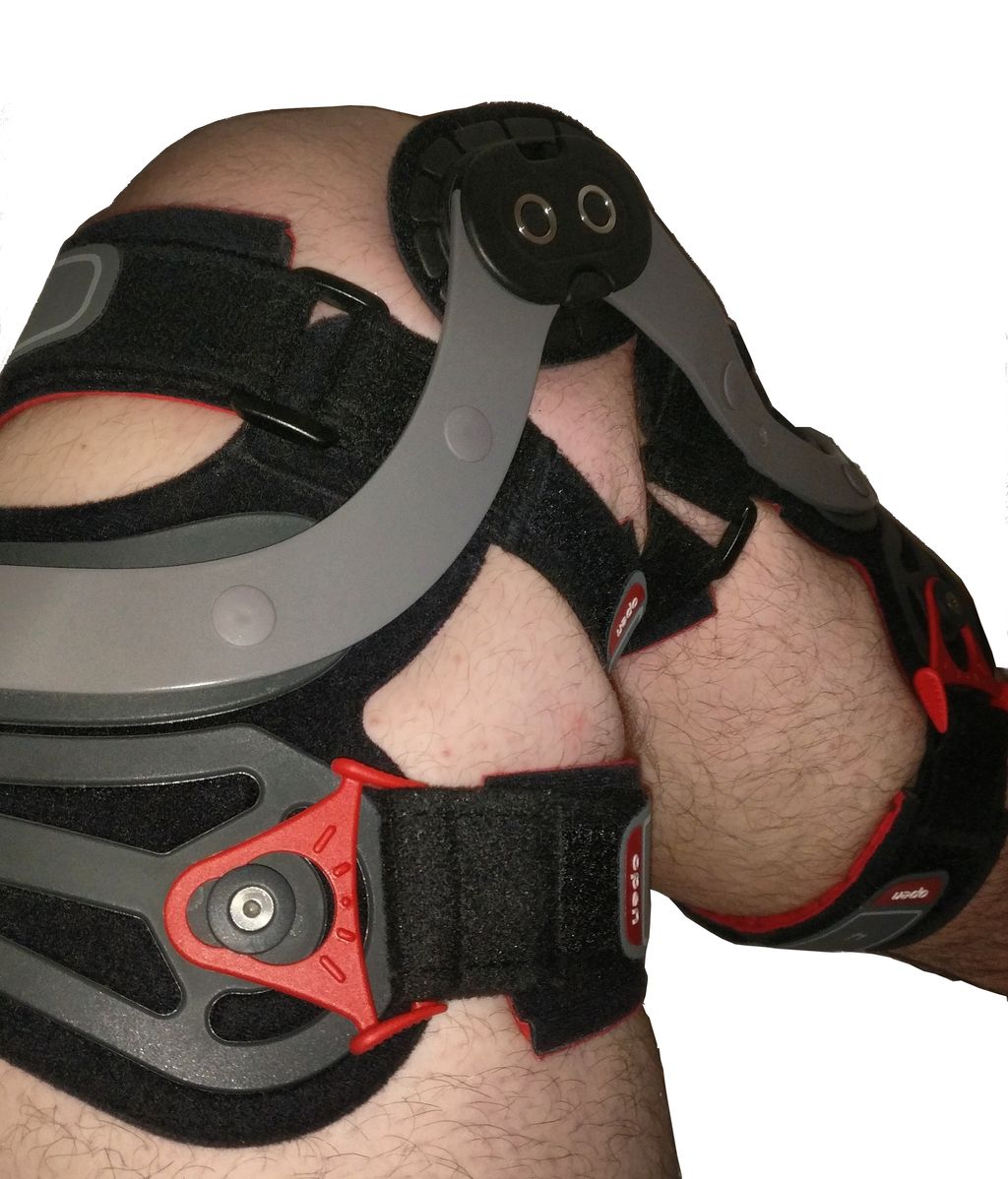
Use assistive devices: Using assistive devices like canes or braces can help reduce pressure on the knee joint and provide support during daily activities.
Tip: Avoid activities that involve repetitive high-impact movements, as they can worsen knee arthritis symptoms.
-
Apply heat or cold: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected knee can help reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Wear supportive footwear: Wearing shoes with good arch support and cushioning can help reduce stress on the knees.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant lifestyle changes or starting a new exercise program.
Exercises for Knee Arthritis
Regular exercise is an essential part of managing knee arthritis. Strength training exercises can help improve the stability and function of the knee joint. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming and cycling, are also beneficial as they put less stress on the knee joint.
In addition to strength training, range of motion exercises can help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness in the knee. These exercises involve gently moving the knee joint through its full range of motion. Examples include knee bends, leg lifts, and heel slides.
It’s important to start with gentle exercises and gradually increase intensity and duration as tolerated. Listen to your body and avoid any exercises that cause pain or discomfort. If you’re unsure about which exercises are suitable for you, consult with a physical therapist or healthcare professional.
Here are some exercises that can be beneficial for knee arthritis:
- Straight Leg Raises: Lie on your back with one leg straight and the other bent. Lift the straight leg off the ground, keeping the knee straight. Hold for a few seconds and then lower it back down. Repeat on the other leg.
- Wall Squats: Stand with your back against a wall and your feet shoulder-width apart. Slowly lower your body into a squat position, keeping your back against the wall. Hold for a few seconds and then slowly stand back up.
- Hamstring Curls: Stand behind a chair or use a wall for support. Bend one knee and bring your heel towards your buttocks. Hold for a few seconds and then lower your leg back down. Repeat on the other leg.
Remember to always warm up before exercising and cool down afterwards. If you experience increased pain or swelling after exercising, it’s important to rest and consult with your healthcare provider.
Medications for Knee Arthritis
When it comes to managing knee arthritis, medications can play a crucial role in reducing pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to relieve pain and reduce swelling. These medications work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation. Some examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen and naproxen.
In addition to NSAIDs, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation in the knee joint. These medications are usually injected directly into the joint and can provide temporary relief. However, corticosteroids should be used cautiously as they may have side effects with long-term use.
Another option is hyaluronic acid injections, also known as viscosupplementation. This treatment involves injecting a gel-like substance into the knee joint to provide lubrication and cushioning. Hyaluronic acid injections can help reduce pain and improve joint function.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate medication for your specific condition. They can provide guidance on the dosage, potential side effects, and any precautions that need to be taken.
Alternative Treatment Options
Physical Therapy for Knee Arthritis
Physical therapy is an essential component of the treatment plan for knee arthritis. It focuses on improving joint mobility, strength, and flexibility while reducing pain and inflammation. The goal of physical therapy is to help patients regain function and improve their quality of life.
During physical therapy sessions, a variety of techniques may be used, including manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and modalities such as heat or ice. These techniques help to reduce pain, improve range of motion, and strengthen the muscles around the knee joint.
In addition to in-clinic sessions, physical therapists often provide patients with home exercise programs to continue their progress outside of therapy sessions. These programs may include exercises to improve balance, stability, and gait. It is important for patients to follow the prescribed exercises and attend regular therapy sessions to achieve the best results.
Here are some key benefits of physical therapy for knee arthritis:
- Pain relief: Physical therapy can help reduce pain and discomfort associated with knee arthritis.
- Improved mobility: Through targeted exercises and techniques, physical therapy can improve joint mobility and range of motion.
- Increased strength: Strengthening exercises can help improve muscle strength and stability around the knee joint.
- Better function: Physical therapy aims to improve overall function and quality of life for individuals with knee arthritis.
Remember, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program or treatment plan.
Acupuncture for Knee Arthritis
Acupuncture is a popular alternative treatment option for knee arthritis. It involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the flow of energy and promote healing. While the effectiveness of acupuncture for knee arthritis is still debated, some studies have shown promising results.
One study published in the Journal of Pain found that acupuncture can provide short-term pain relief for people with knee osteoarthritis. Another study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine reported that acupuncture combined with exercise therapy can improve knee function and reduce pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Benefits of acupuncture for knee arthritis:
- Pain relief: Acupuncture may help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee joint.
- Improved mobility: Some people find that acupuncture improves their range of motion and makes it easier to perform daily activities.
- Minimal side effects: Acupuncture is generally considered safe and has few side effects when performed by a trained professional.
It’s important to note that acupuncture should be used as a complementary therapy and not as a substitute for conventional medical treatment. If you’re considering acupuncture for knee arthritis, it’s best to consult with a qualified acupuncturist and your healthcare provider to determine if it’s a suitable option for you.
Supplements for Knee Arthritis
Supplements can be a helpful addition to the treatment plan for knee arthritis. While they may not provide a cure, they can help manage symptoms and improve joint health. Here are some key supplements that have shown promise in relieving knee arthritis:
- Glucosamine and chondroitin: These supplements are commonly used to support joint health and reduce pain. They are believed to help protect and repair cartilage in the knee.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil, these fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce joint pain and stiffness.
- Turmeric: This spice contains a compound called curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory effects. It may help reduce pain and improve function in people with knee arthritis.
It’s important to note that while supplements can be beneficial, they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They may interact with other medications or have side effects. Always consult with your doctor before starting any new supplement regimen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, living with knee arthritis can be challenging, but there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Early diagnosis and regular exercise are key in preventing further damage and reducing pain. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for individual needs. With the right approach, individuals with knee arthritis can lead fulfilling and active lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of knee arthritis?
Common symptoms of knee arthritis include pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the knee joint.
How is knee arthritis diagnosed?
Knee arthritis can be diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI, and sometimes joint fluid analysis.
What are the treatment options for knee arthritis?
Treatment options for knee arthritis include lifestyle changes, exercises, medications, physical therapy, acupuncture, and supplements.
Can knee arthritis be cured?
Knee arthritis cannot be cured, but its symptoms can be managed through various treatment options to improve quality of life and reduce pain.
Are there any natural remedies for knee arthritis?
Some natural remedies for knee arthritis include using hot or cold packs, practicing low-impact exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and taking certain supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin.
When should I consider surgery for knee arthritis?
Surgery for knee arthritis is usually considered when other conservative treatment options have failed to provide relief and the pain and disability significantly affect daily activities.