As individuals age, the risk of experiencing a torn meniscus increases, leading to significant challenges in recovery and treatment. Understanding the anatomy of the meniscus, the diagnosis and classification of torn meniscus in older adults, and the available treatment options is crucial for effective management. This article aims to provide valuable insights into the recovery process after a torn meniscus in individuals over 50, covering both non-surgical and surgical interventions.
Key Takeaways
- Recovery from a torn meniscus in individuals over 50 requires a comprehensive understanding of the anatomy and age-related changes in the meniscus.
- Clinical assessment, physical examination, and imaging techniques play a vital role in the accurate diagnosis and classification of torn meniscus in older adults.
- Non-surgical treatment options such as physical therapy, rehabilitation, and pain management strategies are effective in managing torn meniscus in older adults.
- Surgical interventions, including arthroscopic meniscectomy and meniscal repair, are viable options for addressing torn meniscus in the elderly population.
- A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, physical therapists, and orthopedic specialists is essential for successful recovery and rehabilitation after a torn meniscus in individuals over 50.
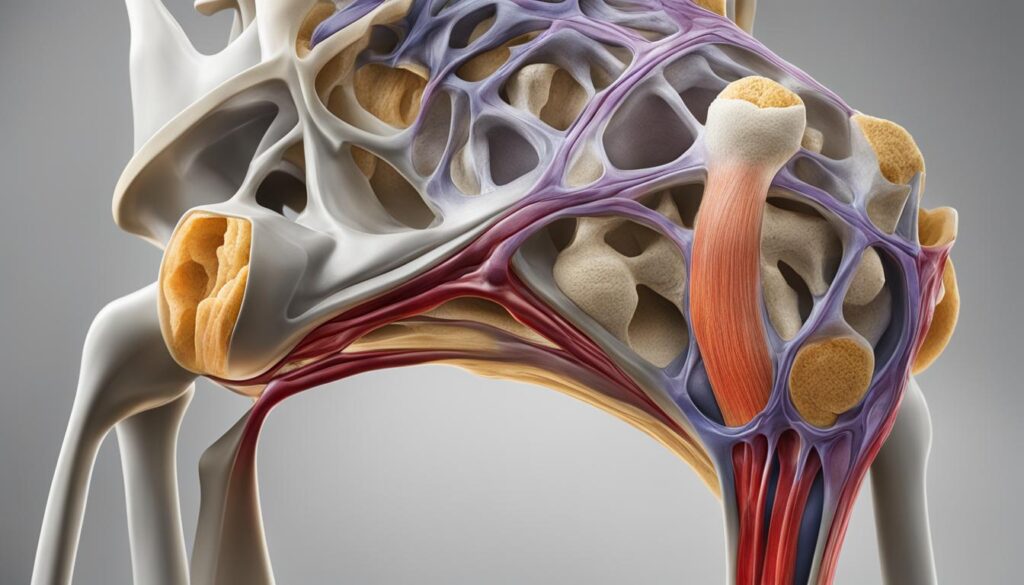
Understanding the Anatomy of the Meniscus
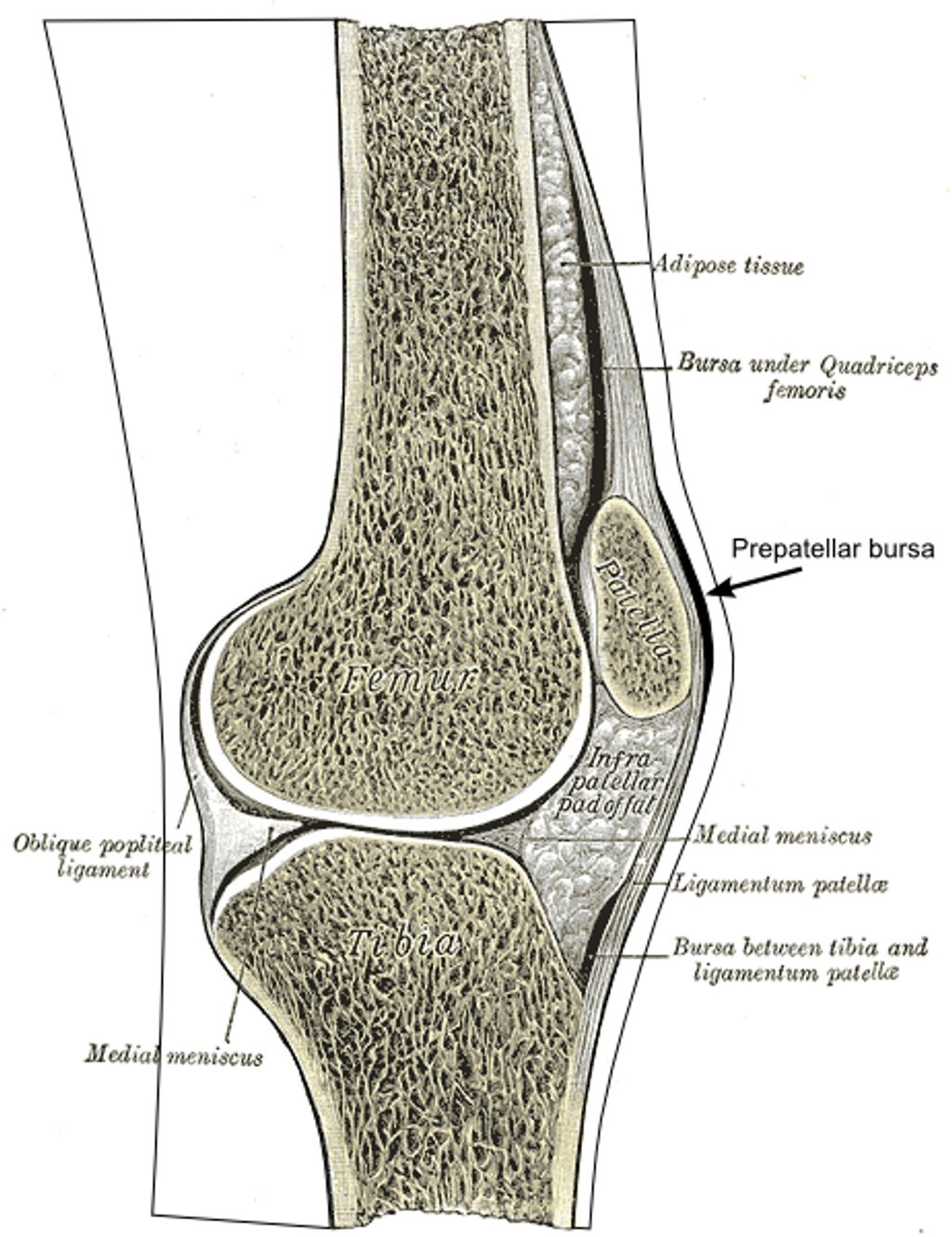
Structure and Function of the Meniscus
The meniscus plays a critical role in our knee joint’s health and functionality. Composed of two crescent-shaped pieces of fibrocartilage, it acts as a shock absorber between the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (shin bone). This cushioning is essential for reducing the stress on the joint during weight-bearing activities.
Stability and lubrication are also key functions of the meniscus. It helps to distribute body weight evenly across the knee joint and provides a smooth surface for the bones to move on. Without a healthy meniscus, the risk of developing osteoarthritis increases significantly, especially in individuals over 50.
- Shock Absorption: Reduces stress on the knee during impact.
- Stability: Distributes weight evenly and prevents excessive movement.
- Lubrication: Ensures smooth articulation of the knee joint.
Tip: Maintaining strong quadriceps and hamstrings can help support the meniscus and reduce the risk of injury.
Age-Related Changes in the Meniscus
As we age, our bodies undergo various changes, and the meniscus is no exception. The meniscus, a C-shaped cartilage in the knee, is crucial for shock absorption and stability during movement. Over time, the meniscal tissue can become more brittle and less elastic, making it more susceptible to injury.
Degeneration of the meniscus is a common issue for individuals over 50. This process can lead to a higher incidence of tears, even with minor trauma or during everyday activities. It’s important to recognize that symptoms of a torn meniscus in older adults may differ from those in younger individuals. Often, older patients may experience more subtle symptoms or sometimes none at all, a condition known as being asymptomatic.
- **Common age-related changes in the meniscus include: **
- Reduced water content
- Thinning of the cartilage
- Increased stiffness
- Compromised healing capacity
Tip: Maintaining an active lifestyle and engaging in knee-strengthening exercises can help mitigate some of the age-related changes in the meniscus and reduce the risk of injury.
Diagnosis and Classification of Torn Meniscus in Individuals Over 50
Clinical Assessment and Physical Examination
When we approach the clinical assessment and physical examination of a torn meniscus in individuals over 50, we prioritize a thorough patient history and a detailed physical examination. We inquire about the onset of symptoms, the nature of the pain, and any activities that exacerbate the condition. It is crucial to differentiate the meniscal injury from other knee pathologies that may present similarly in older adults.
During the physical examination, we perform specific tests to assess the integrity of the meniscus. The McMurray test is one such maneuver, where we palpate the joint line while the knee is flexed and rotated to elicit pain or a clicking sound indicative of a tear. Joint line tenderness is another key sign we look for.
Note: While these tests are valuable, they are not infallible. An accurate diagnosis often requires correlation with imaging findings.
Here is a list of common clinical signs that may suggest a torn meniscus in older patients:
- Joint line tenderness
- Swelling or effusion
- Limited range of motion
- Pain during rotation or squatting
- A positive McMurray test
It’s important to remember that the clinical presentation can vary, and some patients may exhibit minimal symptoms despite significant meniscal damage.
Imaging Techniques for Torn Meniscus
In our pursuit of diagnosing a torn meniscus, we rely heavily on imaging techniques. These methods provide us with a clear view of the internal structure of the knee, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for visualizing meniscal damage. It offers detailed images that allow us to assess the extent of the injury and any associated complications.
Ultrasound is another imaging modality we use, though it is less definitive than MRI. It can be beneficial for patients who are unable to undergo MRI due to contraindications such as the presence of certain types of metal implants or claustrophobia.
Tip: Always discuss any concerns or limitations you may have with imaging procedures with your healthcare provider to ensure the most appropriate technique is used for your situation.
The choice between these imaging options often depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history, the severity of symptoms, and the presence of other knee pathologies. Here is a list of considerations we take into account when selecting an imaging technique:
- Patient’s overall health and medical history
- Specific symptoms and physical examination findings
- Potential contraindications to certain imaging modalities
- The need for detailed visualization of the meniscus structure
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Torn Meniscus in Older Adults

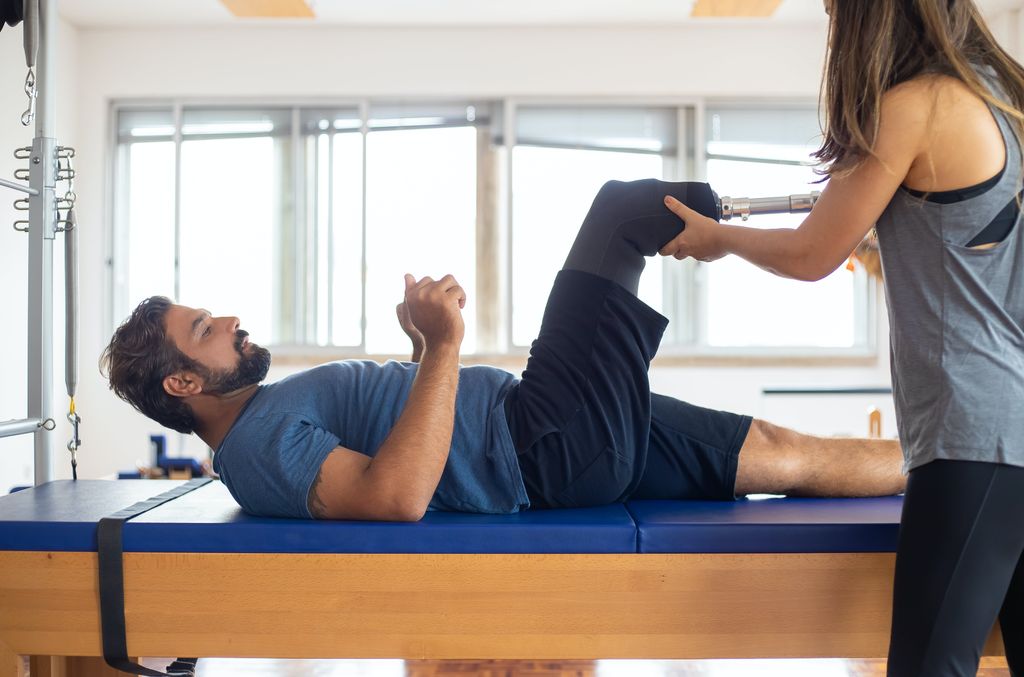
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
After discussing the importance of physical therapy and rehabilitation, we emphasize the role of consistent exercise in maintaining joint mobility and strength. Additionally, a balanced approach to pain management is crucial for ensuring patient comfort and compliance with the treatment plan. Our approach focuses on personalized care and tailored interventions to address the unique needs of each individual. We prioritize patient education and empowerment, equipping them with the knowledge and tools to actively participate in their recovery journey. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Pain Management Strategies
In our pursuit of alleviating discomfort for those over 50 with a torn meniscus, we must consider a variety of pain management strategies. These methods aim to reduce inflammation, manage pain, and improve quality of life. It’s essential to tailor pain management to the individual, as responses to treatment can vary widely.
One effective approach is the use of medications. Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be beneficial. For more severe pain, prescription medications may be necessary. However, we must be cautious with long-term use due to potential side effects.
Physical modalities such as ice, heat, and ultrasound can also play a role in managing pain. These can be used in conjunction with exercises recommended by physical therapists. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, including weight management and activity modification, are crucial in reducing stress on the knee joint.
Tip: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new pain management regimen to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific condition and health profile.
Surgical Interventions for Torn Meniscus in the Elderly Population
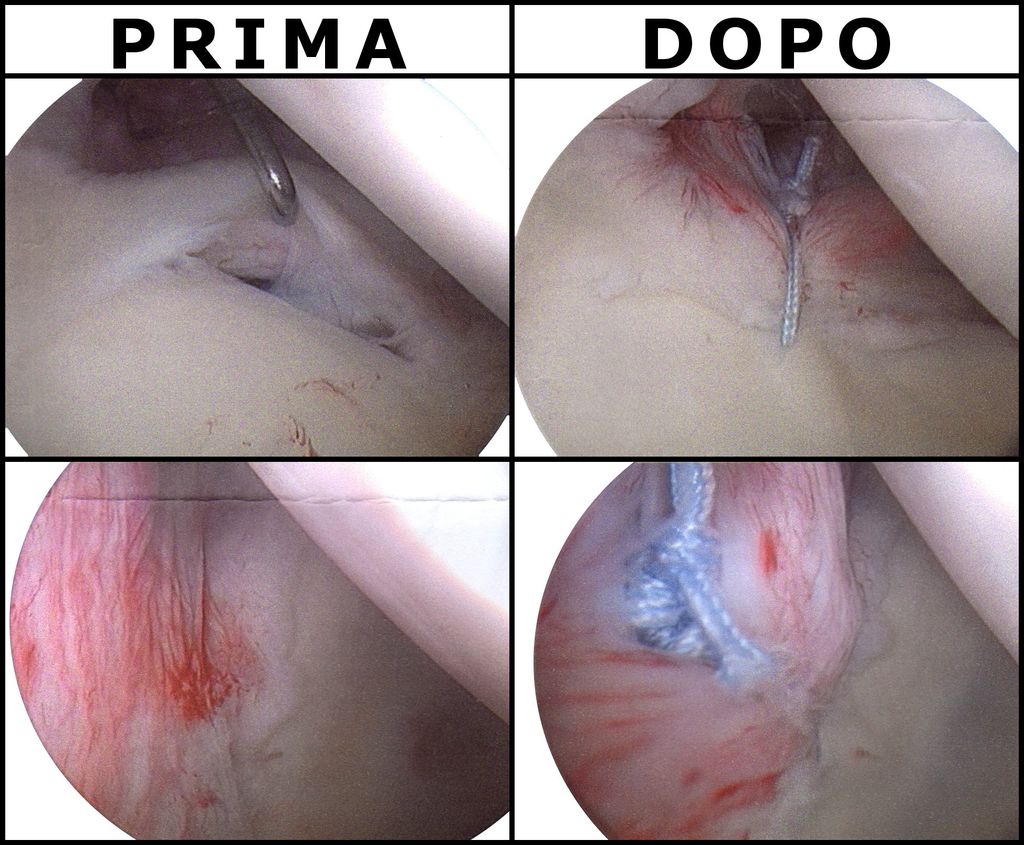
Arthroscopic Meniscectomy
After undergoing arthroscopic meniscectomy, rehabilitation and physical therapy are crucial for a successful recovery. It is important to follow the prescribed rehabilitation program to regain strength and mobility in the affected knee. Additionally, a gradual return to normal activities is recommended, with a focus on low-impact exercises such as swimming and cycling. Here is a brief overview of the recommended rehabilitation program:
| Week | Activity |
|---|---|
| 1-2 | Gentle range of motion exercises |
| 3-4 | Strengthening exercises for quadriceps and hamstrings |
| 5-6 | Balance and proprioception training |
| 7-8 | Gradual return to low-impact activities |
It is important to note that each individual’s recovery may vary, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
Meniscal Repair and Reconstruction
In our exploration of treatment options for torn meniscus in individuals over 50, we recognize that meniscal repair and reconstruction are critical surgical interventions. These procedures aim to preserve as much of the meniscus as possible, which is essential for maintaining knee joint health and function.
Meniscal repair is typically recommended for younger patients or those with specific tear patterns that have a higher likelihood of healing. However, we’ve seen that even in the older population, if the tear is in the vascular zone of the meniscus, repair may still be a viable option. Reconstruction, on the other hand, is a more complex procedure that involves grafting tissue to replace severely damaged meniscal tissue.
Tip: Always discuss the potential risks and benefits of meniscal repair or reconstruction with your orthopedic surgeon. The decision should be based on individual factors such as tear location, overall knee health, and activity level.
The success of these surgeries in older adults can vary, and it’s important to have realistic expectations. Rehabilitation after surgery is crucial and can be a lengthy process, often involving:
- Controlled physical therapy to regain strength and mobility
- Pain management strategies
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor healing
Conclusion
In conclusion, recovery after a torn meniscus for individuals over 50 requires patience and dedication to rehabilitation. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized recovery plan that considers the unique needs of older adults. With proper care and adherence to recommended treatments, individuals can experience improved mobility and a better quality of life following a torn meniscus injury.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of a torn meniscus in individuals over 50?
Common symptoms include knee pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty in fully extending the knee.
Can a torn meniscus heal on its own without surgery in older adults?
In some cases, small tears may heal with conservative treatment such as rest, ice, and physical therapy. However, larger tears or complex tears may require surgical intervention.
Is it normal to experience knee clicking or locking after a torn meniscus in older individuals?
Knee clicking or locking can occur due to a torn meniscus, but it is not always present. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the potential risks and complications associated with surgical interventions for torn meniscus in older adults?
Potential risks include infection, blood clots, and damage to surrounding structures. Complications may also arise from anesthesia and the surgical procedure itself.
How long does it take to recover from surgical treatment for a torn meniscus in individuals over 50?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgical intervention and the individual’s overall health. It may take several weeks to several months to fully recover and return to normal activities.
Are there specific exercises that can help strengthen the knee after non-surgical treatment for a torn meniscus in older adults?
Yes, physical therapy often includes exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance in the knee joint. These exercises can help support the knee and prevent future injuries.