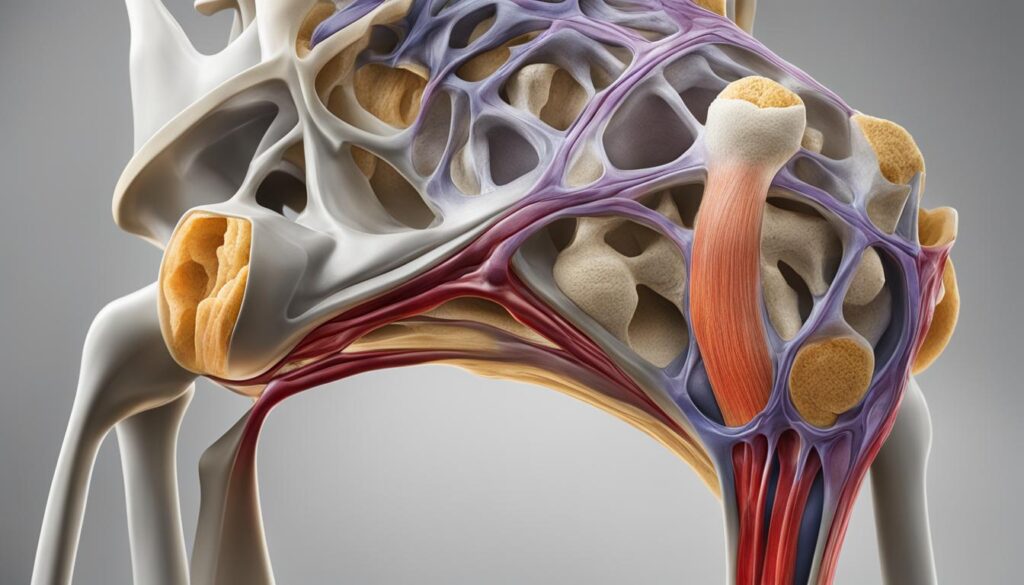
The knee is the largest joint in the human body and serves as the point where the bones of the lower and upper legs meet. It functions as a hinge, allowing us to perform various movements such as sitting, squatting, walking, and jumping. The knee joint consists of three bones: the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). These bones are covered with a layer of cartilage that provides shock absorption and allows for smooth movement. The knee also contains crescent-shaped pads of cartilage called menisci, which reduce friction and distribute the weight across the joint. Ligaments and tendons hold the bones together and provide stability to the knee. The knee is supported by muscles, including the quadriceps and hamstrings.
Key Takeaways:
- The knee joint consists of the femur, tibia, and patella.
- Cartilage provides shock absorption and smooth movement.
- Menisci distribute weight and reduce friction in the knee joint.
- Ligaments and tendons provide stability.
- Muscles, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, support the knee joint.
Knee Bone Structure
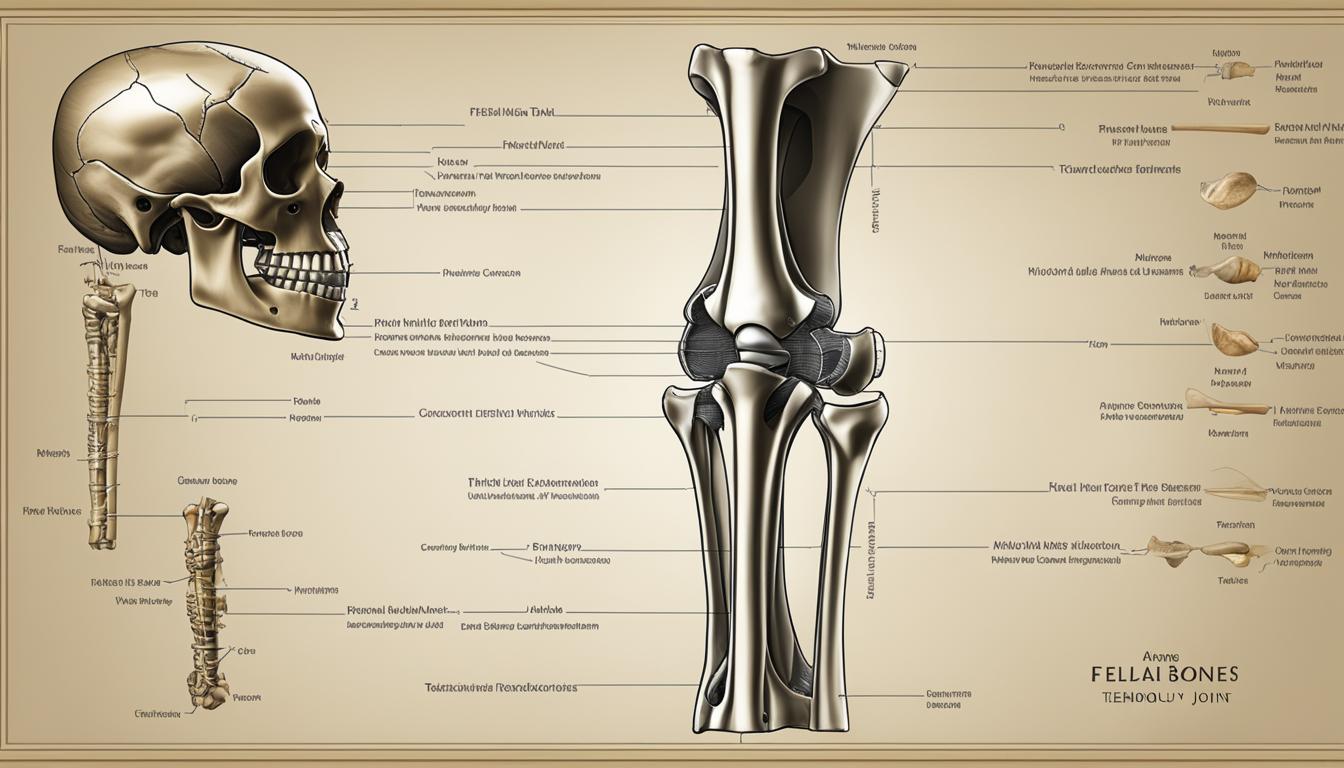
The knee joint consists of three main bones: the femur, tibia, and patella. These bones work together to support the body in an upright position and facilitate various movements. The femur, also known as the thigh bone, is the longest and strongest bone in the body. It connects to the hip joint and extends down to the knee joint. The tibia, or shin bone, is located at the front of the lower leg and is larger and stronger than the fibula, which runs parallel to it. The patella, commonly known as the kneecap, is a small triangular bone that sits in front of the knee joint, protecting it from direct impact.
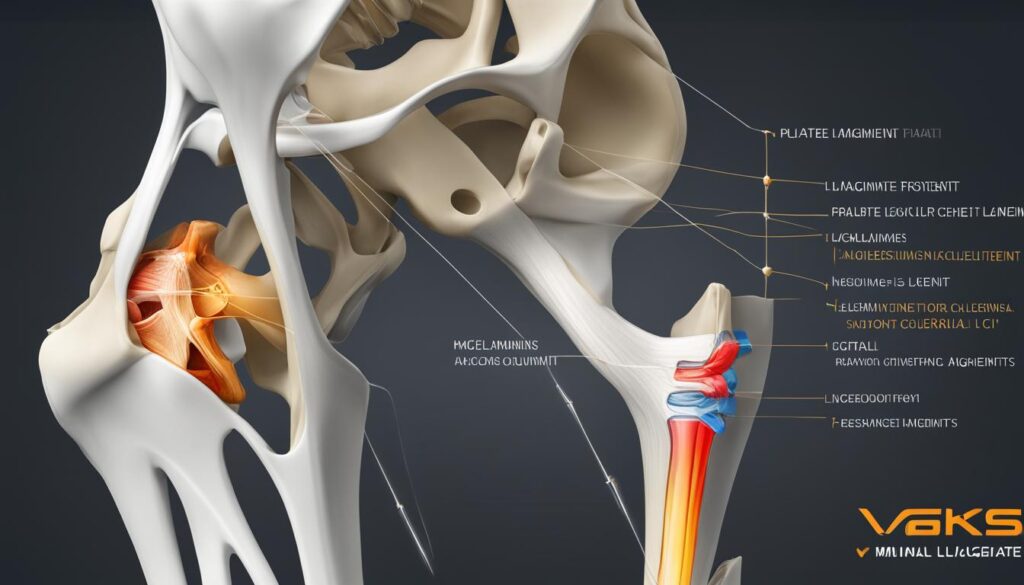
In addition to these bones, the knee joint is supported by various ligaments and tendons that help stabilize the joint and prevent excessive movement. The ligaments of the knee include the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). These ligaments play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the knee joint and providing stability during activities.
In summary, the knee bone structure consists of the femur, tibia, and patella, which form the knee joint. Ligaments and tendons provide support and stability to the joint, allowing for efficient movement and preventing injuries.
| Knee Joint Bones | Function |
|---|---|
| Femur | Upper leg bone |
| Tibia | Bone at the front of the lower leg |
| Patella | Triangular bone in front of the knee |
Knee Joint Components
The knee joint is composed of several components that work together to facilitate movement and provide stability. These components include bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, muscles, joint capsule, and bursa.
The bones of the knee joint have already been mentioned in the previous section. Cartilage, specifically the menisci and articular cartilage, play a crucial role in cushioning the joint and allowing smooth movement.
Ligaments are tough connective tissues that connect the bones and prevent excessive motion. Tendons connect muscles to bones and provide stability. Muscles, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, work together to move and stabilize the knee joint.
The joint capsule surrounds the knee joint and contains synovial fluid to lubricate and nourish the joint. Bursa, small fluid-filled sacs, reduce friction within the knee joint.
Please refer to the diagram below for a visual representation of the knee joint components:
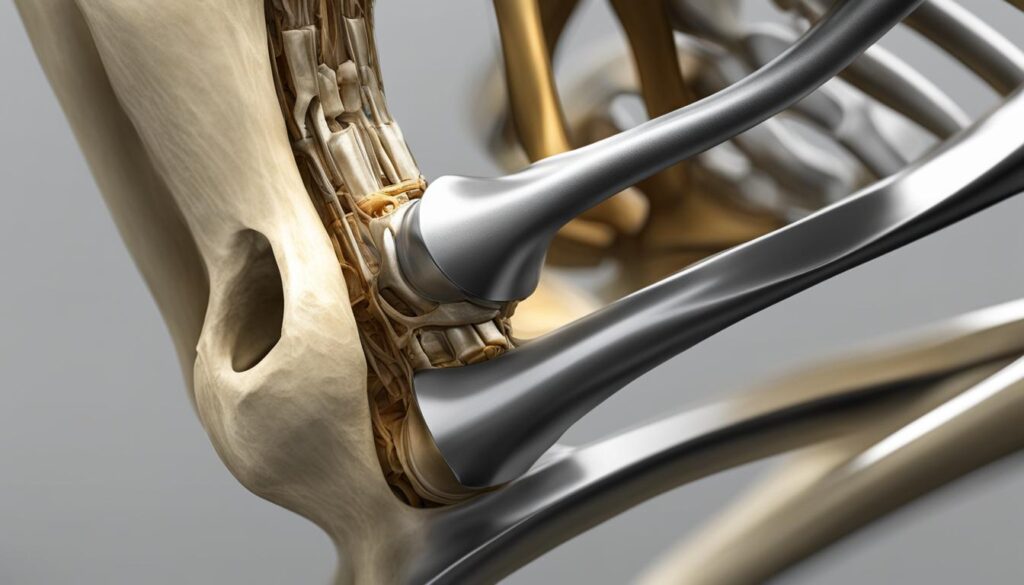
The Role of Knee Bones in Movement
When it comes to movement, knee bones play a crucial role in our ability to navigate the world around us. The knee joint, consisting of the femur, tibia, and patella, allows for the bending and straightening of the leg, enabling essential actions such as walking, running, and jumping.
The flexion and extension of the knee joint are made possible by the interaction of these bones, which act as a hinge. As we bend and straighten our knees, the bones glide smoothly against each other, allowing for fluid motion and stability.
However, the bones alone are not solely responsible for making these movements happen. The knee joint also relies on the support of ligaments, tendons, and muscles, which work together to provide stability and control motion.
The ligaments, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), connect the bones and prevent excessive movement. Tendons, on the other hand, connect muscles to bones, facilitating smooth and controlled motion. The muscles surrounding the knee joint, including the quadriceps and hamstrings, contract and relax to move the bones and stabilize the knee.
| Bone | Ligament |
|---|---|
| femur | ACL, PCL |
| tibia | ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL |
| patella | None |
Table: Knee Bones and Corresponding Ligaments
Understanding the anatomy of the knee bones is essential in comprehending the complex mechanics of movement in the lower extremities. With a strong foundation in knee joint anatomy, we can better appreciate the intricate interplay between bones, ligaments, tendons, and muscles that allow us to move with ease and agility.
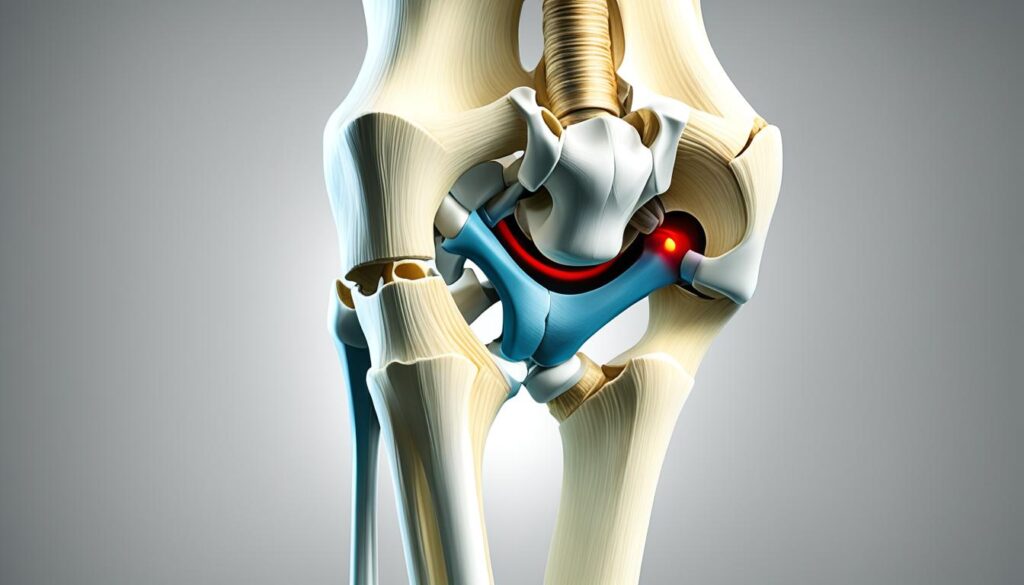
Maintaining Healthy Knee Function
Taking care of your knee joint is essential for maintaining healthy knee function and preventing injuries. Here are some tips for knee joint care:
- Regular exercise: Engage in exercises that specifically target and strengthen the muscles around the knee joint. This helps to improve stability and support for the joint. Examples of beneficial exercises include leg presses, squats, lunges, and step-ups.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put added stress on the knees, increasing the risk of joint pain and damage. By maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise, you can reduce the strain on your knee joints.
- Use proper techniques and equipment: When engaging in physical activities or sports, ensure you use proper techniques and equipment to minimize the risk of knee injuries. This may include wearing appropriate footwear that provides support and cushioning for the knees.
- Avoid sudden changes in intensity or duration of activity: Gradually increase the intensity or duration of your physical activities to allow your knees to adapt and avoid overloading them. Sudden increases in activity can put strain on the joints and lead to injuries.
- Practice proper body mechanics: When lifting heavy objects, always remember to bend your knees and use your leg muscles instead of putting excessive strain on your back. Maintaining proper body mechanics reduces the stress on your knees and prevents unnecessary injuries.
- Avoid prolonged periods of standing or sitting: Prolonged standing or sitting can put pressure on your knees, leading to stiffness and discomfort. Take regular breaks to stretch and move around to keep your knee joints mobile and well-lubricated.
- Incorporate flexibility exercises: Maintain a good range of motion in your knee joints by incorporating flexibility exercises into your routine. Stretching and low-impact activities such as yoga or tai chi can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of knee stiffness.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort in your knees. If you experience pain during or after physical activity, it’s important to listen to your body and rest. Pushing through the pain can worsen existing injuries and prevent proper healing.
By following these tips for knee joint care, you can promote the health and longevity of your knee joints, reduce the risk of injuries, and maintain optimal knee joint function.
Common Knee Injuries
The knee joint is susceptible to various injuries, especially during physical activities and sports. Common knee injuries include:
- Ligament sprains and strains: such as ACL and MCL injuries
- Meniscus tears: which can occur due to twisting, pivoting, or sudden movements
- Fractures: particularly in the patella
- Overuse injuries: like runner’s knee or patellofemoral pain syndrome
These injuries can cause pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty with weight-bearing. Prompt medical evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Treatments may include rest, ice, elevation, pain relievers, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgery. Preventing knee injuries involves proper warm-up, maintaining muscle strength, using appropriate protective gear, and avoiding sudden changes in activity.
| Injury Type | Symptoms | Treatment | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ligament Sprains and Strains | Pain, swelling, instability | Rest, physical therapy, surgery in severe cases | Proper warm-up, strengthening exercises, wearing protective gear |
| Meniscus Tears | Pain, swelling, clicking, catching | Rest, physical therapy, arthroscopic surgery in some cases | Proper technique, avoiding sudden movements |
| Fractures | Pain, swelling, limited range of motion | Immobilization, surgery in some cases | Avoiding high-impact activities, using protective gear |
| Overuse Injuries | Dull aching pain, stiffness | Rest, physical therapy, modifying activities | Gradual increase in activity, adequate rest |
Conclusion
The knee joint is a marvel of engineering and plays a crucial role in our ability to move and perform daily activities. Its complex structure, comprising of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and other components, allows for smooth and efficient motion. Understanding the anatomy of the knee joint is essential for maintaining its healthy function and preventing injuries.
By taking proactive measures such as regular exercise, weight management, and practicing proper body mechanics, we can significantly reduce the risk of knee injuries and promote long-term joint health. Regular physical activity helps strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing stability and support. Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce unnecessary stress on the knee joint, while proper body mechanics ensure proper alignment and minimize the risk of strain.
However, accidents and injuries can still happen. In the unfortunate event of a knee injury, seeking prompt medical attention and following appropriate treatment and rehabilitation protocols are crucial for a full recovery. From rest and physical therapy to more advanced interventions like surgery, the recommended course of action will depend on the severity and nature of the injury. Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan and taking an active role in rehabilitation can help restore function and mobility.
By prioritizing knee joint care and injury prevention, we can maintain an active and pain-free lifestyle. Paying attention to our bodies, listening to any discomfort or pain, and seeking professional advice when needed will ensure the health and longevity of our knee joints. Let’s empower ourselves to protect and preserve this remarkable joint, allowing us to continue enjoying life’s activities with freedom and mobility.
FAQ
What are the bones of the knee joint?
The bones of the knee joint include the femur (thigh bone), tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap).
What is the structure of the knee bones?
The knee joint is comprised of the femur, tibia, and patella, which work together to facilitate movement and provide stability.
What components make up the knee joint?
The knee joint consists of bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, muscles, joint capsule, and bursa.
What role do knee bones play in movement?
Knee bones, including the femur and tibia, enable actions such as walking, running, and jumping by allowing flexion and extension of the leg.
How can I maintain healthy knee function?
To maintain healthy knee function, you can engage in regular exercise, maintain a healthy weight, use proper techniques during activities, wear appropriate footwear, practice proper body mechanics, and incorporate flexibility exercises.
What are some common knee injuries?
Common knee injuries include ligament sprains and strains, meniscus tears, fractures, and overuse injuries such as runner’s knee.