Introduction
Chronic knee joint pain is a pervasive issue that affects millions of individuals worldwide, transcending age, gender, and lifestyle boundaries. What often begins as a subtle discomfort can progressively evolve into a debilitating condition, significantly impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. The knee, being one of the largest and most complex joints in the human body, is particularly susceptible to various forms of pain and injury due to its frequent use and the substantial stress it endures.
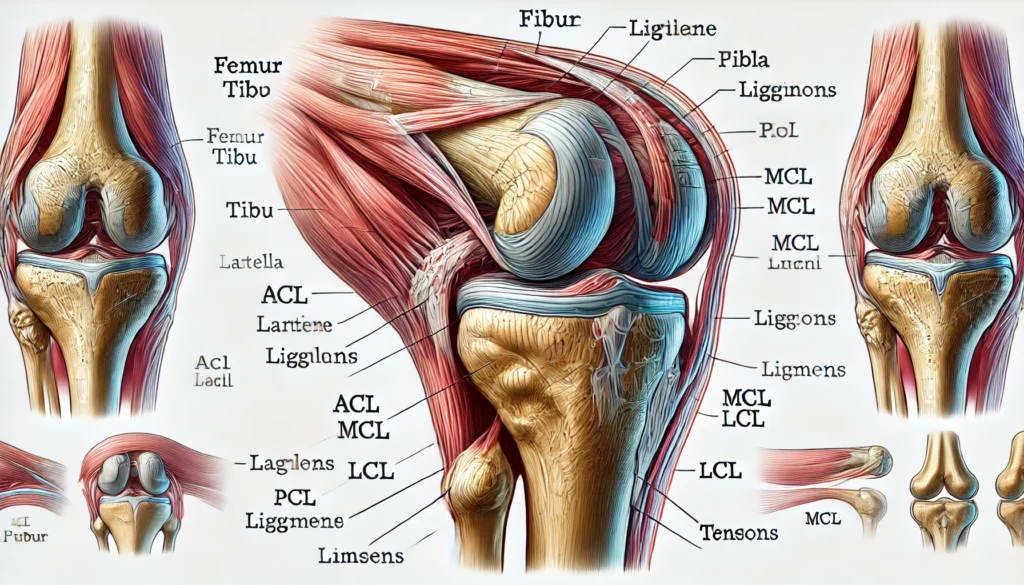
Understanding the multitude of relief options available is crucial for effectively managing and alleviating chronic knee pain. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of knee pain relief, exploring a wide array of non-surgical treatments, alternative therapies, and surgical interventions. Additionally, we’ll discuss preventive measures that can be incorporated into daily life to manage and potentially reduce the occurrence of chronic knee pain.
Common Causes of Chronic Knee Joint Pain
Before delving into treatment options, it’s essential to understand the root causes of chronic knee joint pain. By identifying the underlying issues, healthcare professionals can tailor treatments more effectively, and individuals can better manage their condition.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis stands as the most prevalent cause of chronic knee pain, particularly among older adults. This degenerative joint disease is characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage, the smooth, cushioning tissue that covers the ends of bones in joints. As the cartilage deteriorates, it leads to increased friction between bones, resulting in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
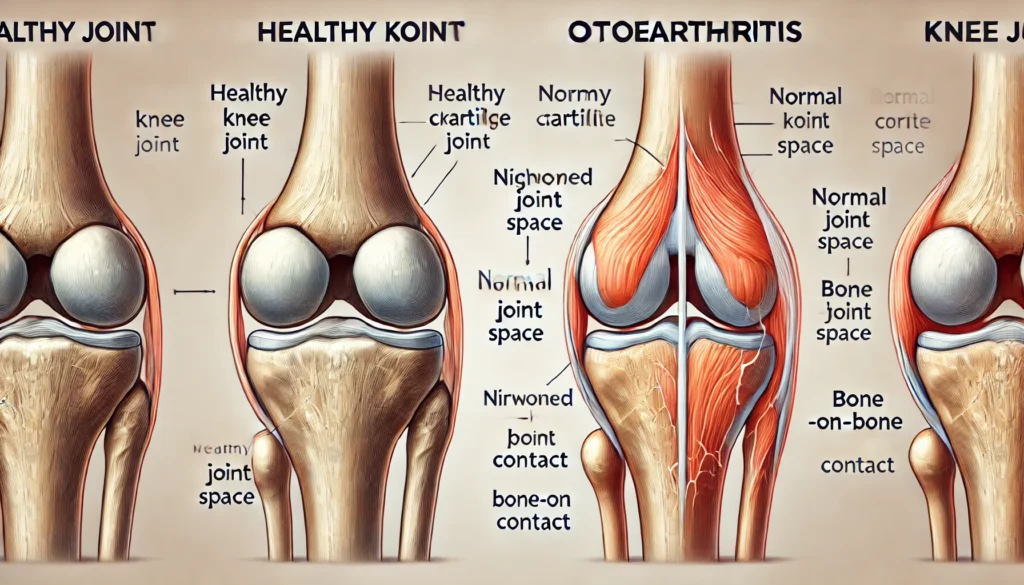
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the synovial membrane, the soft tissue that lines the joint capsule. This attack causes inflammation, pain, and eventual damage to the joint. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis often affects both knees simultaneously and can occur at any age.
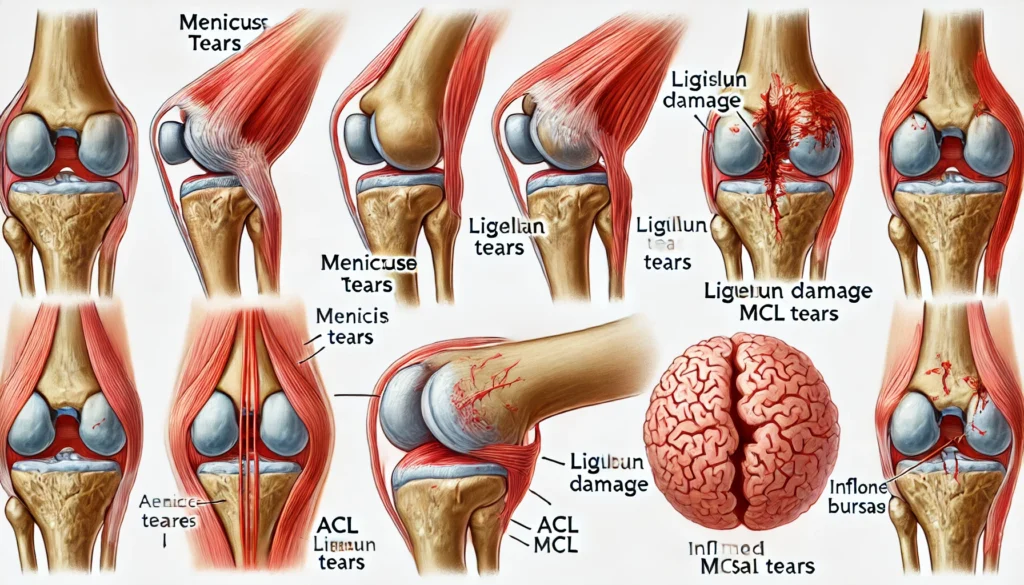
Injuries and Overuse
Traumatic injuries and repetitive stress can lead to chronic knee pain. Common injuries include:
- Meniscus tears: Damage to the cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the thighbone and shinbone.
- Ligament injuries: Tears or sprains in the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), or medial collateral ligament (MCL).
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of the tendons connecting muscles to bones, often resulting from overuse.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the small, fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion the knee joint.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For many individuals suffering from chronic knee pain, non-surgical treatments offer significant relief and improved functionality. These conservative approaches should typically be explored before considering surgical interventions.
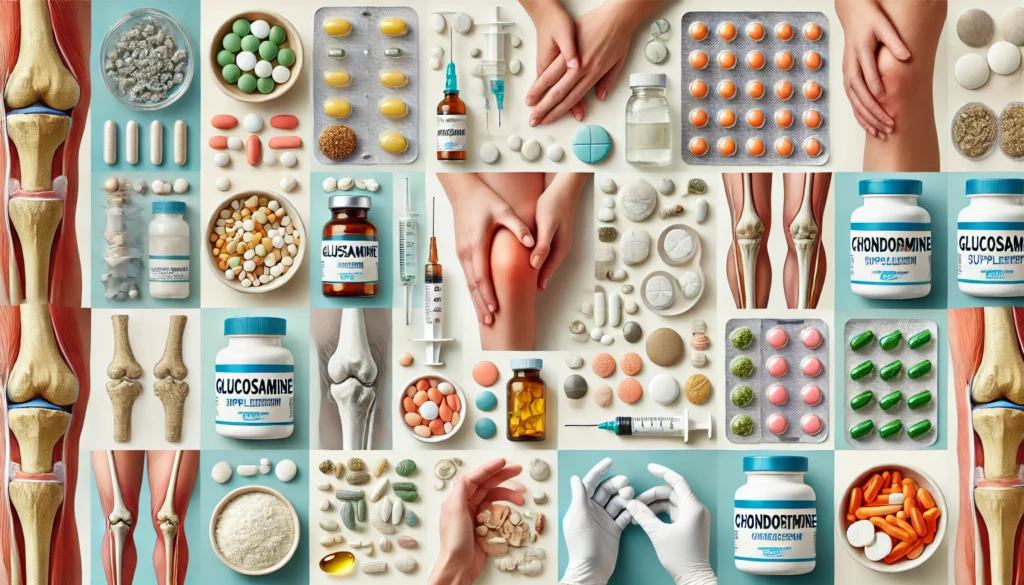
Medications and Supplements
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen and naproxen help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Acetaminophen: Effective for pain relief without anti-inflammatory properties.
Prescription Medications
- Stronger NSAIDs: For more severe pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid injections: Powerful anti-inflammatory drugs injected directly into the knee joint for temporary relief.
- Hyaluronic acid injections: Also known as viscosupplementation, these injections aim to improve joint lubrication and shock absorption.
Supplements
- Glucosamine and chondroitin: These supplements may support joint health, though their effectiveness varies among individuals.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil, these may help reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing chronic knee pain by strengthening the muscles around the knee, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall joint stability.
Personalized Exercise Programs
A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise regimen that may include:
- Strengthening exercises: Focus on quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
- Flexibility exercises: Improve range of motion and reduce stiffness.
- Low-impact aerobic activities: Such as swimming, cycling, or using an elliptical machine.
- Balance and proprioception exercises: Enhance joint stability and reduce the risk of falls.

Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle modifications can significantly impact chronic knee pain management:
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing stress on the knee joints. Even a modest weight loss can lead to substantial improvements in pain and function.
Balanced Diet
Consuming a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help manage pain and support joint health:
- Fruits and vegetables: High in antioxidants and vitamins.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Whole grains: Provide fiber and nutrients.
- Lean proteins: Support muscle health.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in low-impact activities helps maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength without exacerbating pain. Suitable activities include:
- Walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Yoga or Tai Chi

Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief through alternative therapies, either as standalone treatments or in conjunction with conventional methods.
Acupuncture
This ancient Chinese technique involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture may help reduce knee pain by:
- Stimulating the release of endorphins, the body’s natural pain-relieving chemicals.
- Improving blood circulation to the affected area.
- Reducing inflammation.
While scientific evidence on acupuncture’s effectiveness for knee pain is mixed, many patients report significant relief.
[Image: A close-up photo of acupuncture needles being applied to a patient’s knee.]
Massage Therapy
Massage can be beneficial for chronic knee pain by:
- Reducing muscle tension around the knee joint.
- Improving circulation and lymphatic drainage.
- Promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
Different massage techniques may be employed, including:
- Swedish massage
- Deep tissue massage
- Myofascial release
- Sports massage
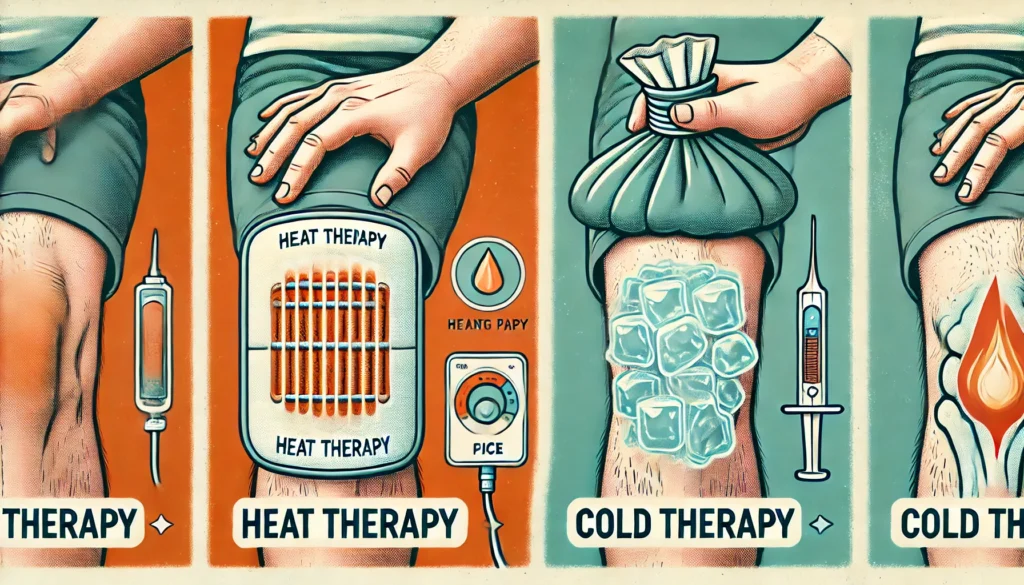
Heat and Cold Therapy
Alternating between heat and cold treatments can provide relief for chronic knee pain:
- Heat therapy: Relaxes muscles and increases blood flow, best used before activities.
- Cold therapy: Reduces inflammation and numbs pain, ideal after activities or during acute pain flare-ups.
Surgical Treatments
When conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical interventions may be considered. The choice of surgery depends on the underlying cause of pain, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s overall health.
Arthroscopy
This minimally invasive procedure involves making small incisions around the knee and inserting a tiny camera (arthroscope) to guide surgical instruments. Arthroscopy can be used to:
- Remove or repair torn cartilage.
- Reconstruct torn ligaments.
- Remove loose bone or cartilage fragments.
Recovery from arthroscopy is typically faster than traditional open surgery, with many patients returning home the same day.
[Image: An illustration or photo of an arthroscopic procedure being performed on a knee joint.]
Osteotomy
In this procedure, the surgeon cuts and reshapes either the tibia (shinbone) or femur (thighbone) to relieve pressure on the damaged part of the knee joint. Osteotomy is often performed to:
- Correct bowlegged or knock-kneed alignment.
- Shift weight from the damaged part of the knee to a healthier area.
This surgery can delay the need for a total knee replacement, especially in younger, active patients.
Knee Replacement Surgery
For severe cases of chronic knee pain, particularly those caused by advanced osteoarthritis, knee replacement surgery may be the most effective option.
Total Knee Replacement
In this procedure, the entire knee joint is replaced with artificial components made of metal and plastic. The surgery involves:
- Removing damaged cartilage and bone.
- Reshaping the bone surfaces to fit the artificial joint.
- Implanting the prosthetic components.
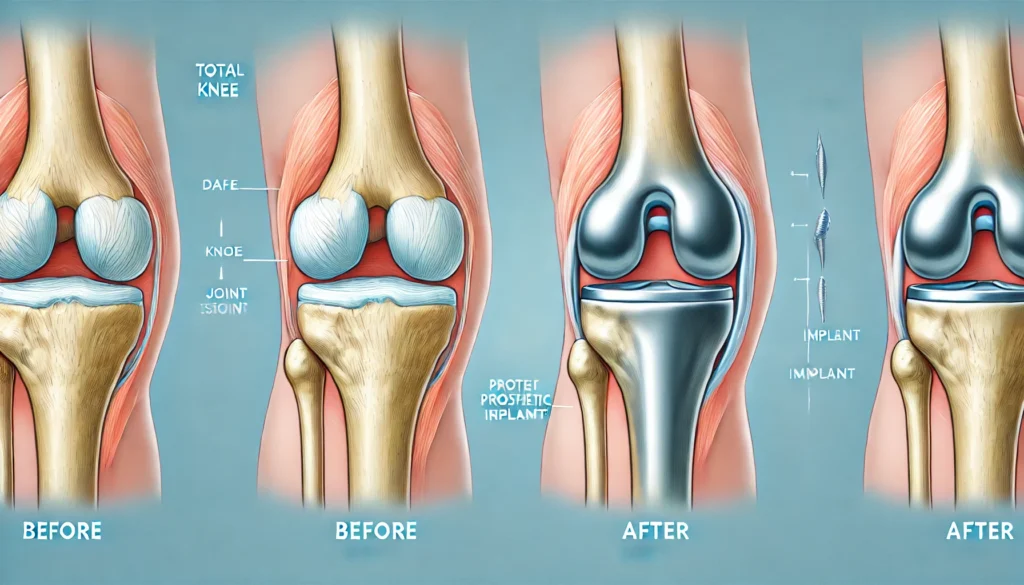
Partial Knee Replacement
In some cases, only one part of the knee needs to be replaced. This less invasive option may be suitable for patients with damage limited to a specific area of the knee.
Recovery from knee replacement surgery typically involves:
- Hospital stay of 1-3 days.
- Physical therapy starting immediately after surgery.
- Gradual return to normal activities over several weeks to months.
- Full recovery and maximum benefit achieved within a year.
Preventive Measures
While not all causes of chronic knee pain are preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating knee problems.
Regular Exercise
Maintaining a consistent exercise routine is crucial for knee health:
- Low-impact cardiovascular activities: Walking, swimming, or cycling to improve overall fitness without stressing the knees.
- Strength training: Focusing on leg muscles to provide better support for the knees.
- Flexibility exercises: Regular stretching to maintain joint mobility and reduce the risk of injury.

Proper Footwear
Wearing appropriate shoes can significantly impact knee health:
- Supportive shoes: Look for footwear with good arch support and cushioning.
- Proper fit: Ensure shoes are neither too tight nor too loose.
- Activity-specific shoes: Use shoes designed for your specific activities or sports.
- Custom orthotics: Consider custom-made shoe inserts for optimal support, especially if you have flat feet or high arches.
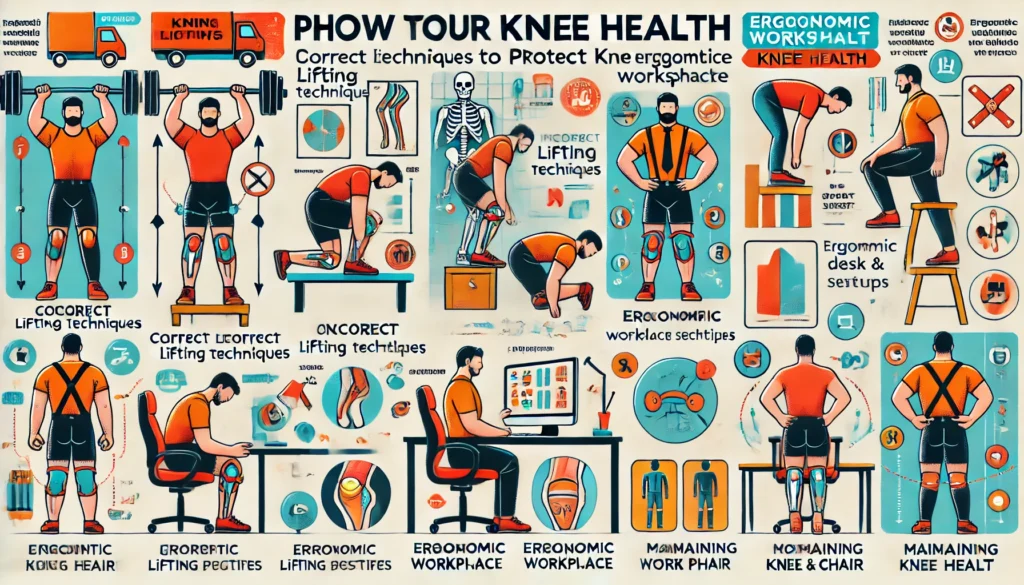
Ergonomic Adjustments
Making ergonomic changes in daily life can help prevent unnecessary stress on the knees:
- Proper lifting techniques: Bend at the knees and hips, not the waist, when lifting heavy objects.
- Ergonomic workplace setup: Use chairs with proper lumbar support and maintain good posture while sitting.
- Regular movement: Avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing; take breaks to move and stretch.
Conclusion
Managing chronic knee joint pain requires a multifaceted approach, often combining various treatment modalities for optimal results. From non-surgical options like medications and physical therapy to alternative treatments and surgical interventions, there are numerous paths to explore in the quest for pain relief and improved functionality.
The key to successful management lies in working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan. This plan should not only address the immediate pain and limitations but also focus on long-term joint health and overall well-being.
Remember, prevention plays a crucial role in maintaining knee health. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, staying physically active, and being mindful of proper body mechanics, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic knee pain or slow its progression.
Ultimately, with the right combination of treatments, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures, many individuals with chronic knee pain can achieve substantial relief and return to a more active, fulfilling life. Whether you’re dealing with the early stages of knee discomfort or managing long-standing pain, there’s always hope for improvement and a path towards better knee health.


Leave a Reply