How Knee Arthritis is Diagnosed: Professional Insights
Knee arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and swelling. While knee arthritis can be a debilitating condition, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage to the joint.

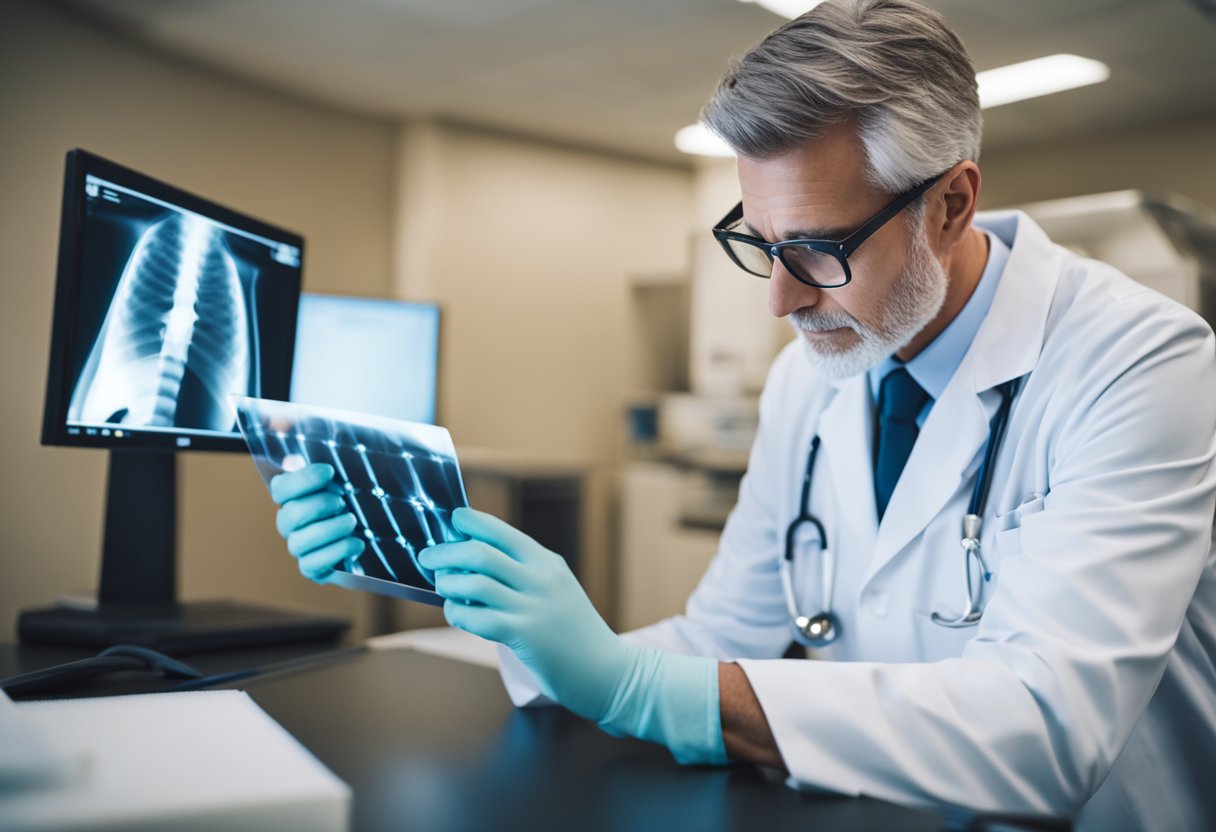
Diagnosing knee arthritis can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis. However, there are several diagnostic tools that doctors use to determine if a patient has knee arthritis. These may include X-rays, MRIs, and blood tests. X-rays are often the first diagnostic tool used and can show signs of joint damage such as bone spurs or narrowing of the joint space. MRIs can provide a more detailed view of the joint and help doctors identify soft tissue damage. Blood tests can help rule out other conditions that may cause joint pain and swelling.
If you are experiencing knee pain, stiffness, or swelling, it is important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms, prevent further joint damage, and improve your quality of life. With the right treatment plan, many people with knee arthritis can continue to lead active and fulfilling lives.
Diagnosis of Knee Arthritis
Diagnosing knee arthritis involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history and physical examination, followed by imaging and laboratory tests, physical therapy assessment, specialist evaluation, and supplementary assessment methods. In this section, we will discuss the various methods used for diagnosing knee arthritis.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Medical history and physical examination are the first steps towards diagnosing knee arthritis. During the physical examination, the doctor will look for signs of inflammation, tenderness, and mobility issues. They will also check for stiffness and joint pain in the knee. The doctor may ask about the patient’s symptoms, such as swelling, stiffness, and pain in the knee. They may also ask about the patient’s family history of arthritis.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are used to diagnose knee arthritis. X-rays are the most common imaging test used to diagnose knee arthritis. X-rays can show bone spurs, cartilage loss, and damaged cartilage. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is another imaging test that can be used to diagnose knee arthritis. MRI can show the joint space and the condition of the cartilage.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests can help diagnose knee arthritis. Blood tests can be used to check for infection, gout, and rheumatoid arthritis. In some cases, a procedure called arthrocentesis, in which a small amount of fluid is removed from within the knee joint with a needle and sent to a laboratory for analysis, may be recommended.
Physical Therapy Assessment
Physical therapy assessment can help diagnose knee arthritis. A physical therapist can evaluate the patient’s exercise routine, flexibility, strength, and joint mobility. They can also evaluate the patient’s walking and other activities of daily living. Physical therapy can help reduce pain and improve mobility in patients with knee arthritis.
Specialist Evaluation
A specialist evaluation may be recommended for patients with knee arthritis. A rheumatologist can help diagnose and treat knee arthritis. They can also provide information about the various treatment options available for knee arthritis.
Supplementary Assessment Methods
Supplementary assessment methods can help diagnose knee arthritis. These methods include joint replacement, arthroscopy, meniscus repair, ligament repair, and tendon repair. These methods are used when other methods have failed to provide relief from knee arthritis.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is the process of ruling out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. In the case of knee arthritis, differential diagnosis may include other types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or post-traumatic arthritis.
Home and Self-Assessment
Home and self-assessment can help diagnose knee arthritis. Patients can track their symptoms and activities of daily living to help identify triggers for knee pain and stiffness. They can also make lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or reducing stress, to help reduce knee pain and stiffness.
Risk Factor Analysis
Risk factor analysis can help diagnose knee arthritis. Risk factors for knee arthritis include age, weight, sports injuries, family history, and lifestyle factors such as stress.
Treatment Response Evaluation
Treatment response evaluation is the process of evaluating the effectiveness of treatment. Patients with knee arthritis may need to try several treatment options before finding the one that works best for them. Treatment options include medications, therapy, injections, exercise, weight loss, and surgery.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Advanced diagnostic techniques can help diagnose knee arthritis. These techniques include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which can show the joint space and the condition of the cartilage, and imaging tests, which can show bone spurs, cartilage loss, and damaged cartilage.
In conclusion, diagnosing knee arthritis involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history and physical examination, followed by imaging and laboratory tests, physical therapy assessment, specialist evaluation, and supplementary assessment methods. By using these methods, doctors can accurately diagnose knee arthritis and recommend the appropriate treatment options for their patients.
Treatment and Management of Knee Arthritis
When it comes to treating knee arthritis, there are various options available that can help manage the condition and alleviate symptoms. Treatment plans may vary depending on the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, overall health, and other factors. Here are some of the most common treatment and management options for knee arthritis:
Non-Pharmacological Therapies
Non-pharmacological therapies are often recommended as a first-line treatment for knee arthritis. These therapies include:
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve joint mobility and strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, which can help reduce pain and improve function.
- Weight loss: Losing weight can help reduce the load on the knee joint, which can help alleviate pain and slow down the progression of the condition.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint flexibility, muscle strength, and overall function.
- Ice and heat therapy: Applying ice or heat to the affected knee can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Rest: Resting the affected knee can help reduce pain and allow the joint to heal.
- Braces: Knee braces can help support the joint and reduce pain during activities.
Medications and Pharmacotherapy
Medications and pharmacotherapy can also be used to manage knee arthritis symptoms. Some common medications used to treat knee arthritis include:
- Acetaminophen: Acetaminophen is a pain reliever that can help reduce mild to moderate knee pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs can help reduce pain and inflammation in the knee joint.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that can be injected directly into the knee joint to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Hyaluronic acid: Hyaluronic acid injections can help lubricate the knee joint and reduce pain.
Surgical and Invasive Procedures
In some cases, surgical and invasive procedures may be necessary to treat knee arthritis. Some common procedures include:
- Knee replacement surgery: Knee replacement surgery involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial joint.
- Knee osteotomy: Knee osteotomy involves cutting and reshaping the bones around the knee joint to shift the weight away from the damaged area.
- Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy involves using a small camera and surgical tools to repair or remove damaged tissue in the knee joint.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation and physical therapy are an important part of knee arthritis treatment and management. These therapies can help improve joint mobility, muscle strength, and overall function.
Lifestyle and Supportive Measures
Making lifestyle changes and using supportive measures can also help manage knee arthritis symptoms. Some common lifestyle and supportive measures include:
- Braces: Knee braces can help support the joint and reduce pain during activities.
- Walking aids: Using a cane or walker can help reduce the load on the knee joint and improve mobility.
- Stress management: Managing stress can help reduce pain and improve overall well-being.
Emerging Treatments and Research
There are several emerging treatments and research studies being conducted to find new and innovative ways to treat knee arthritis.
Long-Term Management and Prognosis
Long-term management and prognosis for knee arthritis depend on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the patient’s age, overall health, and other factors.
Patient Education and Self-Care
Patient education and self-care are important aspects of knee arthritis treatment and management. Patients should be educated on the condition, its symptoms, and how to manage it through lifestyle changes and other treatments.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Monitoring and follow-up appointments are important to ensure that the treatment plan is working effectively and to make any necessary adjustments.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management strategies can help reduce pain and improve overall well-being. These strategies may include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Alternative and complementary therapies, such as acupuncture and capsaicin, may also be used to manage knee arthritis symptoms.
Nutritional Considerations and Supplements
Nutritional considerations and supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and glucosamine, may also be helpful in managing knee arthritis symptoms.
Assistive Devices and Orthotics
Assistive devices and orthotics, such as knee braces and shoe inserts, can help support the knee joint and improve mobility.
Psychological Support and Coping
Psychological support and coping strategies can help patients manage the emotional toll of knee arthritis.
Surgical Outcomes and Recovery
Surgical outcomes and recovery time depend on several factors, including the type of surgery performed and the patient’s overall health.
Complications and Risk Management
Complications and risk management are important considerations for patients undergoing surgery or other invasive treatments for knee arthritis.
Advancements in Surgical Techniques
Advancements in surgical techniques are making knee arthritis treatment and management more effective and less invasive than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the initial signs of arthritis in the knee?
The initial signs of knee arthritis include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the knee joint. You may also experience a grinding or popping sensation when you move your knee. These symptoms may be mild at first but can worsen over time.
Can knee arthritis be effectively treated without surgery?
Yes, knee arthritis can be effectively treated without surgery. Non-surgical treatments for knee arthritis include physical therapy, weight loss, and medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as avoiding high-impact activities and using assistive devices can help manage symptoms.
What exercises are recommended for someone with knee osteoarthritis?
Low-impact exercises such as walking, cycling, and swimming are recommended for someone with knee osteoarthritis. Strengthening exercises that target the muscles around the knee joint can also help reduce pain and improve mobility. It is important to consult with a physical therapist or healthcare provider before starting any exercise program.
What are the most effective non-surgical treatments for knee arthritis?
The most effective non-surgical treatments for knee arthritis include physical therapy, weight loss, and medications such as NSAIDs and corticosteroids. Additionally, assistive devices such as knee braces and shoe inserts can help manage symptoms. In some cases, injections of hyaluronic acid or platelet-rich plasma may also be recommended.
How can rheumatoid arthritis in the knees be identified?
Rheumatoid arthritis in the knees can be identified through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as blood tests and imaging studies. Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the knees may include pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
Is walking beneficial for managing knee arthritis symptoms?
Yes, walking can be beneficial for managing knee arthritis symptoms. Low-impact aerobic exercise such as walking can help improve joint mobility and reduce pain. It is important to wear appropriate footwear and to start with short distances and gradually increase the duration and intensity of the exercise.