Attendees
Eighteen male members of the National Polish Rowing Team (heavyweight rowers) were recruited, but only 10 met the inclusion criteria and participated in the study; all participants completed the two ergometer tests of 2000 meters. Before each test, anthropometric parameters were assessed using an electronic scale to the nearest 0.05 kg (Tanita BC-980 MA, Tanita Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The results are shown in Table 1. The study was conducted by following the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee of Poznań University of Medical Sciences (decision No. 314/22 in 2022). All participants were informed of the study procedures and gave their written consent.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were a minimum of 5 years of training, a minimum total training time of 240 minutes per week, membership of the Polish rowing team and completion of the 2000 meter ergometer test.
Exclusion criteria
The exclusion criteria were antibiotic therapy, probiotics, prebiotics, metformin, dietary regimen, and health problems in the past three months.
Training program
The exercise profile, including intensity, volume (in minutes), and type (specific, i.e., rowing: endurance, speed, technical; and nonspecific: strength, jogging), was recorded daily. In addition, the intensity of the training was classified based on the LA threshold (4 mmol/l): an extensive (below the LA threshold) or an intensive (above the LA threshold) workload (Table 2).
Food intake
Total food intake was analyzed by a dietitian before each test using the 24-hour dietary recall method. The dietitian carefully checked each questionnaire and was available to participants during all meals. Energy, carbohydrates, proteins and fats were then measured via the commercially available DietetykPro program (DietetykPro, Wrocław, Poland).
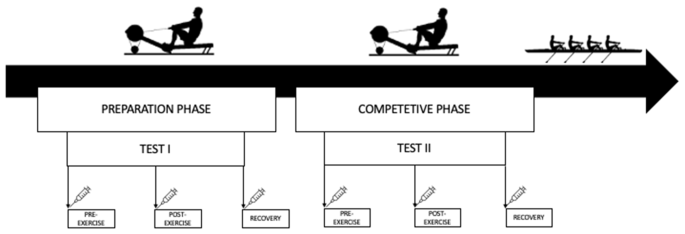
The research design and timeline
Exercise test
For tests I and II, the athletes performed a controlled test at a distance of 2000 m (Fig. 1). The break between tests was almost 10 weeks (68 days). Test I was conducted at the beginning of the preparatory phase, while Test II was conducted at the beginning of the competitive phase. The participants rowed a distance of 2000 m as quickly as possible on the ergometer (Concept II, USA), as the test results were taken into account when selecting for the champion team. The athletes were therefore highly motivated to perform both tests with maximum effort. The exercise test was performed every day at 10:00 am. Before the test, participants ate a small, light meal and were hydrated (Table 1). Before testing, each participant completed an individual 5-minute warm-up.
Collect and research material
Samples were collected at the same three time points: before (before training), after an overnight fast; Post (immediately after training) and recovery (after 1 hour of recovery) for tests I II.
Blood samples were collected from the antecubital vein into 9 ml polyethylene tubes (to obtain serum) and centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes. The serum was frozen and stored at −80°C until analysis. In addition, capillary blood samples were collected from the earlobe before and immediately after the exercise test to assess LA levels.
Dimensions
Serum zonulin, intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP), LPS, LBP, and interleukin 6 (IL-6) were measured using commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs; SunRed Biotechnology Company, Shanghai, China). The test range was 0.25–70 ng/ml for zonulin, 0.3–80 ng/ml for I-FABP, 12–4000 endotoxin units (EU)/l for LPS, 0.2–60 µg/ml for LBP and 1–300 ng/l for IL-6. In addition, LA in capillary blood was measured immediately after sampling using a commercially available kit (Diaglobal, Berlin, Germany). The LA concentrations are presented as mmol/l.
static analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software, USA). Descriptive statistics such as mean and standard deviation were used to identify patterns and trends. To investigate whether the variables had a normal distribution, the Shapiro-Wilk test was performed. To measure the equality of variances, the Brown-Forsythe test was used. One-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA), with Tukey’s post hoc analysis, was used to assess differences in measured variables from the three assessment points (Pre, Post, and Recovery) for Tests I and II. A t test was used to compare food intake, anthropometric characteristics and 2000-m test results (power, time and LA) between tests I and II. Cohen’s d was calculated to determine effect size. It was interpreted as small (0.2), moderate (0.5), or large (0.8) (Cohen, 1988). For correlation analysis, Pearson linear correlation coefficients were calculated. Significance of all statistical analyzes was set at p ≤ 0.05. Based on a power analysis, all tests that produced significant results had a power above 0.9, as calculated by G Power 3.1(G Power, (13).

Leave a Reply