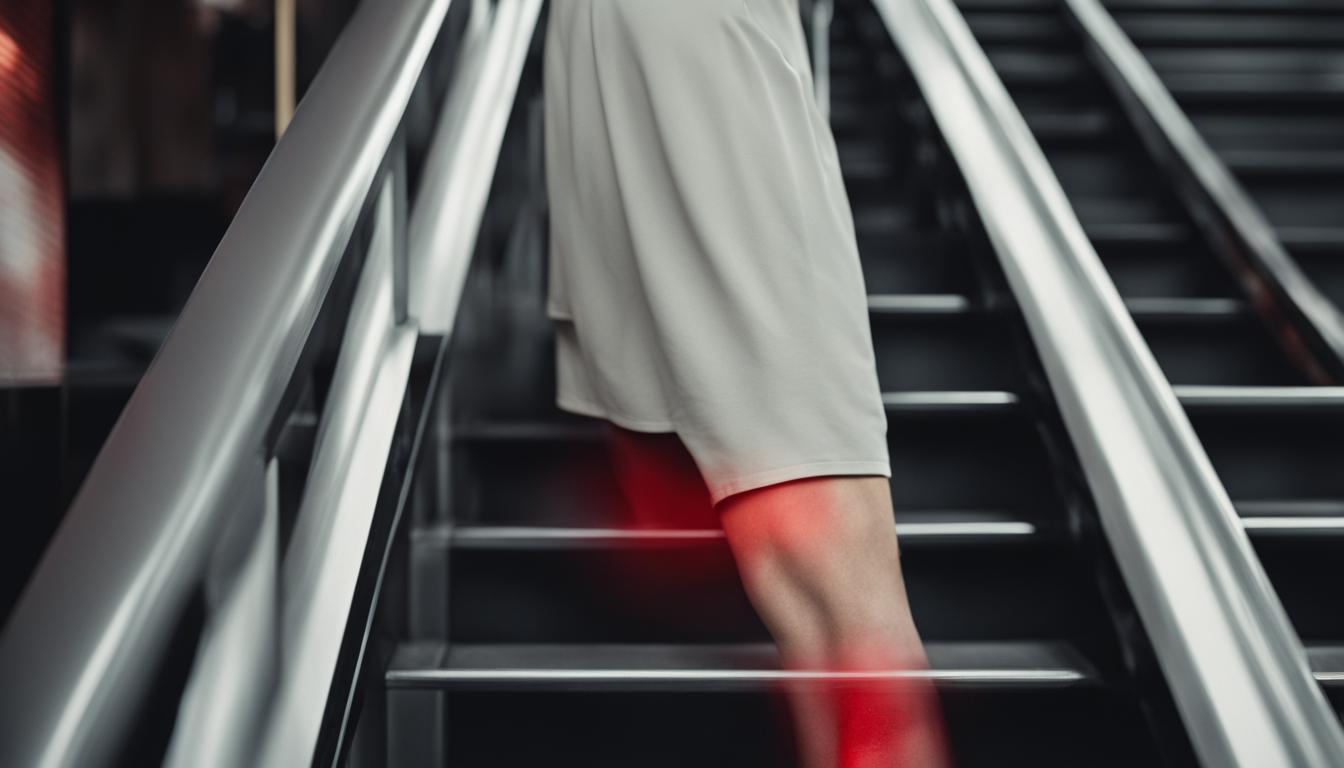
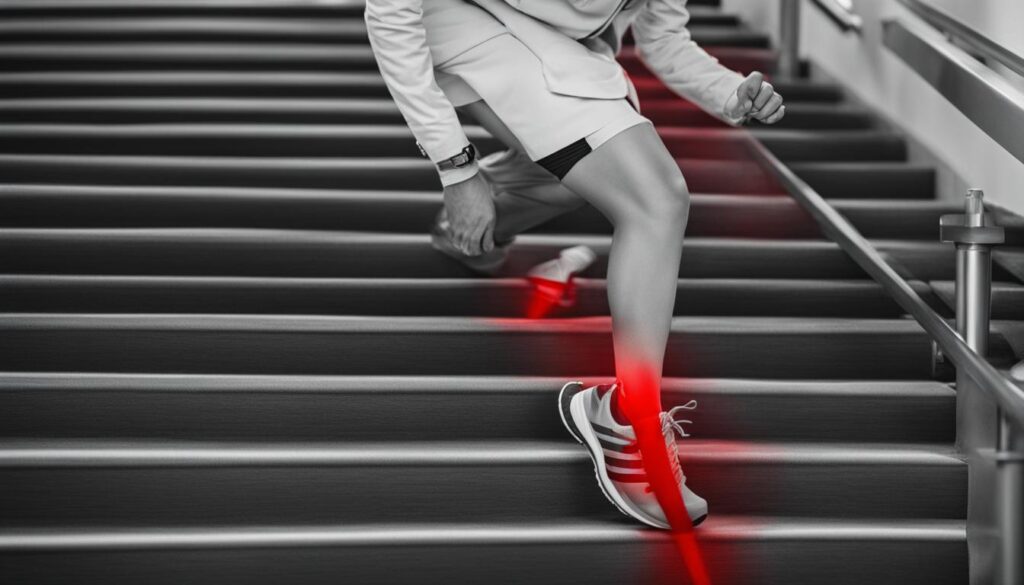
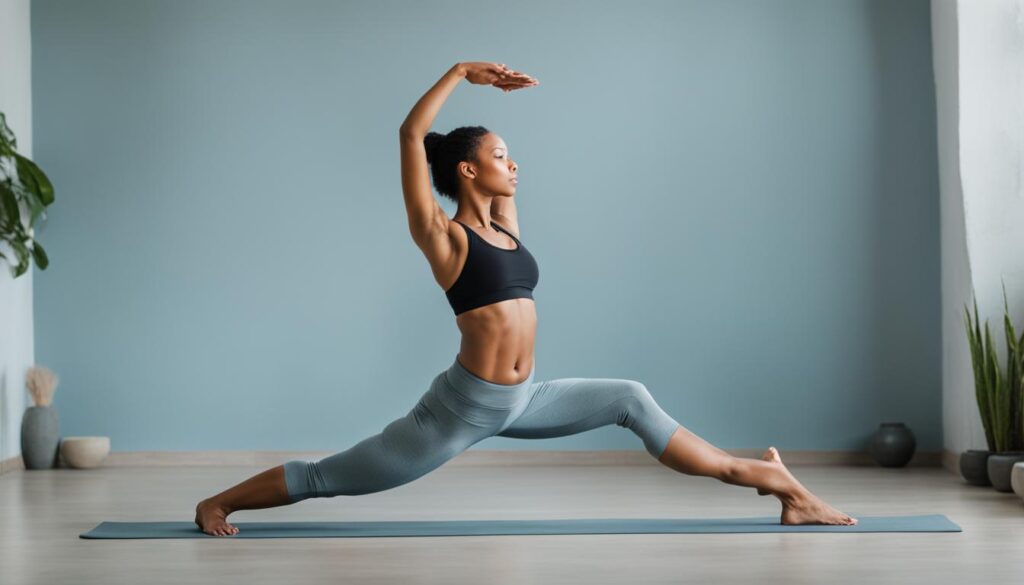
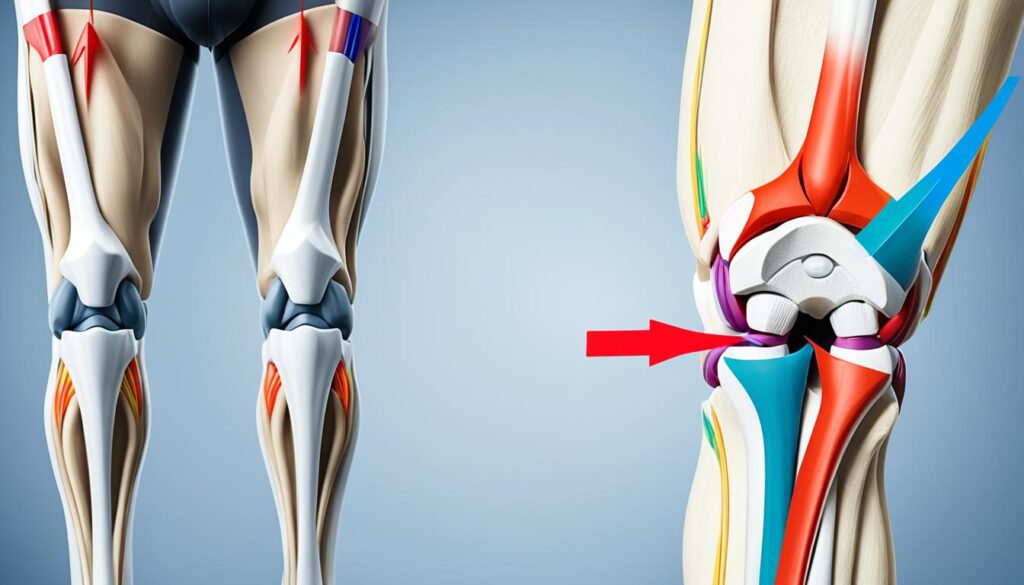
If you experience knee pain specifically when climbing stairs, you may be wondering what could be causing it. Climbing stairs puts added pressure on your knees, as they have to bear a force that is several times your body weight. While this pressure alone should not cause pain, there are several potential causes of knee pain when stair climbing. Understanding these causes is important in order to find relief and prevent further discomfort.
If you experience knee pain when going up stairs or while stair climbing, it’s crucial to identify the underlying causes. In this article, we will explore the common causes of knee pain when climbing stairs, the anatomy of the knee, effective treatment strategies, and preventive measures to maintain joint health.
Key Takeaways:
- Knee pain when climbing stairs can be caused by various factors, such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tear, chondromalacia patella, IT band syndrome, and muscle imbalance.
- Understanding the anatomy of the knee and its components is essential in identifying the potential causes of knee pain.
- Treatment strategies for knee pain when climbing stairs may include targeted exercises, body awareness, and modified movement techniques.
- Seeking professional help, such as consulting with a physical therapist, can provide personalized guidance in managing knee pain.
- Preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy weight, wearing proper footwear, and staying physically active, can help prevent knee pain and maintain overall joint health.
Understanding the Knee and its Anatomy
When it comes to knee pain when climbing stairs, understanding the complex anatomy of the knee is crucial. The knee joint is composed of various components that work together to facilitate movement and provide stability.
Let’s explore the different parts of the knee:
- Bones: The knee joint consists of three main bones – the patella (kneecap), femur (thigh bone), and tibia (shin bone). These bones form the structural foundation of the knee.
- Ligaments: Ligaments are strong bands of connective tissue that help stabilize the knee joint. They connect the bones and provide support during movement.
- Tendons: Tendons connect muscles to bones and play a crucial role in the functioning of the knee joint.
- Cartilage: The knee joint is lined with cartilage, a smooth and durable tissue that acts as a cushion and reduces friction during movement.
- Menisci: Menisci are thick cartilage wedges that sit between the femur and tibia. They play a crucial role in shock absorption and improving the stability of the knee.
- Bursae: Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that provide cushioning and reduce friction between different knee structures.
- Muscles: Muscles surrounding the knee joint, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, enable movement and provide strength and stability.
- Nerves: Nerves transmit signals to and from the knee, including sensations of pain.
By comprehending the intricacies of knee anatomy, we can better understand the potential causes of knee pain when climbing stairs. This knowledge serves as a foundation for effective diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies to alleviate discomfort and restore optimal knee function.
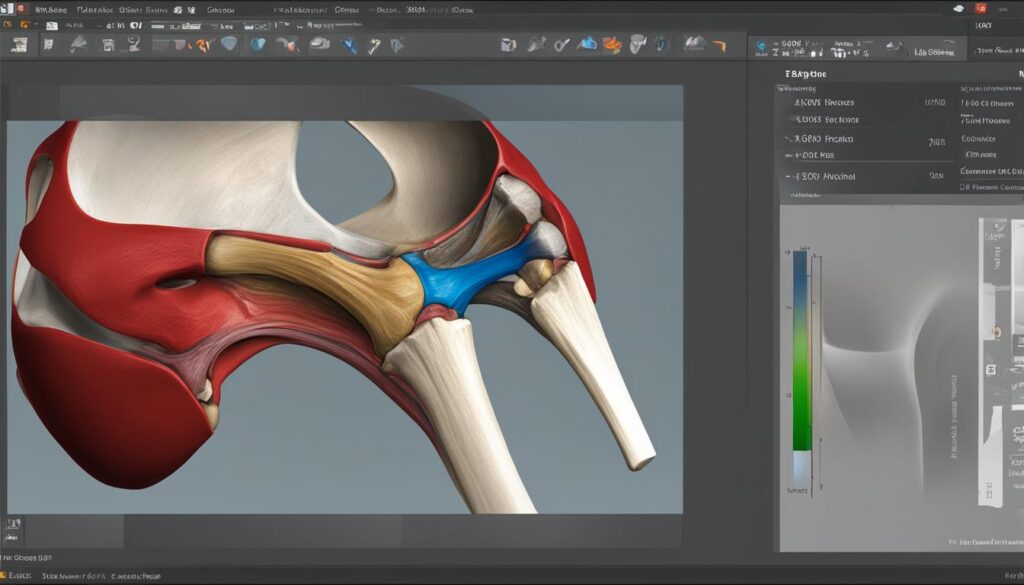
Common Causes of Knee Pain When Climbing Stairs
There are several common causes of knee pain when climbing stairs. It is important to understand these causes in order to determine the appropriate treatment and management strategies. The most common causes of knee pain when stair climbing include:
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Also known as runner’s knee, this condition refers to pain in the front of the knee often caused by overuse or a sudden increase in physical activity.
- Meniscus Tear: A meniscus tear can occur from twisting or pivoting, leading to knee pain, especially on the inner or outer aspect of the knee.
- Chondromalacia Patella: This condition refers to the wearing of the cartilage behind the kneecap, causing pain and irritation.
- IT Band Syndrome: IT band syndrome is caused by friction and irritation of the iliotibial band on the outside of the knee, resulting in pain when going down stairs.
- Muscle Imbalance: Relying too heavily on the quadriceps muscles can create an imbalance and put excessive pressure on the front of the knee, leading to pain.
Understanding these common causes is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and finding relief from knee pain when climbing stairs.
Signs and Symptoms to Look Out For
When experiencing knee pain when climbing stairs, it is important to pay attention to certain signs and symptoms that can help determine the underlying cause. These may include:
- Localized pain in the front, sides, or back of the knee
- Swelling or tenderness around the knee joint
- A popping or clicking sensation in the knee
- Increased pain when bearing weight on the affected knee
- Difficulty straightening or bending the knee fully
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treating Knee Pain When Climbing Stairs
When it comes to treating knee pain while climbing stairs, there are several effective strategies that can provide relief and improve your condition. By incorporating targeted exercises, body awareness, and modified walking techniques into your daily routine, you can address the underlying causes of knee pain and enhance your overall well-being.
Targeted Exercises
One of the most effective ways to treat knee pain is through targeted exercises that focus on strengthening the structures around the knee. These exercises help to stabilize the joint, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. Some examples of targeted exercises include:
- Hip flexor stretches
- Single-leg lifts
- Hamstring stretches
| Exercise | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Flexor Stretches | Stand upright, take a step forward with one leg, and lower your body into a lunge position. Lean forward slightly to stretch the hip flexors of the back leg. | Hold each stretch for 30 seconds and repeat 3 times on each leg. |
| Single-Leg Lifts | Stand behind a chair and hold onto it for support. Lift one leg straight back while keeping your knee straight. Hold for a few seconds and slowly lower your leg. | Perform 10-15 repetitions on each leg for 3 sets. |
| Hamstring Stretches | Sit on the edge of a chair with one leg extended. Lean forward at the hips until you feel a stretch in the back of your thigh. Hold for 30 seconds and repeat on the other leg. | Perform 3-5 stretches on each leg. |
Body Awareness
Body awareness plays a crucial role in identifying and addressing the underlying causes of knee pain. By being mindful of your movement patterns and muscle imbalances, you can make necessary adjustments to reduce stress on your knees. Here are some tips for enhancing body awareness:
- Pay attention to your posture and alignment during daily activities.
- Avoid excessive twisting or pivoting movements that can strain the knee joint.
- Engage different muscle groups when performing activities to distribute the load more evenly.
Modified Walking Technique
Modifying your walking technique can provide quick relief from knee pain when climbing stairs. Consider the following techniques:
“Engage the glutes and hamstrings when climbing stairs to shift the load away from the knees and onto the larger muscles of the hips and thighs. This can be achieved by focusing on pushing off from the heel and using a slightly wider step.”
By making these adjustments, you can reduce the impact on your knees and improve your overall stability and comfort.

Remember, it’s important to listen to your body and do what works best for you. If you’re unsure about any exercises or techniques, consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs. With targeted exercises, body awareness, and modified walking techniques, you can effectively treat knee pain when climbing stairs and improve your quality of life.
Recommended Exercises for Knee Pain Relief
When it comes to alleviating knee pain, specific exercises can play a crucial role in strengthening the knees, improving flexibility, and providing much-needed relief. These exercises have been recommended by physical therapists and target the muscles surrounding the knee, while also addressing any tightness or pain in the hip and lower back. Regularly performing these exercises can help build strength, enhance stability, and ultimately reduce knee pain when climbing stairs.
Here are some examples of recommended exercises:
- Hip Flexor Stretches: Stretching the hip flexors can help alleviate knee pain by reducing tension in the muscles surrounding the knee joint. To perform this exercise, start by kneeling on one knee, keeping the other foot flat on the ground. Gently lean forward until you feel a stretch in the front of your hip. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds on each side, repeating 2-3 times.
- Single-Leg Squats: Single-leg squats are an effective exercise for strengthening the muscles around the knee. Stand with one foot slightly in front of the other and slowly lower yourself into a squat position, keeping your knee aligned with your toes. Return to the starting position and repeat 10-12 times on each leg.
- Wall Squats: Wall squats are another great exercise for building strength in the knees. Stand with your back against a wall and slowly slide down into a squat position, keeping your knees bent at a 90-degree angle. Hold this position for 30-60 seconds, then gradually rise back up. Repeat 10-12 times.
- Hamstring Stretches: Stretching the hamstring muscles can help relieve tension and improve flexibility in the knees. Lie on your back with one leg extended, and gently raise the other leg towards your chest, keeping it straight. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds on each side, repeating 2-3 times.
- Glute Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening the glutes can help provide stability to the knees and reduce pain. Try exercises like glute bridges or clamshells to target these muscles and improve knee functionality.
Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise routine, especially if you have pre-existing knee conditions or injuries. They can provide personalized guidance and help tailor the exercises to your specific needs.
Exercise Frequency and Progression
It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises. Aim to perform these exercises at least 2-3 times a week to experience the benefits. As your strength and flexibility improve, you can gradually increase the number of repetitions or add resistance to further challenge your muscles.
By incorporating these recommended exercises into your routine, you can strengthen your knees, improve stability, and reduce knee pain while climbing stairs. Always listen to your body, modify the exercises as needed, and seek professional guidance if you experience any persistent pain or discomfort.
Importance of Building Resilience and Seeking Professional Help
Building resilience and strength in the knee muscles is crucial for effective knee pain management and prevention of further discomfort. In order to achieve this, incorporating targeted exercises, improving body awareness, and modifying movement patterns can greatly contribute to building resilience and providing relief.
However, it is equally important to seek professional guidance and expertise in managing knee pain. By consulting with a physical therapist, you can receive personalized assessment and treatment plans tailored to your specific condition. A physical therapist will guide you throughout the rehabilitation process, ensuring that you are performing exercises correctly and progress at a pace suitable for your unique needs and goals.
A valuable resource that can complement professional guidance is a knee pain relief app. These digital tools offer convenient access to a wide range of exercises designed to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knees and help manage pain. With a knee pain relief app, you can easily follow exercise programs, track your progress, and receive consistent support in your journey towards relieving and managing knee pain.
“Building resilience and seeking professional help are key components of an effective knee pain management plan. Strengthening exercises, combined with expert guidance and the convenience of a knee pain relief app, can provide the support and resources needed to effectively address knee pain and promote overall knee health.”
Building resilience, seeking professional guidance, and utilizing digital resources such as knee pain relief apps are essential steps in effectively managing knee pain and regaining strength. By taking proactive measures and seeking the right support, you can improve your quality of life and maintain optimal knee health.
Preventing Knee Pain and Maintaining Joint Health
Preventing knee pain and maintaining joint health require adopting several key strategies. These strategies include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of knee pain. By maintaining a healthy weight through proper nutrition and regular exercise, you can reduce the strain on your knees and prevent pain.
- Regular Exercise and Stretching: Engaging in regular exercise that focuses on strengthening the muscles around the knee can help stabilize the joint and improve overall joint health. Incorporating stretching exercises can also maintain flexibility and reduce the risk of knee pain.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing appropriate footwear that provides adequate support and cushioning is essential in preventing knee pain. Choose shoes that are specifically designed for the activity you engage in and ensure a proper fit to maintain proper alignment and reduce stress on the knees.
- Avoiding Sudden Changes in Activity Levels: Gradually increasing your activity level and avoiding sudden intense activities can help prevent knee pain. Sudden changes in activity levels may put excessive strain on the knees and lead to discomfort.
- Using Proper Techniques: Whether it’s climbing stairs or engaging in sports activities, using proper techniques can significantly reduce the risk of knee pain. Maintain good posture, use proper body mechanics, and avoid unnecessary twisting or pivoting motions that can strain the knee joints.
By incorporating these strategies into your lifestyle, you can effectively prevent knee pain and maintain optimal joint health. Taking proactive measures to care for your knees will allow you to enjoy a pain-free and active life.
| Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Maintaining a Healthy Weight | Reduces stress on knee joints |
| Regular Exercise and Stretching | Strengthens knee muscles and maintains flexibility |
| Proper Footwear | Provides support and cushioning to reduce knee strain |
| Avoiding Sudden Changes in Activity Levels | Prevents excessive strain on knee joints |
| Using Proper Techniques | Reduces the risk of knee injuries |
Implementing these preventive strategies will not only help you avoid knee pain but also contribute to maintaining long-term joint health.
Conclusion
Knee pain when climbing stairs can be a significant source of discomfort, but there are ways to find relief and manage this issue. Understanding the various causes of knee pain, such as patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tear, chondromalacia patella, IT band syndrome, and muscle imbalance, is crucial in developing appropriate treatment strategies.
Implementing targeted exercises, such as stretching and strengthening exercises, can help provide relief and improve knee function. Body awareness and modifications in movement patterns while climbing stairs can also alleviate knee pain. Additionally, building resilience in the knee muscles through regular exercise and seeking professional guidance, such as consulting with a physical therapist, can further enhance the management of knee pain and discomfort.
Preventive measures play an essential role in maintaining joint health and reducing knee pain in the long term. Maintaining a healthy weight, wearing proper footwear that provides support and cushioning, and staying physically active are key factors in preventing knee pain. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can find relief from knee pain, manage discomfort effectively, and maintain overall joint strength.
FAQ
What could be causing knee pain when climbing stairs?
There are several potential causes of knee pain when stair climbing, including patellofemoral pain syndrome, meniscus tear, chondromalacia patella, IT band syndrome, and muscle imbalance. Understanding these causes is crucial for finding relief and preventing further discomfort.
How can I treat and manage knee pain when climbing stairs?
Targeted exercises, such as hip flexor stretches and single-leg lifts, can help strengthen the knee and alleviate pain. Body awareness and modifying your walking technique, like using a handrail or engaging different muscles, can also provide relief.
What exercises can help relieve knee pain when climbing stairs?
Recommended exercises for knee pain relief include hip flexor stretches, single-leg squats, wall squats, hamstring stretches, and glute strengthening exercises. These exercises target the muscles around the knee and improve flexibility.
Why is it important to build resilience and seek professional help for knee pain?
Building strength in the knee muscles is crucial for managing knee pain and preventing further discomfort. Seeking professional guidance, like consulting with a physical therapist, can provide personalized treatment plans and expertise in managing knee pain.
How can I prevent knee pain and maintain joint health?
Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise that strengthens the knee muscles, and proper footwear can prevent knee pain. Avoiding sudden changes in activity levels and using proper techniques during physical activities also helps preserve joint health.