Did you know that knee injuries are one of the most common musculoskeletal problems worldwide?
With more than 100 million cases reported each year, knee injuries affect people of all ages and can have a significant impact on their daily lives.
Whether you’re an athlete, an active individual, or simply going about your daily activities, understanding knee pain causes, and effective knee pain management strategies is crucial for maintaining your overall health and mobility.
In this article, we will explore the various symptoms of knee injuries and highlight which ones matter the most. We will also delve into the diagnosis and treatment options available, as well as discuss preventive measures and recovery strategies to help you minimize the risk of knee injuries and enhance your overall well-being.
Knee Injury Diagnosis and Treatment
When it comes to knee injuries, accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for effective recovery and pain relief. Healthcare providers employ various methods to diagnose knee injuries, including:
- Physical examinations: A comprehensive examination helps assess the extent of the injury, identify specific symptoms, and determine the range of motion and stability of the knee.
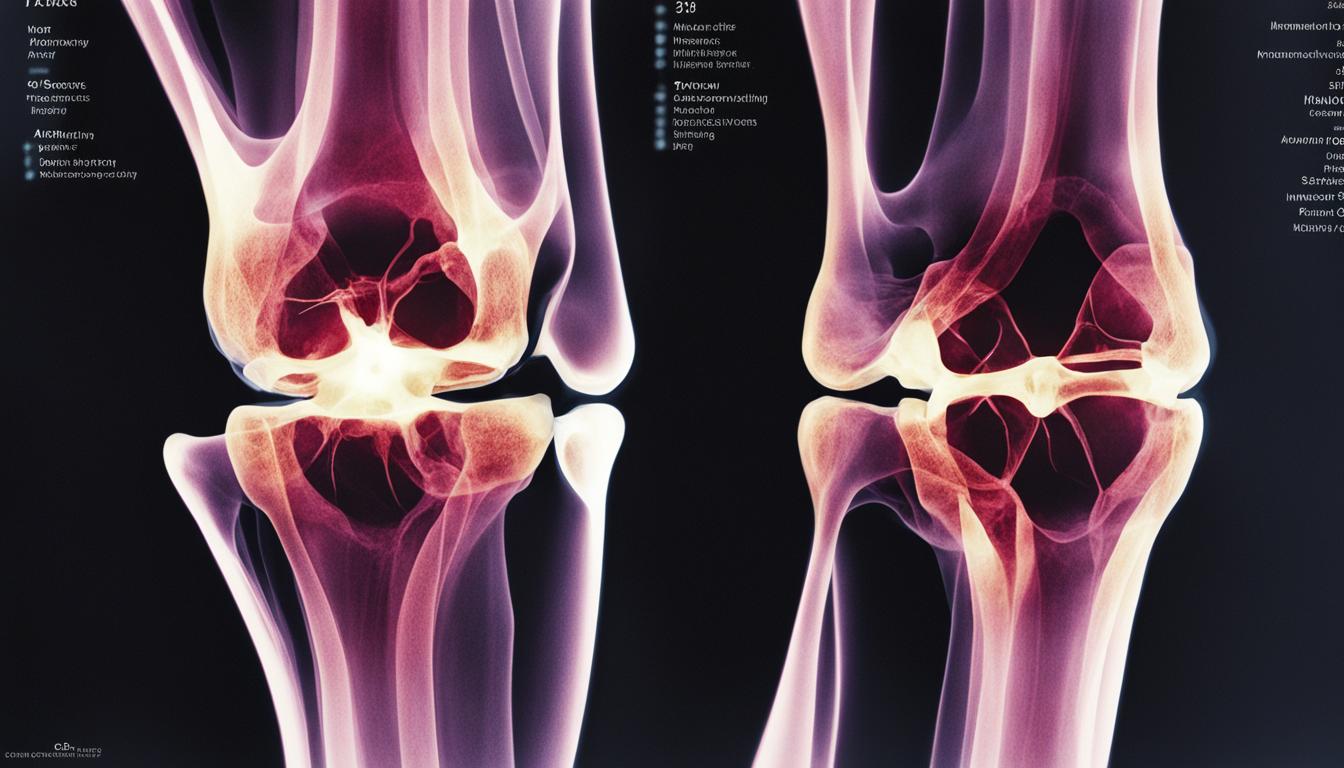
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans provide detailed images of the knee, allowing healthcare professionals to identify fractures, ligament tears, meniscus tears, or other structural abnormalities.
- Joint aspiration or arthroscopy: In some cases, fluid may be extracted from the knee joint for analysis or an arthroscopy procedure may be performed to visualize the internal structures of the knee.
Regarding the treatment of knee injuries, the approach depends on the type and severity of the injury. Common treatment options include:
“Proper diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for successful recovery from knee injuries.”
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE): These basic measures help reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and facilitate the healing process.
- Pain medication: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers can provide temporary relief from knee pain.
- Physical therapy: Tailored exercises and therapies help restore strength, flexibility, and mobility to the knee. Physical therapists play a vital role in designing individualized rehabilitation programs to suit the patient’s specific needs.
- Braces or splints: These supportive devices help provide stability and protect the knee during physical activities.
- Surgical interventions: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as ACL reconstruction, meniscus repair, or total knee replacement may be required to restore optimal function and alleviate persistent pain.
Rehabilitation and exercises are integral to the recovery process. They help strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve joint stability, and enhance overall functionality. Additionally, following a healthcare provider’s guidance and adhering to the prescribed rehabilitation plan are essential for successful recovery.
Pain Management for Knee Injuries
Pain management strategies form a crucial part of knee injury treatment. Effective pain relief measures may include:
- Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications: These can help provide temporary relief from moderate to severe knee pain. It’s important to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare professional.
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises and manual techniques employed by physical therapists can alleviate pain and facilitate healing.
- Hot or cold therapy: Applying heat or cold to the affected knee can reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in low-impact activities, and avoiding excessive stress on the knee can contribute to long-term pain management and overall joint health.
By implementing appropriate diagnosis, comprehensive treatment plans, and effective pain management strategies, individuals with knee injuries can experience relief, improved mobility, and a faster path to recovery.
Knee Injury Prevention and Recovery
To prevent knee injuries, it is crucial to implement several preventive measures. First and foremost, maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as excess weight puts additional stress on the knees. Proper training and warm-up exercises are also vital in preparing the muscles and joints for physical activities. Additionally, using the correct equipment and protective gear, such as supportive shoes or knee pads, can help minimize the risk of injury.
Knee injury prevention exercises play a significant role in keeping the knees strong and flexible. Incorporating stretching exercises into your routine can improve joint mobility and reduce the likelihood of strain. Strengthening exercises, like squats and lunges, target the muscles around the knee, providing stability and support. Balance exercises further enhance stability, while low-impact aerobic exercises, such as swimming or cycling, offer cardiovascular benefits without excessive stress on the knees.
Recovery from knee injuries varies depending on the severity and type of injury. In most cases, a comprehensive approach involving rest, physical therapy, exercises, and following a healthcare provider’s recommendations is crucial. Adhering to the prescribed rehabilitation plan is essential to facilitate a successful recovery. Gradually returning to physical activities and sports while using proper techniques and protective gear helps prevent reinjury and ensures a safe and effective recovery process.
FAQ
What are the symptoms of a knee injury?
Symptoms of a knee injury may include pain, swelling, difficulty moving the knee, catching or locking of the knee, stiffness, warmth to the touch, inability to fully straighten the knee, and knee instability.
What can cause knee injuries?
Knee injuries can be caused by fractures, dislocations, ligament tears (such as the ACL), meniscus tears, tendonitis, and sprains.
What are the risk factors for knee injuries?
Risk factors for knee injuries include participation in high-impact sports, being overweight, and lack of muscle strength or flexibility.
How can knee injuries be prevented?
Preventive measures for knee injuries include maintaining a healthy weight, practicing correct form during sports and exercise, conditioning to stay strong and flexible, and considering low-impact sports.
How are knee injuries diagnosed and treated?
Knee injuries can be diagnosed by a healthcare provider through physical examinations, imaging tests (such as X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans), and sometimes joint aspiration or arthroscopy. Treatment options depend on the type and severity of the injury and may include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), pain medication, physical therapy, braces or splints, and in some cases, surgical interventions.
What exercises can aid in the recovery of knee injuries?
Rehabilitation and exercises are often recommended to aid in the recovery of knee injuries and to improve strength, flexibility, and stability.
How can knee pain be managed?
Pain management strategies for knee injuries may include over-the-counter or prescription pain medications, physical therapy, hot or cold therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
What can be done to prevent knee injuries?
To prevent knee injuries, it is important to maintain a healthy weight, engage in proper training and warm-up exercises, use proper equipment and protective gear, and avoid activities that put excessive stress on the knees.
What exercises can help prevent knee injuries?
Knee injury prevention exercises may include stretching, strengthening exercises (such as squats and lunges), balance exercises, and low-impact aerobic exercises.
How long does it take to recover from a knee injury?
Recovery from a knee injury can vary depending on the severity and type of injury but often involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, exercises, and following a healthcare provider’s recommendations.
How can reinjury be prevented after a knee injury?
It is important to adhere to the prescribed rehabilitation plan and take steps to prevent reinjury, such as gradually returning to physical activities and using proper techniques and protective gear.
Leave a Reply