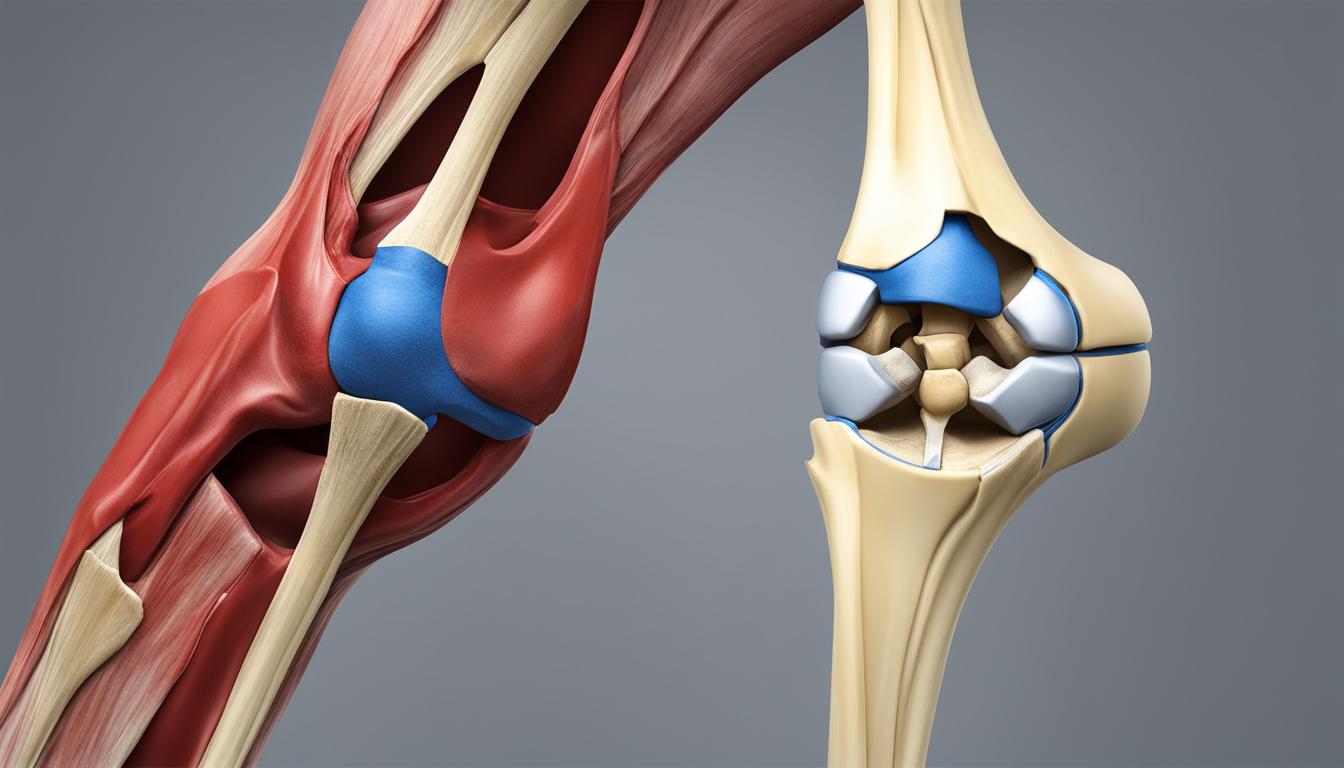
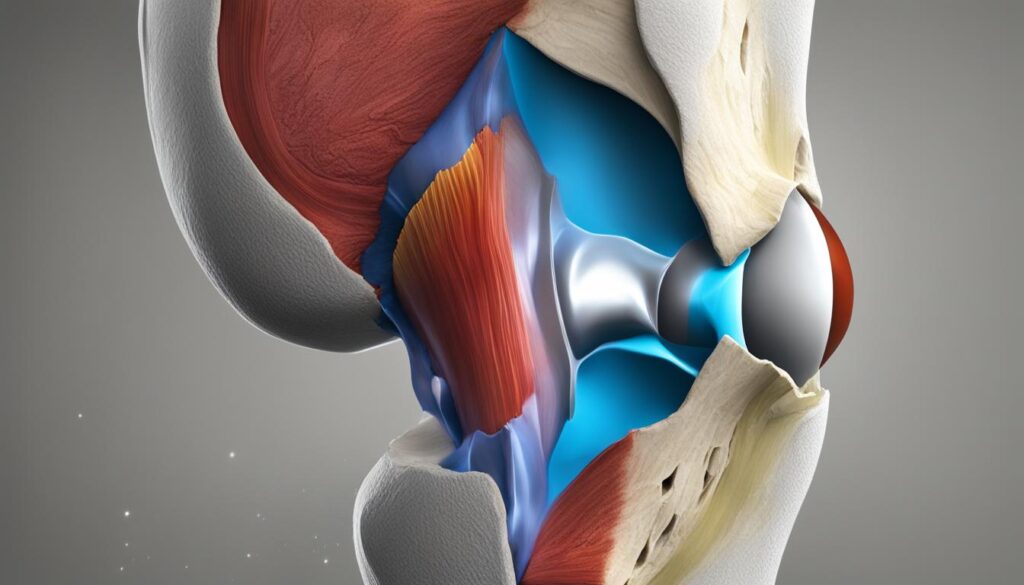
Medial and lateral meniscus injuries are common orthopedic conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s mobility and quality of life. Understanding the anatomy, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for these injuries is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This article provides an overview of the key aspects related to medial and lateral meniscus injuries, offering valuable insights into their management and recovery.
Key Takeaways
- The medial meniscus provides stability to the knee joint and is more commonly injured than the lateral meniscus.
- Traumatic injuries, such as sports-related activities, are a common cause of meniscus injuries, while degenerative changes can occur with aging and repetitive stress.
- Physical examination and imaging techniques, such as MRI, play a crucial role in diagnosing meniscus injuries.
- Conservative management, including rest, ice, and physical therapy, is often the first-line treatment for meniscus injuries.
- Surgical interventions, such as arthroscopic meniscus repair or partial meniscectomy, may be necessary for severe or complex meniscus injuries.
Anatomy of the Medial and Lateral Meniscus
Structure and Function of the Medial Meniscus
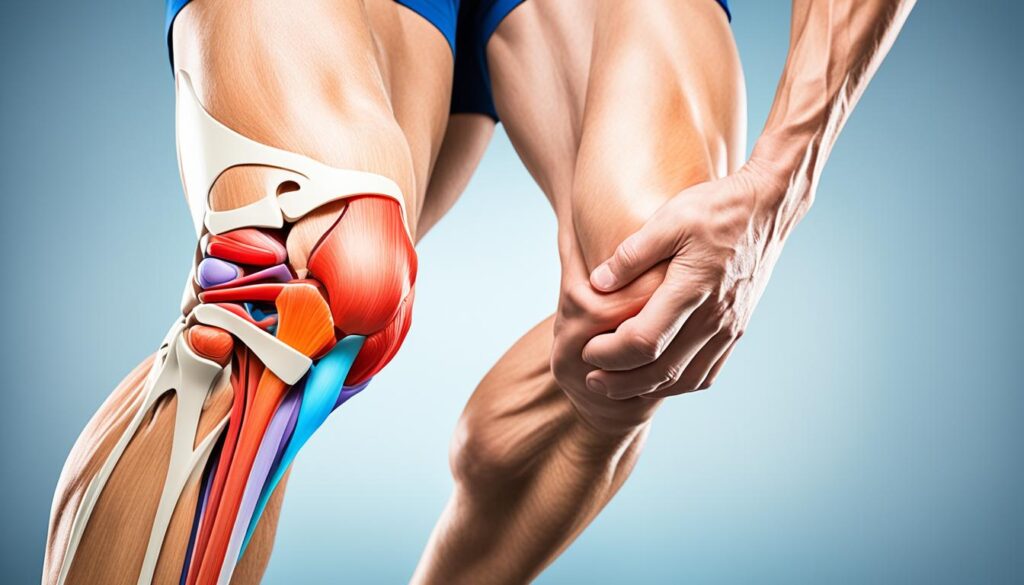
We understand the medial meniscus as a crucial component of the knee joint, primarily responsible for absorbing shock and stabilizing the joint during movement. Composed of fibrocartilaginous tissue, it is a C-shaped structure that conforms to the medial compartment of the knee, offering a cushion between the femur and the tibia.
The medial meniscus performs several vital functions, including:
- Load distribution: It evenly disperses the weight of the body across the knee joint.
- Joint lubrication: It aids in the reduction of friction between the articulating surfaces of the knee.
- Proprioception: It provides sensory feedback that helps in coordinating movement and balance.
Remember, maintaining the integrity of the medial meniscus is essential for knee health and function. Any injury to this structure can significantly impair mobility and lead to joint instability.
Injuries to the medial meniscus are often associated with twisting motions or forceful impacts, particularly in athletic activities. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical attention is key to preventing long-term damage.
Structure and Function of the Lateral Meniscus
The lateral meniscus, located on the outer edge of the knee joint, plays a vital role in distributing weight and reducing friction during movement. It works in conjunction with the medial meniscus to provide stability and cushioning to the knee. In a healthy knee, the lateral meniscus contributes to approximately 70% of the load-bearing capacity of the joint. This distribution of weight ensures that the knee joint remains stable and functional during various activities, including walking, running, and jumping. Maintaining the integrity of the lateral meniscus is essential for optimal knee function and overall joint health.
Causes of Medial and Lateral Meniscus Injuries
Traumatic Injuries
We understand that the menisci are vulnerable to traumatic injuries, particularly during activities that involve aggressive twisting or hyperflexion of the knee. Such injuries are common in sports that require quick turns and stops, such as soccer, basketball, and skiing.
The mechanism of injury often involves a combination of compression and shear forces that exceed the tissue’s ability to absorb shock and maintain stability. This can result in tears ranging from minor to severe, with symptoms that may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the knee.
- Early recognition and appropriate management are crucial to prevent further damage and ensure the best possible outcome. *
Here is a list of common movements that can lead to traumatic meniscus injuries:
- Sudden pivoting or cutting maneuvers
- Deep squatting or kneeling
- Direct impact to the knee
- Forceful hyperextension or rotation
Tip: To reduce the risk of meniscus injuries, it is advisable to engage in strength and flexibility training, particularly for the muscles surrounding the knee.
Degenerative Changes
As we delve into the causes of meniscus injuries, we must consider the impact of degenerative changes. Over time, the menisci can deteriorate due to aging and wear-and-tear, reducing their ability to cushion and stabilize the knee joint. This process is often asymptomatic initially but may eventually lead to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Osteoarthritis is a common condition associated with meniscal degeneration. The breakdown of cartilage that characterizes osteoarthritis can exacerbate the weakening of the meniscus, making it more susceptible to tears even with minor trauma.
Tip: Maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise can help slow the progression of degenerative changes in the menisci.
Risk factors for degenerative meniscus injuries include:
- Age, typically affecting individuals over 40
- History of knee injuries
- Occupations or activities that place excessive stress on the knees
- Metabolic and genetic factors that may predispose individuals to joint degeneration
Diagnosis of Meniscus Injuries
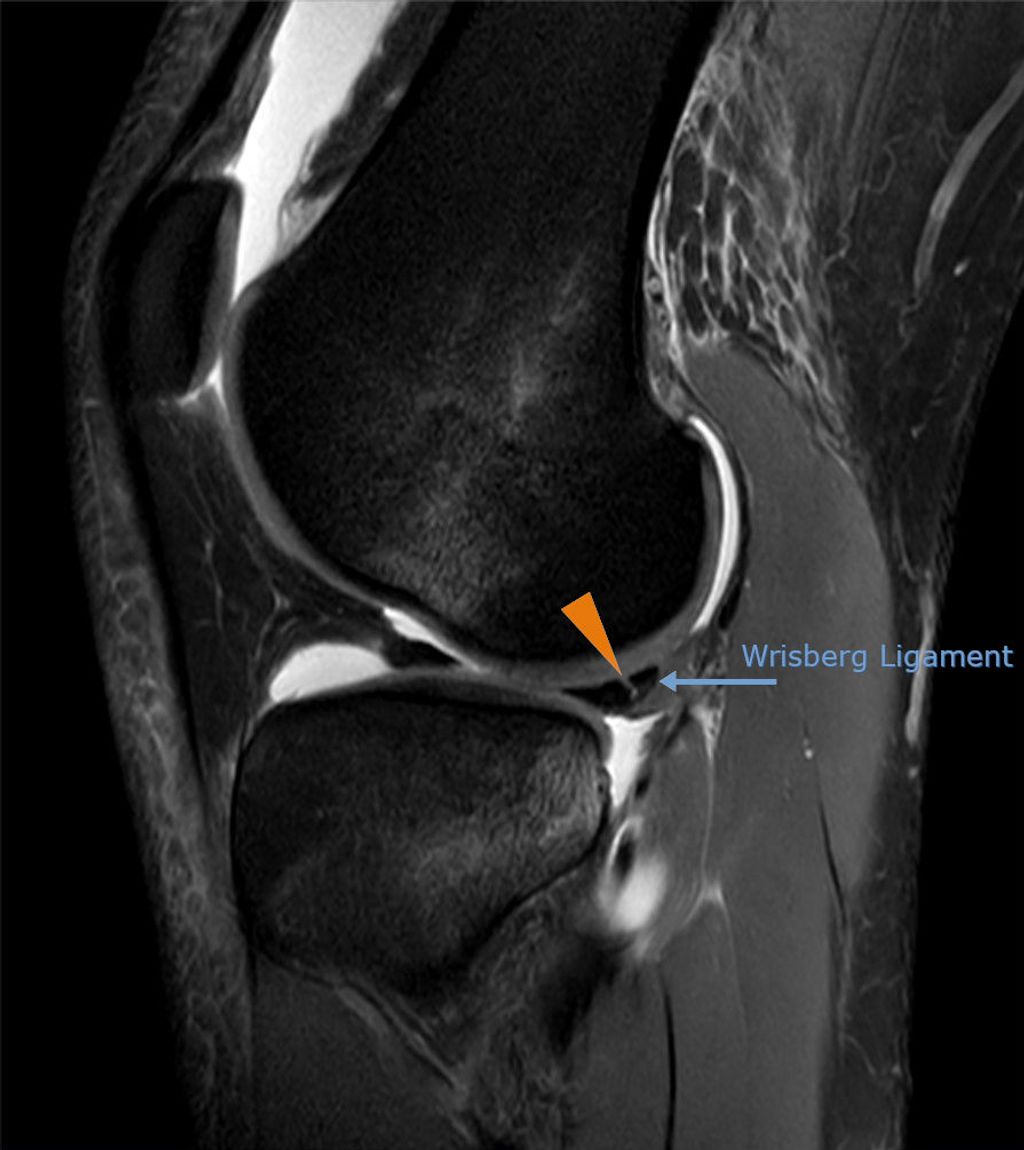
Physical Examination
In our clinical practice, we place significant emphasis on the physical examination when assessing potential meniscus injuries. This step is crucial as it allows us to evaluate the knee’s range of motion, stability, and the presence of any joint line tenderness, which can be indicative of a meniscus tear. We perform specific maneuvers, such as the McMurray test, where we rotate the knee while it is bent and then straighten it to check for pain or a clicking sound, which may suggest a tear.
We also assess for effusion, or swelling within the knee joint, which can be a sign of internal knee damage including meniscus injuries. It’s important to note that while these tests are valuable, they are not infallible. A lack of symptoms during these tests does not necessarily rule out a meniscus injury.
Tip: Always consider the patient’s history and symptomatology in conjunction with the physical examination findings to form a more accurate clinical picture.
Imaging Techniques
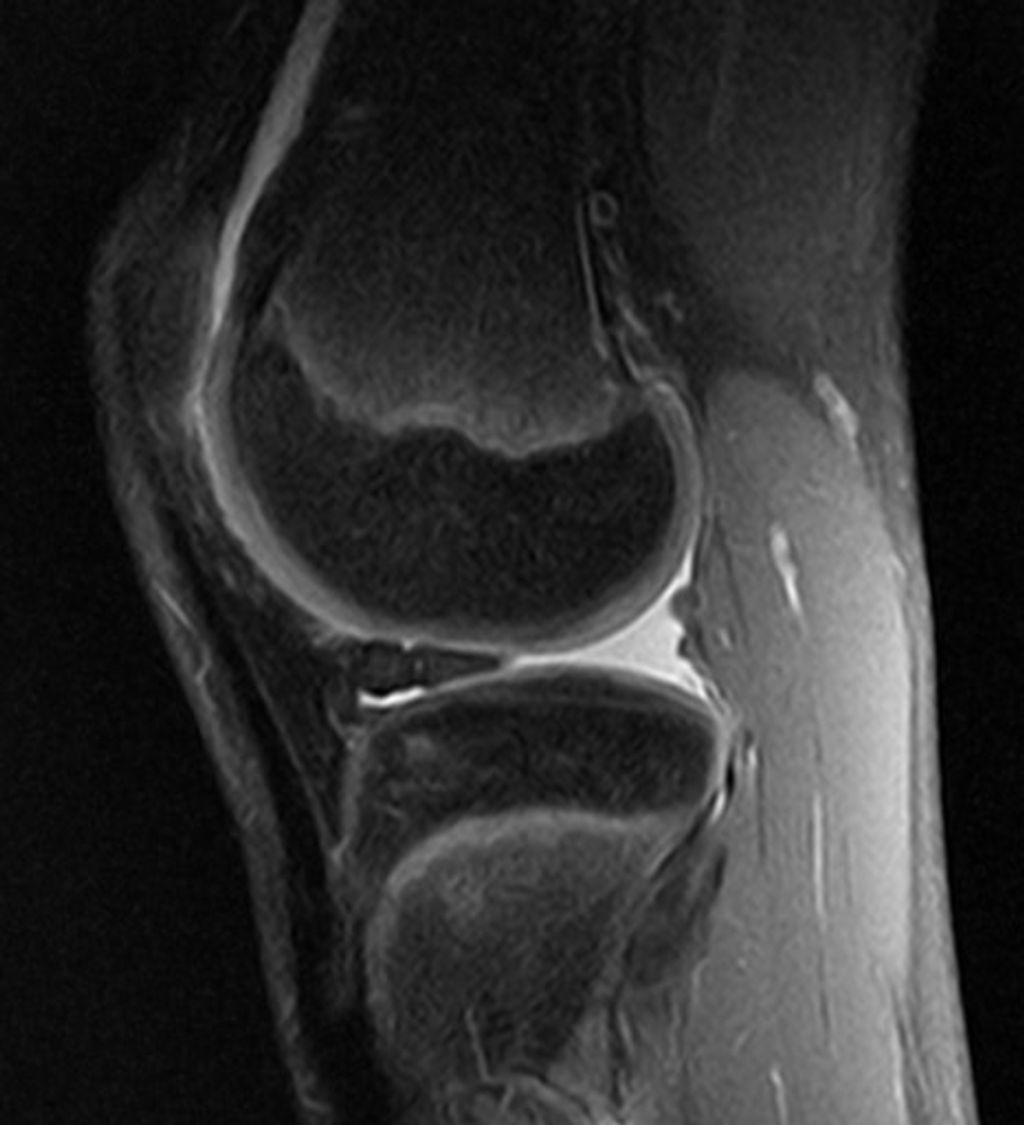
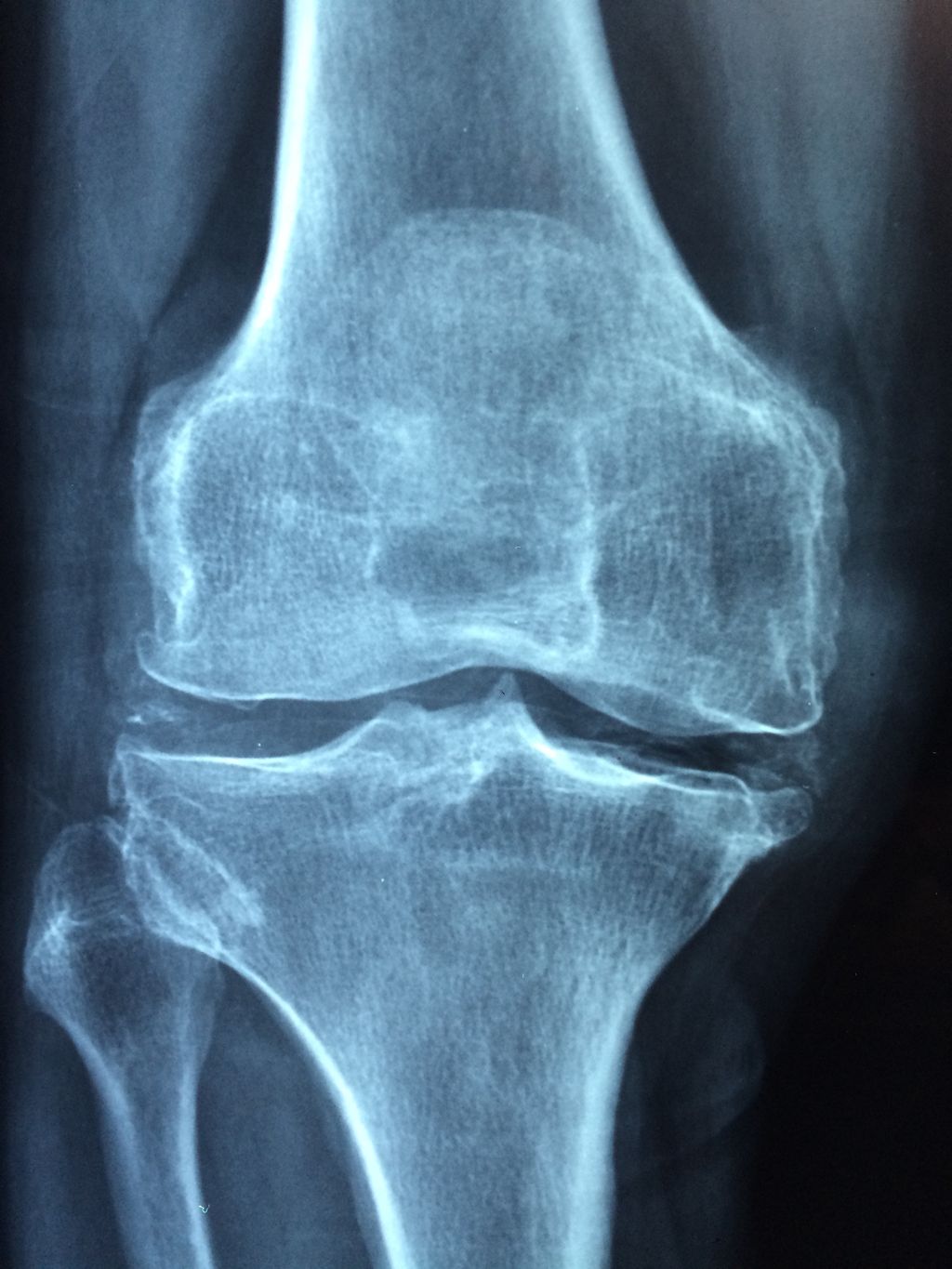
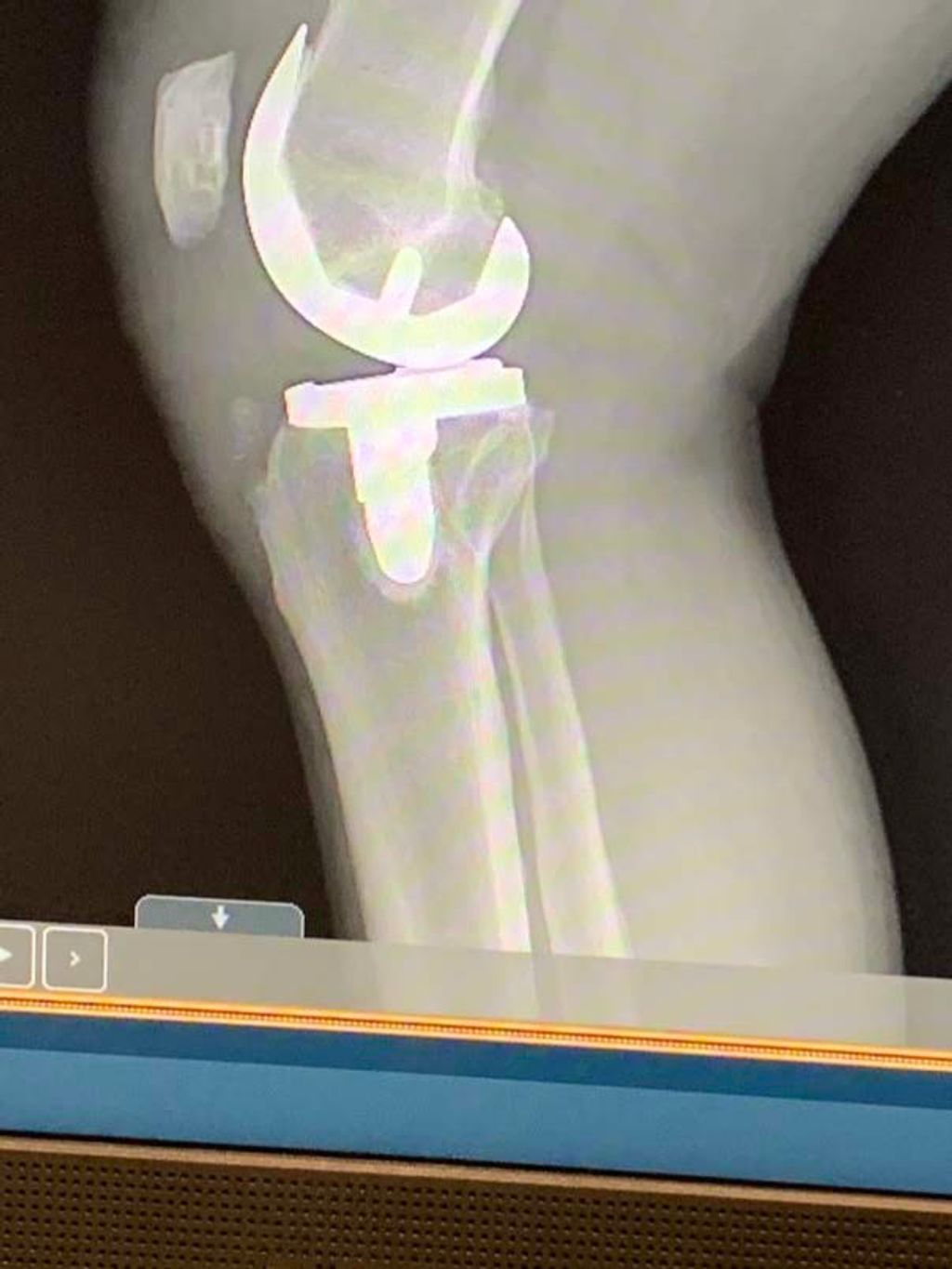
In our quest to accurately diagnose meniscus injuries, we often turn to imaging techniques. These methods provide us with a clear picture of the internal structures of the knee, allowing us to assess the extent of the injury. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for visualizing meniscus tears due to its high sensitivity and specificity. However, we also consider other modalities such as ultrasound and X-rays, particularly when MRI is contraindicated or unavailable.
Ultrasound is advantageous for its real-time imaging capabilities, which can be particularly useful in dynamic assessments. X-rays, while not as detailed for soft tissue injuries, can help rule out other conditions such as fractures or osteoarthritis. It’s important to note that while imaging provides valuable information, it should be interpreted in conjunction with clinical findings.
Tip: Always correlate imaging results with physical examination findings to ensure a comprehensive assessment of the meniscus injury.
Treatment Options for Meniscus Injuries
Conservative Management
After considering the various conservative management options, surgical interventions may be necessary in cases of severe or persistent symptoms. It is important to note that arthroscopic surgery is the most common surgical procedure for meniscus injuries. This minimally invasive technique allows for precise visualization and treatment of the affected area. In some cases, partial meniscectomy or meniscal repair may be recommended based on the location and severity of the injury.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive surgical procedure that provides precise visualization and treatment of meniscus injuries.
- Partial Meniscectomy: Surgical removal of a portion of the damaged meniscus.
- Meniscal Repair: Surgical technique to repair the torn or damaged meniscus.
It is crucial to follow post-operative rehabilitation guidelines to optimize recovery and prevent complications. Adequate rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity are essential components of the recovery process.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative management fails to provide relief or when the injury is severe, we often recommend surgical interventions. These procedures aim to repair or remove damaged tissue, thereby restoring function and alleviating pain. The most common surgeries for meniscus injuries are meniscectomy, where part of the meniscus is removed, and meniscus repair, which involves suturing the torn edges.
-
Meniscectomy is typically performed arthroscopically, a minimally invasive technique that reduces recovery time and postoperative complications. However, it’s important to note that removing meniscal tissue can increase the risk of osteoarthritis in the knee.
-
Meniscus repair is preferred when the tear is in the meniscus’s outer region, where blood supply is sufficient for healing. This procedure aims to preserve as much of the meniscus as possible, which is crucial for maintaining knee health and function.
Tip: Always discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgical options with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision about your treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of medial and lateral meniscus injuries is crucial for both medical professionals and individuals seeking to prevent or manage such conditions. The intricate interplay between anatomy, biomechanics, and injury mechanisms underscores the importance of comprehensive knowledge in this area. Further research and clinical advancements are essential for improving the diagnosis, treatment, and long-term outcomes of meniscus injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of a meniscus injury?
Symptoms of a meniscus injury may include pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving the knee.
How are meniscus injuries diagnosed?
Meniscus injuries are diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging techniques such as MRI or X-ray.
What causes degenerative changes in the meniscus?
Degenerative changes in the meniscus can be caused by aging, wear and tear, and repetitive stress on the knee joint.
Can meniscus injuries heal on their own?
Minor meniscus injuries may heal on their own with rest, ice, and physical therapy. However, more severe injuries may require surgical intervention.
What are the risks of surgical intervention for meniscus injuries?
Risks of surgical intervention for meniscus injuries include infection, blood clots, and the potential for further damage to the knee.
How long does it take to recover from meniscus surgery?
Recovery time from meniscus surgery varies, but it generally takes several weeks to months to fully recover and return to normal activities.